当前位置:网站首页>Process and planned task management
Process and planned task management
2022-07-27 01:41:00 【Strange mushrooms】
- Process and plan task management outline
- 1. Basic concepts
- Program
- process
- Father child process
- Threads
- Single thread
- 2. static state / Dynamic statistics of process and system load
- 1.ps
- 2. top
- 3.jobs( Including some background operations )
- 4.pstree
- 5.pgrep
- 6. Terminate the process
- 3. Periodic tasks
- 1. Basic concepts
- Basic concepts ( Program process Threads )

- 1. Program
- The definition of program : Executable code or data stored on CD or hard disk , It's a static concept , Only load the program into memory , The system can only execute after allocating resources for it , This state of execution is called process
- 2. process
- Process definition : A process is a process of dynamic execution of a program , A program can create multiple processes , Complete tasks by consuming system resources , Is the basic unit of resources allocated by the operating system , Most processes are independent of each other , Each process has its own independent address space , Processes can create threads to complete more refined operations , Processes are safer than threads , If the process fails, it should be independent of each other and will not affect , And thread failure ,os When feedback to the process is detected , There may be something wrong .
- The concept of parent-child process : The parent process affects the child process , There is a relationship between them , The child process is logically derived from the parent process , If the parent process exits , And one or more of its subprocesses is still running , These processes are called orphan processes , The orphan process will be init Process adoption , And by the init The process completes the status collection for it . If the child process exits the parent process and is too busy to withdraw the child process, a zombie process will occur , The zombie process is essentially dead, so you can't kill it , You need to kill its parent process to kill it
- 3. Threads
- Definition of thread : A thread is an instance in a process , Relying on the process , Shared process space address ,cpu Resources, etc , It should be that threads are not independent of each other, so a thread problem may affect all threads
- Single thread concept : Single core and single thread can only execute one task at a time , When the task volume is large, it will cause congestion ,CPU At the micro level, the time to process threads is very short , It's called a time slice , In theory CPU Deal with tasks one by one , You can complete multithreaded tasks at your own speed .
- 1. Program
- static state / Dynamic statistics of process and system load (ps jobs top pgrep pstree)
- 1.ps( View static process statistics )
- ps -aux:( Briefly display the information of all processes in the system )(aux The detailed content )

- -u: Output process information in user oriented format
- -x: Display the output process information in user oriented format
- -a: Display the information of all processes under the current terminal , Including other processes
- ps -elf:( Display system process information in long format )(elf The detailed content )

- -e: Display all process information in the system
- -l: Use long format to display process information
- -f: Display process information in full format
- ps -aux:( Briefly display the information of all processes in the system )(aux The detailed content )
- 2. top( Dynamically view the status of the process and the load of the system )

- 1.(15:51:20 up 3:41) Time of the system now System process running time
- 2.(2 user) Two users
- 3.(load average:0.0 0.01 0.05)CPU Average load value A minute Five minutes 15 Average load in minutes
- 4.(Tasks) How many tasks are there
- 5.(running) There are several running
- 6.(sleeping) There are several ready
- 7.(stopped) There are several stops
- 8.(zombie) There are several zombie processes
- 9. Using a digital 1 You can see all cpu The proportion of
- 1. us: user cpu Proportion
- 2.sy: System cpu Proportion
- 3.ni: Priority scheduling occupies
- 4.id: Free cpu
- 5.wa:I/O Waiting for occupation
- 6.hi: System interrupt occupancy
- 7.si: Software interrupt occupancy
- 8.st: Virtualization takes up
- 3.jobs( View background processes )
- 1.jobs -l( View all processes in the background and display pid)
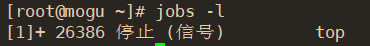
- ######( Some scattered knowledge points about the backstage )######
- ctrl + z: Pause the current process and suspend in the background
- &: Added at the end of the order , Indicates that the command is run in the background
- fg: Turn the suspended background to the foreground to start
- bg: Keep the process suspended in the background starting in the background
- nohup xxxx &: Run the program in the background , However, closing the terminal does not affect the operation of the program
- 1.jobs -l( View all processes in the background and display pid)
- 4.pstree( List process information in a tree structure )

- pstree -pua
- -p: When using this option, you can list the corresponding PID Number
- -u: Option to list the corresponding user names
- -a: Select to list the complete commands
- pstree -pua
- 5.pgrep( Query process information )
- pgrep -l: Query the process with the specified name , And show their PID Number

- pgrep-u: Query the specified user PID Number

- pgrep-t: Query the processes allowed on a specific terminal
- pgrep -l: Query the process with the specified name , And show their PID Number
- 6. Terminate the process (Kill ,killall,pkill)
- 1.kill( Terminate the process adopt PID Number )
- kill xxxx(PID Number ) Terminate the process
- kil -9 xxxx(PID Number ) Force process termination
- 2.killall( End process by process name )
- killall xxxx( The name of the process ) Terminate the process with the specified process name
- killall -9 xxxx( Process name ) Forcibly terminate the process with the specified process name
- 3.pkill( Through the user to which the process belongs -u Or terminal -l The end of the process )
- pkill -9 -u “ xxxx”( end xxxx The user's process )
- pkill-9 -i “xxxxx”( end xxxx The process of the terminal )
- 1.kill( Terminate the process adopt PID Number )
- 1.ps( View static process statistics )
- Planning task management (at and crontab)
- One time task setup

- at [HH:MM] [yyyy-mm-dd]
- Finally using ctrl+d end
- Periodic task setup
- crontab Schedule tasks through multiple directories and files , Different types of tasks are set by different configuration files
- -e : Manually add recurring tasks

- If you want to start some tasks automatically, you need to enter the configuration file to modify

- -r: Delete configured recurring tasks
- -e : Manually add recurring tasks
- One time task setup
- a key
- Understand the concept of process thread , adopt Top Check the process , Observe for one minute, ten minutes 15 Minute load trend , Analyze the cause of the failure
- Skillfully use ,ptree( The tree displays process information ),pgrep( Specify a name / User query process ),jobs( View background processes ),ps( Static view process )
- Understand process termination Kill, How to exit gracefully
- Set up scheduled tasks , Single task at And periodic tasks crontab, understand * * * * * , Setting of time sharing day, month and week
- difficulty
- ps/top SATAT Process type , Processing of the value of system load , And the commands of each query process , Format compilation of periodic tasks
- Summary of notes
- This chapter mainly understands the commands for viewing system process information (ps-elf ps-aux), And specify to view user processes (pgrep -u) And through the pgrep- i and kill The specified termination process is carried out in the form of combination , Set periodic tasks , Complete regular functions
- Use Technology Association links
- http://t.csdn.cn/LdpCF【loadaverage analysis 】
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

Finding the greatest common divisor

Jenkins -- Basic -- 03 -- post installation setup wizard

ESP8266 STA_ Server

Lnmp+discuz Forum

Web services (07) - LNMP one click deployment
Shell编程规范与变量

Jenkins -- Foundation -- 02 -- Installation
![[ctf real question] 2018 WANGDING cup web unfinish](/img/d8/a367c26b51d9dbaf53bf4fe2a13917.png)
[ctf real question] 2018 WANGDING cup web unfinish

22FTP

Buuctf casual note, exec, easysql, secret file
随机推荐
8、 Definition of array
C language automatically generates code comments: korofileheader plug-in
14、 Sed
Shell
MakeFile
八、数组的定义
Producer consumer model of concurrent programming
27shell之条件语句
ESP8266 STA_ TCP_ Client
ESP8266 AP_ UDP_ Server
Unity[1] learning directory
[Oracle] get the latest working day and the previous N working days
iptables防火墙(二)
Problem feedback: the synchronization of mobile app failed: the external changes of the data warehouse were damaged. The iPad app also downloaded the warehouse as soon as it was opened, and then flash
Suggestions for beginners of MySQL (strongly recommended ~ don't regret ~ ~)
ESP8266 AP_ MODE
4.1 It is super simple to install QT without using Sogou Chinese input method
Adding, deleting, checking and modifying dynamic sequence table with C language
How should CDC be configured for Oracle cluster mode? I can run normally in stand-alone mode, but I can't read the increment in cluster mode
[unity] unity interface scene view [1]









