当前位置:网站首页>Overview of understanding the physical layer of transmission media
Overview of understanding the physical layer of transmission media
2022-07-27 21:01:00 【Hua Weiyun】
Q1: What is the role of the physical layer ?
The difference between shielding transmission media and communication means , Provide services for the data link layer
Q2: What is a data communication system ?
The data communication system includes three parts , Namely : Source system → Transmission system → Purpose system
Some basic concepts
- data (data)—— The entity carrying the message .
- The signal (signal)—— The electrical or electromagnetic representation of data .
- “ Simulated ”(analogous)—— The value of the parameter representing the message is continuous .
- “ Digital ”(digital)—— The value of the parameter representing the message is discrete .
- Code element (code)—— In use time domain ( Or time domain for short ) When the waveform of the signal represents a digital signal , Basic waveforms representing different discrete values .
Q3: The concept of channel
The way the channel interacts with information :
- One-way communication ( Simplex communication )—— There can only be one direction of communication without interaction in the opposite direction .
- Two way alternating communication ( Half duplex communication )—— Both sides of the communication can send messages , But it can't be sent by both sides at the same time ( Of course, we can't receive it at the same time ).
- Two way simultaneous communication ( Full duplex communication )—— Both sides of communication can send and receive information at the same time .
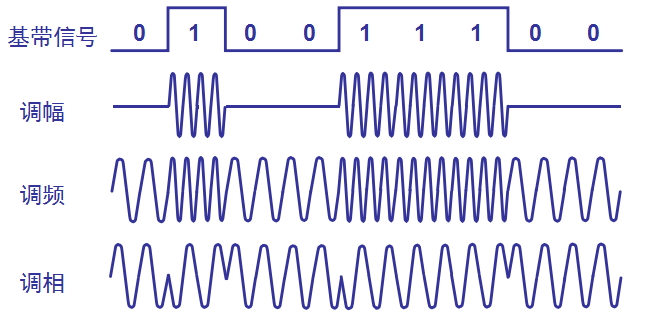
baseband signal —— Signal from source , It contains more low-frequency components , In order to enable the channel to transmit low-frequency components and DC components , Modulation required , Modulation can be divided into the following two categories :
- Baseband modulation ( Transform only the waveform ), Also known as encoding ;
- Bandpass modulation ( Use carrier modulation ):① amplitude modulation ;② frequency modulation ;③ Phase modulation ;

The limit capacity of the channel :
Shannon's theorem :
Limit information transmission rate C = W log2(1+S/N) b/s ; lower than C Error free transmission can be realized
Methods of improving information transmission rate :
Let each symbol carry more bits of information —— That is, a symbol is 3 individual bit Words , Compared with the original situation , At the same time, the amount of information transmitted increases 3 times , Because the transmission rate has nothing to do with the amount of data .
Q4: Transmission media under the physical layer
1. Leading to transmission media
1.1 Twisted pair
It is the oldest but most commonly used transmission medium . Put two insulated copper wires together , Then twisted in a regular way to form a twisted pair . The stranding can reduce the electromagnetic interference to the adjacent wires .
The most common use of twisted pair is the ubiquitous telephone system . Almost all telephones are connected to telephone exchanges with twisted pair cables . This section of twisted pair from subscriber telephone to switch is called subscriber line or subscriber loop . A certain number of such twisted pairs are usually bundled into cables , Wrap it with a sheath .
1.2 Coaxial cable :
Copper core wire made of inner conductor ( Single strand is new wire or stranded wire ), Insulating layer , Mesh braided outer conductor shield ( It can also be a single share ) And protective plastic outer layer . Because of the shielding layer of the outer conductor , Coaxial cable has good Anti interference characteristics , By It is widely used to transmit high-speed data .
1.3 optical cable :
It is the transmission medium of optical fiber communication . There is a light source at the transmitting end , Light emitting diodes or semiconductor lasers can be used , They can produce light pulses under the action of electric pulses . At the receiving end, a photodiode is used to make a photodetector , When the light pulse is detected, the electric pulse can be restored .
2. Undirected transmission media
2.1 Short wave communication : High frequency communication , Mainly by the reflection of the ionosphere . However, the fading phenomenon caused by ionospheric instability and the multipath effect caused by ionospheric reflection , The communication quality of short wave channel is poor .
2.2 Microwave communication
Ground microwave relay communication
Satellite communications
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

用户登录切换案例

Recommend a powerful search tool listary

征服所有程序员的3件IT装备 →

API Gateway介绍

Hcip day 5

【R语言】【1】初学R语言语法使用Rstudio编辑

82. (cesium article) cesium points move on 3D models

北京/上海/广州/深圳DAMA-CDGA/CDGP数据治理认证报名条件

自动化测试----unittest框架

Xdc 2022 Intel technology special session: Intel Software and hardware technology builds the cornerstone of cloud computing architecture
随机推荐
CPDA|如何拥有数据分析思维?
认识传输介质物理层概述
五大知名人士对于AI的忧虑
北京/上海/广州/深圳DAMA-CDGA/CDGP数据治理认证报名条件
走马灯案例
文件上传绕过WAF的技巧大全
Vant component library
坚持做一件事情
怎样实现文档协同?
Hcip day 5
R语言使用t.test函数执行t检验验证总体均值是否是某个特定的值(从样本集推论总体均值)
Uncaught SyntaxError: redeclaration of let page
一文了解Pycharm快捷键
如何查看蓝牙耳机的蓝牙版本
MySQL design optimization generates columns
一文读懂Plato Farm的ePLATO,以及其高溢价缘由
Rk3399 platform development series explanation (process part) 15.36, understanding process and collaboration process
R语言使用lm函数构建多元回归模型(Multiple Linear Regression)、并根据模型系数写出回归方程、使用deviance函数计算出模型的残差平方和
User login switching case
重复的DNA序列[hash判定重复+滑动窗口+二进制编码之位运算]