当前位置:网站首页>数据库系列之MySQL中的执行计划
数据库系列之MySQL中的执行计划
2022-06-28 02:40:00 【solihawk】
执行计划是SQL在数据库中执行情况的客观反映,也是SQL性能分析和优化的参考。本文简要介绍了MySQL中的执行计划有哪些内容,以引申到后续分布式数据库中执行计划的探索。
1、MySQL中的执行计划
1.1 什么是执行计划
执行计划是什么,简单来说就是SQL在数据库中执行时的表现情况。当一条SQL下发到数据库的时候,怎么扫描表、怎样使用索引这些行为对用户来说是不知道的,能够明显感受到的是查询的时间。而执行计划可以提前预估SQL究竟需要运行多长时间、查询中需要涉及到哪些表、走了哪些索引,这些通过优化器经过基于成本和规则的优化后生成的执行计划能够用来进行性能分析和优化。
查看某条语句的执行计划很简单,通过explain+sql即可完成,如下所示:
mysql> explain select 1;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | No tables used |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+----------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
1.2 一条SQL执行过程
在分析执行计划之前,看一下MySQL中一条SQL具体的执行过程,如下所示:
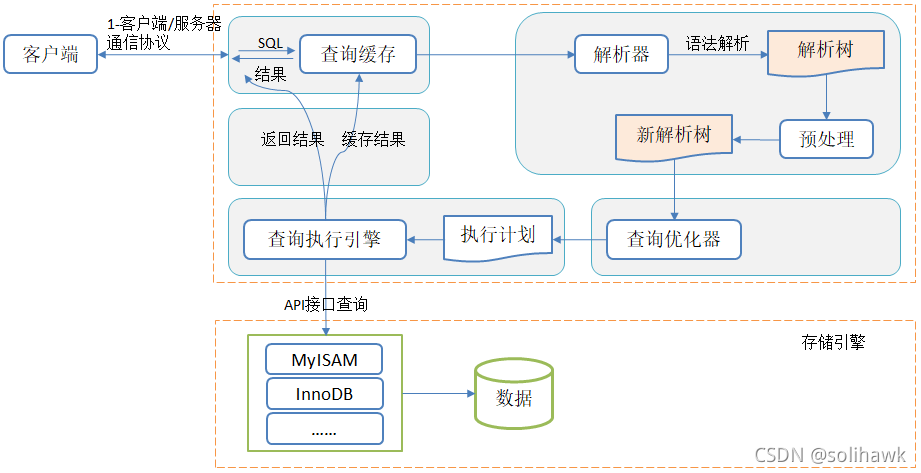
总的来说分为6个步骤:请求、缓存、SQL解析、优化SQL查询、调用引擎执行、返回结果。
- 连接:客户端向MySQL服务器发送一条查询请求,与connectors交互,连接池认证相关处理。请求会暂时存放在连接池(connection pool)中并由处理器(Management Serveices & Utilities)管理。当该请求从等待队列进入到处理队列,管理器会将该请求丢给SQL接口(SQL Interface)。
- 缓存:SQL接口接收到请求后会将请求进行hash处理,并与缓存中的结果进行比对,如果命中缓存,则立刻返回存储在缓存中的结果,否则进入下一阶段
- 解析:服务器进行SQL解析(词法语法)、预处理
- 优化:再由优化器生成对应的执行计划
- 执行:MySQL根据执行计划,调用存储引擎的API来执行查询
- 结果:将结果返回给客户端,同时缓存查询结果。
具体可参看“数据库系列之InnoDB存储引擎解密”
1.3 MySQL中执行计划
MySQL中explain执行计划的信息包括:id、select_type、table、partitions、type、possible_keys、key、key_len、ref、rows、filtered和Extra。
以下部分将介绍explain结果中的不同字段含义,首先建立两张表
CREATE TABLE s1 (
id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
key1 VARCHAR(100),
key2 INT,
key3 VARCHAR(100),
key_part1 VARCHAR(100),
key_part2 VARCHAR(100),
key_part3 VARCHAR(100),
common_field VARCHAR(100),
PRIMARY KEY (id),
KEY idx_key1 (key1),
UNIQUE KEY idx_key2 (key2),
KEY idx_key3 (key3),
KEY idx_key_part(key_part1, key_part2,
key_part3)
) Engine=InnoDB CHARSET=utf8;
分别插入100000条数据:
mysql> DROP PROCEDURE BatchInsert;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> delimiter //
mysql> CREATE PROCEDURE BatchInsert(IN init INT, IN loop_time INT)
-> BEGIN
-> DECLARE Var INT;
-> DECLARE ID INT;
-> SET Var = 0;
-> SET ID = init;
-> WHILE Var < loop_time DO
-> insert into s1(id, key1, key2, key3, key_part1, key_part2, key_part3, common_field) values(ID, CONCAT('A', ID), ID+10, CONCAT('B', ID), CONCAT('C', ID), CONCAT('D', ID), CONCAT('E', ID), CONCAT('F', ID));
-> insert into s2(id, key1, key2, key3, key_part1, key_part2, key_part3, common_field) values(ID, CONCAT('A', ID), ID+10, CONCAT('B', ID), CONCAT('C', ID), CONCAT('D', ID), CONCAT('E', ID), CONCAT('F', ID));
-> SET ID = ID + 1;
-> SET Var = Var + 1;
-> END WHILE;
-> END;
-> //
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> delimiter ;
mysql>
mysql>
mysql> CALL BatchInsert(1, 100000);
1.3.1 id
id是select查询的序列号,包含一组数字,表示查询中执行select子句或操作表的顺序:
1)当id相同时,执行顺序是从上至下
mysql> explain select * from s1 inner join s2;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s1 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 99688 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | s2 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 100325 | 100.00 | Using join buffer (hash join) |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------------------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.09 sec)
上述join查询中参与连接的s1和s2表分别对应一条记录,但两条对应的记录id都是1。当记录的id相同时,出现在前面的表为驱动表,后面的表为被驱动表,也就是执行顺序从s1到s2。
2)id不同:如果是子查询,id的序号会递增,id值越大优先级越高,越先被执行
mysql> explain select * from s1 where key1 in (select key1 from s2) or key3 like 'B%';
+----+--------------------+-------+------------+----------------+---------------+----------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+--------------------+-------+------------+----------------+---------------+----------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | s1 | NULL | ALL | idx_key3 | NULL | NULL | NULL | 99688 | 100.00 | Using where |
| 2 | DEPENDENT SUBQUERY | s2 | NULL | index_subquery | idx_key1 | idx_key1 | 303 | func | 1 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+--------------------+-------+------------+----------------+---------------+----------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
对于子查询来说,每个select关键字都会对应一个唯一的id值。从上述结果中看到s1表在外层查询中,外层查询有一个独立的SELECT关键字,s2表在子查询中,执行顺序是先s1表再到s2表。
1.3.2 select_type
MySQL为每一个select查询都定义了一个select_type属性,主要用于区分普通查询、联合查询、子查询等复杂的查询语句。
1)simple
简单的select查询,查询中不包含子查询或者union都算作simple查询,比如:
mysql> explain select * from s1 inner join s2;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s1 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 99688 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | s2 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 100325 | 100.00 | Using join buffer (hash join) |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------------------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.09 sec)
2)primary
查询中包含任何复杂的子部分比如UNION、UNION ALL或子查询,最外层查询则被标记为primary,比如:
mysql> explain select * from s1 union select * from s2;
+----+--------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-----------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+--------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-----------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | s1 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 99688 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 2 | UNION | s2 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 100325 | 100.00 | NULL |
| NULL | UNION RESULT | <union1,2> | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | Using temporary |
+----+--------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-----------------+
3 rows in set, 1 warning (0.39 sec)
从上可以看到最左边的查询对应的是执行计划中的第1条记录,它的select_type为primary
3)UNION
对于包含UNION或UNION ALL的查询语句来说,除了最左边的查询,其它查询的select_type都为UNION。
4)UNION RESULT
MySQL使用临时表来完成UNION查询的去重,针对该临时表查询的select_type为UNION RESULT,具体参加上例。
5)SUBQUERY/DEPENDENT SUBQUERY
如果包含子查询的查询语句不能转换为对应的semi-join形式,并且该子查询是不相关子查询,并且优化器采用将子查询物化的方案执行该子查询时,那么该子查询第一个关键字select代表的select_type为subquery,如果不会物化优化,则为dependent subquery:
mysql> explain select * from s1 where key1 in (select key1 from s2 where s1.key2=s2.key2) or key3 like 'B%';
+----+--------------------+-------+------------+--------+-------------------+----------+---------+---------------+-------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+--------------------+-------+------------+--------+-------------------+----------+---------+---------------+-------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | s1 | NULL | ALL | idx_key3 | NULL | NULL | NULL | 99688 | 100.00 | Using where |
| 2 | DEPENDENT SUBQUERY | s2 | NULL | eq_ref | idx_key2,idx_key1 | idx_key2 | 5 | tango.s1.key2 | 1 | 10.00 | Using where |
+----+--------------------+-------+------------+--------+-------------------+----------+---------+---------------+-------+----------+-------------+
2 rows in set, 2 warnings (0.00 sec)
需要注意的是select_type为DEPENDENT SUBQUERY的查询可能会被执行多次
6)DEPENDENT UNION
在UNION或UNION ALL的大查询中,如果各个小查询都依赖于外层查询,那除了最左边的小查询外,其余的小查询的select_type都为DEPENDENT UNION
mysql> explain select * from s1 where key1 in (select key1 from s2 where key1 ='a' union select key1 from s1 where key1='b');
+----+--------------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+-------+----------+--------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+--------------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+-------+----------+--------------------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | s1 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 99688 | 100.00 | Using where |
| 2 | DEPENDENT SUBQUERY | s2 | NULL | ref | idx_key1 | idx_key1 | 303 | const | 1 | 100.00 | Using where; Using index |
| 3 | DEPENDENT UNION | s1 | NULL | ref | idx_key1 | idx_key1 | 303 | const | 1 | 100.00 | Using where; Using index |
| NULL | UNION RESULT | <union2,3> | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | Using temporary |
+----+--------------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+-------+----------+--------------------------+
4 rows in set, 1 warning (0.36 sec)
从执行计划可以看到,子查询由UNION连起来的两个小查询,select key1 from s1 where key1='b’这个查询的select_type为DEPENDENT UNION。
7)DERIVED
对于采用物化的方式执行的包含派生表的查询,该派生表对应的子查询的select_type为derived,如下所示:
mysql> explain select * from (select key1,count(*) as c from s1 group by key1) as derived_s1 where c>1;
+----+-------------+------------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+------------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | <derived2> | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 99688 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 2 | DERIVED | s1 | NULL | index | idx_key1 | idx_key1 | 303 | NULL | 99688 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+-------------+------------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.39 sec)
从执行计划中可以看出,id为2的子查询的select_type为DERIVED,id为1的代表外层查询,该查询是将派生表物化之后的表进行查询的。
1.3.3 type
访问类型type是查询优化中的一个重要指标,结果值从好到坏依次是:
system > const > eq_ref > ref > fulltext > ref_or_null > index_merge > unique_subquery > index_subquery > range > index > ALL
1)system
当表中只有一条记录,并且该表使用的存储引擎的统计数据是精确的,比如MyISAM、Memory,那么该表的访问方式就是system的
2)const
表示通过索引一次就找到了,const用于比较primary key或者unique索引,如下所示:
mysql> explain select * from s1 where id=5;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s1 | NULL | const | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 4 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.01 sec)
3)eq_ref
在连接查询时,如果被驱动表是通过主键或者唯一索引列等值匹配的方式进行访问时,则对该被驱动表的访问方法是eq_ref,如下所示:
mysql> explain select * from s1 inner join s2 on s1.id=s2.id;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+-------------+-------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+-------------+-------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s1 | NULL | ALL | PRIMARY | NULL | NULL | NULL | 99688 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | s2 | NULL | eq_ref | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 4 | tango.s1.id | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+-------------+-------+----------+-------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
从以上可以看出,s2的访问方式是eq_ref,表明在访问s2表的时候可以通过主键的等值匹配来进行访问。
4)ref
当通过普通的非唯一索引与常量进行等值匹配来查询某个表,它会返回匹配某个单独值的所有行。其本质上也是一种索引访问,只是可能会找到多个符合条件的行记录。
mysql> explain select * from s1 where key1='a';
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s1 | NULL | ref | idx_key1 | idx_key1 | 303 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
5)ref_or_null
当对普通的二级索引进行等值匹配查询,该索引列的值也可以是NULL时,那么对该表的访问方法可能为ref_or_null,如下所示:
mysql> explain select * from s1 where key1='a' or key1 IS NULL;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s1 | NULL | ref_or_null | idx_key1 | idx_key1 | 303 | const | 2 | 100.00 | Using index condition |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
6)index_merge
使用索引合并的方式对某个表进行查询,如下所示:
mysql> explain select * from s1 where key1='a' or key3='a';
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------------+-------------------+-------------------+---------+------+------+----------+---------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------------+-------------------+-------------------+---------+------+------+----------+---------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s1 | NULL | index_merge | idx_key1,idx_key3 | idx_key1,idx_key3 | 303,303 | NULL | 2 | 100.00 | Using union(idx_key1,idx_key3); Using where |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------------+-------------------+-------------------+---------+------+------+----------+---------------------------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
7)unique_subquery
在一些包含IN子查询的查询语句中,如果查询优化器决定将IN子查询转换为EXISTS子查询,而且子查询可以使用到主键进行等值匹配时,则该子查询执行计划的type为unique_subquery,如下所示:
mysql> explain select * from s1 where key2 in (select id from s2 where s1.key1=s2.key1) or key3='a';
+----+--------------------+-------+------------+-----------------+------------------+---------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+--------------------+-------+------------+-----------------+------------------+---------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | s1 | NULL | ALL | idx_key3 | NULL | NULL | NULL | 99688 | 100.00 | Using where |
| 2 | DEPENDENT SUBQUERY | s2 | NULL | unique_subquery | PRIMARY,idx_key1 | PRIMARY | 4 | func | 1 | 10.00 | Using where |
+----+--------------------+-------+------------+-----------------+------------------+---------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
2 rows in set, 2 warnings (0.00 sec)
8)range
如果使用索引获取某些范围区间的记录,就可能使用到range的访问方法,如下所示:
mysql> explain select * from s1 where key1 in ('a','b','c');
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s1 | NULL | range | idx_key1 | idx_key1 | 303 | NULL | 3 | 100.00 | Using index condition |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.46 sec)
9)index
使用索引覆盖并遍历所有的索引记录时,该表的访问方式为index:
mysql> explain select key_part2 from s1 where key_part3='a';
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+--------------+---------+------+-------+----------+--------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+--------------+---------+------+-------+----------+--------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s1 | NULL | index | idx_key_part | idx_key_part | 909 | NULL | 99688 | 10.00 | Using where; Using index |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+--------------+---------+------+-------+----------+--------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
上述查询中,select列表中只有key_part2一个列,where条件中只有key_part3一个列,这两个列恰好又在idx_key_part索引中。但是where条件key_part3不能使用该索引进行ref或者range访问,只能扫描整个索引idx_key_part的记录,查询计划的type为index。
10)ALL
即全表扫描,遍历全表以找到匹配的行
mysql> explain select * from s1;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s1 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 99688 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
1.3.4 possible_keys和key
在EXPLAIN语句输出的执行计划中,possible_keys列表示对某个表进行单表查询时可能使用到的索引有哪些,key列表示实际使用到的索引列有哪些。如下所示:
mysql> explain select * from s1 where key1 > 'Z' and key3 ='a';
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+-------------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+-------------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s1 | NULL | ref | idx_key1,idx_key3 | idx_key3 | 303 | const | 1 | 5.00 | Using where |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+-------------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
上述执行计划中possible_keys的值为idx_key1,idx_key3,key列的值为idx_key3,表示经过优化器计算使用不同索引的成本后,决定使用idx_key3。需要注意的是,possible_keys的值不是越多越好,因为优化器计算查询成本会花费更长的时间,因此要删除不使用的索引。
1.3.5 key_len
表示当优化器决定使用某个索引执行查询时,该索引记录的最大长度,它由三部分构成:
- 对于使用固定长度的列作为索引列来说,实际占用存储空间的最大长度为该固定值;对于变长类型,就是变长的最大长度
- 如果该索引列可以存储NULL值,则key_len又会多一个字节
- 对于变长字段来说,会有2个字节的空间来存储该变长列的实际长度
mysql> explain select * from s1 where key1='a';
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s1 | NULL | ref | idx_key1 | idx_key1 | 303 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
由于key1列的类型为varchar(100),该列实际最多占用的存储空间为300字节,同时该列又允许存储NULL,又是变长列,则key_len变成300+1+2=303。
1.3.6 ref
这里的ref和type中的不同,这个ref的作用主要是指明当前表所参照的字段。
mysql> explain select * from s1 inner join s2 on s1.id=s2.id;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+-------------+-------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+-------------+-------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s1 | NULL | ALL | PRIMARY | NULL | NULL | NULL | 99688 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | s2 | NULL | eq_ref | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 4 | tango.s1.id | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+-------------+-------+----------+-------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
可以看到s2对应的ref列的值为tango.s1.id,说明s2在访问时会用到全局索引与一个列进行等值匹配条件,也就是tango.s1.id。
1.3.6 rows
rows表示预计扫描的记录数或者索引记录行数,比如:
mysql> explain select * from s1 where key1 > 'a';
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s1 | NULL | ALL | idx_key1 | NULL | NULL | NULL | 99688 | 50.00 | Using where |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
从上可以看到执行计划的rows列为99688,也就是优化器在分析使用idx_key1进行查询的成本后,觉得满足条件的记录有99688条。
1.3.7 filtered
MySQL在计算filtered时候采用一个策略:如果使用的是全表扫描执行的单表查询,那么在计算filtered时候需要估计出满足filter条件的记录到底有多少条;如果使用的索引执行的单表扫描,则需要估计出使用到的索引对应的搜索条件外其它搜索条件的记录有多少条。
mysql> explain select * from s1 where key1 > 'z' and common_field='a';
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s1 | NULL | range | idx_key1 | idx_key1 | 303 | NULL | 1 | 10.00 | Using index condition; Using where |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
从执行计划可以看出使用索引idx_key1进行查询,从rows列看出满足条件的记录有1条。执行计划中的filtered就代表优化器预测在这1条中有多少条记录满足其余的搜索条件,也就是common_field='a’这个条件的百分比,此处filtered列的值为10%,也就是优化器预测有10%的记录满足这个条件。对于关联查询中,filter更有意义。
1.3.8 extra
Extra列是用来说明一些额外信息的,通过这些额外信息可以更为准确的分析SQL性能。
1)Impossible where
查询语句的where语句永远为FALSE时将会提示额外信息:
mysql> explain select * from s1 where 1!=1;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | Impossible WHERE |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+------------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
2)Using Index
当查询列表和where条件中只包含属于某个索引的列,也就是在使用索引覆盖的情况下,extra中会提示该信息。
mysql> explain select key1 from s1 where key1='a';
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s1 | NULL | ref | idx_key1 | idx_key1 | 303 | const | 1 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
上述查询只需要访问索引,而不需要回表操作。
3)Using where
当使用全表扫描执行某个表的查询并且where条件中有该表的搜索条件,或者一部分数据在索引中没有全部包含并且需要到原表中查询时,extra会提示using where的信息:
mysql> explain select * from s1 where key1='a' and common_field='a';
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s1 | NULL | ref | idx_key1 | idx_key1 | 303 | const | 1 | 10.00 | Using where |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
4)Using join buffer(Block Nested loop)
在join查询过程中,如果被驱动表不能有效的利用索引加快访问速度,MySQL会为其分配一块join buffer的内存来加快查询速度,也就是基于块的嵌套循环算法。如下所示:
mysql> explain select * from s1 inner join s2 on s1.common_field=s2.common_field;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+--------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+--------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s1 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 99688 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | s2 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 100325 | 10.00 | Using where; Using join buffer (hash join) |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+--------------------------------------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
上述中s2表的extra信息中提示using join buffer,因为对表s2的访问不能有效利用索引,只好退而求其次的使用join buffer来减少对s2表的访问次数,从而提高性能。
5)Using filesort
Extra字段中如果出现using filesort,表示当前的SQL语句中除了必要的查询外,还需要一次额外的非必要查询,这种情况多出现在带有order by的SQL语句中。因为很多时候排序操作无法使用到索引,只能在内存或者磁盘上进行排序,这种在内存或磁盘上排序的操作统一称为文件排序filesort。如下所示:
mysql> explain select * from s1 order by common_field limit 10;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+-------+----------+----------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+-------+----------+----------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s1 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 99688 | 100.00 | Using filesort |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+-------+----------+----------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
Using filesort一般分为两种情况来优化:单索引和复合索引
- 对于单索引,如果查找和排序是同一个字段,则不会出现using filesort
mysql> explain select * from s1 where key1='a' order by key2;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+----------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+----------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s1 | NULL | ref | idx_key1 | idx_key1 | 303 | const | 1 | 100.00 | Using filesort |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+----------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from s1 where key1='a' order by key1;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s1 | NULL | ref | idx_key1 | idx_key1 | 303 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
由上可以看出,当order by列和where列都为索引字段是,避免使用filesort
- 对于复合索引,where和order by后的字段尽量按照复合索引的顺序来使用,不要跨列和无序使用
mysql> explain select * from s1 where key_part1='a' order by key_part3;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------------+---------+-------+------+----------+----------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------------+---------+-------+------+----------+----------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s1 | NULL | ref | idx_key_part | idx_key_part | 303 | const | 1 | 100.00 | Using filesort |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------------+---------+-------+------+----------+----------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from s1 where key_part1='a' order by key_part2;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s1 | NULL | ref | idx_key_part | idx_key_part | 303 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
由上可以看出,在复合索引下,当where语句中的列和order by语句中的列按照复合索引字段的顺序,也避免出现了filesort问题。
6)Using temporary
Extra中出现using temporary信息,说明查询过程中使用了临时表,对性能损耗也较大,一般出现在distinct或group by语句中。如下所示:
mysql> explain select common_field,count(*) as amount from s1 group by common_field;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+-------+----------+-----------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+-------+----------+-----------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s1 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 99688 | 100.00 | Using temporary |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+-------+----------+-----------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
查询过程中使用临时表对性能影响很大,最好是使用索引来替换掉临时表。另外在查询的时候尽量做到查询哪些列就对那些列进行group by,比如下面两个语句:
mysql> explain select common_field,count(*) as amount from s1 where key1='a' group by common_field;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s1 | NULL | ref | idx_key1 | idx_key1 | 303 | const | 1 | 100.00 | Using temporary |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+----------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select common_field,count(*) as amount from s1 where common_field='a' group by common_field;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | s1 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 99688 | 10.00 | Using where |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
当where条件中的列和group by列一致时,不会涉及到临时表的操作。
以上是MySQL中的执行计划内容,适用于分布式数据库中以MySQL为原生的数据节点上执行计划的分析。
参考资料:
- https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/execution-plan-information.html
- 《MySQL是怎样运行的》,小孩子著
- https://blog.csdn.net/Hi_Red_Beetle/article/details/88778731
- https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41558728/article/details/81704916
- 数据库系列之InnoDB存储引擎解密
转载请注明原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/solihawk/article/details/120756584
文章会同步在公众号“牧羊人的方向”更新,感兴趣的可以关注公众号,谢谢!
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
如何给Eclips自动添加作者,时间等…
Notepad++--常用的插件
Ten years' experience of Software Engineer
Inference optimization implementation of tensorrt model
Artifact for converting pcap to JSON file: joy (installation)
项目实战!手把手教你 Jmeter 性能测试
基于流的深度生成模型
matlab习题 —— 矩阵的常规运算
TypeError:&nbsp;&#039;module&amp;#03…
The same is MB. Why is the gap so large?
Is it better for a novice to open a securities account? Is it safe to open a stock trading account
如何获取GC(垃圾回收器)的STW(暂停)时间?
Excel知识技能汇总
Summary of the use of composition API in the project
剑指 Offer 47. 礼物的最大价值(DP)
Apache, IIS6 and ii7 independent IP hosts screen and intercept spider crawling (applicable to VPS virtual machine servers)
启牛商学院赠送证券账户是真的吗?开户到底安不安全呢
collections.defaultdict()的使用
Redis cluster setup [simple]
mysql获取当前时间是一年的第多少天