当前位置:网站首页>Introduction to Seata
Introduction to Seata
2022-07-26 19:04:00 【Liu Chu, Ge Nian】
List of articles
1. Distributed transaction problems
First of all, let's review the previous single machine ( Local ) Business :
1.1. Local transactions
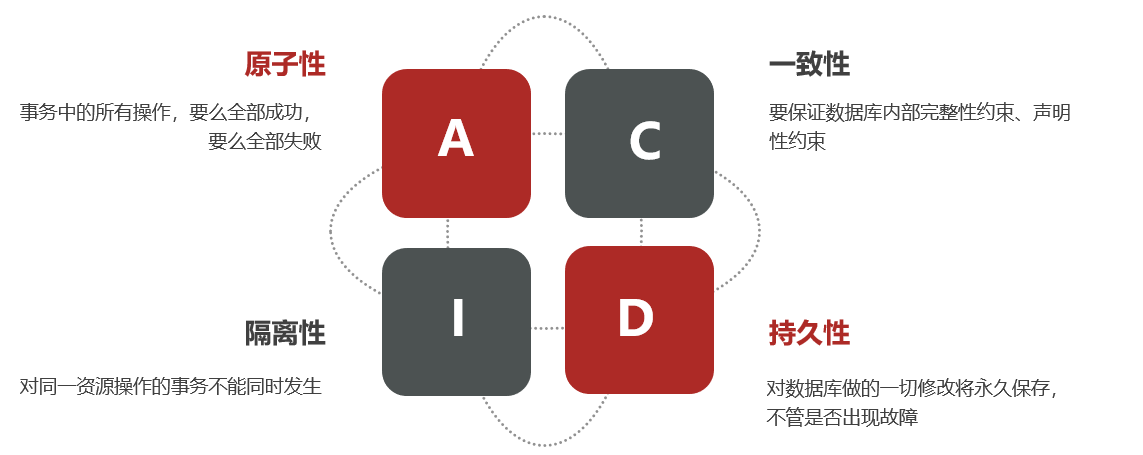
Local transactions , It's traditional Stand alone business . In traditional database transactions , Four principles must be met :
Atomicity : All operations in a transaction , All or nothing , All or nothing
Uniformity : To ensure the internal integrity of the database 、 Declare line constraints
Isolation, : Transactions on the same resource cannot occur at the same time
persistence : All modifications to the database will be permanently saved , Whether or not there is a fault
1.2. Distributed transactions
Distributed transactions , It means not under a single service or a single database architecture , Generated transactions .
for example :
- Distributed transactions across data sources
- Distributed transactions across services
- Distributed transaction of integrated situation
Split at database level 、 After the service is vertically split , A business operation usually spans multiple databases 、 Service can complete . For example, the more common cases of order payment in the e-commerce industry , Including the following behaviors :
- Create new order
- Deduct merchandise stock
- Deduct the amount from the user account balance
To complete the above operations, you need to access three different microservices and three different databases .
The business logic for users to purchase goods (Business). The whole business logic consists of 3 Micro services provide support :
- Warehousing services (Storage): Deduct the storage quantity from the given goods .
- Order service (Order): Create an order based on purchase requirements .
- Account Services (Account): Deduct balance from user account .
The calling relationship is shown in the following figure :
Order creation 、 Deduction of inventory 、 Account deduction is a local transaction in each service and database , Can guarantee ACID principle .
But when we think of three things as one " Business ", To meet the guarantee “ Business ” The atomicity of , Or all operations are successful , All or nothing , Partial success and partial failure are not allowed , This is it. Transactions in distributed systems 了 .
here ACID Hard to meet , This is the problem to be solved by distributed transactions
2. Theoretical basis
Solve distributed transaction problems , Some basic knowledge of distributed system is needed as theoretical guidance .
2.1.CAP Theorem
1998 year , Computer scientist at the University of California Eric Brewer Put forward ,
There are three indicators of a distributed system :
- Consistency( Uniformity )
- Availability( Usability )
- Partition tolerance ( Partition tolerance )
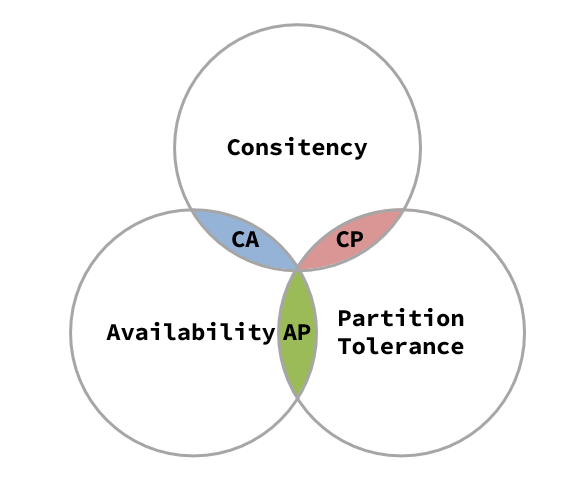
Their first letters are C、A、P.
Eric Brewer say , These three indicators cannot be achieved at the same time . This conclusion is called CAP Theorem .
2.1.1. Uniformity
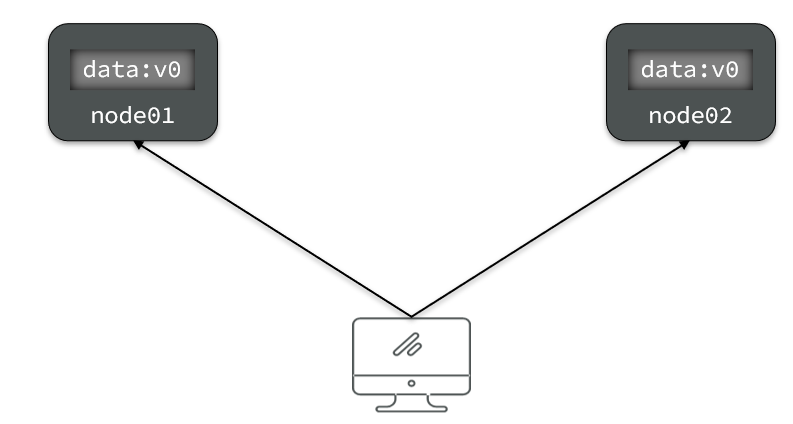
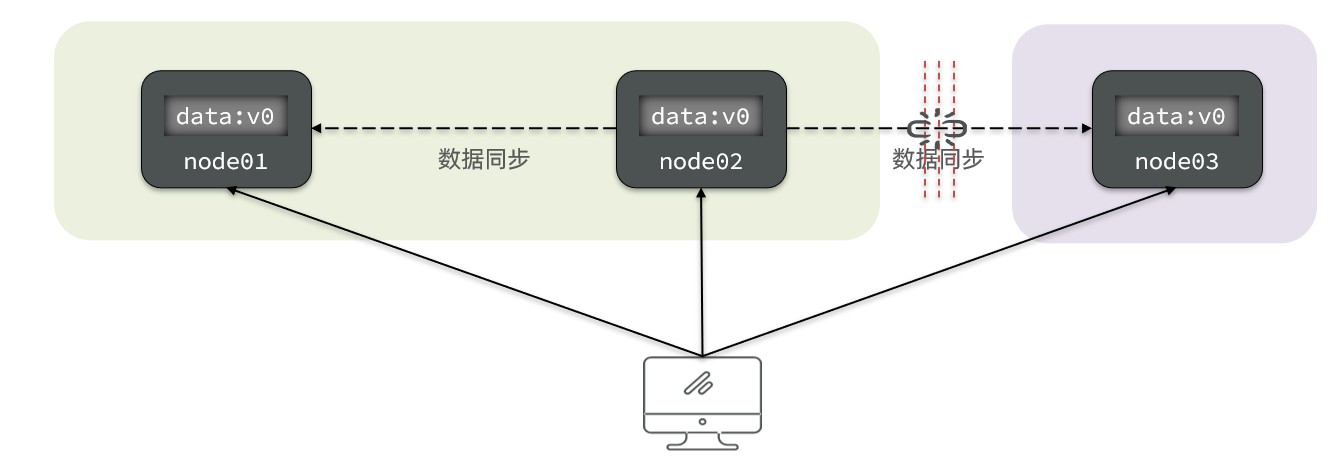
Consistency( Uniformity ): Users access any node in the distributed system , The data obtained must be consistent .
For example, it now contains two nodes , The initial data are consistent :
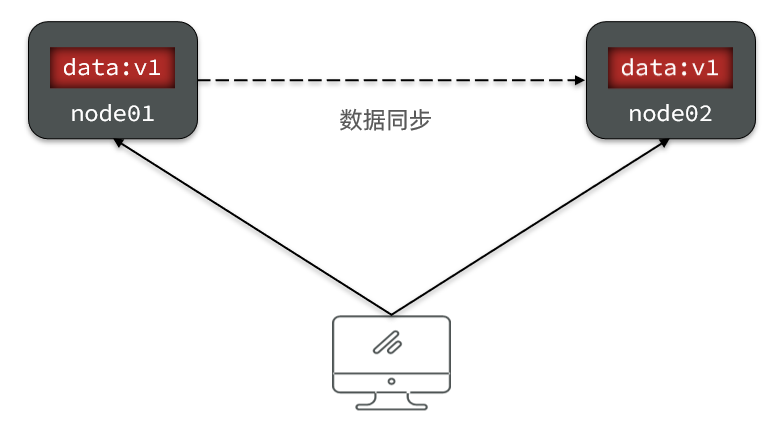
When we modify the data of one of the nodes , There is a difference between the two data :

To keep consistency , It has to happen node01 To node02 The data of Sync :
2.1.2. Usability
Availability ( Usability ): The user accesses any healthy node in the cluster , Must be able to get a response , Instead of timeout or rejection .
Pictured , A cluster with three nodes , Access to any one can get a timely response :

When some nodes are inaccessible due to network failure or other reasons , Indicates that the node is not available :

2.1.3. Partition fault tolerance
Partition( Partition ): Some nodes in the distributed system lose connection with other nodes due to network failure or other reasons , Form a separate partition .
Tolerance( Fault tolerance ): When partitions appear in the cluster , The whole system should also continue to provide external services
2.1.4. contradiction
In distributed systems , The network between systems cannot 100% Keep healthy , There must be trouble , And the service must guarantee the service . therefore Partition Tolerance Inevitable .
When the node receives a new data change , There will be problems :
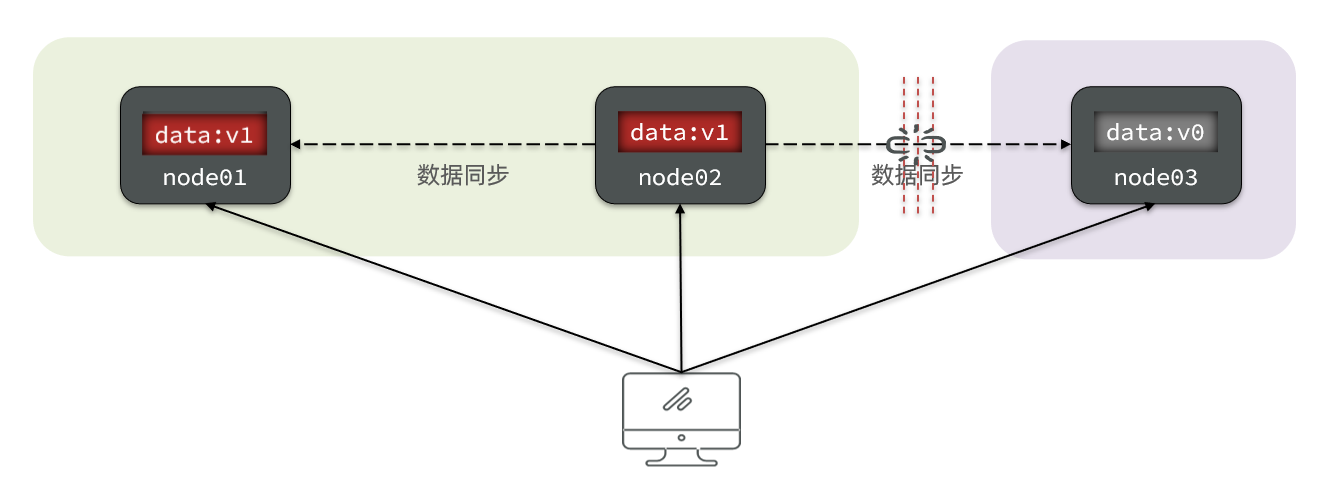
If you want to ensure Uniformity , You have to wait for the network to recover , After data synchronization , The whole cluster provides services to the outside world , The service is blocked , Unavailable .
If you want to ensure Usability , You can't wait for the network to recover , that node01、node02 And node03 There will be data inconsistencies between .
in other words , stay P There must be a situation ,A and C There can only be one .
2.2.BASE theory
BASE The theory is right CAP A solution to , Contains three ideas :
- Basically Available( Basic available ): When a distributed system fails , Partial loss of availability is allowed , That is to ensure that the core is available .
- Soft State( Soft state ): In a certain amount of time , An intermediate state... Is allowed , Such as temporary inconsistency .
- Eventually Consistent( Final consistency ): Although strong consistency cannot be guaranteed , But at the end of the soft state , Finally, the data is consistent .
2.3. The idea of solving distributed transactions
The biggest problem of distributed transaction is the consistency of each sub transaction , Therefore, we can learn from CAP Theorem and BASE theory , There are two solutions :
AP Pattern : Each sub transaction is executed and submitted separately , Inconsistent results are allowed , Then take remedial measures to recover the data , Achieve final agreement .
CP Pattern : Each sub transaction waits for each other after execution , Submit at the same time , Roll back at the same time , Reach a strong agreement . But while the transaction is waiting , In a weakly available state .
But no matter which model , All need to communicate with each other between subsystem transactions , Coordination transaction status , That is, you need a A business coordinator (TC):

Subsystem transactions here , be called Branch business ; The associated branch transactions are called Global transaction .
3. First time to know Seata
Seata yes 2019 year 1 In May, ant financial and Alibaba jointly opened a distributed transaction solution . Committed to providing high-performance and easy-to-use distributed transaction services , Create a one-stop distributed solution for users .
Chinese official website address :https://seata.io/zh-cn/

3.1.Seata The architecture of
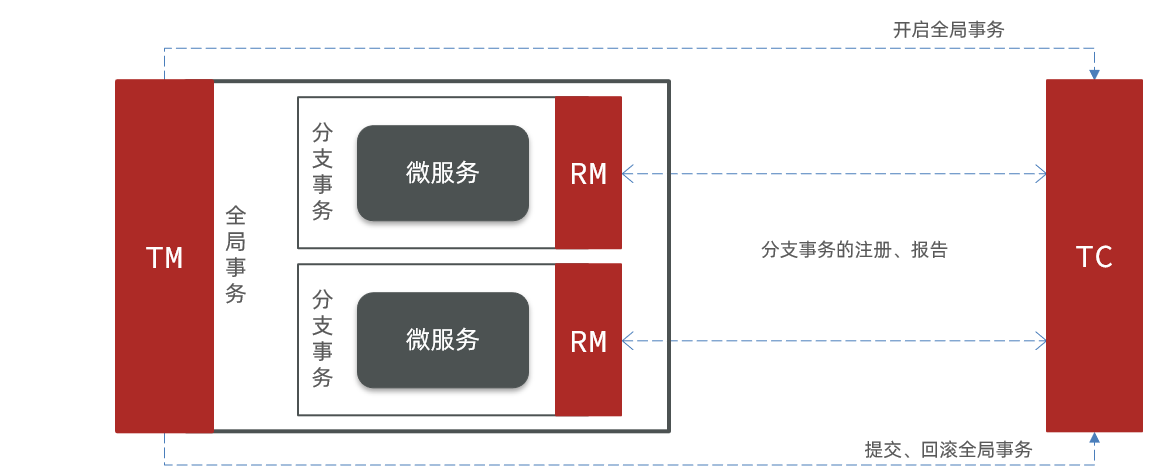
Seata There are three important roles in transaction management :
TC (Transaction Coordinator) - ** A business coordinator :** Maintain the state of global and branch transactions , Coordinate global transaction commit or rollback .
TM (Transaction Manager) - ** Transaction manager :** Define the scope of the global transaction 、 Start global transaction 、 Commit or roll back global transactions .
RM (Resource Manager) - ** Explorer :** Manage resources for branch transactions , And TC Talk to register branch transactions and report the status of branch transactions , And drive branch transaction commit or rollback .
The overall architecture is shown in the figure :
Seata Based on the above architecture, four different distributed transaction solutions are provided :
- XA Pattern : Strong consistency phased transaction mode , At the expense of some availability , No business intrusion
- TCC Pattern : Finally, a consistent phased transaction pattern , There is business intrusion
- AT Pattern : Finally, a consistent phased transaction pattern , No business intrusion , It's also Seata Default mode
- SAGA Pattern : Long transaction mode , There is business intrusion

Either way , Cannot leave TC, That is, the coordinator of affairs .
边栏推荐
- Model definition pytorch learning
- Test cases of common functions
- 2022上海市安全员C证操作证考试题库模拟考试平台操作
- .net CLR GC dynamic loading transient heap threshold calculation and threshold excess calculation
- Microsoft silently donated $10000 to curl, which was not notified until half a year later
- Utility website recommendations
- rancher部署kubernetes集群
- MySQL - function and constraint commands
- [yuntu said] issue 246 digital asset chain - your God of digital asset property protection!
- FTP协议
猜你喜欢
2022g1 industrial boiler stoker certificate question bank and simulation examination
SSM integration - functional module and interface testing

我酷故我在

Agenda express | list of sub forum agenda on July 27

Huawei cloud · cloud sharing experts~

微软默默给 curl 捐赠一万美元,半年后才通知

OpenSSF 基金会总经理 Brian Behlendorf :预计 2026 年将有 4.2 亿个开源

2022茶艺师(中级)考试题模拟考试题库及答案

Unity 农场 2 —— 种植系统

支持代理直连Oracle数据库,JumpServer堡垒机v2.24.0发布
随机推荐
Brian behrendorf, general manager of openssf Foundation: it is estimated that there will be 420million open sources in 2026
手写一个Starter
2022 Shanghai safety officer C certificate operation certificate examination question bank simulated examination platform operation
Test cases of common functions
Arrangement of information security emergency plan
Tensor Rt的int8量化原理
NFT数字藏品系统开发:上线即售罄,网民“秒杀”数字藏品
Racher deploys kubernetes cluster
NFT digital collection development: digital collections help enterprise development
Basic module and example pytorch learning
此章节用于补充3
Meta Cambria handle exposure, active tracking + multi tactile feedback scheme
MySQL learning notes -2. how to improve the query performance of SQL statements
手机申请公募reits账户安全吗?
NFT数字藏品系统开发:“中国旅游日”山西首次发布古建筑数字藏品
如何成为一名优秀的测试/开发程序员?专注谋定而后动......
模板进阶(跑路人笔记)
In this competition, you who can understand the topic have great potential
Accused of excessive patent licensing fees! The U.S. Court ruled that Qualcomm violated the antitrust law: Qualcomm's share price fell 10.86%!
Visual VM positioning oom, fullgc usage