当前位置:网站首页>Balanced binary tree (AVL tree)
Balanced binary tree (AVL tree)
2022-06-11 23:42:00 【Run after XX】
Balanced binary trees (AVL Trees )
Look at a case ( Explain the possible problem of binary sort tree )
I'll give you a sequence {1,2,3,4,5,6}, A binary sort tree is required (BST), And analyze the problem .
On the left BST Analysis of existing problems :
- All left subtrees are empty , In form , It's more like a single linked list .
- The insertion speed has no effect
- The query speed is significantly reduced ( Because we need to compare ), Can't play BST The advantages of , Because every time you need to compare the left subtree , The query speed is faster than that Single linked list is slow
- Solution - Balanced binary trees (AVL)
Basic introduction
- Balanced binary tree is also called balanced binary search tree (Self-balancing binary search tree) Also known as AVL Trees , It can ensure high query efficiency .
- It has the following characteristics : It's one The absolute value of the height difference between an empty tree or its left and right subtrees shall not exceed 1, And both the left and right subtrees are one Balanced binary trees .
The common way to realize balanced binary tree is red black tree 、AVL、 Scapegoat tree 、Treap、 Stretch the trees, etc . - Illustrate with examples , Take a look at the following AVL Trees , Why? ?

The application case - Single rotation ( Left rotation )
- requirement : I'll give you a sequence , Create the corresponding balanced binary tree . The sequence {4,3,6,5,7,8} 2) Thought analysis ( Sketch Map )
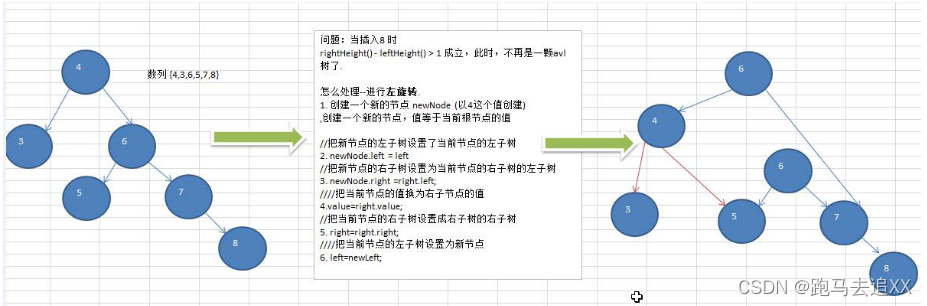
- Code implementation
public void leftRotate() {
// Create a new node , With the value of the current root
Node newNode = new Node(value);
// Set the new node's left subtree to the current node's left subtree
newNode.left = left;
// Set the right subtree of the new node to the left subtree of the right subtree with your past nodes
newNode.right = right.left;
// Replace the value of the current node with the value of the right child node
value = right.value;
// Set the right subtree of the current node to the right subtree of the current node
right = right.right;
// Put the left subtree of the current node ( Left child node ) Set to a new node
left = newNode;
}
The application case - Single rotation ( Right rotation )
- requirement : I'll give you a sequence , Create the corresponding balanced binary tree . The sequence {10,12, 8, 9, 7, 6}
- Thought analysis ( Sketch Map )

- Code implementation
public void rightRotate() {
Node newNode = new Node(value);
newNode.right = right;
newNode.left = left.right;
value = left.value;
left = left.left;
right = newNode;
}
The application case - Double rotation
The first two sequences , Make a single spin ( It's a rotation ) We can turn a non-equilibrium binary tree into a balanced binary tree , But in some cases , Single rotation Can't complete the transformation of balanced binary tree .
Like a sequence of numbers int[] arr = { 10, 11, 7, 6, 8, 9 }; Run the original code to see , It didn't turn into AVL Trees .
int[] arr = {2,1,6,5,7,3}; // Run the original code to see , It didn't turn into AVL Trees
- Problem analysis

- Solution analysis
- When the symbol is rotated to the right
- If the height of the right subtree of its left subtree is greater than the height of its left subtree
- First, rotate the left node of the current node
- Right rotate the current node
- Code implementation [AVL Tree summary code ( Complete code )]
package com.iflytek.avl;
public class AVLTreeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {
10, 11, 7, 6, 8, 9};
// Create a AVLTree object
AVLTree avlTree = new AVLTree();
// Add node
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
avlTree.add(new Node(arr[i]));
}
// Traverse
System.out.println(" In the sequence traversal ");
avlTree.infixOrder();
System.out.println(" In balancing ~~");
System.out.println(" The height of the tree =" + avlTree.getRoot().height()); //3
System.out.println(" The height of the left subtree of the tree =" + avlTree.getRoot().leftHeight()); // 2
System.out.println(" The height of the right subtree of the tree =" + avlTree.getRoot().rightHeight()); // 2
System.out.println(" Current root =" + avlTree.getRoot());//8
}
}
// establish AVLTree
class AVLTree {
private Node root;
public Node getRoot() {
return root;
}
// Find the node to delete
public Node search(int value) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
} else {
return root.search(value);
}
}
// Find the parent node
public Node searchParent(int value) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
} else {
return root.searchParent(value);
}
}
// Compiling method :
// 1. Back to With node The value of the maximum node of the left subtree of the binary sort tree with root node
// 2. Delete node The largest node of the left subtree of the binary sort tree with root node
/** * @param node Incoming node ( As the root node of binary sort tree ) * @return Back to With node Is the value of the smallest node of the binary sort tree of the root node */
public int delLeftTreeMax(Node node) {
Node target = node;
// Loop to find the right child node , You'll find the maximum
while (target.right != null) {
target = target.right;
}
// At this time target It points to the largest node
// Delete maximum node
delNode(target.value);
return target.value;
}
// Delete node
public void delNode(int value) {
if (root == null) {
return;
} else {
Node targetNode = search(value);
// If the node to be deleted is not found
if (targetNode == null) {
return;
}
// If we find that there is only one node in the current binary sorting tree
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
root = null;
return;
}
// Go find targetNode The parent node
Node parent = searchParent(value);
// If the node to be deleted is a leaf node
if (targetNode.left == null && targetNode.right == null) {
// Judge targetNode Is the left child of the parent node , Or the right child node
if (parent.left != null && parent.left.value == value) {
// It's the left child node
parent.left = null;
} else if (parent.right != null && parent.right.value == value) {
// It's the right child node
parent.right = null;
}
} else if (targetNode.left != null && targetNode.right != null) {
// Delete the node with two subtrees
int maxVal = delLeftTreeMax(targetNode.left);
targetNode.value = maxVal;
} else {
// Delete a node with only one subtree
// If the node to be deleted has left child nodes
if (targetNode.left != null) {
if (parent != null) {
// If targetNode yes parent Left child node of
if (parent.left.value == value) {
parent.left = targetNode.left;
} else {
parent.right = targetNode.left;
}
} else {
root = targetNode.left;
}
} else {
// If the node to be deleted has a right child
if (parent != null) {
// If targetNode yes parent Left child node of
if (parent.left.value == value) {
parent.left = targetNode.right;
} else {
parent.right = targetNode.right;
}
} else {
root = targetNode.right;
}
}
}
}
}
// How to add nodes
public void add(Node node) {
if (root == null) {
root = node;
} else {
root.add(node);
}
}
// In the sequence traversal
public void infixOrder() {
if (root != null) {
root.infixOrder();
} else {
System.out.println(" Binary sort tree is empty , Can not traverse ");
}
}
}
// establish Node node
class Node {
int value;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" +
"value=" + value +
'}';
}
// return The height of the tree with this node as the root
public int height() {
return Math.max(left == null ? 0 : left.height(), right == null ? 0 : right.height()) + 1;
}
// Return to the height of the right subtree
public int rightHeight() {
if (right == null) {
return 0;
}
return right.height();
}
public void leftRotate() {
// Create a new node , With the value of the current root
Node newNode = new Node(value);
// Set the new node's left subtree to the current node's left subtree
newNode.left = left;
// Set the right subtree of the new node to the left subtree of the right subtree with your past nodes
newNode.right = right.left;
// Replace the value of the current node with the value of the right child node
value = right.value;
// Set the right subtree of the current node to the right subtree of the current node
right = right.right;
// Put the left subtree of the current node ( Left child node ) Set to a new node
left = newNode;
}
public void rightRotate() {
Node newNode = new Node(value);
newNode.right = right;
newNode.left = left.right;
value = left.value;
left = left.left;
right = newNode;
}
// Return to the height of the left subtree
public int leftHeight() {
if (left == null) {
return 0;
}
return left.height();
}
// Find the node to delete
/** * @param value The value you want to delete * @return If found, return the node , Otherwise return to null */
public Node search(int value) {
if (this.value == value) {
return this;
} else if (value < this.value) {
if (this.left == null) {
return null;
}
return this.left.search(value);
} else {
if (this.right == null) {
return null;
}
return this.right.search(value);
}
}
// Find the parent of the node you want to delete
/** * @param value The value of the node to find * @return Return the parent of the node to be deleted , If not, go back null */
public Node searchParent(int value) {
// If the current node is the parent of the node to be deleted , Just go back to
// The program is executed from left to right , You must first judge that the child node is not empty , Then the values can be compared
if ((this.left != null && this.left.value == value) ||
(this.right != null && this.right.value == value)) {
return this;
} else {
// If the search value is less than the value of the current node , And the left child of the current node is not empty
if (this.value > value && this.left != null) {
return this.left.searchParent(value);// Search left subtree recursively
} else if (this.value <= value && this.right != null) {
return this.right.searchParent(value);// Search right subtree recursively
} else {
return null;// No parent found
}
}
}
// How to add nodes
// Add nodes recursively , Note that the binary sort tree needs to be satisfied
public void add(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
// Determine the value of the incoming node , The value relationship with the root node of the current subtree
if (node.value < this.value) {
// The value of the added node is less than The value of the current node
// If the left child of the current node is null
if (this.left == null) {
this.left = node;
} else {
// Recursively add... To the left subtree
this.left.add(node);
}
} else {
// The value of the added node is greater than The value of the current node
if (this.right == null) {
this.right = node;
} else {
// Recursively add... To the right subtree
this.right.add(node);
}
}
// After adding a node , If : ( The height of the right subtree - The height of the left subtree ) > 1 , Left rotation
if (rightHeight() - leftHeight() > 1) {
// If the height of the left subtree of its right subtree is greater than the height of its right subtree
if (right != null && right.leftHeight() > right.rightHeight()) {
// First, rotate the right child node to the right
right.rightRotate();
// Then rotate the current node to the left
leftRotate();// Left rotation ..
} else {
// Just rotate it to the left
leftRotate();
}
return;// It has to be !!!
}
// After adding a node , If ( The height of the left subtree - The height of the right subtree ) > 1, Right rotation
if (leftHeight() - rightHeight() > 1) {
// If the height of the right subtree of its left subtree is greater than the height of its left subtree
if (left != null && left.rightHeight() > left.leftHeight()) {
// First, for the left node of the current node ( The left subtree )-> Left rotation
left.leftRotate();
// Then rotate the current node to the right
rightRotate();
} else {
// Just rotate right
rightRotate();
}
}
}
public void infixOrder() {
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.infixOrder();
}
System.out.println(this);
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.infixOrder();
}
}
}
边栏推荐
- 产品力进阶新作,全新第三代荣威RX5盲订开启
- DOM知识点总结
- [signals and systems] (XXII) Laplace transform and complex frequency domain analysis - s-domain analysis
- C language Niuke net string space substitution
- 05 classification learning notes lihongyi's in-depth study 2021
- Here we go! Dragon lizard community enters PKU classroom
- mysql5和mysql8同时安装
- Solr之基础讲解入门
- (dp) acwing 899. Edit distance
- 2022安全员-C证判断题模拟考试平台操作
猜你喜欢

MySQL 8.0 decompressed version installation tutorial

One to one correspondence of multiple schematic diagrams and PCB diagrams under Altium designer project

HMS core shows the latest open capabilities in mwc2022, helping developers build high-quality applications

Lake Shore—SuperVariTemp 低温恒温器

Lake Shore - supertran continuous flow cryogenic thermostat system

2022 R1 quick opening pressure vessel operation test questions and online simulation test

Simulated examination question bank and simulated examination of 2022 crane driver (limited to bridge crane)

How many steps does it take for C language to become Fibonacci number

2022 high voltage electrician test question simulation test question bank and online simulation test
![[signals and systems] (XXII) Laplace transform and complex frequency domain analysis - s-domain analysis](/img/35/a23646ac8501ac646cd44eeecd5b79.jpg)
[signals and systems] (XXII) Laplace transform and complex frequency domain analysis - s-domain analysis
随机推荐
require. context
Wake up wrist - neural network and deep learning (tensorflow application) updating
Lake Shore—SuperTran 连续流低温恒温器系统
2022 high voltage electrician test question simulation test question bank and online simulation test
【BBC learningenglish】with Tango
2022安全员-C证判断题模拟考试平台操作
(linear DP) acwing 898 Number triangle
(dp) acwing 899. Edit distance
Application of Lora wireless communication module Lora technology in smart home light control
图及图的遍历
Solr之基础讲解入门
New Year Countdown JS case
Read 5g RF terminal industry
Node version control tool NVM
Setting alias alias and @ reference note
Application of Lora technology in long distance wireless transmission of water meter reading
(dp+ group backpack) acwing 9 Group knapsack problem
Jenkins basic configuration
Introduction to Solr Basics
Are you still struggling with the gold content of PMP