当前位置:网站首页>软件体系结构实验汇总
软件体系结构实验汇总
2022-06-29 04:35:00 【无处安放的小曾】
1、数据流风格系统实验
2、事件驱动系统实验
3、eclipse中搭建tomcat集群实验
4、基于规则系统实验
5、黑板系统实现计算器的设计
6、KWIC系统实验一
7、KWIC系统实验2
8、KWIC系统实验三
实验报告内容
实验题目:1、数据流风格系统实验
实验目的: 理解数据的流动过程
实验要求: 对于同一数据流问题分别用理解管道-过滤器和顺序批处理两种风格实现解决
实验器材: 计算机
实验电路图/程序流程图:
批处理风格:

管道-过滤器风格:

实验步骤/程序源代码:
管道-过滤器风格:
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class TestPiped{
public static void main(String [] args){
sender s = new sender();
receiver r = new receiver();
PipedOutputStream out = s.getOut();
PipedInputStream in = r.getIn();
try{
in.connect(out);
s.start();
r.start();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class sender extends Thread {
PipedOutputStream out = new PipedOutputStream();
publicPipedOutputStream getOut(){
return out;
}
public void run() {
String str = "Hello,receiver ! I`msender\n";
try {
out.write(str.getBytes());
out.close();
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class receiver extends Thread {
PipedInputStream in = new PipedInputStream();
public PipedInputStream getIn() {
return in;
}
public void run(){
byte [] buf = new byte[1024];
try {
int len = in.read(buf);
System.out.println("the following is from sender:\n"+newString(buf,0,len));
in.close();
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
批处理风格:
#include <iostream>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
bool writeFile(constchar* strPath,char strConcern[],int length)
{
ofstream outfile;
outfile.open(strPath,ios::app);
if(!outfile)
{
cerr<<"openerror!"<<endl;
return false;
}
outfile.write(strConcern,length);
outfile.close();
return true;
}
bool ReadFile(constchar * strPath,char strConcern[],int length)
{
ifstream infile;
infile.open(strPath,ios::binary);
if(!infile)
{
cerr<<"openerror"<<endl;
return false;
}
while(!infile.eof())
{
infile.read(strConcern,length);
}
return true;
}
bool factory1()
{
char str[20]="helloworld";
charstrpath[20]="E:\\text1.txt";
bool b=writeFile(strpath,str,sizeof(str));
if(!b)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
bool factory2()
{
char str[20];
char strpath[20]="E:\\text1.txt";
bool b=ReadFile(strpath,str,sizeof(str));
cout<<str<<endl;
cout<<str<<endl;
charstrpath1[20]="E:\\text2.txt";
boolbw=writeFile(strpath1,str,sizeof(str));
bw=writeFile(strpath1,"第二道工序",sizeof(str));
if(!b||!bw)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
char strpath[40]="E:\\text2.txt";
char str[20];
bool b1=factory1();
bool b2=factory2();
bool b=ReadFile(strpath,str,sizeof(str));
if(b&&b1&&b2)
{
cout<<str<<endl;
}
//cout <<"Hello world!"<< endl;
return 0;
实验结果分析:
批处理与过滤器比较
共同点是处理过程之间均互不调用。
前者数据以整体的形式传输,数据总量有限。
后者数据用数据流的形式传输,数据量可以无限制。
实验日期: 2022.3.24
成绩评定:
□优秀(100-90分)
□良好(89-80分)
□中等(79-70分)
□及格(69-60分)
□不及格(60-0分)
教师签名:
年 月 日
实验报告内容
实验题目: 2、事件驱动系统实验
实验目的: 熟练运用事件驱动系统知识
实验要求: 运用事件驱动系统知识,实现一个事件系统
实验器材: 计算机,IDEA,java语言
实验电路图/程序流程图:
1.实验概要图
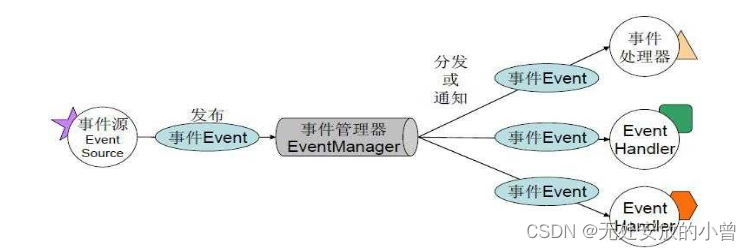
2.组成部分具体实现:

实验步骤/程序源代码:
1. 订阅者接口:

- 订阅者实现类:
public class D implements Subscribe {
private EventManger eventManger;
private String SubscribeName;//订阅者名字
public D(EventManger eventManger, String subscribeName) {
SubscribeName = subscribeName;
this.eventManger = eventManger;
}
@Override
public void get(Event event, String subscribeName) {
List list= eventManger.subscribe(event,subscribeName);
if(event==null){
System.out.println("pp"+list);
}
if (list.get(0)==null) {
System.out.println("目前还没有满足要求的事件");
} else {
System.out.println(subscribeName + " : " + list+ "此任务满足要求");
}
}
@Override
public void cancel(Event event, String subscribeName) {
eventManger.unsubscribe(subscribeName);
}
public String getSubscribeName() {
return SubscribeName;
}
public void setSubscribeName(String subscribeName) {
SubscribeName = subscribeName;
}
}
2.事件管理器类:
public class EventManger {
private Queue<Event> eventQueue = new LinkedList<>();//发布消息存储队列
private List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
private List<Event> list1;
public void publish(Event event) {//发布
System.out.println(event.getPublisherName() + "发布了" + event);
eventQueue.add(event);
}
public List subscribe(Event event, String SubscribeName) {//订阅
System.out.println(SubscribeName + "开启了订阅");
list.add(SubscribeName);
if (event == null) {
list1 = new ArrayList<>();
System.out.println(list1);
} else {
list1 = new ArrayList<>();
list1.add(position(event));
return list1;
}
return null;
}
public Event position(Event event) {
int size = eventQueue.size();
int flag = event.getFalg();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Event event1 = eventQueue.poll();
if (flag == 1) {//
if (event.getMoney() <= event1.getMoney() && event.getTypeName().equals(event1.getTypeName())) {
return event1;
}
} else if (flag == 0) {
if (event.getMoney() >= event1.getMoney() && event.getTypeName().equals(event1.getTypeName())) {
return event1;
}
} else {
eventQueue.add(event1);
}
}
return null;
}
public void unsubscribe(String SubscribeName) {//取消订阅
System.out.println(SubscribeName + "取消了订阅");
list.remove(SubscribeName);
}
}
3.发布者接口

3.1 发布者实现类
public class A implements Publisher {
String publishName;
EventManger eventManger;
public A(String publishName, EventManger eventManger) {
this.publishName = publishName;
this.eventManger = eventManger;
}
@Override
public void add(Event event) {
event.setPublisherName(publishName);
eventManger.publish(event);//发布事件
}
}
4.事件实体类
public class Event {
private String publisherName;
private int money;
private String typeName;
private int falg;
public int getFalg() {
return falg;
}
public void setFalg(int falg) {
this.falg = falg;
}
public String getPublisherName() {
return publisherName;
}
public void setPublisherName(String publisherName) {
this.publisherName = publisherName;
}
public int getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(int money) {
this.money = money;
}
public String getTypeName() {
return typeName;
}
public void setTypeName(String typeName) {
this.typeName = typeName;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Event{" +
"publisherName='" + publisherName + '\'' +
", money=" + money +
", typeName='" + typeName + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
实验结果分析:

实验日期: 2022.3.24
成绩评定:
□优秀(100-90分)
□良好(89-80分)
□中等(79-70分)
□及格(69-60分)
□不及格(60-0分)
教师签名:
年 月 日
实验报告内容
实验题目: 3、eclipse中搭建tomcat集群实验
实验目的: 掌握搭建集群系统实验
实验要求: 运用集群系统知识,搭建一个tomcat集群。
实验器材: 计算机
- 集群简介
集群(cluster)技术是一种较新的技术,通过集群技术,可以在付出较低成本的情况下获得在性能、可靠性、灵活性方面的相对较高的收益,其任务调度则是集群系统中的核心技术。
集群是一组相互独立的、通过高速网络互联的计算机,它们构成了一个组,并以单一系统的模式加以管理。一个客户与集群相互作用时,集群像是一个独立的服务器。集群配置是用于提高可用性和可缩放性。
- 设置maven、创建项目
Window->Preferences->Maven,在installations中添加你的maven

在User Settings中添加你的settings.xml文件
Settings.xml中的一些配置
阿里云中央仓库镜像:

在Package Explorer中右键NEW->Maven Project





在pom.xml中添加tomcat插件来启动
<finalName>Jiqun</finalName>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.2</version>
<configuration>
<port>8092</port>
<path>/</path>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
鼠标放到项目上右击->Run As->Run Configurations
- 修改pom文件、编写jsp代码
<projectxmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.shida</groupId>
<artifactId>Jiqun</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>Jiqun Maven Webapp</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>Jiqun</finalName>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.2</version>
<configuration>
<port>8093</port>
<path>/</path>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Index.jsp
<%@page contentType ="text/html;charset=utf-8"%>
<html>
<body>
<h2>Hello 集群系统实验!!!</h2>
<div id=""style="background-color: pink;width: 18.75rem;">
<h1>集群实验调查表</h1>
<ol>喜欢吃的水果
<li>苹果</li>
<li>榴莲</li>
<li>香蕉</li>
</ol>
<ul>你关注的设计类网站有哪些?
<li>花瓣</li>
<li>站酷</li>
<li>觅元素</li>
<li>千图</li>
</ul>
<form action="" method="post">
账号:<input type="text" name="" id="" value=""placeholder="请输入您的账号" /><br>
密码:<input type="password" name="" id="" value=""placeholder="请输入您的密码" /><br>
<p>性别
<input type="radio" name="sex" id="" value="" />男
<input type="radio" name="sex" id="" value="" />女
</p>
<p>你学会了哪些标签?
<input type="checkbox" name="" id="" value="" />div
<input type="checkbox" name="" id="" value="" />p
<input type="checkbox" name="" id="" value="" />img
<input type="checkbox" name="" id="" value="" />h
</p>
<p>
你的城市在哪里?
<select name="">
<option value="">请选择</option>
<option value ="">北京</option>
<option value ="">上海</option>
<option value ="">广州</option>
<option value ="">深圳</option>
</select>
</p>
<input type="submit" name="" id="" value="提交" />
<input type="reset" name="" id="" value="重置" />
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
- 不同端口号中运行




端口号8092启动成功
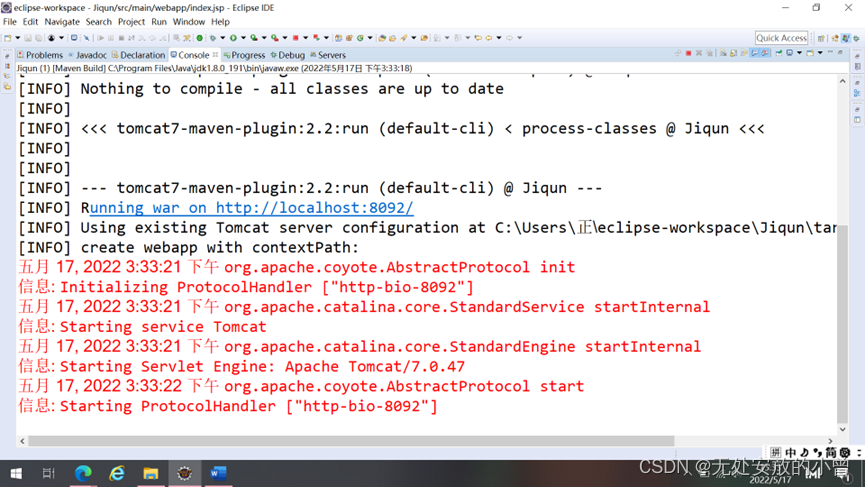

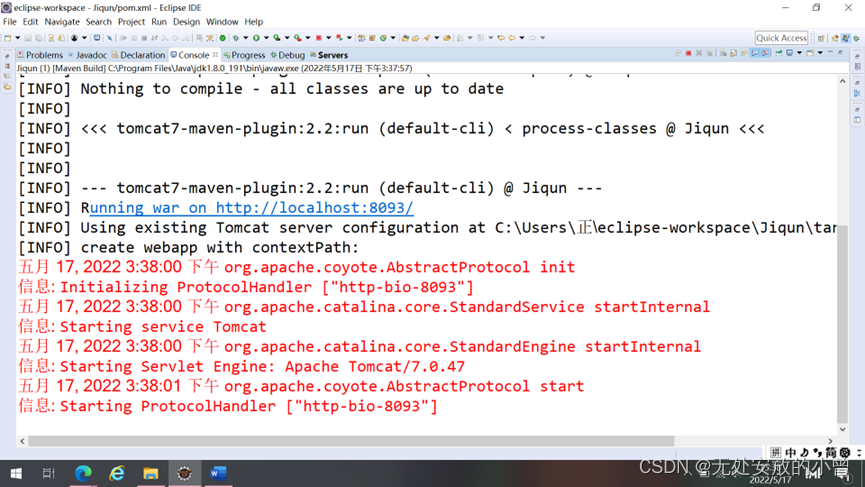
修改端口号为8093后保存文件并运行

端口8093启动成功并运行
实验日期:2021年5月27日
成绩评定:
评语 | ||
实验态度 | 完成实验的态度 | □认真□一般□不认真 |
实验设计 | 问题分析、算法及流程图 | □正确□较正确□不正确 |
程序代码 | 程序代码设计、修改、调试 | □完整□较完整□不完整 |
实验结果 | 实验测试数据及结果 | □正确□部分正确□不正确 |
格式书写 | 报告书面格式符合要求程度 | □符合□基本符合□不符合 |
实验成绩 | □优秀□良好□中等□合格□不合格 | |
教师签名:
2022 年5 月 17 日
实验报告内容
实验题目:4、基于规则系统实验
实验目的: 理解规则系统
实验要求: 运用规则系统相关知识,实现一个可修改规则系统
实验器材: 计算机
实验电路图/程序流程图:

实验步骤/程序源代码:
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
public class Rule {
public static String str4="";
public Rule() {
List<String> TaArea = new LinkedList<String>();
List<String> Fea = new LinkedList<String>();
int b=0;
for(int i=0;i<JFrameText.s.length();i++)
{
if(JFrameText.s.charAt(i)=='\n') {
TaArea.add(JFrameText.s.substring(b, i));
b=i+1;
}
}
new FileRead();
String str1="";
String str2="";
String str3="";
for(int i=0;i<TaArea.size();i++) {
if(str1!="") {
str1=str2;
}
for(int j=i;j<TaArea.size();j++) {
str1+=TaArea.get(j);
if(FileRead.key .contains(str1)) {
i=j;
str2+=FileRead.value .get(FileRead.key.indexOf(str1));
System.out.println(str1+"->"+FileRead.value .get(FileRead.key.indexOf(str1)));
str3=str1+"->"+FileRead.value .get(FileRead.key.indexOf(str1))+"\n";
Fea.add(str3);
str1="";
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<Fea.size();i++) {
str4+=Fea.get(i);
}
}
}
实验结果分析:
使用大量的list集合。
实验日期: 2022.3.24
成绩评定:
□优秀(100-90分)
□良好(89-80分)
□中等(79-70分)
□及格(69-60分)
□不及格(60-0分)
教师签名:
年 月 日
实验报告内容
实验题目: 5、黑板系统实现计算器的设计
实验目的: 理解黑板系统
实验要求: 利用黑板系统的原理设计一个计算器
实验器材: 计算机
实验分析:
黑板系统:黑板系统是一种问题求解模型,是组织推理的步骤、控制状态数据和问题求解之领域知识的概念框架,它将问题的解空间组织成一个或多个应用相关的分级结构。分级结构的每一层信息由一个唯一的词汇来描述,它代表了问题的部分解。
黑板系统主要由以下三部分组成。
(1)知识源:包含独立的、与应用程序相关的知识,知识源之间不直接进行通讯,
它们之间的交互只通过黑板来完成。
(2)黑板数据结构:按照与应用程序相关的层次来组织并解决问题的数据,知识源
通过不断地改变黑板数据来解决问题。
(3)控制:
完全由黑板的状态驱动,黑板状态的改变决定了需要使用的特定知识。
影响黑板系统设计的最大因素是引用问题本身的特性,但是支撑应用程序的黑板体系结构有许多相似的特征和构件。对于特定应用问题,黑板系统可通过选取各种黑板、知识源和控制模块的构件来设计;也可以利用预先制定的黑板体系结构的编程环境。
黑板系统的典型应用是信号处理领域,如网络信息检索、电子商务、自动控制、商业管理智能决策、语音和模式识别、智能控制领域等。
实验电路图/程序流程图:

实验步骤/程序源代码:
#include<stdio.h>
void Counter1(int a,int b,char op);
void Counter2(double c,double d,char op);
void Show_Sum1(int a,char op,int b,int sum);
void Show_Sum2(double c,double d,char op,double sum);
int Add(int a,int b);
int Sub(int a,int b);
int Mul(int a,int b);
double Div(double a,double b);
int main(){
int a=0,b=0;//初始化
double c=0.0,d=0.0;
char op='#';
char ch='#';
int choi=0;
do{
printf("请输入数据:(想使用加法减法乘法功能输入1,使用除法功能输入2)\n");
scanf("%d",&choi);
if(choi==1){
printf("输入数据的格式:数值 运算符 数值\n");
scanf("%d %c %d",&a,&op,&b);
fflush(stdin);
Counter1(a,b,op);
}
else if(choi==2){
printf("输入数据的格式:数值 运算符 数值\n");
scanf("%lf %c %lf",&c,&op,&d);
fflush(stdin);
Counter2(c,d,op);
}
printf("是否继续?(Y/N):\n");
ch=getchar();
}while(ch=='Y'||ch=='y');
return 0;
}
void Counter1(int a,int b,char op){
int sum=0;
int optag=true;
switch(op){
case '+':sum=Add(a,b);break;
case '-':sum=Sub(a,b);break;
case '*':sum=Mul(a,b);break;
default:{
printf("运算符错误!\n");
optag=false;
break;
}
}
if(optag) Show_Sum1(a,op,b,sum);
}
void Counter2(double c,double d,char op){
double sum=0.0;
int optag=true;
switch(op){
case '/':{
if(d==0){
optag=false;
printf("被除数为零,发生错误!\n");
}
else sum=Div(c,d);
break;
}
default:{
printf("运算符错误!\n");
optag=false;
break;
}
}
if(optag) Show_Sum2(c,d,op,sum);
}
void Show_Sum1(int a,char op,int b,int sum){
printf("%d %c %d=%d",a,op,b,sum);//输出计算结果
}
void Show_Sum2(double c,double d,char op,double sum){
printf("%.4f %c %.4f=%.4f",c,op,d,sum);
}
int Add(int a,int b){
return a+b;
}
int Sub(int a,int b){
return a-b;
}
int Mul(int a,int b){
return a*b;
}
double Div(double a,double b){
return a/b; }
实验结果分析:

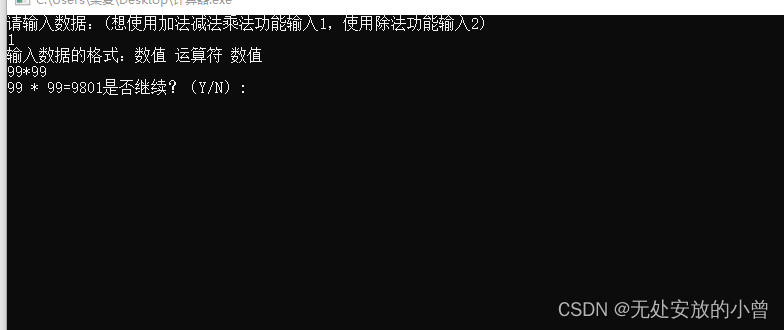

程序可以正常运行,能够进行加减乘除的一系列运算。
实验日期: 2022年5月27日
成绩评定:
□优秀(100-90分)
□良好(89-80分)
□中等(79-70分)
□及格(69-60分)
□不及格(60-0分)
教师签名:
2022年 5月 27日
实验报告内容
实验题目: 6、KWIC系统实验一
实验目的: 解决KWIC问题
实验要求: 采用带有共享数据的主程序-子过程体系结构风格解决KWIC问题
实验器材: 计算机、Visual Studio 2022。
一、实验步骤/程序源代码:
#include<fmt/core.h>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<fstream>
#include<sstream>
#include<filesystem>
#include<iterator>
#include<algorithm>
std::vector<std::vector<std::string>> line_words;
std::vector<std::string> afterShift;
void readFromFile(const std::filesystem::path& file){
std::ifstream file_stream(file);
while (!file_stream.eof()) {
std::string line;
std::getline(file_stream, line);
std::stringstream line_stream(line);
std::vector<std::string> words;
std::for_each(std::istream_iterator<std::string>(line_stream), std::istream_iterator<std::string>(),
[&words](constauto& word) {
words.emplace_back(word);
}
);
line_words.emplace_back(std::move(words));
}
}
void shift(){
for (constauto& line : line_words) {
auto length = line.size();
for (auto index = 0; index < length; ++index) {
std::string tmp;
for (auto j = 0; j < length - 1; ++j) {
tmp += (line[(index + j) % length] + " ");
}
tmp += line[(index + length - 1) % length];
afterShift.emplace_back(std::move(tmp));
}
}
}
int main(){
std::filesystem::path file_path("data.txt");
if (!std::filesystem::exists(file_path)) {
fmt::print(stderr, "file does not exist");
return -1;
}
readFromFile(file_path);
shift();
std::sort(afterShift.begin(), afterShift.end());
for (constauto& line : afterShift)
fmt::print("{}\n", line);
return 0;
}
实验结果:

实验日期: 2022.5.17
成绩评定:
□优秀(100-90分)
□良好(89-80分)
□中等(79-70分)
□及格(69-60分)
□不及格(60-0分)
教师签名:
年 月 日
实验报告内容
实验题目: 7、KWIC系统实验2
实验目的: 解决KWIC问题
实验要求: 采用抽象数据类型的系结构风格解决KWIC问题
实验器材: 计算机、IntelliJ IDEA Community Edition 2022.1。
一、实验步骤/程序源代码:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ArrayList<String>ls=new ArrayList<String>();
InputStore inputStore=new InputStore(ls);
inputStore.input("input.txt");
CircularShifter cs=new CircularShifter(ls);
cs.shift();
Alphabetizer alp=new Alphabetizer(cs.ls);
alp.alpha();
Output output=new Output(alp.ls);
output.output("output.txt");
}
}
}
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class InputStore {
public ArrayList<String> ls;
public InputStore(ArrayList<String> ls){
this.ls=ls;
}
public void input(String inputFile){
FileReader fr=null;
try {
fr=new FileReader(inputFile);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(fr);
try {
while(br.ready()){
ls.add(br.readLine());//向列表中添加对象
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class CircularShifter {
public ArrayList<String> ls;
public CircularShifter(ArrayList<String> ls){
this.ls=ls;
}
public void shift(){
ArrayList<String> shiftedLineIndexes=new ArrayList<String>();
for(int i=0;i<ls.size();i++){
String orinLine=ls.get(i);
String sarray[]=orinLine.split(" "); //分割字符串
for(int j=0;j<sarray.length;j++){
String newLine=sarray[j];
if(sarray.length>1){
if(j==sarray.length-1){
for(int k=0;k<(sarray.length-1);k++){
newLine=newLine+" "+sarray[k];
}
}
else{
for(int k=j+1;k<sarray.length;k++){
newLine=newLine+" "+sarray[k];
}
for(int m=0;m<j;m++){
newLine=newLine+" "+sarray[m];
}
}
}
shiftedLineIndexes.add(newLine);
}
}
ls=shiftedLineIndexes;
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Alphabetizer {
public ArrayList<String> ls;
public Alphabetizer(ArrayList<String> ls){
this.ls=ls;
}
public void alpha(){
String[] tmpArray = new String[ls.size()];
ls.toArray(tmpArray);
Arrays.sort(tmpArray);
for(int i=0;i<ls.size();i++){
ls.set(i, tmpArray[i]);
}
}
}
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Output {
public ArrayList<String> ls;
public Output(ArrayList<String> ls){
this.ls=ls;
}
public void output(String outputAddress){
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
fw = new FileWriter(outputAddress);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(fw);
for(int i=0;i<ls.size();i++){
try {
bw.write(ls.get(i));
bw.newLine();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
try {
bw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
实验结果:

实验日期: 2022.5.24
成绩评定:
□优秀(100-90分)
□良好(89-80分)
□中等(79-70分)
□及格(69-60分)
□不及格(60-0分)
教师签名:
年 月 日
实验报告内容
实验题目: 8、KWIC系统实验三
实验目的: 掌握KWIC隐式调用体系结构风格。
实验要求: 采用隐式调用体系结构风格解决KWIC风格。
实验器材: 计算机、Eclipse
实验电路图/程序流程图:
为了降低各模块之间的耦合度,提高复用性能,将模块之间的“直接调用”改为“隐式调用”——事件驱动的体系结构风格。
采用方式:
– 四个功能模块
– 共享数据
不同之处:
– 共享数据并不直接对外暴露数据格式,而是借鉴了面向过程中的方式,对数据进行封装,通过接口向外暴露对数据的操作;
– 各功能模块之间不再通过主程序来控制,而是事件驱动
实验步骤/程序源代码:
部分源代码:
Alphabetizer.java:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class Alphabetizer implements KWICListener{
private TextLines textlines=null;
@Override
public void handleEvent(KWICEvent event) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(event instanceof InsertToTextLinesEvent){
textlines=((CircularShifter) event.getSource()).getTextLines();
Collections.sort(textlines.getLineList());
try {
Outputer.println(textlines);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
CircularShifter.java:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class CircularShifter implements KWICListener{
private TextLines textlines=null;
@Override
public void handleEvent(KWICEvent event) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(event instanceof InsertToTextLineEvent){
TextLine textline=((Inputer) event.getSource()).getTextLine();
int number_of_lines=textline.numberOfLines();
ArrayList<ArrayList> exlist=new ArrayList<ArrayList>(0);
ArrayList<String> inlist=new ArrayList<String>(0);
for(int i=0;i<number_of_lines;i++){
for(int j=0;j<textline.numberOfWords(i);j++){
if(j==0) {
inlist.add(textline.getLine(i));
}
else {
inlist.add(textline.shiftwords(i));
}
}
exlist.add(inlist);
inlist=new ArrayList<String>(0);
}
textlines=new TextLines();
for(int i=0;i<number_of_lines;i++){
for(int j=0;j<exlist.get(i).size();j++){
textlines.addLine((String)exlist.get(i).get(j));
}
}
InsertToTextLinesEvent ittles=new InsertToTextLinesEvent(this);
EventManager.broadcast(ittles);
}
}
public TextLines getTextLines(){
return textlines;
}
}
EventManager.java:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.EventObject;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.EventListener;
public class EventManager {
// 监听器列表
private static List<KWICListener> listenerList = new ArrayList<KWICListener>();
// 监听器注册方法
public static void addListener(KWICListener listener) {
listenerList.add(listener);
}
// 监听器注销方法
public static void removeListener(KWICListener listener) {
listenerList.remove(listener);
}
// 事件广播方法
public static void broadcast(KWICEvent event) {
for(KWICListener listener : listenerList)
listener.handleEvent(event);
}
}
Inputer.java:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Inputer {
private TextLine textline=null;
public Inputer(FileReader fr) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
input(fr);
}
public void input(FileReader fr) throws IOException{
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(fr);
textline=new TextLine();
while(br.ready()){
textline.addLine(br.readLine());
InsertToTextLineEvent ittle=new InsertToTextLineEvent(this);
EventManager.broadcast(ittle);
}
}
public TextLine getTextLine(){
return textline;
}
}
Outputer.java:
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Outputer {
public static void println(TextLines textlines)throws IOException{
FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("output.txt");
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(fw);
for(int i=0;i<textlines.numberOfLines();i++){
bw.write(textlines.getLine(i));
bw.newLine();
}
bw.close();
}
}
实验结果分析:
运行结果:

实验日期: 2022.3.24
成绩评定:
□优秀(100-90分)
□良好(89-80分)
□中等(79-70分)
□及格(69-60分)
□不及格(60-0分)
教师签名:
年 月 日
边栏推荐
- ECS 四 Sync Point、Write Group、Version Number
- How to create a subtype like relationship between two generic classes when the classes are generic related
- Error accessing database
- Rapid development project -vscode plug-in
- How to write MySQL scheduled backup script in Linux
- What are the circular statements of MySQL
- Here comes Wi Fi 7. How strong is it?
- 剑指 Offer II 040. 矩阵中最大的矩形
- What are the ways to simulate and burn programs? (including common tools and usage)
- 波形记录仪MR6000的实时波形运算功能
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Research Report on the overall scale, major manufacturers, major regions, product and application segmentation of GSM and GPRS modules in the global market in 2022
Remediation for Unsafe Cryptographic Encryption
Five thousand years of China
Is the interviewer too difficult to serve? A try catch asks so many tricks
Observer pattern
What exactly does GCC's -Wpsabi option do? What are the implications of supressing it?
1019 digital black hole
Idea modifying JVM memory
Using assetstudio/unitystudio uabe, etc
Log in to the MySQL database and view the version number on the command line
Iterator pattern
The last week! Summary of pre competition preparation for digital model American Games
[C language] address of stack memory associated with local variable 'num' returned
Proxy mode (proxy)
力扣解法汇总324-摆动排序 II
CTO and programmer were both sentenced because the crawler was out of control!
人民银行印发《关于支持外贸新业态跨境人民币结算的通知》
Research Report on the overall scale, major manufacturers, major regions, products and applications of power battery laser welding machines in the global market in 2022
How to use the select statement of MySQL
安捷伦数字万用表软件NS-Multimeter,实时数据采集数据自动保存









