当前位置:网站首页>Pytorch(一) —— 基本语法
Pytorch(一) —— 基本语法
2022-07-01 04:35:00 【CyrusMay】
Pytorch(一) —— 基本语法
1.基本数据类型
1.1 torch.FloatTensor与torch.cuda.FloatTensor
- torch.FloatTensor为CPU上的数据类型
- torch.cuda.FloatTensor为GPU上的数据类型

1.2 torch.DoubleTensor与torch.cuda.DoubleTensor

1.3 torch.IntTensor与torch.cuda.IntTensor

1.4 torch.LongTensor与torch.cuda.LongTensor
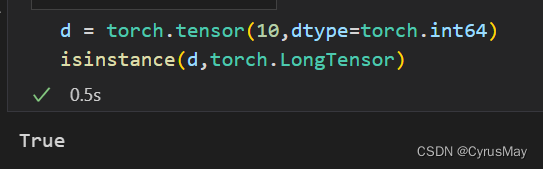
1.5 torch.BoolTensor与torch.cuda.BoolTensor

2 Tensor创建的常用操作
2.1 判断是否为本机是否有可用的GPU资源

2.2 CPU类型数据转换为GPU类型数据
- 使用数据的.cuda()方法

2.3 获取Tensor的形状
- 使用.shape属性
- 使用.size()方法

2.4 将numpy格式的数据转换为Tensor格式

2.4 将List格式的数据转换为Tensor格式

2.5 创建未初始化的Tensor
- torch.empty()
- torch.FloatTensor(d1,d2,d3)

2.6 设置Tensor的默认格式
- torch.set_default_tensor_type

2.7 创建均匀分布与纯整数Tensor
- 均匀分布:torch.rand() / torch.rand_like()
- 纯整数: torch.randint() / torch.randint_like()

2.8 创建正态分布的Tensor
- torch.randn()
- torch.normal()


2.9 创建元素全相同的Tensor
- torch.full()

2.10 torch.arange()

2.10 torch.linespace()

2.10 torch.logspace()
- 创建对数均分的1维Tensor

2.11 torch.ones / .zeros / eye

2.12 随机打散
- torch.randperm 随机打乱一个数字序列

3. 索引与切片
3.1 对指定维度进行索引
- Tensor.index_select()

3.2 使用…进行索引

3.3 使用masked_select进行索引
- torch.masked_select()
- Tensor.ge() 是否大于某个数值

4. 维度变换
4.1 torch.view() / reshape()
- torch.view() 将数据以某种排列方式展示给我们,不改变存储区的真实数据,只改变头信息区,数据存储不连续是不能使用 view() 方法的。
- torch.reshape(),当 tensor 满足连续性要求时,reshape() = view(),和原来 tensor 共用存储区 当 tensor;不满足连续性要求时,reshape() = **contiguous() + view(),会产生新的存储区的 tensor,与原来tensor 不共用存储区。


4.2 添加一个维度torch.unsqueeze()

4.3 减少一个维度torch.squeeze()

4.4 broadcasting:使用expand方法
- 函数对返回的张量不会分配新内存,即在原始张量上返回只读视图,返回的张量内存是不连续的

4.4 内存复制:使用repeat方法
- 与torch.expand不同的是torch.repeat返回的张量在内存中是连续的

4.5 维度交换与转置:使用transpose和permute方法
- .t() 为二维矩阵转置
- .transpose() 交换任意两个维度的顺序
- .permute() 任意交换维度顺序

5 Tensor的合并与拆分
5.1 合并
- torch.cat() 在已有维度上进行合并
- torch.stack() 新建一个维度并进行合并
a = torch.randn(4,28,64)
b = torch.randn(4,28,64)
print(torch.cat([a,b],dim=0).size())
print(torch.stack([a,b],dim=0).size())
torch.Size([8, 28, 64])
torch.Size([2, 4, 28, 64])
5.2 拆分
- torch.split() 按照给定长度进行拆分
- torch.chunk() 按照给定份数进行拆分
a = torch.rand(9,28,28)
print([i.size() for i in a.split([4,5],dim=0)])
print([i.size() for i in a.chunk(2,dim=0)])
[torch.Size([4, 28, 28]), torch.Size([5, 28, 28])]
[torch.Size([5, 28, 28]), torch.Size([4, 28, 28])]
6. 数学运算
6.1 基础运算
- +、-、*、/
a = torch.rand(64,128)
b = torch.rand(128)
print(torch.all(torch.eq(a+b,torch.add(a,b))))
print(torch.all(torch.eq(a-b,torch.sub(a,b))))
print(torch.all(torch.eq(a/b,torch.div(a,b))))
print(torch.all(torch.eq(a*b,torch.mul(a,b))))
tensor(True)
tensor(True)
tensor(True)
tensor(True)
6.2 矩阵运算
- torch.mm() 适用于二维tensor之间的矩阵乘法
- torch.matmul() 适用于二维及大于二维tensor之间的矩阵乘法
- @ 与.matmul()方法的用法一致
x = torch.rand(100,32)
w = torch.rand(32,64)
print(torch.mm(x,w).size())
print(torch.matmul(x,w).size())
print(([email protected]).size())
torch.Size([100, 64])
torch.Size([100, 64])
torch.Size([100, 64])
x = torch.rand(128,64,100,32)
w = torch.rand(32,64)
print(torch.matmul(x,w).size())
print(([email protected]).size())
print(torch.mm(x,w).size())
torch.Size([128, 64, 100, 64])
torch.Size([128, 64, 100, 64])
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
RuntimeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-15-df2761074153> in <module>
3 print(torch.matmul(x,w).size())
4 print(([email protected]).size())
----> 5 print(torch.mm(x,w).size())
RuntimeError: self must be a matrix
6.3 幂运算
- .pow() 幂运算
- .sqrt() 开根运算
- .rsqrt() 开根再求倒数运算
a = torch.full([3,3],3.)
print(a)
print(a.pow(2))
print(a.sqrt())
print((a**2).rsqrt())
tensor([[3., 3., 3.],
[3., 3., 3.],
[3., 3., 3.]])
tensor([[9., 9., 9.],
[9., 9., 9.],
[9., 9., 9.]])
tensor([[1.7321, 1.7321, 1.7321],
[1.7321, 1.7321, 1.7321],
[1.7321, 1.7321, 1.7321]])
tensor([[0.3333, 0.3333, 0.3333],
[0.3333, 0.3333, 0.3333],
[0.3333, 0.3333, 0.3333]])
6.4 指数和对数运算
- torch.exp()
- torch.log()
a = torch.exp(torch.full([2,2],3.))
print(a)
print(torch.log(a))
## 以3为底的对数运算
print(torch.log(a)/torch.log(torch.tensor(3.)))
tensor([[20.0855, 20.0855],
[20.0855, 20.0855]])
tensor([[3., 3.],
[3., 3.]])
tensor([[2.7307, 2.7307],
[2.7307, 2.7307]])
6.5 近似计算
- torch.floor() 向下取整
- torch.ceil() 向上取整
- torch.round() 四舍五入
- torch.trunc() 取出整数部分
- torch.frac()取出小数部分
a = torch.tensor(3.14)
b = torch.tensor(3.54)
print(a.floor())
print(a.ceil())
print(a.round())
print(b.round())
print(a.trunc())
print(a.frac())
tensor(3.)
tensor(4.)
tensor(3.)
tensor(4.)
tensor(3.)
tensor(0.1400)
6.6 梯度裁剪计算
- torch.clamp()
| min, if x_i < min
y_i = | x_i, if min <= x_i <= max
| max, if x_i > max
grad = torch.rand(3,3)*30
print(grad)
print(grad.clamp(0,10))
tensor([[ 0.5450, 3.1299, 0.0786],
[22.1880, 27.4744, 2.3748],
[10.4793, 5.7453, 20.6413]])
tensor([[ 0.5450, 3.1299, 0.0786],
[10.0000, 10.0000, 2.3748],
[10.0000, 5.7453, 10.0000]])
7. Tensor的统计计算
7.1 范数计算
- Tensor.norm§ 进行p范数计算
a = torch.randn(8)
b = a.view(2,4)
c = a.view(2,2,2)
print(a.norm(1),b.norm(1),c.norm(1))
print(a.norm(2),b.norm(2),c.norm(2))
print(b.norm(2,dim=1))
print(c.norm(2,dim=0))
tensor(5.4647) tensor(5.4647) tensor(5.4647)
tensor(2.1229) tensor(2.1229) tensor(2.1229)
tensor([1.6208, 1.3711])
tensor([[1.1313, 0.8043],
[1.2935, 0.9523]])
7.2 统计指标计算
- Tensor.sum() 求和
- Tensor.min() / .max() 求最小值和最大值
- Tensor.argmin() / .Tensor.argmax() 求最小值或最大值对应的索引
- Tensor,prod() 求取累乘的结果
- Tensor.mean() 求取均值
- 可以对keepdim关键词进行赋值,以确定计算结果是否要维持原有维度
a = torch.rand(3,4)
print(a)
print(a.mean(),a.max(),a.min(),a.prod())
print(a.argmax(),a.argmin())
print(a.argmin(dim=1))
print(a.argmin(dim=1,keepdim=True))
tensor([[0.7824, 0.4527, 0.4538, 0.6727],
[0.2269, 0.9950, 0.9010, 0.2681],
[0.3563, 0.2929, 0.5285, 0.6461]])
tensor(0.5480) tensor(0.9950) tensor(0.2269) tensor(0.0002)
tensor(5) tensor(4)
tensor([1, 0, 1])
tensor([[1],
[0],
[1]])
7.3 计算前k个值或第k小的值
- Tensor.topk() 计算前k个最小或最大的值
- Tensor.kthvalue() 返回第k小的值
a = torch.rand(3,4)
print(a)
print(a.topk(2,dim=0,largest=True))
print(a.kthvalue(3,dim=0))
tensor([[0.9367, 0.3146, 0.6258, 0.2656],
[0.8911, 0.6364, 0.7013, 0.2946],
[0.4879, 0.5836, 0.0198, 0.2136]])
torch.return_types.topk(
values=tensor([[0.9367, 0.6364, 0.7013, 0.2946],
[0.8911, 0.5836, 0.6258, 0.2656]]),
indices=tensor([[0, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 2, 0, 0]]))
torch.return_types.kthvalue(
values=tensor([0.9367, 0.6364, 0.7013, 0.2946]),
indices=tensor([0, 1, 1, 1]))
8. where和gather函数
8.1 torch.where()
torch.where(condition,a,b) -> Tensor
满足条件返回a,否则返回b
condition = torch.rand(2,2)
a = torch.full([2,2],1)
b = torch.full([2,2],0)
print(condition)
print(a)
print(b)
print(torch.where(condition>= 0.5,a,b))
tensor([[0.5827, 0.1495],
[0.8753, 0.6246]])
tensor([[1, 1],
[1, 1]])
tensor([[0, 0],
[0, 0]])
tensor([[1, 0],
[1, 1]])
8.1 torch.gather()
- 用于查表
- torch.gather(input,dim,index)
- 对于指定维度按索引进行查询
- index除了指定维度的大小与input可以不一致外,其它均需一致
prob = torch.rand(5,10)
index = prob.topk(3,dim=1,largest=True)[1]
print(index)
table = torch.arange(150,160).expand(5,10)
print(table)
print(torch.gather(table,dim=1,index=index))
tensor([[8, 7, 3],
[2, 0, 1],
[4, 3, 2],
[8, 4, 0],
[0, 6, 1]])
tensor([[150, 151, 152, 153, 154, 155, 156, 157, 158, 159],
[150, 151, 152, 153, 154, 155, 156, 157, 158, 159],
[150, 151, 152, 153, 154, 155, 156, 157, 158, 159],
[150, 151, 152, 153, 154, 155, 156, 157, 158, 159],
[150, 151, 152, 153, 154, 155, 156, 157, 158, 159]])
tensor([[158, 157, 153],
[152, 150, 151],
[154, 153, 152],
[158, 154, 150],
[150, 156, 151]])
by CyrusMay 2022 06 28
最深刻 的故事 最永恒 的传说
不过 是你 是我 能够 平凡生活
——————五月天(因为你 所以我)——————
边栏推荐
- Tcp/ip explanation (version 2) notes / 3 link layer / 3.4 bridge and switch / 3.4.2 multiple registration protocol (MRP)
- [difficult] sqlserver2008r2, can you recover only some files when recovering the database?
- 离线安装wireshark2.6.10
- 2022 a special equipment related management (elevator) simulation test and a special equipment related management (elevator) certificate examination
- How to do the performance pressure test of "Health Code"
- OdeInt与GPU
- Difference between cookie and session
- Shell之分析服务器日志命令集锦
- Caijing 365 stock internal reference | the first IPO of Beijing stock exchange; the subsidiary of the recommended securities firm for gambling and gambling, with a 40% discount
- 2022年煤气考试题库及在线模拟考试
猜你喜欢

Execution failed for task ‘:app:processDebugResources‘. > A failure occurred while executing com. and
![[recommended algorithm] C interview question of a small factory](/img/ae/9c83efe86c03763710ba5e4a2eea33.jpg)
[recommended algorithm] C interview question of a small factory

Kodori tree board

OdeInt與GPU

Question bank and online simulation examination for special operation certificate of G1 industrial boiler stoker in 2022

OdeInt与GPU

Concurrent mode of different performance testing tools

2022 G2 power station boiler stoker examination question bank and G2 power station boiler stoker simulation examination question bank

Software testing needs more and more talents. Why do you still not want to take this path?

Pytorch(二) —— 激活函数、损失函数及其梯度
随机推荐
TCP server communication flow
I also gave you the MySQL interview questions of Boda factory. If you need to come in and take your own
Obtain detailed ideas for ABCDEF questions of 2022 American Games
Strategic suggestions and future development trend of global and Chinese vibration isolator market investment report 2022 Edition
LM小型可编程控制器软件(基于CoDeSys)笔记十九:报错does not match the profile of the target
Extension fragment
One click shell to automatically deploy any version of redis
Execution failed for task ‘:app:processDebugResources‘. > A failure occurred while executing com. and
网站服务器:好用的网站服务器怎么选这五方面要关注
Internet winter, how to spend three months to make a comeback
【LeetCode】100. Same tree
Codeworks round 449 (Div. 1) C. Kodori tree template
2022 hoisting machinery command registration examination and hoisting machinery command examination registration
JVM栈和堆简介
Advanced application of ES6 modular and asynchronous programming
What is uid? What is auth? What is a verifier?
Web server: how to choose a good web server these five aspects should be paid attention to
Use winmtr software to simply analyze, track and detect network routing
Caijing 365 stock internal reference | the first IPO of Beijing stock exchange; the subsidiary of the recommended securities firm for gambling and gambling, with a 40% discount
Basic usage, principle and details of session