当前位置:网站首页>Initial i/o and its basic operations
Initial i/o and its basic operations
2022-06-30 00:29:00 【Slang H.】
List of articles
One 、 File storage structure
File is made up of OS And file system management
1、 The file is in a tree structure ( It's like a binary tree , But not a binary tree ) Conduct management , Files are nodes in the tree (node)
2、 Documents can be divided into two categories :
1)、 File to store data —— Ordinary documents ( Commonly known as file )
2)、 Manage files organized in a tree structure —— Catalog / Folder 
3、 This tree is just a logical structure , It is not the physical structure on the hard disk ( A file may be a combination of multiple parts on the disk )
Two 、 Path to file
What is the file path : The path to the file is , According to a rule , Uniquely identify a location from the file tree , This position must correspond to a node , This node may not exist .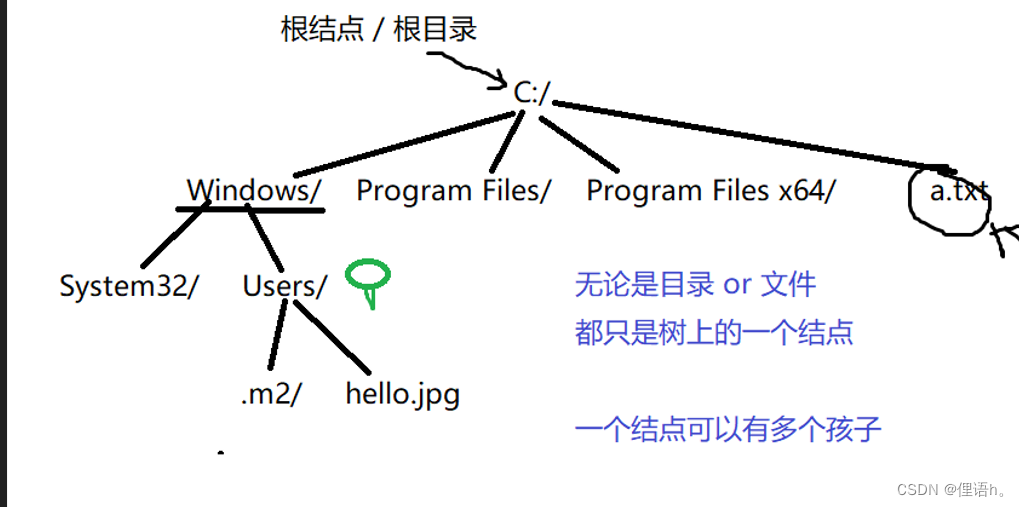

1、 Absolute path
The path described from the root node of a tree
For example, we use absolute path to express hello.jpg file
C:/Windows/Users/hello.jgp
2、 Relative paths
Starting from the current position , Describe the location of the target file
For example, in hello.jpg Location description a.txt The location of
hello.jpg Parent node Users Parent node Windows Parent node C: In the catalog a.txt;
3、 Special symbols for path representation
“.”: Indicates in the current position
“…”: Represents the parent node returning to the current position ( Catalog ) On
3、 ... and 、 Operation of file
In the file system , Operate in node units ( The code level )
for example :
File movement ( File rename , File cutting + Paste ): Node movement ( rename or Move to another node )
File copy operation : New node + Copy of content
Directory move operation ( Rename the directory 、 Catalog clipping + Paste ): The movement of a subtree rooted in the node bit
Directory copy operation : Copy of a subtree rooted in the node bit
Delete : By default, only normal files or non empty directories can be deleted . Only nodes can be deleted , Cannot delete subtree
Delete non empty directory : Deletion of the entire tree ( You should traverse and delete the leaf node first , Then delete the whole tree );
Four 、 utilize Java The code implements the basic operation of the file
1、 Construction method

Create a File object , For this File Object , modify , Delete and other operations
//1. Create an absolute path
File file1 = new File("D:/IO/hello.txt");
//2. Pass in the parent directory + Subpath
File file2 = new File("D:/IO", "hello.txt");
//3. With File Pass in parent
File parent = new File("D:/IO");
File file3 = new File(parent, "hello.txt");
2、 Common methods
Test file permissions 
Create a new file 
for example
File file=new File("D:/IO/test.txt");
file.createNewFile();// It will be in D:/IO Create a directory called test Of txt file ( Be careful , If the file already exists in the directory, the creation will fail )
Delete file 
According to the previous example , We created one test.txt file
We can call delete() Method to delete it
file.delete();// Only leaf nodes can be operated
// Be careful : When the file is being used by another thread , Deletion will fail . At the same time, if this file does not exist in the current directory, it will also fail to delete
// Deleting a non empty directory will also fail
3、 Delete non empty directory
When deleting a non empty directory , We need to analogy binary tree , You need to delete all its leaf nodes before deleting the whole tree , The following is a method of depth first traversal to delete non empty directories
Delete non empty directory some_dir
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file=new File("D:/IO/some_dir");
traversal(file);
}
/** * Depth first traverses the child nodes of the current file directory ( Similar to the traversal of binary tree ) * @param file * @throws IOException */
private static void traversal(File file) throws IOException {
File[] files=file.listFiles();
for (File file1 : files) {
if (file1.isDirectory()){
System.out.println(file1.getCanonicalPath()+"\\");
traversal(file1);
// Add delete operation
file1.delete();
}else {
System.out.println(file1.getCanonicalPath());
// Add delete operation
file1.delete();
}
}
}
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

What is the essential difference between get and post requests?
![[daily question 1] traversal of binary tree](/img/e2/313251d574f47708abca308c4c8d5d.png)
[daily question 1] traversal of binary tree

Stack space of JVM

HDCP Paring

MySQL deadlock

自动融合,驰骋海外丨跨境电商YescomUSA携手云扩实现一站式自动化服务

网工常见面试题分享:Telnet、TTL、路由器与交换机

Mysql Duplicate entry ‘xxx‘ for key ‘xxx‘

01 backpack problem
![[dynamic programming] - linear DP](/img/cb/4ad8dce1da1d1110d6e79fadca4293.png)
[dynamic programming] - linear DP
随机推荐
[advanced C language] file operation (I)
Sofaregistry source code | data synchronization module analysis
YuMinHong: my retreat and advance; The five best software architecture patterns that architects must understand; Redis kills 52 consecutive questions | manong weekly VIP member exclusive email weekly
Summarize Flink runtime architecture in simple terms
@ConfigurationProperties使用不当引发的bug
关联性——典型相关分析
Stack space of JVM
swift笔记
Vulnhub target -moriartycorp
SOFARegistry 源码|数据同步模块解析
Solr basic operations 15
初始I/O及其基本操作
[review and Book delivery] 6 interesting R language projects for beginners
modbus-tcp-rtu协议图表
网络方向哪个发展更好?数据通信工程师学习路线分享
TwinCAT 3 EL7211模塊控制倍福伺服
TwinCAT 3 EL7211模块控制倍福伺服
Can't recognize the original appearance
Summary of DOM knowledge points
MySQL basics 1