当前位置:网站首页>Seven common sorts
Seven common sorts
2022-06-29 08:14:00 【Gentleman · Yong】
Catalog
3、 ... and 、 Direct selection sorting
3. Front and back pointer method
One 、 Direct insert sort
thought : Direct insertion sort is a simple insertion sort method , The basic idea is this :
Insert the records to be sorted into an ordered sequence one by one according to their key values , Until all records are inserted as stop , We get a new ordered sequence .
for example : When playing poker , Touching cards is the embodiment of inserting ideas

Implementation logic : When inserting the i(i>=1) Element time , Ahead array[0],array[1],…,array[i-1] It's in order , Use at this time array[i] The sort code of and array[i-1],array[i-2],… Compare the sort code order of , Find the insertion position array[i] Insert , The elements in the original position move backward in order
Summary of the features of direct insertion sort :
1. The closer the set of elements is to order , The more time efficient the direct insertion sort algorithm is
2. Time complexity :O(N^2)
3. Spatial complexity :O(1), It's a stable sort algorithm
4. stability : Stable
// Insertion sort Time complexity O(N^2) Think better than bubbling
void InsertSort(int* a, int n)
{
// take end + 1, Insert into [0,end] This ordered sequence , send [0,end + 1] Orderly
// Worst case scenario 1 + 2 + 3 + ..... + n - 1 Sub arithmetic sequence
// The best situation N-1
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
int end = i;
int tmp = a[end + 1];
while (end >= 0)
{
if (a[end] > tmp)
{
a[end + 1] = a[end];
end--;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
a[end + 1] = tmp;
}
}
Two 、 Shell Sort
Hill's ranking method is also called reducing increment method . The basic idea of Hill's ranking is : Choose an integer first , Divide all records in the file to be sorted into Group , All records at a distance of are in the same group , And sort the records in each group . then , take , Repeat the above grouping and sorting process do . When they arrive in =1 when , All records are arranged in a unified group .

A summary of the characteristics of Hill sort :
1. Hill sort is an optimization of direct insert sort .
2. When gap > 1 It's all pre sorted , The goal is to make arrays more ordered . When gap == 1 when , The array is nearly ordered , So you It will be soon . So on the whole , Can achieve the effect of optimization . We can compare the performance test after implementation .
3. The time complexity of Hill sort is not easy to calculate , because gap There are many ways to get the value of , Makes it difficult to calculate , So in many trees The time complexity of hill sorting is not fixed :
In fact, the efficiency of Hill sort is very considerable :
// Shell Sort Time complexity O(N^1.3) O(N*log3N)
void ShellSort(int* a, int n)
{
//gap The larger the value, the faster the data moves , The faster the pre sort
// When gap == 1 Is to insert sort
int gap = n;
while (gap > 1)
{
gap = gap / 3 + 1;// O(log2N, With 2 Base logarithm )
for (int i = 0; i < n - gap; i++)//gap When a large O(N),gap Very small has been very close to order, close to O(N)
{
int end = i;
int tmp = a[end + gap];
while (end >= 0)
{
if (a[end] > tmp)
{
a[end + gap] = a[end];
end -= gap;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
a[end + gap] = tmp;
}
}
}
3、 ... and 、 Direct selection sorting
thought : Each time, the largest... Is selected from the array ( Minimum ) The elements of , Put it at the beginning of the sequence , Until all the data is selected , To complete the order .
Selection sort :
- In the element set array[i]--array[n-1] Select the largest key in ( Small ) Data elements
- If it's not last of the these elements ( first ) Elements , Then it is combined with the last element in the group ( first ) Element exchange
- In the remaining array[i]--array[n-2](array[i+1]--array[n-1]) Collection , Repeat the above steps , Until the set remains 1 Elements
It can be said that the efficiency of direct selection sorting is one of the lowest .
Then the characteristics of selection sorting are summarized :
1. It's very easy to understand how to think directly , But the efficiency is not very good . It is seldom used in practice
2. Time complexity :O(N^2)
3. Spatial complexity :O(1)
4. stability : unstable
// Direct selection sorting Time complexity o(N^2)
void SelectSort(int* a, int n)
{
int begin = 0, end = n - 1;
while (begin < end)
{
int mini = begin, maxi = begin;
for (int i = begin; i <= end; i++)
{
if (a[mini] > a[i])
{
mini = i;
}
if (a[maxi] < a[i])
{
maxi = i;
}
}
Swap(&a[mini], &a[begin]);
if (begin == maxi)
{
maxi = mini;
}
Swap(&a[maxi], &a[end]);
begin++;
end--;
}
}Four 、 Heap sort
Heap sort (Heapsort) It's the use of stacked trees ( Pile up ) A sort algorithm designed by this data structure , It's a sort of selective sort . It is Select data through the heap . It's important to note that in ascending order you have to build lots of , Build small piles in descending order .
Logical structure : Binary tree
Physical structure : One dimensional array
Build lots of drawings :

Then select the elements at the top of the heap and exchange them with the elements at the end of the heap , Then iterate on .
Summary of heap sorting features :
1. Heap sort uses heap to select numbers , It's a lot more efficient .
2. Time complexity :O(N*logN)
3. Spatial complexity :O(1)
4. stability : unstable
// Adjust the algorithm down Adjust the height at most times O(logN)
void AdjuDown(int* a, int n, int root)
{
int parent = root;
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < n) // Use the child's subscript to judge the end , Perfect binary tree , The left child crossed the line , It must be the last parent node
{
if ((child + 1) < n && a[child + 1] > a[child]) // Judge the condition pay attention to the condition that only the left child exists
{
child += 1;
}
if (a[parent] < a[child])
{
Swap(&a[parent], &a[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
// Heap sort Time complexity O(N*logN)
void heapSort(int* a, int n)
{
// Building the heap O(N)
// Use a stack to sort
for (int i = (n - 1 - 1) / 2; i > 0; i--)// O(N)
{
AdjuDown(a, n, i);
}
int end = n - 1;
while (end > 0)
{
Swap(&a[0],&a[end]);
AdjuDown(a, end, 0);
--end;
}
}5、 ... and 、 Bubble sort
The basic idea : So called exchange , It is to exchange the positions of the two records in the sequence according to the comparison results of the key values of the two records in the sequence , Exchange row The characteristic of order is : Move the record with large key value to the end of the sequence , Records with smaller key values move to the front of the sequence .
It can be said that it is the most familiar sorting algorithm for beginners , It is also the most well-known sorting algorithm
Summary of bubble sorting characteristics :
1. Bubble sort is a sort that is very easy to understand
2. Time complexity :O(N^2)
3. Spatial complexity :O(1)
4. stability : Stable
// Bubble sort Time complexity o(N^2)
void BubbleSort(int* a, int n)
{
int exchange = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n - 1; ++j)
{
for (int i = 1; i < n - j; ++i)
{
if (a[i - 1] < a[i])
{
int tmp = a[i];
a[i] = a[i - 1];
a[i - 1] = tmp;
exchange = 1;
}
}
if (exchange == 0)
{
break;
}
exchange = 0;
}
}6、 ... and 、 Quick sort
Time complexity :N*logN
Quick sort is Hoare On 1962 A binary tree structure of the exchange sort method , Its basic idea is : In any element sequence to be sorted As a reference value , According to the sorting code, the set to be sorted is divided into two subsequences , All elements in the left subsequence are less than the base value , Right All elements in the subsequence are greater than the base value , Then the leftmost and rightmost subsequences repeat the process , Until all the elements are aligned in their respective positions .
1.Hore edition
Ideas : Adjust a value to the correct position in a single trip , Make the value on the left smaller than him , The ones on the right are bigger than that
notes :
Select the left as the reference value , It must be ensured that the right side goes first .( Ensure that the value ratio of the last meeting point key Small )
Pay attention to the conditions , Like the equal sign .


// Hore edition
void QuickSort1(int *a, int begain, int end)
{
if (begain >= end)
{
return;
}
int keyi = begain;
int left = begain;
int right = end;
while (left < right)
{
while (left < right && a[right] >= a[keyi])// Pay attention to the judgment conditions here
{
right--;
}
while (left < right && a[left] <= a[keyi])
{
left++;
}
Swap(&a[left], &a[right]);
}
Swap(&a[left], &a[keyi]);
keyi = left;
QuickSort1(a, begain, keyi - 1);
QuickSort1(a, keyi + 1, end);
}2. Excavation method
comparison Hore Version of the method , Dig a hole to better understand why the right side goes first

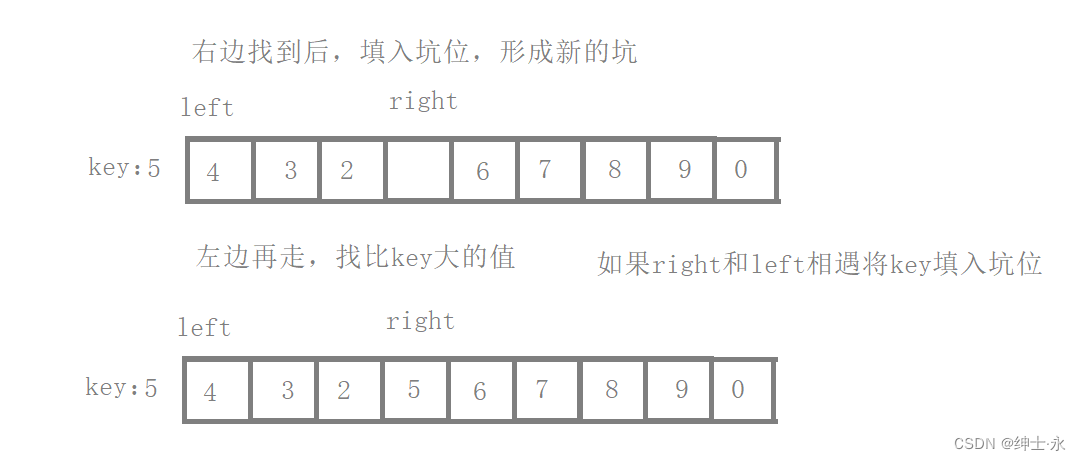
// Quick sort ( Excavation method )
void QuickSort(int* a, int begain, int end)
{
if ( begain >= end )
{
return;
}
int left = begain;
int right = end;
int key = a[left];
int pivot = left;
while (left < right)
{
while (left < right && a[right] >= key)
{
right--;
}
Swap(&a[pivot], &a[right]);
pivot = right;
while (left < right && a[left] <= key)
{
left++;
}
Swap(&a[pivot], &a[left]);
pivot = left;
}
pivot = left;
a[pivot] = key;
QuickSort(a, begain, pivot - 1);
QuickSort(a, pivot + 1, end);
}3. Front and back pointer method
Definition prev and cur The pointer , Objective to compare key Small ones are adjusted to the front


// Front and back pointer
void QuickSort4(int* a, int begain, int end)
{
if (begain >= end)
{
return;
}
int key = begain;
int* cur = &a[begain] + 1;
int* prev = &a[begain];
while (cur <= a + end)
{
if (*cur < a[key] && ++prev != cur)
{
Swap(prev, cur);
}
cur++;
}
Swap(&a[key], prev);
key = prev - a;
QuickSort4(a, begain, key - 1);
QuickSort4(a, key + 1, end);
}4. Partial optimization
Insert sorting inter cell optimization , When the number to be recursively sorted is less than 10 Insert sort is used when
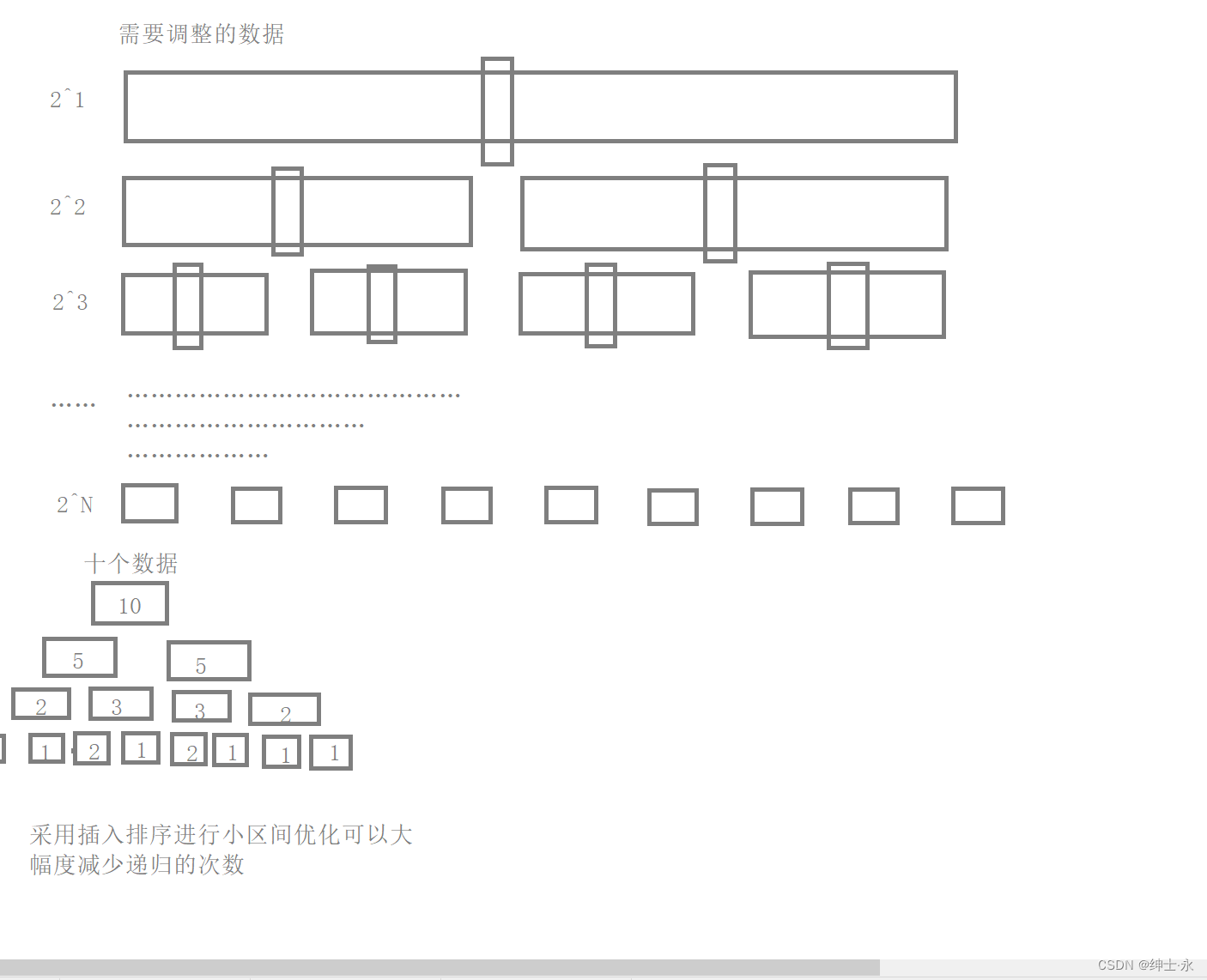
void QuickSort1(int *a, int begain, int end)
{
if (begain >= end)
{
return;
}
int keyi = begain;
int left = begain;
int right = end;
if (end - begain < 10)// Optimization if only ten numbers of recursion , Sorting directly with inserts saves more time
{
InsertSort(a + begain, end - begain - 1);
}
while (left < right)
{
while (left < right && a[right] >= a[keyi])
{
right--;
}
while (left < right && a[left] <= a[keyi])
{
left++;
}
Swap(&a[left], &a[right]);
}
Swap(&a[left], &a[keyi]);
keyi = left;
QuickSort1(a, begain, keyi - 1);
QuickSort1(a, keyi + 1, end);
}Three numbers take the middle optimization : The beginning, the end, and the middle , Take the middle number

int GetMid(int* a, int begain, int end)
{
int midi = (begain + end) / 2;
if (a[begain] > a[midi])
{
if(a[midi] > a[end])
{
return midi;
}
else if (a[end] > a[begain])
{
return begain;
}
else
{
return end;
}
}
else // a[bagain] <= a[midi]
{
if (a[begain] > a[end])
{
return begain;
}
else if (a[midi] < a[end])
{
return midi;
}
else
{
return end;
}
}
}
void QuickSort1(int *a, int begain, int end)
{
cout++;
if (begain >= end)
{
return;
}
int keyi = begain;
int left = begain;
int right = end;
int mid = GetMid(a, begain, end);
Swap(a + keyi, a + mid);
while (left < right)
{
while (left < right && a[right] >= a[keyi])
{
right--;
}
while (left < right && a[left] <= a[keyi])
{
left++;
}
Swap(&a[left], &a[right]);
}
Swap(&a[left], &a[keyi]);
keyi = left;
QuickSort1(a, begain, keyi - 1);
QuickSort1(a, keyi + 1, end);
}5. Fast non recursive
Why change to non recursive ?
The flaw of recursion :
1. Low efficiency
2. If the stack frame is too deep , The stack will run out , It might spill over
// Single pass sorting
int PartSort(int* a, int left, int right)
{
int keyi = left;
while (left < right)
{
while (left < right && a[right] >= a[keyi])
{
right--;
}
while (left < right && a[left] <= a[keyi])
{
left++;
}
Swap(&a[left], &a[right]);
}
Swap(&a[left], &a[keyi]);
keyi = left;
return keyi;
}
// Non recursive fast scheduling
void QuickSortNotR(int* a, int begain, int end)
{
ST S;
StackInit(&S);
StackPush(&S, end);
StackPush(&S, begain);
while (!StackEmpty(&S))// Simulate the process of recursive stack entry and stack exit in the heap
{
int left = StackTop(&S);
StackPop(&S);
int right = StackTop(&S);
StackPop(&S);
int keyi = PartSort(a, left, right);
if (keyi + 1 < right)// If the interval is greater than 1 It into the stack
{
StackPush(&S, right);
StackPush(&S, keyi + 1);
}
if (keyi - 1 > left)// If the interval is greater than 1 It into the stack
{
StackPush(&S, keyi - 1);
StackPush(&S, left);
}
}
}summary :
1. The overall performance and usage scenarios of quick sort are quite good , That's why we call it quick sort
2. Time complexity :O(N*logN)
3. Spatial complexity :O(logN)
4. stability : unstable
7、 ... and 、 Merge sort
The basic idea : Merge sort (MERGE-SORT) It is an effective sorting algorithm based on merge operation , The algorithm is a divide-and-conquer method (Divide and Conquer) A very typical application . Merges ordered subsequences , You get a perfectly ordered sequence ; That is, first make each subsequence have order , Then make the subsequence segments in order . If two ordered tables are merged into one ordered table , It's called a two-way merge .
void _MergeSort(int* a, int left, int right, int* tmp)
{
if (left >= right)
{
return;
}
int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
_MergeSort(a, left, mid, tmp);
_MergeSort(a, mid + 1, right, tmp);
// Merger
int begain1 = left, end1 = mid;
int begain2 = mid + 1, end2 = right;
int index = left;
while (begain1 <= end1 && begain2 <= end2)
{
if (a[begain1] < a[begain2])
{
tmp[index++] = a[begain1++];
}
else
{
tmp[index++] = a[begain2++];
}
}
while (begain1 <= end1)
{
tmp[index++] = a[begain1++];
}
while (begain2 <= end2)
{
tmp[index++] = a[begain2++];
}
// Copy back
for (int i = 0; i <= right; i++)
{
a[i] = tmp[i];
}
}
// Merge sort
void MergeSort(int* a, int n)
{
int* tmp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
_MergeSort(a, 0, n - 1, tmp);
free(tmp);
}Merged non recursive
/ Return is not recursive
void MergeSortNonR(int* a, int n)
{
int* tmp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
exit(-1);
}
int gap = 1;
while (gap < n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += 2*gap)
{
// Section [i, i+gap-1],[i+gap, i+2*gap-1]
int begain1 = i, end1 = i + gap - 1;
int begain2 = i + gap, end2 = i + 2 * gap - 1;
int index = i;
// When you merge The right interval is out of bounds and does not exist
if (begain2 >= n)
{
break;
}
// When you merge The right section is missing
if (end2 >= n)
{
end2 = n - 1;
}
while (begain1 <= end1 && begain2 <= end2)
{
if (a[begain1] < a[begain2])
{
tmp[index++] = a[begain1++];
}
else
{
tmp[index++] = a[begain2++];
}
}
while (begain1 <= end1)
{
tmp[index++] = a[begain1++];
}
while (begain2 <= end2)
{
tmp[index++] = a[begain2++];
}
// Copy back
for (int j = 0; j <= end2; j++)
{
a[j] = tmp[j];
}
}
gap *= 2;
}
free(tmp);
}The nature of amalgamation :
1. The disadvantage of merging is that it requires O(N) Spatial complexity of , The thinking of merge sort is more about solving the problem of external sort in disk .
2. Time complexity :O(N*logN)
3. Spatial complexity :O(N)
4. stability : Stable
边栏推荐
- PostgreSQL installation: the database cluster initialization failed, stack hbuilder installation
- 在iframe标签中操作外层dom
- 常见的七大排序
- [eye of depth wuenda machine learning homework class phase IV] regularization regularization summary
- mysql 主键约束删除问题
- Line features & surface features of vSLAM features
- In PHP version 7.1.13, it is found that floating-point data passes through JSON during use_ There will be precision problems after encode
- SizeBalanceTree
- Audio and video development cases 99 lectures - Contents
- SizeBalanceTree
猜你喜欢
![[6G] collation of white paper on computing network technology](/img/a3/8e60eef55ebcd91fa6188722c87a70.png)
[6G] collation of white paper on computing network technology
U盘内存卡数据丢失怎么恢复,这样操作也可以

Automatic operation and maintenance management platform - construction and daily use of SPuG
![[eye of depth wuenda machine learning homework class phase IV] regularization regularization summary](/img/24/3d0b892c0eaa330f0c69764de5da13.png)
[eye of depth wuenda machine learning homework class phase IV] regularization regularization summary

Soliciting articles and contributions - building a blog environment with a lightweight application server

Segment tree and use

ROS2中的行为树 BehaviorTree
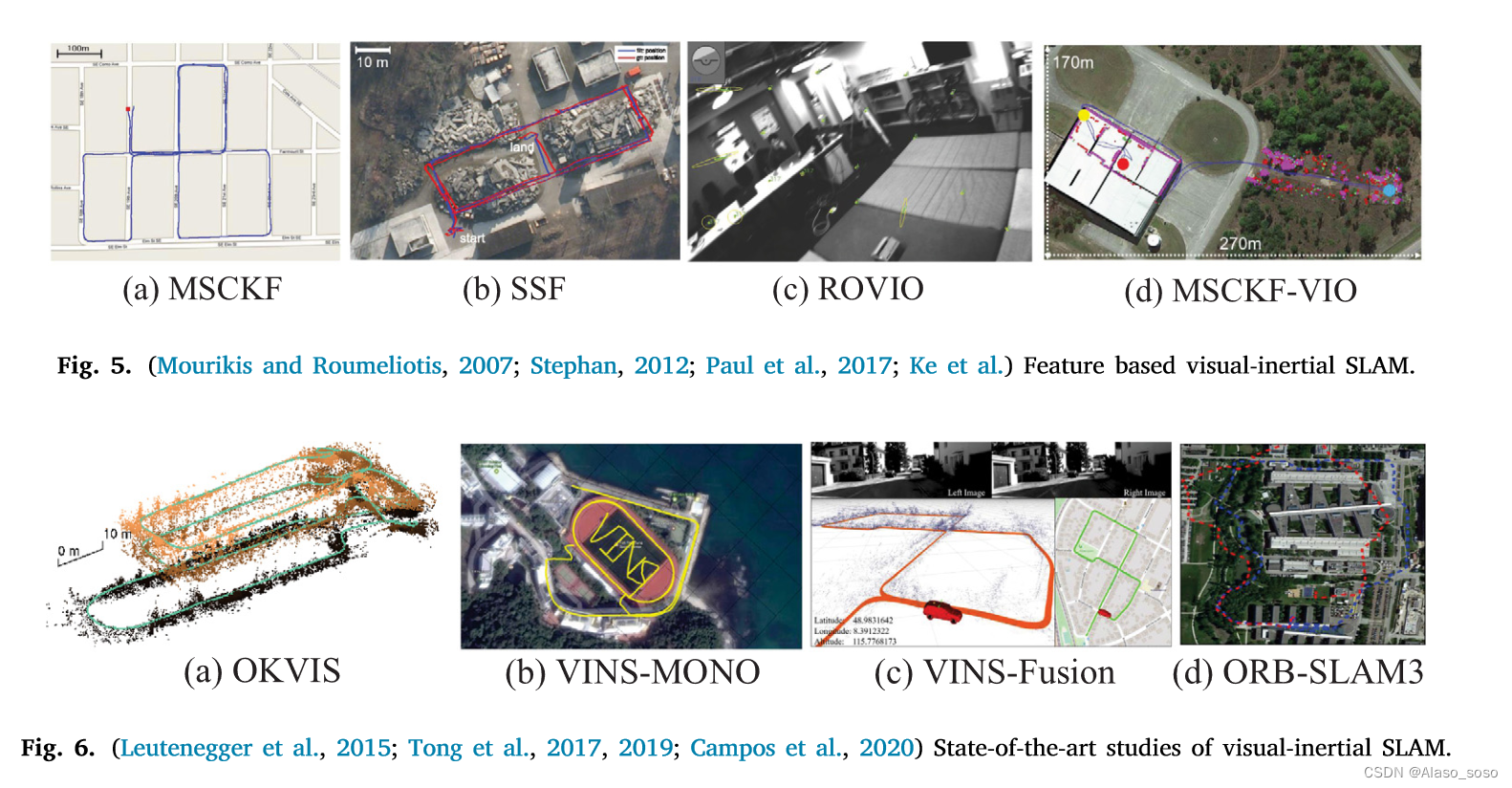
A review of visual SLAM methods for autonomous driving vehicles
Should product managers learn from ink knife or Axure?

蓝图基础
随机推荐
Segment tree and use
laravel 中 distinct() 的使用方法与去重
Django - installing mysqlclient error: mysqlclient 1.4.0 or newer is required; you have 0.9.3
PHP 7.1.13 版本,在使用过程中发现 浮点类型 数据经过 json_encode 之后会出现精度问题
jsp学习部分
AI deep dive of Huawei cloud
【修复收藏功能、更新登录接口】知识付费小程序、博客小程序、完整版开源源码、资源变现小程序,带299整站资源数据
Introduction to taro
互联网公司的组织结构与产品经理岗位职责是什么?
VSLAM特征之线特征&面特征
mysql 主键约束删除问题
基础知识 - 语法标准(ANSI C、ISO C、GNU C)
RobotFramework学习笔记:Robot Framework和BrowserLibrary(PlayWright)简介
【kerberos】kerberos 认证浅析
音视频开发案例99讲-目录
IndexTree以及应用
AC自动机
About the many to many cascading insertion of sqlsugar (the ID of the collection attribute cannot be obtained, so the intermediate table cannot be maintained)
C # import CSV into MySQL database
SQL Server enable CDC