当前位置:网站首页>Day_ eleven
Day_ eleven
2022-06-25 16:25:00 【grp_ grp_ grp】
Day11 Always review
1 Program basis
1.1 data type
The nature of data types : Specify the size of the occupied memory space , Restrict the format type of data
Data types include :
Basic data types and reference data types
Basic data types include integer floating-point Character Boolean type
Integers include int byte short long;
Floating point types include float( Single floating point 32 position ) double( Double floating point 64 position );
Character char;
Boolean type boolean;
Reference data types include class Array Interface
ASCII code : Mapping between characters and integers
a = 97 ; A = 65 ; 0 = 48…….
Automatic type conversion :
Byte ->short -> int -> long -> float -> double
char ->int ->long -> float ->double
Be careful :
When byte,short,char,int Of the four types , Any one or more operations , The result is int
1.2 Variable
Definition : Variable quantity , It is convenient to operate the data in the space
Statement : data type Variable name = value ;
int i1 = 0;
Byte b1 = 0;
Short s1 = 10;
Long l1 = 10L;
Char c1 = ‘c’;
Double d1 = 2.2;
Float f1 = 1.2F;
Boolean b1 = true;
classification :
local variable : Method , Can only be used in the current method , No default , The scope is a brace
Static variables : Use Static Decorated variable , And methods are level relations
Member variables : Not used static Decorated variable
call :
local variable : Call the variable directly by name in the method , No default , Assignment must be made.
Static variables : adopt Class name . Static variable name call , Call the static variable of the current class in the current class , Class names can be omitted
Member variables : Class body through Object reference . Member variables call
The default value is : Integers 0 ; decimal 0.0 ; Boolean type false ; Character \u0000 ; The reference type defaults to null
1.3 Operator
i++ : Assign first , One more
++i : Add one first , To assign a value
Operator priority :
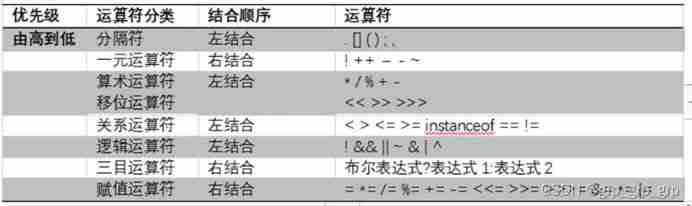
An operator :
& Bit and , It is true that both sides are true , Whether or not the first condition is false, The second condition will still be implemented
&& Short circuit and , Suppose the first condition is false, The second condition is not executed
| : or , One on both sides is true That's true , Whether the first condition is false still true, The second condition is implemented
|| : Short circuit or , If the first condition is true, Then the second condition is no longer executed
1.4 Process control
Sequential structure :
Strictly from top to bottom , From left to right
Branching structure :
Through the specified judgment conditions , Selectively take different branches
If…else…. :
Single branch : There are cases of non implementation
If( Boolean expressions ){
Code executed when true
}
Double branch : There must be a branch that performs
If( Boolean expressions ){
Code executed when true
}else{
Code executed when is false
}
Switch
grammar :
Switch( value ){
Case value ;
Break;
}
1.5 Loop structure
A loop is a code that is repeated many times
For loop
for( expression 1, expression 2, expression 3){
The loop body
}
Three elements : Starting value , Termination conditions , step
While loop
while( Boolean type ){
The loop body
}
Break : Can be used in switch in , end case Branch , prevent case through
It can also be used in loops , End the current cycle
Continue : Skip the current cycle , Continue next time
1.6 Method
A method is a collection of many statements , Put the code in the method , It can be used multiple times , The purpose is code reuse , Make the program shorter and clearer , Improve development efficiency
Statement :
List of modifiers return type Method name ( parameter list ){ Method body }
classification :
Static methods : Use static The method of decoration
Member method : No, static The method of decoration
Construction method : Modifier Method name (), even void either
call :
Static methods : Class name . Static method name ( Parameters )
Member method : Object reference . Legal name of member ( Parameters )
Method does not call, does not execute , Call to execute
1.7 Memory division

Static zone / Method area :
Save program files (class file ) And static data , Before the method is called , Also stored in the static area , There is also a runtime constant pool inside
VM Stack : Also called stack memory
Stack memory is a space opened up based on stack data structure , The feature is first in and last out
Stack : It's a data structure , First in, then out , Like a clip
The components of the stack
Stack space : Stack memory is stack space
Stack frame : Every stack element in the stack space It's called stack frame ( such as Every bullet in the magazine It's called stack frame )
Stack bottom element : The first stack frame put in
Top element of stack : The last stack frame put in
Stack operation
Pressing stack : It refers to the process of putting elements into stack space
Bomb stack : Is the process of ejecting elements
Stack memory , Is used to execute methods , Execution of all methods , Must be done in stack memory
Native Method Stack :
Used to execute some local methods , such as hashCode etc. , The model and operation are similar to VM Stack consistency
Heap memory : To save objects
1.8 recursive
Recursion is to call the current method in a method
2 Array
Arrays are reference data types , Used to store multiple data
2.1 data structure
Data structure is computer storage 、 How to organize data . Data structure refers to the collection of data elements that have one or more specific relationships with each other . Usually , Well chosen data structure can bring higher operation or storage efficiency . Data structures are often related to efficient retrieval algorithms and indexing techniques
Data manipulation : Additions and deletions
2.2 Array
characteristic :
Continuous storage , Subscript from 0 Start , Use memory address offset
Once the length is determined, it cannot be changed
When adding or deleting , You should create a new array , Copy the required values into the new array
Query changes are extremely efficient
Statement :
Static declaration : When each element is known , Use static declarations
data type [] Variable name = { value , value };
data type [] Variable name = new data type { value };
Dynamic statement : When I don't know every element , Use dynamic declarations
data type [] Variable name = new data type { length };
storage :

Use :
Inquire about : Array [ Subscript ]
change : Array [ Subscript ]= value
Sort :
API : Arrays.sort( Array );
Bubbling : Comparing the two , Greater than swap position
choice : Suppose the first one is the smallest , Compare with the following in turn , Greater than the swap subscript swap value
Two points search :
Define the starting position , End position , In the middle
If The goal is bigger than the middle be End unchanged start = middle +1
If the target is smaller than the middle be Initial invariance end = middle -1
Regenerate the middle position
Start is greater than end
Two dimensional array :
Static declaration :int[][] arr = { { The number };};
Dynamic statement :int[][] arr = new int[5][];

3 object-oriented
3.1 Object oriented and process oriented
Object oriented is a software development method , A programming paradigm . The concept of object orientation has gone beyond programming and software development , Extend to, for example, databases 、 Interactive interface 、 Application structure 、 Application platform 、 Distributed systems 、 Network management structure 、CAD technology 、 Artificial intelligence and other fields . Object oriented is a way to understand and abstract the real world , It is the product of the development of computer programming technology to a certain stage .
Process oriented : Focus on step by step
For example, when you want to do something , Analysis first
What should be done in the first step
What should be done in the second step
object-oriented : Focus on sub modules
For example, when you want to do something , Analyze who should do the job
summary :
Object - oriented has the advantage : Extensibility , Maintainability , flexibility , Reduce program coupling
shortcoming : Performance is relatively worse than process oriented
3.2 Classes and objects
class : Describe the properties and characteristics of such things , Abstract the template
object : Is a specific thing
Objects are implementations of classes , Saved the value of the attribute
If between objects Have the same attribute, the same value , Use Static variables
If between objects Have the same attribute but different values ( It can be the same ), Use Member variables
3.3 Construction method
Constructors are common to every class , The object used to create the class , By default, there is a parameterless construct
grammar :
Modifier Class name ( parameter list ){ Method body }
Out of commission static, no return value , even void None
3.4 Instantiation
1 Load the corresponding class file
2 new Create space in heap memory
3 Execute construction , Initialize the heap memory object
4 Construction method: pop stack , And return the heap memory address to the variable
3.5 call
Object invokes static properties
1 You can use the class name to call
2 You can use objects to call , Because the object will be converted into a class name call in the compilation phase
Static call member :
In the static method , Non static attributes cannot be used directly , An object call is required to call
Distinguish between member methods and constructor methods :
What has no return value is the constructor , even void None , What has a return value is the member method
3.6 This
Definition :
Is in each object , A reference variable that holds its own address this It means that the current object
function :
1 In a member method or constructor , Distinguish between member variables and local variables with the same name
2 Used in construction methods , Overload calls other constructor methods in the current class , But it must be written in the first line of the constructor
3 return this Returns the memory address of the current object , You can chain call
Be careful :
This Cannot appear in a static context
3.7 encapsulation
Put all the components together , You can also hide the data through the permission control modifier , It can control the modification degree of class data by users
Proper encapsulation can make the code easier to understand , Easy to maintain , It improves the security of the code
Package
Package mechanism , It mainly solves the problem of naming conflicts
Import
Used to load other classes required in the current class , Must be in class above ,package Under the statement
3.8 Access control

3.9 Inherit
Definition :
Existing classes , Derive a new class , The new class is used for the properties and behaviors of the parent class
Purpose :
Code reuse , Increase of efficiency
grammar :
class Class name extends Parent class name { The class body }
Super :
Represents the characteristics of the parent class , It is used to distinguish methods and variables of the same name between parent and child classes in member methods and constructor methods super.xxx
It can also be used in subclass methods , Call the specified parent class constructor super(xxx), Must appear in the first line of the subclass constructor
3.10 overwrite
Overrides refer specifically to member methods , When the function of the parent class cannot meet the needs of the child class , Overwrite
Definition :
Write a method that is the same as the parent class , But the function is different
The rules :
1 Method name , Return value , parameter list Must be consistent with the parent class
2 Cannot have lower access rights than the original method
3 You cannot have a broader exception than the original method
边栏推荐
- Uncover gaussdb (for redis): comprehensive comparison of CODIS
- 10款超牛Vim插件,爱不释手了
- Flutter assembly
- 揭秘GaussDB(for Redis):全面对比Codis
- Prototype chain analysis
- The paid video at station B caused the up master to lose more than ten thousand fans
- Geographic location data storage scheme - redis Geo
- What exactly is a handler
- How to reload the win10 app store?
- Shuttle pop-up returns to the upper level
猜你喜欢

Learning notes of rxjs takeuntil operator
绕过技术聊'跨端'......
Why does golang's modification of slice data affect the data of other slices?

cmd。。。。。。

Describe your understanding of the evolution process and internal structure of the method area

Record learning of hystrix knowledge --20210929

炮打司令部,别让一个UI框架把你毁了
Create raspberry PI image file of raspberry pie

数字经济时代文化消费新特征

The style of the mall can also change a lot. DIY can learn about it!
随机推荐
Detailed explanation of IVX low code platform series -- Overview (I)
The style of the mall can also change a lot. DIY can learn about it!
Check whether the port number is occupied
[untitled]
Reverse series to obtain any wechat applet code
Lifeifei's team applied vit to the robot, increased the maximum speed of planning reasoning by 512 times, and also cued hekaiming's MAE
Precautions for function default parameters (formal parameter angle)
Time wheel and implementation analysis of time wheel in go zero
MySQL_ JDBC
一文带你搞懂 JWT 常见概念 & 优缺点
Shuttle pop-up returns to the upper level
Go development team technical leader Russ Cox sends a document to share go's version control history
Based on neural tag search, the multilingual abstracts of zero samples of Chinese Academy of Sciences and Microsoft Asiatic research were selected into ACL 2022
cmd。。。。。。
TensorFlow加载cifar10数据集
After flutter was upgraded from 2.2.3 to 2.5, the compilation of mixed projects became slower
Deep learning pytorch cifar10 dataset training "suggestions collection"
不要小看了积分商城,它的作用可以很大!
揭秘GaussDB(for Redis):全面对比Codis
Advanced SQL statement 1 of Linux MySQL database

