当前位置:网站首页>Summary of clustering methods
Summary of clustering methods
2022-06-11 17:31:00 【Mark_ Aussie】
clustering (Clustering): According to a certain standard ( Such as : distance ) Divide a data set into different classes or clusters , bring The similarity of data objects in the same cluster should be as large as possible , Data objects that are not in the same cluster are as different as possible ; After clustering, the data of the same class should be clustered together as much as possible , Try to separate different types of data .
The general process of clustering :
- Data preparation : Feature Standardization 、 Dimension reduction
- feature selection : Select the most effective feature from the initial features , And store it in a vector
- feature extraction : The selected features are transformed to form new prominent features
- clustering : Measure the similarity based on some distance function , Get cluster
- Evaluation of clustering results : Analyze the clustering results , Such as
Distance error and (SSE)etc.
Numerical data similarity measurement :

Minkowski Namely LP norm (P >= 1), and Manhattan 、Euclidean、Chebyshev Corresponding P = 1、2、 infinite
Distance measurement between clusters :Ci and Cj For two clusters

Single-link:The distance between two clusters is the distance between the nearest two points between two clusters , Will be generated in the clustering processChain effect, There may be very largeclusterComplete-link:The distance between two clusters is two clustersThe distance between the two farthest points , You can avoidChain effect `, Very sensitive to abnormal sample points , It is easy to produce unreasonable clustering .UPGMA:Single-linkandComplete-linkA compromise of , The distance between two clusters is the mean distance of all points between two clustersWPGMA:The weighted average of the distance between two clusters , The purpose of weighting is to make the influence of two clusters on the calculation of distance at the same level , Not affected by cluster size , The specific formula is related to the weight scheme adopted .
Clustering method

Partition clustering : You need to specify the number of cluster classes or cluster centers in advance , Iterate over and over to The points in the cluster are close enough , The points between clusters are far enough The goal of ; Such as :k-means、k-means++、bi-kmeans、kernel k-means etc. ; about Convexity data It has a good effect .

k-means given : It needs to be determined in advance k value 、 Sensitive to the initial centroid point 、 Sensitive to abnormal data .
k-mean++:

bi-kmeans: in the light of kmeans The algorithm will fall into the defect of local optimization . be based on SSE The principle of minimization , First, treat all data points as a cluster , Then divide the cluster into two , Then select one of the clusters to continue the division , Choosing which cluster to partition depends on whether the partition can be reduced to the greatest extent SSE Value .SSE(Sum of Squared Error), A measure of clustering effect , Represents the sum of squares of the distance from the cluster center after clustering ,SSE The smaller it is , The better the clustering effect is .

bi-kmeans yes A globally optimal approach , So every time I calculate SSE The values are basically the same .
Density clustering : Two parameters need to be defined , Neighborhood radius and neighborhood density threshold .




To construct the neighborhood radius, you can use kd-tree Optimize ;
DBSACN Density clustering characteristics :
- The neighborhood radius and neighborhood density threshold should be determined in advance
- It is not necessary to set the number of clusters in advance
- Sensitive to initial value selection , Insensitive to noise
- Poor data aggregation for uneven density
OPTICS clustering :DBSCAN The algorithm uses a uniform neighborhood radius , When the data density is uneven , If a smaller value is set , Are sparse cluster The node density in is less than the neighborhood density threshold , Will be considered as boundary points and not used for further expansion ; If a larger value is set , The density is larger and closer to cluster Easy to be classified as the same cluster .
Core distance : Given neighborhood radius and neighborhood density , The minimum radius that can reach the neighborhood density within the neighborhood radius .
Reach distance : Given the domain radius and density , The distance between points outside the core distance and within the radius of the field .

insert_list() The algorithm process :

The ultimate knowledge acquisition algorithm is a Output sequence , The sequence aggregates points of similar density according to different densities , Instead of outputting the specific category that the point belongs to , Get the type of the point , You need to set parameters again ![]() Extract specific categories .
Extract specific categories .
Hierarchical clustering : Divide the data set into layer by layer clusters , The latter layer is based on the results of the previous layer .
The previous algorithm can get better results with less complexity , But there is Chain effect , Such as :A And B be similar ,B And C be similar , Clustering will A、B、C Come together , But if A And C Dissimilarity , It will cause clustering error , The error may go on . Hierarchical clustering can solve the chain effect problem .
- Agglomerative Hierarchical clustering : Bottom up (bottom-up) Hierarchical clustering of , Every object starts with a cluster , Each time according to certain criteria, the two closest clusters are merged to generate a new cluster , Until the end, all objects belong to a cluster .
- Divisive Hierarchical clustering : The top-down (top-down) Hierarchical clustering of , At first all objects belong to a cluster , Each time a cluster is divided into multiple clusters according to certain criteria , Until each object is a cluster .
Hierarchical clustering is a greedy algorithm (greedy algorithm), Every merge or partition is based on some local optimal choice .
Comparison of clustering methods
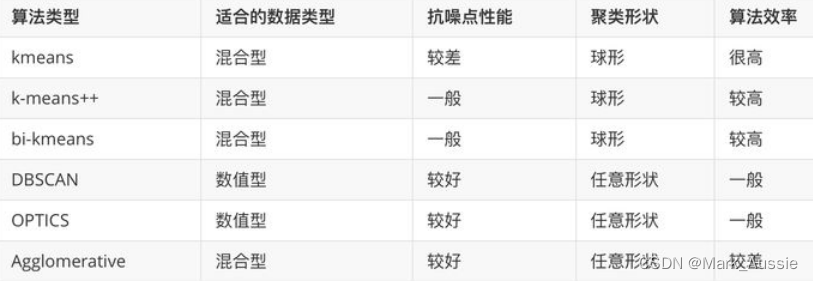
Reference resources :
边栏推荐
- mysql 大表的拆分方式
- What subclasses inherit, polymorphism, and upward transformation
- Error: error summary of pointer as function parameter
- Talk about the interview questions of the collection
- Go path: goroot & gopath
- My C の errors
- Authoring share | understanding saml2 protocol
- Service学习笔记04- 其他服务实现方式与替代方式
- 6-3 批量求和(*)
- 【Mysql】redo log,undo log 和binlog详解(四)
猜你喜欢

Docker安装mysql5.7(开启binlog功能、修改字符)

which is not functionally dependent on columns in GROUP BY clause; this is incompatible with sql_ mod

有效的括号---2022/02/23

Dynamic: capturing network dynamics using dynamic graph representation learning

10 times faster than 5g. Are you ready for 10 Gigabit communication?

vscode保存代码时自动eslint格式化

聚类方法汇总

Connect the server with springboard / fortress through xshell
端口规划与APJ

threejs利用indexeddb缓存加载glb模型
随机推荐
How to become an optimist organization?
adb 命令学习笔记
Chapter II relational database
sql server中移除key lookup书签查找
Sohu tout le personnel a été escroqué, quels problèmes ont été exposés?
tidb-lightning配置数据还原路由
Service学习笔记03- 前台服务实战
Go path: goroot & gopath
Export data prompt -- solution to the problem of secure file priv option
LeetCode-1005. Maximized array sum after K negations
LeetCode-859. 亲密字符串
Arraylist集合、对象数组
Qlineedit set input mask
require和ES6 import的区别
Use exe4j to convert The jar file is packaged as Exe file
DFS and BFS notes (I) breadth first search based on C language
JPA failed to save multiple entities circularly
My C の errors
threejs利用indexeddb缓存加载glb模型
Talk about the interview questions of the collection