当前位置:网站首页>Return, const, volatile keywords
Return, const, volatile keywords
2022-06-24 00:00:00 【Cloud C】
List of articles
return keyword
Have you thought about a question ? When we download a video , Assuming that 3 individual G, We need a long time , And when we delete this video , Almost instantly deleted . Is that reasonable? ?
As we all know , Any data in memory is in binary form 01 Storage . When downloading the video , Just download it 3 individual G Of 0 and 1, So when deleting a video, it should be the normal way of thinking to delete the video 3 individual G Of 0 and 1 Delete , But if so , The time spent should be the same as the time spent downloading .
But since we have discovered from the phenomenon , The deletion time is much shorter than the download time , Then it means , The deletion is not to delete 3 individual G Of 0 and 1 Delete . But for this 3 individual G Memory to do some tricks , Let this 3 individual G Become invalid . Actually , In the computer , Deleting data is not really deleting , Instead, the data can be overwritten instead of being overwritten .
How to correctly understand this code ?
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <Windows.h>
char* func() {
char str[] = "hello world!";
return str;
}
int main()
{
char* p = func();
printf("%s\n", p);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
C Language is a process oriented language , almost 90% The above code is in the code block , Variables created in code blocks , It will be destroyed when the code block comes out . So actually these variables , Are created on the stack , Each function is called a stack frame .
Let's first analyze the above code ,func The function creates a string and returns a pointer to that string , Then the function returns , The function is destroyed , That is, any code in the function will disappear , Then the created string will disappear , Then the returned pointer becomes a wild pointer . But is this really the case ?

During commissioning ,func After the function returns the pointer, it should be destroyed , And from above, the surveillance found , Not destroyed , The pointer p Still point to that string .

And when we're done printf After the function , Find the pointer p It becomes a wild pointer .
This is because , What we call function out code block destruction is not really destruction , It just makes the code block overwritable , So when func Function time , You can find func Not destroyed , And when executed printf You will find p Into a wild pointer , This is because printf Is also a function ,printf The function covers func function .
What is the nature of receiving return value temporary variables ? Let's take another look at the code
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <Windows.h>
int func() {
int n = 1;
return n;
}
int main()
{
int num = func();
printf("%d\n", num);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
There is a problem that arises , When func After returning , The function will be destroyed , Variable n Will be destroyed , Then when you return , use num When receiving, you will receive n Medium 1 Do you ?
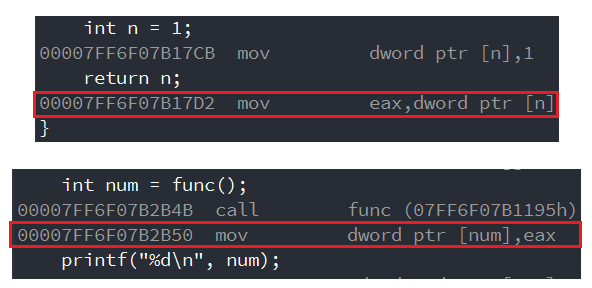
When viewing disassembly , You can see ,func return , The returned value is stored in a general-purpose register eax in , While using num Reception time , Will eax And then put the value in num in .
So if we don't use num What happens to reception ?
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <Windows.h>
int func() {
return 1;
}
int main()
{
func();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
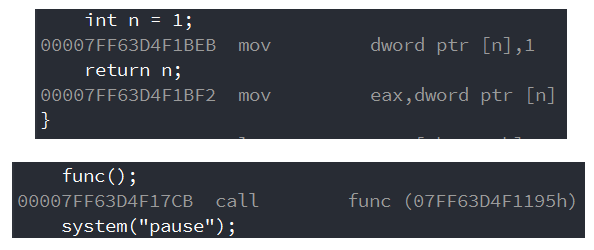
You can find , Whether we receive it or not , As long as the function returns this integer value , The value is stored in a register .
in other words , When we receive , This register will be used . No reception , Do not use registers . But the return value must be stored in the register .
const Perhaps the keyword should be replaced with readonly
const Decorated read-only variable

You can see , By const Modified variables , Cannot be modified directly , Can it be modified indirectly ?

Despite the warning , But we can modify it .
therefore ,const A modified variable is not really a constant that cannot be modified
that const What is the meaning of modifying variables ?
- Let the compiler do direct modification checking
Add... To the variable const after , This tells the compiler that this variable cannot be modified , And if this variable is modified somewhere , Then the compiler reports an error , in other words , Combined with the const It tells the compiler that it cannot be modified , If it is modified, you will report an error to remind the user .
- Tell other programmers ( Changing your code or reading your code ) Don't change this variable . It's one of them “ Since the description ” meaning
Add... To the variable const after , Just tell other users , This variable should not be modified , If you modify it, an error will be reported to remind the user .
const Decorated variable , Can it be part of the array definition ?

Obviously not , Even if you variable n By const Modify the , It is still a variable , It just can't be modified directly .
const Can only be initialized directly at the time of definition , You cannot assign values twice . Why? ?
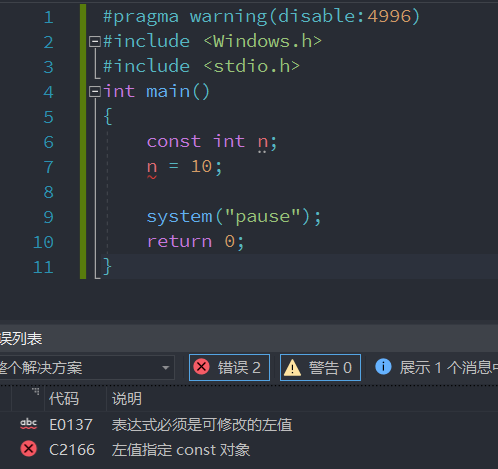
It's simple , Because you can't directly control variables n Make changes , Of course, the second assignment is not allowed .
case Whether the statement can be followed by const What about the modified variables ?

Obviously , It can't be !
We usually call it const The modified variable is A read-only variable , Because this variable is not allowed to be modified in a sense , Just for reading .
const Modify general variables
A general variable is a simple type of read-only variable . This read-only variable is defined , Modifier const Can be used before a type specifier , It can also be used in the back .
//demo
const int a = 5;
int const b = 10;
const Modify the array
//demo
const int arr1 = {
0,1,2,3,4 };
int const arr2 = {
5,6,7,8,9 };
Yes, of course , The elements of an array are not allowed to be modified directly

const Modify a pointer
const int* p; //p The content pointed to cannot be modified , however p Itself can be modified
int const* p; //p The content pointed to cannot be modified , however p Itself can be modified
int* const p; //p The content pointed to can be modified , however p Itself cannot be modified
const int* const p; //p Point to the content and p It cannot be modified
There is a good way to remember the above four situations
if const stay * Of On the left , be What the pointer points to It can't be modified
if const stay * Of On the right , be The pointer itself It can't be modified
const Modify the parameters of the function

Look at the above. show function , Its function is just to output strings , So to prevent show Function may change the string , Let's add one const Qualifiers decorate , If the string is changed, the compiler will alarm , add const Also to tell other users not to modify the string .
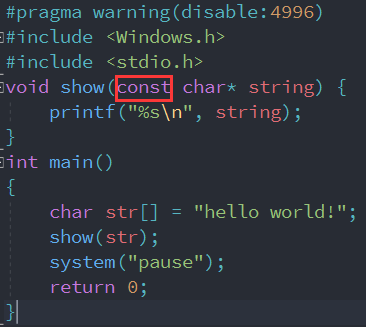
In fact, add or not const, The effect on this function is not particularly large , But as programmers, when we write code , Try to figure out what problems this code might have , So we can use some means to solve these problems or tell us that there are problems !const It's a typical example , To prevent a variable from changing , To add const modification .
const Modify the return value of the function

The return value of this function is added with const, It means that you don't want to change the return value n Size , And if you assign the return value to a non - const Decorated pointer , The pointer can be modified n The size of the , This is against the will of the function . So the compiler warns .
In this case , There would be no warning , And it cannot be changed by the return value n Size , It also conforms to the intention of the function .
by the way , For general built-in types , Add const It's meaningless , Because the general built-in type itself is a temporary copy ,return The function is then destroyed . add const What's the meaning of ?
Look at the picture below , A rule can be drawn

stay C In language , A variable limits the assignment of a lower rank to a higher rank , Generally no warning . And the higher grade is assigned to the lower grade , It usually warns .
It's easy to understand , For variables a Come on , We made it a little safer , Variables b Security will get worse , It's against the rules b A willingness not to be modified .
The most changeable keyword - volatile

First look at while function , It's obviously an endless cycle
Its normal execution process is cpu The register in is read from memory pass The value in , Then make logical judgment , Execute an empty statement , Read from memory again ……
however ,cpu It may be true while Function to optimize , The current understanding of the optimization scheme is to directly pass Put the value in the register , No longer read from memory , Direct logic judgment for each cycle , perform , Logical judgment execution ……, So just in case pass The value in is modified so that while When there is no longer an infinite loop , At this time cpu New values are not read from memory , Make every logical judgment always be the value in the register .
and volatile That's the solution , to pass add volatile after , Make the function after optimization , Still every time I read from memory , This will make it possible to be pass When something changes , The value in the register can also change in time .
Put the value of into the register , No longer read from memory , Direct logic judgment for each cycle , perform , Logical judgment execution ……, So just in case pass The value in is modified so that while When there is no longer an infinite loop , At this time cpu New values are not read from memory , Make every logical judgment always be the value in the register .
and volatile That's the solution , to pass add volatile after , Make the function after optimization , Still every time I read from memory , This will make it possible to be pass When something changes , The value in the register can also change in time .
边栏推荐
- Total number of combinations ii[each element can only be solved by + once]
- Flux in three dimensional vector field
- Kubernetes basic concept
- [technical grass planting] use the shared image function to realize the offline switching from CVM to LH
- Unity text component space newline problem
- 生成式对抗网络(GANs)及变体
- Chrome plug-in features and case analysis of actual combat scenarios
- MySQL architecture (basic)
- Some common tool functions in work
- I was cheated by my colleagues to work overtime on weekends. I haven't seen redis used like this...
猜你喜欢

测试 - 用例篇 - 细节狂魔

Inftnews | where should the future of the creator economy go in the Web3 world?

Web site SSL certificate

What is the use of AI technology in the medical field?

How to ensure reliable power supply of Expressway

合成大西瓜小游戏微信小程序源码/微信游戏小程序源码

Cvpr2019/ image translation: transgaga: geometry aware unsupervised image to image translation

1. < tag dynamic programming and path combination problem > lt.62 Different paths + lt.63 Different paths II

依赖倒置原则
Gbase observation: extended analytical database
随机推荐
逆向工具IDA、GDB使用
[bug] the element in C iqueryable cannot change its value
.NET 中的 Worker Service 介绍
PMP考试相关计算公式汇总!考前必看
电子元器件行业B2B交易管理系统:提升数据化驱动能力,促进企业销售业绩增长
Nice input edit box
【Bug】C# IQueryable里的元素更改不了值
The group procurement management system of daily chemical supplies industry changes the traditional procurement mode and reduces the procurement cost
Detailed explanation of index invalidation caused by MySQL
Gbase observation: extended analytical database
Wechat applet picture verification code display
log Network Execution Time
量化投资模型——高频交易做市模型相关(Avellaneda & Stoikov’s)研究解读&代码资源
docker 部署redis
What are the good solutions for industrial control safety of production line
Thinking (87): Protocol encryption and compression
Loop caused by add of sublist in list
老龄化下背景下,综合能效管理平台为医院保驾护航
Revit API:明细表 ViewSchedule
Quantitative investment model -- research interpretation of high frequency trading market making model (Avellaneda & Stoikov's) & code resources