当前位置:网站首页>The usage and Simulation Implementation of vector in STL
The usage and Simulation Implementation of vector in STL
2022-07-28 12:34:00 【Xiao Li, who loves programming】
STL in vector Usage and simulation implementation
One 、vector The introduction and use of
1、vector Introduction to
- vector Is a sequence container that represents a variable size array .
- It's like an array ,vector It also uses continuous storage space to store elements . That means subscript pairs can be used vector Element to access , As efficient as arrays . But it's not like an array , Its size can be changed dynamically , And its size is automatically handled by the container .
- Essence ,vector Use a dynamic allocation array to store its elements . When a new element is inserted , This array needs to be resized to increase storage space . This is done by , Assign a new array , Then move all the elements to this array . In terms of time , This is a relatively expensive task , Because every time a new element is added to the container ,vector It doesn't re size every time .
- vector Space allocation strategy :vector Some extra space will be allocated to accommodate possible growth , Because the storage space is larger than the actual need . Different libraries use different strategies to balance space use and reallocation . But anyway , Redistribution should be the interval size of logarithmic growth , So that inserting an element at the end is done in constant time complexity .
- therefore ,vector It takes up more storage space , To get the ability to manage storage space , And grow dynamically in an effective way .
- Compared with other dynamic sequence containers (deques, lists and forward_lists), vector More efficient when accessing elements , Adding and removing elements at the end is relatively efficient . For other delete and insert operations not at the end , Less efficient . Compared with lists and forward_lists Uniform iterators and references are better .
2、vector Use
2.1 vector The definition of
| Constructors | explain |
|---|---|
| vector() | No arguments structure |
| vector(size_type n, const value_type& val = value_type()) | Construct and initialize n individual val |
| vector (const vector& x) | Copy structure |
| vector (InputIterator first, InputIterator last) | Using iterator interval to construct |
usage :
// constructing vectors
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
int main ()
{
// constructors used in the same order as described above:
std::vector<int> first; // empty vector of ints
std::vector<int> second (4,100); // four ints with value 100
std::vector<int> third (second.begin(),second.end()); // iterating through second
std::vector<int> fourth (third); // a copy of third
// The following section deals with iterator initialization , Let's look at this part after learning iterators
// the iterator constructor can also be used to construct from arrays:
int myints[] = {
16,2,77,29};
std::vector<int> fifth (myints, myints + sizeof(myints) / sizeof(int) );
std::cout << "The contents of fifth are:";
for (std::vector<int>::iterator it = fifth.begin(); it != fifth.end(); ++it)
std::cout << ' ' << *it;
std::cout << '\n';
return 0;
}
2.2 vector iterator Use
| iterator Use | explain |
|---|---|
| begin + end | Get the first data location of iterator/const_iterator, Get the next location of the last data iterator/const_iterator |
| rbegin + rend | Get the last data location of reverse_iterator, Get the first data of the previous position reverse_iterator |
begin and end Icon :

rbegin and rend Icon :

Usage example :
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void PrintVector(const vector<int>& v)
{
// const Object use const Iterator for traversal
vector<int>::const_iterator it = v.begin();
while (it != v.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
// Use push_back Insert 4 Data
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(4);
// Use iterators to traverse and print
vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin();
while (it != v.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
cout << endl;
// Use iterators to modify
it = v.begin();
while (it != v.end())
{
*it *= 2;
++it;
}
// Use the reverse iterator to traverse and then print
vector<int>::reverse_iterator rit = v.rbegin();
while (rit != v.rend())
{
cout << *rit << " ";
++rit;
}
cout << endl;
PrintVector(v);
return 0;
}
}
2.3 vector Spatial growth problem
| function | explain |
|---|---|
| size | Get the number of data |
| capacity | Get container capacity |
| empty | Judge whether the container is empty |
| resize | change vector Of size |
| reserve | Reserve space |
It is worth mentioning that :
- capacity Code in vs and g++ Running separately will find that ,vs Next capacity Is in accordance with the 1.5 Multiplied by ,g++ Is in accordance with the 2 Multiplied by . This problem is often examined , Don't take it for granted that , The capacity of the sequence table is 2 times , How much growth is defined by specific needs .vs yes PJ edition STL,g++ yes SGI edition STL.
- reserve Only responsible for opening up space , If you know how much space is needed ,reserve Can ease vector The cost of capacity expansion is flawed .
- resize In the open space at the same time also will carry on the initialization , influence size.
2.4 vector Add or delete check change
| vector Add or delete check change function | explain |
|---|---|
| push_back | Tail insertion |
| pop_back | Deletion at the end |
| find | lookup ( Note that this is the algorithm module implementation , No vector Member interface of ) |
| insert | stay position Insert before val |
| erase | Delete position Location data |
| swap | Two exchanges vector Data space of |
| operator[] | heavy load [] , Make it accessible like an array |
Usage example :
- push_back/pop_back
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[] = {
1, 2, 3, 4 };
vector<int> v(a, a+sizeof(a)/sizeof(int));
vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin();
while (it != v.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
v.pop_back();
v.pop_back();
it = v.begin();
while (it != v.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
- find / insert / erase
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[] = {
1, 2, 3, 4 };
vector<int> v(a, a + sizeof(a) / sizeof(int));
// Use find lookup 3 At the location of iterator
vector<int>::iterator pos = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 3);
// stay pos Insert before position 30
v.insert(pos, 30);
vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin();
while (it != v.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
pos = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 3);
// Delete pos Location data
v.erase(pos);
it = v.begin();
while (it != v.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
- operator[]+index and C++11 in vector New for+auto The traversal
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[] = {
1, 2, 3, 4 };
vector<int> v(a, a + sizeof(a) / sizeof(int));
// adopt [] Reading and writing 0 A place .
v[0] = 10;
cout << v[0] << endl;
// adopt [i] The way to traverse vector
for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i)
cout << v[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
vector<int> swapv;
swapv.swap(v);
cout << "v data:";
for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i)
cout << v[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << "swapv data:";
for (size_t i = 0; i < swapv.size(); ++i)
cout << swapv[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
// C++11 New range of support for Traverse
for(auto x : v)
cout<< x << " ";
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
Two 、vector Iterator failure
The main function of iterators is to make the algorithm don't care about the underlying data structure , The bottom layer is actually a pointer , Or encapsulate the pointer , such as :vector The iterator of is the primitive pointer T*. So the iterator fails , In fact, the space pointed to by the corresponding pointer at the bottom of the iterator is destroyed , And use a space that has been released , The consequence is that the program crashes ( That is, if you continue to use an iterator that has expired , The program could crash ).
about vector The operations that may cause its iterators to fail are :
- An operation that causes a change in its underlying space , It is possible that the iterator fails , such as :resize、reserve、insert、assign、push_back etc.
for example :
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <vector>
int main()
{
vector<int> v{
1,2,3,4,5,6};
auto it = v.begin();
// Increase the number of valid elements to 100 individual , Use... For extra locations 8 fill , During operation, the bottom layer will expand
// v.resize(100, 8);
// reserve The function of is to change the expansion size without changing the number of effective elements , The underlying capacity may change during operation
// v.reserve(100);
// During element insertion , May cause capacity expansion , And cause the original space to be released
// v.insert(v.begin(), 0);
// v.push_back(8);
// to vector Reassign , May cause the underlying capacity to change
v.assign(100, 8);
/* Cause of error : The above operation , Can lead to vector Capacity expansion , in other words vector The underlying principle is that the old space is released , And when printing ,it Also used is to release the old space between , In the face of it Iterator operation , The actual operation is a piece that has been released Space , And cause the code to crash at run time . Solution : After the above operations are completed , If you want to continue through the iterator vector The elements in , Just give it again Assignment can . */
while(it != v.end())
{
cout<< *it << " " ;
++it;
}
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
- Delete the specified location element :erase
for example :
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <vector>
int main()
{
int a[] = {
1, 2, 3, 4 };
vector<int> v(a, a + sizeof(a) / sizeof(int));
// Use find lookup 3 At the location of iterator
vector<int>::iterator pos = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 3);
// Delete pos Location data , Lead to pos Iterator failure .
v.erase(pos);
cout << *pos << endl; // This will lead to illegal access
return 0;
}
erase Delete pos After the position element ,pos The element after the position will move forward , No change in the underlying space , Theoretically, iterators should not fail , however : If pos Just the last element , After deleting pos just end The location of , and end Position has no element , that pos Is failure . So delete vector When an element is at any position in ,vs It is considered that the position iterator has failed .
Iterator failure resolution : Before using , Just reassign the iterator .
3、 ... and 、vector In depth analysis and simulation implementation
1、 Implementation code
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
namespace my_vector
{
template<class T>
class vector
{
public:
typedef T* iterator;
typedef const T* const_iterator;
vector()
:_start(nullptr)
, _finish(nullptr)
, _endofstoage(nullptr)
{
}
template <class InputIterator>
vector(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
: _start(nullptr)
, _finish(nullptr)
, _endofstoage(nullptr)
{
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
++first;
}
}
vector(size_t n, const T& val = T())
: _start(nullptr)
, _finish(nullptr)
, _endofstoage(nullptr)
{
reserve(n);
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
push_back(val);
}
}
vector(int n, const T& val = T())
: _start(nullptr)
, _finish(nullptr)
, _endofstoage(nullptr)
{
reserve(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
push_back(val);
}
}
void swap(vector<T>& v)
{
std::swap(_start, v._start);
std::swap(_finish, v._finish);
std::swap(_endofstoage, v._endofstoage);
}
// rest 11:37 continue
//vector(const vector& v);
vector(const vector<T>& v)
: _start(nullptr)
, _finish(nullptr)
, _endofstoage(nullptr)
{
vector<T> tmp(v.begin(), v.end());
swap(tmp);
}
//vector& operator=(vector v)
vector<T>& operator=(vector<T> v)
{
swap(v);
return *this;
}
// Resource management
~vector()
{
if (_start)
{
delete[] _start;
_start = _finish = _endofstoage = nullptr;
}
}
iterator begin()
{
return _start;
}
iterator end()
{
return _finish;
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _start;
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _finish;
}
size_t size() const
{
return _finish - _start;
}
size_t capacity() const
{
return _endofstoage - _start;
}
void reserve(size_t n)
{
size_t sz = size();
if (n > capacity())
{
T* tmp = new T[n];
if (_start)
{
memcpy(tmp, _start, size()*sizeof(T));
delete[] _start;
}
_start = tmp;
}
_finish = _start + sz;
_endofstoage = _start + n;
}
//void resize(size_t n, const T& val = T())
void resize(size_t n, T val = T())
{
if (n > capacity())
{
reserve(n);
}
if (n > size())
{
while (_finish < _start + n)
{
*_finish = val;
++_finish;
}
}
else
{
_finish = _start + n;
}
}
void push_back(const T& x)
{
/*if (_finish == _endofstoage) { size_t newCapacity = capacity() == 0 ? 4 : capacity() * 2; reserve(newCapacity); } *_finish = x; ++_finish;*/
insert(end(), x);
}
void pop_back()
{
/*if (_finish > _start) { --_finish; }*/
erase(end() - 1);
}
T& operator[](size_t pos)
{
assert(pos < size());
return _start[pos];
}
const T& operator[](size_t pos) const
{
assert(pos < size());
return _start[pos];
}
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
// Inspection parameters
assert(pos >= _start && pos <= _finish);
// Capacity expansion
// After the expansion pos Is failure , Need to update
if (_finish == _endofstoage)
{
size_t n = pos - _start;
size_t newCapacity = capacity() == 0 ? 4 : capacity() * 2;
reserve(newCapacity);
pos = _start + n;
}
// Move data
iterator end = _finish - 1;
while (end >= pos)
{
*(end + 1) = *end;
--end;
}
*pos = x;
++_finish;
return pos;
}
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos >= _start && pos < _finish);
iterator it = pos + 1;
while (it != _finish)
{
*(it - 1) = *it;
++it;
}
--_finish;
return pos;
}
void clear()
{
_finish = _start;
}
private:
iterator _start;
iterator _finish;
iterator _endofstoage;
};
}
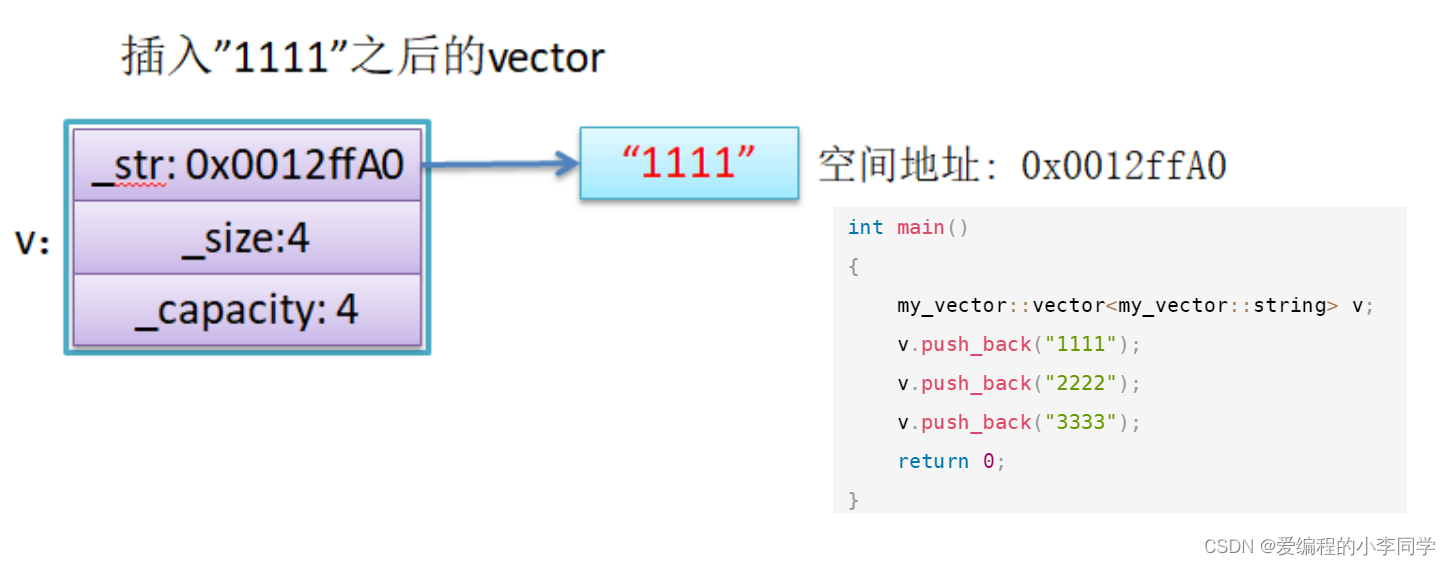
2、 Use memcpy Copy problem
Suppose the simulation implements vector Medium reserve Interface , Use memcpy A copy of , What happens to the following code ?
int main()
{
my_vector::vector<my_vector::string> v;
v.push_back("1111");
v.push_back("2222");
v.push_back("3333");
return 0;
}
Problem analysis :
- memcpy Is a binary copy of memory , Copy the contents of one memory space intact to another memory space
- If you copy a custom type element ,memcpy Efficient and error free , But if you copy a custom type element , And when resource management is involved in custom type elements , Will go wrong , because memcpy The copy of is actually a shallow copy .

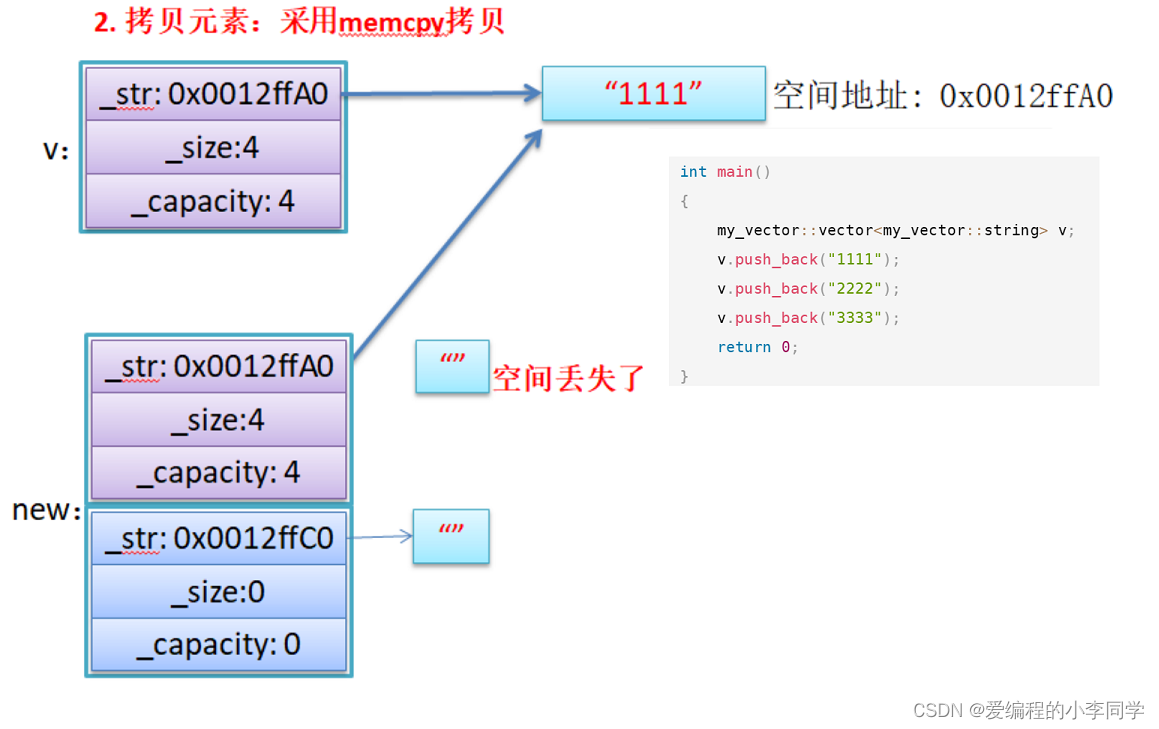

Conclusion : If resource management is involved in the object , Never use memcpy Copy between objects , because memcpy Is a shallow copy , Otherwise, it may cause memory leakage and even program crash .
3、 Implemented using simulation vector Realize the deep-seated copy problem in Yang Hui triangle
3.1 vector Deep level copy problem
Construct a Yanghui triangle , Print it and return to the Yang Hui triangle after the construction :
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> generate(int numRows) {
vector<vector<int>> vv;
vv.resize(numRows);
for (size_t i = 0; i < vv.size(); ++i)
{
// Yang hui triangle , The number of each line increases in turn
vv[i].resize(i + 1, 0);
// The first and last are initialized to 1
vv[i][0] = 1;
vv[i][vv[i].size() - 1] = 1;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < vv.size(); ++i)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < vv[i].size(); ++j)
{
if (vv[i][j] == 0)
{
// The middle position is equal to the previous line j-1 and j Add up
vv[i][j] = vv[i - 1][j - 1] + vv[i - 1][j];
}
}
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < vv.size(); ++i)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < vv[i].size(); ++j)
{
cout << vv[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
return vv;
}
};
Receive Yang Hui triangle after construction and print :
void test()
{
vector<vector<int>> ret = Solution().generate(5);
for (size_t i = 0; i < ret.size(); ++i)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < ret[i].size(); ++j)
{
cout << ret[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
result : Program crash 
Debugging shows that : utilize memcpy Capacity expansion , The elements in the first four rows of Yang Hui triangle before and after the expansion point to the same address , Shallow copies that occur , When delete_start When it comes to tmp It's also released . To solve this problem, we must use deep copy method to replace memcpy that will do .

3.2 resolvent —— to update reserve function
Use deep copy method to replace memcpy:
void reserve(size_t n)
{
size_t sz = size();
if (n > capacity())
{
T* tmp = new T[n];
if (_start)
{
//memcpy(tmp, _start, size()*sizeof(T));
for (size_t i = 0; i < size(); ++i)
{
tmp[i] = _start[i];
}
delete[] _start;
}
_start = tmp;
}
_finish = _start + sz;
_endofstoage = _start + n;
}


here , The problem has been solved perfectly .
边栏推荐
- Developing NES games with C language (cc65) 09, scrolling
- Tencent two sides: @bean and @component are used in the same class, what will happen?
- 用C语言开发NES游戏(CC65)04、完整的背景
- PHP获取本周所有日期或者最近七天所有日期
- 论治理与创新 | 2022 开放原子全球开源峰会 OpenAnolis 分论坛圆满召开
- Redis实现分布式锁
- On Governance and innovation | the openanolis sub forum of the 2022 open atom global open source summit was successfully held
- SQL injection LESS18 (header injection + error injection)
- Latex矩阵简单使用
- Gecko competition 2.0 is new! Come and show your flexible operation skills!
猜你喜欢

Redis实现分布式锁

Lyscript get previous and next instructions

产学研用 共建开源人才生态 | 2022 开放原子全球开源峰会教育分论坛圆满召开
Brief discussion on open source OS distribution

易观分析:以用户为中心提升手机银行用户体验,助力用户价值增长

【萌新解题】爬楼梯

Laravel form data validation

arduino pro mini ATMEGA328P 连线和点亮第一盏LED(同时记录烧录失败的问题stk500_recv)

Huawei releases harmonyos 3 and all scene new products, and the smart experience goes further

HMS core audio editing service supports 7 kinds of audio effects to help one-stop audio processing
随机推荐
Configure jupyter remote server
8000 字讲透 OBSA 原理与应用实践
Exploration on cache design optimization of community like business
Multi Chain and multi currency wallet system development cross chain technology
If you don't roll the golden nine and silver ten, it's too late
Kafaka丢消息吗
[Nuxt 3] (十二) 项目目录结构 3
【vulnhub】presidential1
Design process sharing of wireless anti loss alarm based on single chip microcomputer
配置Jupyter远程服务器
30 years of open source community | 2022 open atom global open source summit 30 years of special activities of open source community were successfully held
Developing NES games with C language (cc65) 11. Metatiles
SQL注入 Less18(头部注入+报错注入)
太赞了!京东研发一哥力荐的高可用网站构建技术PDF,备好水,慢慢啃
How to build knowledge management system in enterprises and institutions
After abolishing Tencent cloud: meiyabaike won the bid of 98.3 million
分布式定时器
Tencent two sides: @bean and @component are used in the same class, what will happen?
SQL injection less24 (secondary injection)
【vulnhub】Raven2