当前位置:网站首页>Index - MySQL
Index - MySQL
2022-06-23 06:27:00 【master cat】
List of articles
Index Overview
Indexes : Help MySQL Efficient access to data Data structure of ( Orderly ). Out of data , The database system also maintains a data structure that satisfies a specific search algorithm , These data structures are referenced in some way ( Point to ) data , In this way, advanced search algorithms can be implemented on these data structures , This data structure is the index
If we want to implement SQL Statement for : select * from user where age = 45;

- No index case
Without index , You need to scan from the first line , Scan until the last line , We call it Full table scan , Very low performance - With an index
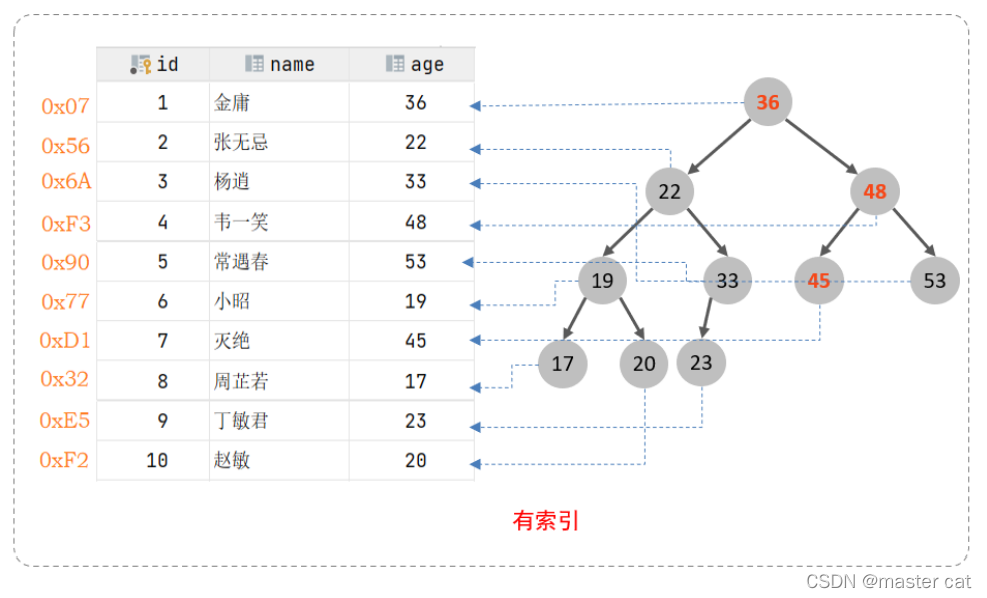 It only takes three scans to find the data , Greatly improve the efficiency of query .
It only takes three scans to find the data , Greatly improve the efficiency of query .
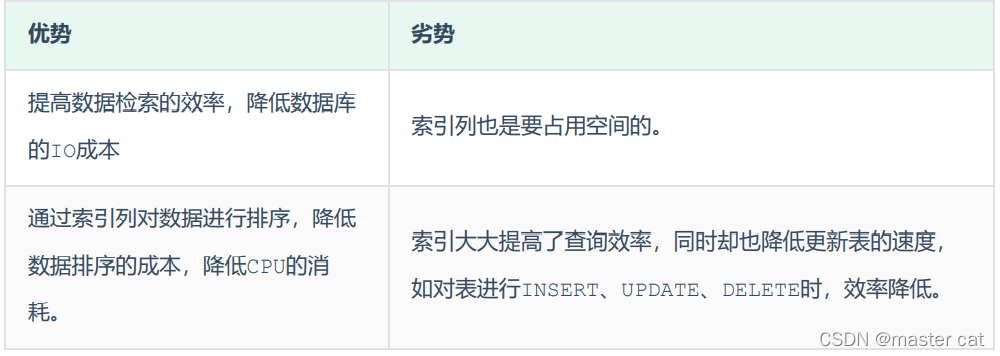
Advantages and disadvantages
Index structure
MySQL The index of is in Storage engine layer Realized , Different storage engines have different index structures , It mainly includes the following :
1.Btree Indexes
After inserting the element sorting, if it exceeds , Phase splitting on intermediate elements , Form trees
B-Tree,B A tree is a kind of multi fork road scale search tree , Relative to a binary tree ,B Each node of the tree can have multiple branches , That is, multi fork .
At a maximum degree (max-degree) by 5(5 rank ) Of b-tree For example , So this one B Each node of the tree can store up to 4 individual key, Corresponding 5
A pointer to the

characteristic :
- 5 Step B Trees , Each node can store up to 4 individual key, Corresponding 5 A pointer to the .
- Once the node stores key The quantity has arrived 5, Will fission , The intermediate element splits up .
- stay B In the tree , Both non leaf nodes and leaf nodes store data .
2. B+tree Indexes
All nodes will appear in the leaf node , And the intermediate element splits upwards

- Green box The framed part , yes Index part , It only plays the role of indexing data , Don't store data .
- The part framed in red , It's the data storage part , Specific data should be stored in its leaf node .

B+Tree And B-Tree comparison , There are three main differences :
- All the data will appear in the leaf node .
- Leaf nodes form a one-way linked list .
- Non leaf nodes only serve to index data , The specific data is stored in the leaf node .
3. hash Indexes
Hash index is to use a certain hash Algorithm , Convert key values to new hash value , Map to the corresponding slot , Then stored in hash In the table .

characteristic
- Hash Indexes Can only be used for peer-to-peer comparison (=,in), Range query is not supported (between,>,< ,…)
- Cannot complete sort operation with index
- High query efficiency , Usually ( non-existent hash Conflict situation ) It only needs one search , Efficiency is usually higher than B+tree Indexes
Storage engine support
stay MySQL in , Support hash The index is Memory Storage engine . and InnoDB It has adaptive function hash function ,hash The index is
InnoDB The storage engine is based on B+Tree The index is automatically built under specified conditions .
Thinking questions : Why? InnoDB The storage engine chooses to use B+tree Index structure ?
- Relative to a binary tree , Fewer levels , High search efficiency ;
- about B-tree, Whether leaf nodes or non leaf nodes , Data will be saved , This results in fewer key values stored in a page , The pointer decreases , Save a lot of data as well , Can only increase the height of the tree , Resulting in reduced performance ;
- relative Hash Indexes ,B+tree Support range matching and sorting operation ;
Index classification

InnoDB In the storage engine , According to the storage form of the index , It can be divided into the following two types :
Clustered index selection rules :
- If Primary key exists , A primary key index is a clustered index .
- If There is no primary key , The first unique... Will be used (UNIQUE) Index as clustered index .
- If the table There is no primary key , Or there is no suitable unique index , be InnoDB Meeting Automatically generate a rowid As a hidden clustered index .

- The data of this row is hung under the leaf node of the clustered index .
- The leaf node of the secondary index is hung with the... Corresponding to the field value Primary key value .
Thinking questions :
Here are two SQL sentence , The execution efficiency is high ? Why? ?
A. select * from user where id = 10 ;
B. select * from user where name = ‘Arm’ ;
remarks : id Primary key ,name Fields are indexed ;
answer :
A The execution performance of the statement is higher than B sentence .
because A Statement goes directly to the clustered index , Direct return data . and B The statement needs to query name The secondary index of the field , Then query the clustered index , That is, you need to query back to the table .
Index creation Syntax
- Create index
keyword :create index
create [unique\fulltext] index Index name on Table name ( Field name 1, Field name 2) ;
// Indicates the field name to be given to the table 1, Create index
- unique: Created is unique index
- fulltext: It means to create Full-text index
- No addition Two options indicate that the created is General index
- Look at the index
show index from table_name ;
View all indexes in the specified table
- Delete index
drop index index_name on Table name ;
SQL performance optimization
SQL Performance analysis
If you want to optimize performance, you must first know , The execution of those commands is inefficient , Performance analysis is required
MySQL After successful client connection , adopt show [session|global] status The command can provide server status messages
Rest .
- global: Global status information
- session: View the status information of the current conversation
By the following instructions , You can view the INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE、SELECT Frequency of visits :
show global status like 'Com_______'; # 7 Underscores

value Value is the number of times the database has executed various commands in the past , According to the execution times of various commands , Make relevant optimization
Slow query log
The slow query log records all execution times that exceed the specified parameters (long_query_time, Company : second , Default 10 second ) All of the SQL Statement log .
MySQL Slow query log Off by default , We can look at the system variables slow_query_log.
View the status of the slow query log
show variables like 'slow_query_log' ;

Open slow query log
Need to be in MySQL Configuration file for (/etc/my.cnf) The following information is configured in
# Turn on MySQL Slow log query switch
slow_query_log=1
# Set the time of slow log to 2 second ,SQL Statement execution time exceeds 2 second , It will be regarded as slow query , Log slow queries
long_query_time=2
You need to restart after setting MySQL database
profile( Check out time-consuming destinations )
Turn on profile
show profiles Be able to do SQL Optimization helps us understand where the time is spent .
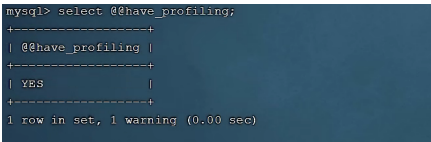
adopt have_profiling Parameters , Be able to see the present MySQL Do you support profile operation :
- View the current MySQL Do you support profile operation
View the current MySQL Do you support profile operation
select @@have_profiling ;
- see profile Open or not
select @@profiling ;

- Turn on profile
set profiling = 1 ;
View the time consumption of all instructions
When we perform a lot select After statement , Want to know this select After the execution instruction of the statement , You can go through show profiles Command to view all the just executed select Statement execution
grammar :show profiles ;
Query formulation item :show profile for query Checked items ;
-- Check each one SQL The time-consuming basic situation of
show profiles;
-- View the specified SQL The time-consuming situation of each stage of the statement
show profile for query query_id;
-- View specified query_id Of SQL sentence CPU Usage situation
show profile cpu for query query_id;
explain( Implementation plan )
The first few methods only judge by the length of time SQL Performance of , Can't really reflect SQL Performance of
adopt explain View the day SQL Statement execution plan
grammar : Directly in select Add the keyword before the statement explain / desc, You can query the execution plan of the current statement
explain select Field list from Table name where Conditions ;
Many columns will be queried 
| Field | meaning |
|---|---|
| id | select The serial number of the query , Represents execution in a query select Clause or the order of the operation table (id identical , Execution order from top to bottom ;id Different , The bigger the value is. , Execute first ) |
| select_type( Reference is of little significance ) | Express SELECT The type of , Common values are SIMPLE( A simple watch , That is, no table join or subquery is used )、PRIMARY( Main query , That is, the outer query )UNION(UNION The second or subsequent query statement in )、SUBQUERY(SELECT/WHERE Then it contains sub queries ) etc. |
| type | Express Connection type , performance The connection type from good to bad is NULL、system、const、eq_ref、ref、range、 index、all |
| possible_key | Displays the indexes that may be applied to this table , One or more . |
| key | Actual index used , If NULL, No index is used . |
| key_len | Represents the number of bytes used in the index , This value is the maximum possible length of the index field , It's not the actual length , Without losing accuracy , The shorter the length, the better . |
| rows | MySQL The number of rows that you think you must execute the query , stay innodb In the engine's table , Is an estimate , It may not always be accurate . |
| filtered | Represents the number of rows returned as a percentage of the number of rows to be read , filtered The greater the value, the better . |
Use of index
The principle of indexing
The leftmost prefix rule
If you index multiple columns ( Joint index ), Follow the leftmost prefix rule . The leftmost prefix rule refers to The query starts with the leftmost column of the index , And don't skip columns in the index . If you jump a column , The index will be partially invalidated ( The following field index is invalid ).
The leftmost column must exist , stay select It doesn't matter where in
stay tb_user In the table , There is a joint index , This The federated index involves three fields , The order is :profession,age,status. For the leftmost prefix, the law refers to , When inquiring , Leftmost column , That is to say profession There must be , Otherwise, all indexes will be invalid . And you can't skip a column in the middle , Otherwise, the field index behind the column will be invalidated .
As long as the leftmost field exists , There is no need to consider the order problem
Range queries (> or < The index on the right will be invalidated )
In the union index , Range query appears (>,<), The column index on the right side of the range query is invalid .explain select * from tb_user where profession = ' Software Engineering ' and age > 30 and status= '0';
When range queries use > or < when , Let's go , But the length of the index is 49, It indicates that the query range is on the right status Fields are not indexed .explain select * from tb_user where profession = ' Software Engineering ' and age >= 30 andstatus = '0';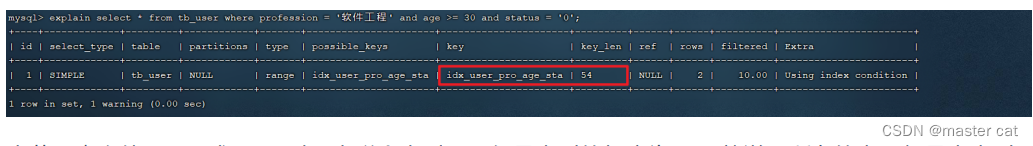
When range queries use >= or <= when , Let's go , But the length of the index is 54, It means that all fields are indexed .
therefore , When business allows , Use as much as possible similar to >= or <= This kind of range query , Avoid using > or <
Index failure
Operation in index column will be invalid
Do not do... On index columns Operation , Index will fail .
stay tb_user In the table , In addition to the union index described earlier , There is also an index , yes phone Single column index of the field .
A. When according to phone When performing equivalent matching query on fields , The index works .explain select * from tb_user where phone = '17799990015';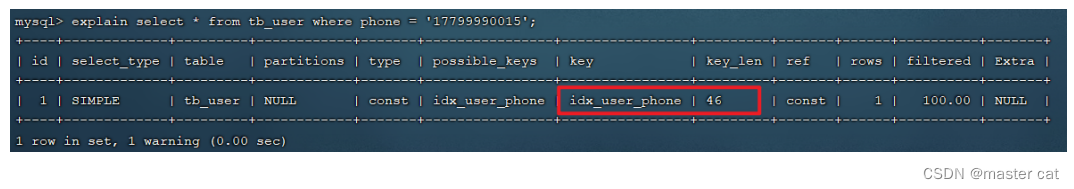
B. When according to phone After the function operation of the field , Index failure .explain select * from tb_user where substring(phone,10,2) = '15';
Strings that are not quoted become invalid
When using string type fields , Without quotes , Index will fail .
Next , We use two sets of examples , Let's look at fields of string type , The difference between single quotation mark and no single quotation mark :explain select * from tb_user where profession = ' Software Engineering ' and age = 31 and status = '0';explain select * from tb_user where profession = ' Software Engineering ' and age = 31 and status = 0;
 We will clearly find , If the string is not in single quotation marks , For query results , It doesn't matter , But the database has implicit type conversion , Index will fail .
We will clearly find , If the string is not in single quotation marks , For query results , It doesn't matter , But the database has implicit type conversion , Index will fail .
Fuzzy queries will be invalidated when they appear in the header
If it's just tail blur matching , The index will not fail . If it's a fuzzy head match , Index failure .
Let's mainly take a look at , Fuzzy query ,% Add before keyword , And the influence added after the keyword .
explain select * from tb_user where profession like ' Software %'; It works explain select * from tb_user where profession like '% engineering '; invalid explain select * from tb_user where profession like '% work %'; invalid

stay like Fuzzy query , Add the keyword after %, The index can work . And if in the keyword
I added %, The index will fail .
or Only when there is an index in the left and right fields of the connection condition can the index take effect
use or The conditions of separation , If or The columns in the previous condition are indexed , And there's no index in the next column , Then the indexes involved will not be used .
because age No index , So even id、phone There is an index , Indexes will also fail . So you need a needle for age Also index .
then , We can age Field indexing .
After indexing , Let's do the above again SQL sentence , Look at the changes in the implementation plan before and after .
explain select * from tb_user where id = 10 or age = 23;
explain select * from tb_user where phone = '17799990017' or age = 23

because age No index , So even id、phone There is an index , Indexes will also fail . So you need a needle for age Also index .
When or The conditions of connection , When the left and right fields have indexes , The index will take effect .
Data distribution affects
If MySQL Evaluation uses indexes more slowly than full tables , Index is not used .
select * from tb_user where phone >= '17799990005';
select * from tb_user where phone >= '17799990015';

After testing, we found that , same SQL sentence , Only the field values passed in are different , The final implementation plan is also completely different , Why is that ?
Because of MySQL In the query , Will evaluate the efficiency of using the index and the efficiency of full table scanning , If you walk the whole table, scanning is faster , Then abandon the index , Take a full scan . Because the index is used to index a small amount of data , If large quantities of data are returned through index query , It's not as fast as scanning the whole table , At this point, the index will be invalidated .
Next , Let's see is null And is not null Whether the operation takes the index .
Execute the following two statements :
explain select * from tb_user where profession is null;
explain select * from tb_user where profession is not null;

profession Of null The number of values will affect the query profession Medium null Whether the value is indexed or full table scanned
When inquiring MySQL Will evaluate , Go fast , Or full table scanning is fast , If the full table scan is faster , Then abandon the index and walk the full table scan . therefore ,is null 、is not null Whether to follow the index , We have to analyze the specific situation , It's not fixed .
SQL Tips
SQL Tips , Is an important means to optimize the database , Simply speaking , Is in the SQL Some artificial hints are added to the statement to achieve optimization
The purpose of the operation .
use index: Suggest MySQL Which index to use to complete this query ( It's just advice ,mysql Internal evaluation will be conducted again ).
explain select * from tb_user use index(idx_user_pro) where profession = ' Software Engineering ';
ignore index: Ignore the specified index .
explain select * from tb_user ignore index(idx_user_pro) where profession = ' Software Engineering ';
force index: Force index .
explain select * from tb_user force index(idx_user_pro) where profession = ' Software Engineering ';
Overlay index
Try to use overlay index , Reduce select *. So what is an overlay index ?
Overlay index means The query uses an index , And the columns that need to be returned , All can be found in this index .
Prefix index
When the field type is string (varchar,text,longtext etc. ) when , Sometimes you need to index long strings , This makes the index big , When inquiring , Waste a lot of disk IO, Affecting query efficiency . At this point, you can prefix only part of the string with , Index , This can greatly save index space , To improve index efficiency .
- grammar :
create index Prefix index name on Table name ( Field name (n)) ;
by tb_user Tabular email Field , Set the length to 5 Prefix index of .
create index idx_email_5 on tb_user(email(5));
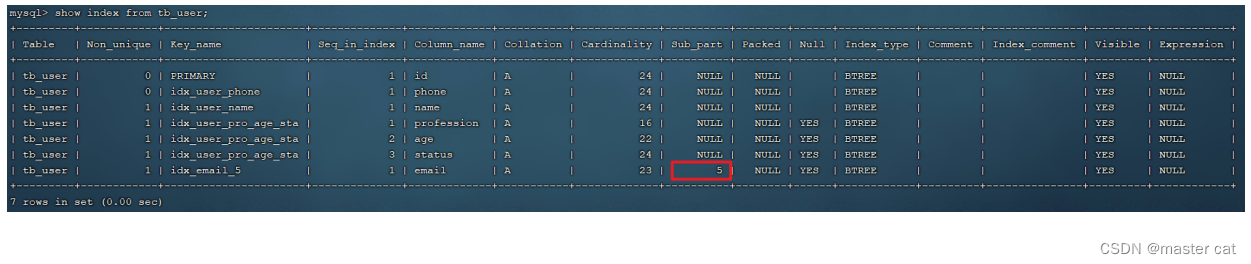
- Prefix length
It can be determined according to the selectivity of the index , Selectivity refers to index values that are not repeated ( base ) And the total number of records in the data table , The higher the index selectivity, the higher the query efficiency , The only index selectivity is 1, This is the best index selectivity , Performance is also the best .
select count(distinct email) / count(*) from tb_user ;
select count(distinct substring(email,1,5)) / count(*) from tb_user ;
- The query process of prefix index

边栏推荐
- Extend your kubernetes API using the aggregation API
- Learning Tai Chi Maker - esp8226 (11) distribution network with WiFi manager Library
- Visual studio debugging tips
- C语言 踩坑:文档编码错误,导致base64中文编码错误
- Pyqt5 设置窗口左上角图标
- Introduction to JVM principle
- 【Vivado那些事儿】XilinxCEDStore介绍
- 去除防火墙和虚拟机对live555启动IP地址的影响
- Wechat tried out the 1065 working system, and was forced to leave work at 18:00; It is said that Apple will no longer develop off screen fingerprint identification; Amd chief independent GPU architect
- Illuminate\Support\Collection 去重 unique 列表去重
猜你喜欢

Infotnews | which Postcard will you receive from the universe?
Docker实战 -- 部署Redis集群与部署微服务项目

Day_ 12 smart health project jasperreports

Pyqt5 setting window top left Icon

图解 Google V8 # 18 :异步编程(一):V8是如何实现微任务的?

Gplearn appears assignment destination is read only

Day_12 传智健康项目-JasperReports

Day_ 03 smart communication health project - appointment management - inspection team management

射频内容学习

11、 Realization of textile fabric off shelf function
随机推荐
Day_04 傳智健康項目-預約管理-套餐管理
C语言 踩坑:文档编码错误,导致base64中文编码错误
Tencent security 2021 report white paper collection (download attached)
Day_ 11 smart communication health project - graphic report and poi Report
【Cocos2d-x】自定义环形菜单
Day_01 传智健康项目-项目概述和环境搭建
JVM原理简介
【Leetcode】431. Encode N-ary Tree to Binary Tree(困难)
Docker实战 -- 部署Redis集群与部署微服务项目
Pyinstaller package exe setting icon is not displayed
程序员的真实想法 | 每日趣闻
Day_10 传智健康项目-权限控制、图形报表
Day_ 07 smart communication health project FreeMarker
原址 交换
Introduction to JVM principle
[open source project] excel export Lua configuration table tool
Cloud native database is the future
C语言 获取秒、毫秒、微妙、纳秒时间戳
微软面试题:打印折纸的折痕
2020 smart power plant industry insight white paper