当前位置:网站首页>golang--channal与select
golang--channal与select
2022-06-26 01:38:00 【IT艺术家-rookie】
channal原理1
channal原理2
channal原理3
为什么channel能在不同的g中传递消息,而对于使用者来说不用担心并发的问题?
其实就是hchan内部使用互斥锁来保证了并发安全
ch := make(chan struct{
})
返回了hchan类型的指针;创建一个channel本质上就是得到一个runtime.hchan的指针,后续对此chan的操作,无非就是对结构体字段进行相对应的操作。
chan的本质hchan
type hchan struct {
qcount uint // 队列中目前元素的个数
dataqsiz uint // 队列的容量 ,它是不可变的(在通道创建后永不写入),因此在通道操作期间的任何时间读取它都是安全的。
buf unsafe.Pointer // 指向长度为 dataqsiz 的底层数组,仅有当 channel 为缓冲型的才有意义。
elemsize uint16 //队列中每个对象大小
closed uint32 //channal是否关闭==> 等于0时是未关闭
elemtype *_type // 队列中的元素类型
sendx uint // 已发送元素在循环队列中的索引位置。
recvx uint // 已接收元素在循环队列中的索引位置。
recvq waitq // 接受者的 sudog 等待队列(缓冲区不足时阻塞等待的 goroutine)。
sendq waitq // 发送者的 sudog 等待队列。
lock mutex //互斥锁
}
type waitq struct {
first *sudog
last *sudog
}
sudog 是 Go 语言中用于存放协程状态为阻塞的 goroutine 的双向链表抽象,你可以直接理解为一个正在等待的 goroutine 就可以了。
sudog 是一个运行时的结构体的,它的主要作用就是表示一个在等待列表中的 Goroutine,其中存储着关于这一次阻塞的信息以及两个分别指向前后的 sudog 指针。
type sudog struct {
// The following fields are protected by the hchan.lock of the
// channel this sudog is blocking on. shrinkstack depends on
// this for sudogs involved in channel ops.
g *g //指向当前的 goroutine。
next *sudog //指向下一个 g。
prev *sudog //指向上一个 g。
elem unsafe.Pointer // data element (may point to stack)
// The following fields are never accessed concurrently.
// For channels, waitlink is only accessed by g.
// For semaphores, all fields (including the ones above)
// are only accessed when holding a semaRoot lock.
acquiretime int64
releasetime int64
ticket uint32
// isSelect indicates g is participating in a select, so
// g.selectDone must be CAS'd to win the wake-up race.
isSelect bool
// success indicates whether communication over channel c
// succeeded. It is true if the goroutine was awoken because a
// value was delivered over channel c, and false if awoken
// because c was closed.
success bool
parent *sudog // semaRoot binary tree
waitlink *sudog // g.waiting list or semaRoot
waittail *sudog // semaRoot
c *hchan // channel
}
makechan
func makechan(t *chantype, size int) *hchan {
elem := t.elem
// compiler checks this but be safe.
if elem.size >= 1<<16 {
throw("makechan: invalid channel element type")
}
if hchanSize%maxAlign != 0 || elem.align > maxAlign {
throw("makechan: bad alignment")
}
mem, overflow := math.MulUintptr(elem.size, uintptr(size))
if overflow || mem > maxAlloc-hchanSize || size < 0 {
panic(plainError("makechan: size out of range"))
}
var c *hchan
switch {
case mem == 0: //队列或者元素大小为 0 的情况下,就会调用 mallocgc 方法分配一段连续的内存空间。
c = (*hchan)(mallocgc(hchanSize, nil, true))
// Race detector uses this location for synchronization.
c.buf = c.raceaddr()
case elem.ptrdata == 0: //当前 channel 存储的元素不存在指针引用,就会连同 hchan 和底层数组同时分配一段连续的内存空间。
c = (*hchan)(mallocgc(hchanSize+mem, nil, true))
c.buf = add(unsafe.Pointer(c), hchanSize)
default: //默认当前 channel 存储的元素存在指针引用------默认分配相匹配的连续内存空间。
// Elements contain pointers.
c = new(hchan)
c.buf = mallocgc(mem, elem, true)
}
c.elemsize = uint16(elem.size)
c.elemtype = elem
c.dataqsiz = uint(size)
lockInit(&c.lock, lockRankHchan)
if debugChan {
print("makechan: chan=", c, "; elemsize=", elem.size, "; dataqsiz=", size, "\n")
}
return c
}
// channel 的创建都是调用的 mallocgc 方法,也就是 channel 都是创建在堆上的。因此 channel 是会被 GC 回收的,自然也不总是需要 close 方法来进行显示关闭了。
chansend 发送数据
func chansend(c *hchan, ep unsafe.Pointer, block bool, callerpc uintptr) bool {
if c == nil {
//一开始 chansend 方法在会先判断当前的 channel 是否为 nil。若为 nil,在逻辑上来讲就是向 nil channel 发送数据,就会调用 gopark 方法使得当前 Goroutine 休眠,进而出现死锁崩溃,表象就是出现 panic 事件来快速失败。
if !block {
return false
}
gopark(nil, nil, waitReasonChanSendNilChan, traceEvGoStop, 2)
throw("unreachable")
}
if debugChan {
print("chansend: chan=", c, "\n")
}
if raceenabled {
racereadpc(c.raceaddr(), callerpc, abi.FuncPCABIInternal(chansend))
}
//紧接着会对非阻塞的 channel 进行一个上限判断,看看是否快速失败。
//失败的场景如下:
//若非阻塞且未关闭,同时底层数据 dataqsiz 大小为 0(缓冲区无元素),则会返回失败。。
//若是 qcount 与 dataqsiz 大小相同(缓冲区已满)时,则会返回失败。
if !block && c.closed == 0 && full(c) {
return false
}
var t0 int64
if blockprofilerate > 0 {
t0 = cputicks()
}
//以上时channel 的前置判断。在完成了 channel 的前置判断后,即将在进入发送数据的处理前,channel 会进行上锁
lock(&c.lock)
//在正式开始发送前,加锁之后,会对 channel 进行一次状态判断(是否关闭):
if c.closed != 0 {
unlock(&c.lock)
panic(plainError("send on closed channel"))
}
//直接发送===>当前 channel 有正在阻塞等待的接收方,那么只需要直接发送就可以了。
if sg := c.recvq.dequeue(); sg != nil {
//通过 dequeue 从 recvq 中取出最先陷入等待的 Goroutine 并直接向它发送数据
send(c, sg, ep, func() {
unlock(&c.lock) }, 3)
return true
}
//缓冲发送===>非直接发送,判断 channel 缓冲区中是否还有空间:
if c.qcount < c.dataqsiz {
// Space is available in the channel buffer. Enqueue the element to send.
//调用 chanbuf 方法,以此获得底层缓冲数据中位于 sendx 索引的元素指针值。
qp := chanbuf(c, c.sendx)
if raceenabled {
racenotify(c, c.sendx, nil)
}
//调用 typedmemmove 方法,将所需发送的数据拷贝到缓冲区中。
typedmemmove(c.elemtype, qp, ep)
c.sendx++ //数据拷贝后,对 sendx 索引自行自增 1。同时若 sendx 与 dataqsiz 大小一致,则归 0(环形队列)。
if c.sendx == c.dataqsiz {
c.sendx = 0
}
c.qcount++ //自增完成后,队列总数同时自增 1。解锁互斥锁,返回结果。
unlock(&c.lock)
return true
}
if !block {
//若没有走进缓冲区处理的逻辑,则会判断当前是否阻塞 channel,若为非阻塞,将会解锁并直接返回失败。
unlock(&c.lock)
return false
}
//阻塞发送
gp := getg()//调用 getg 方法获取当前 goroutine 的指针,用于后续发送数据。
mysg := acquireSudog()//调用 acquireSudog 方法获取 sudog 结构体,并设置当前 sudog 具体的待发送数据信息和状态。
mysg.releasetime = 0
if t0 != 0 {
mysg.releasetime = -1
}
// No stack splits between assigning elem and enqueuing mysg
// on gp.waiting where copystack can find it.
mysg.elem = ep
mysg.waitlink = nil
mysg.g = gp
mysg.isSelect = false
mysg.c = c
gp.waiting = mysg
gp.param = nil
c.sendq.enqueue(mysg)//调用 c.sendq.enqueue 方法将刚刚所获取的 sudog 加入待发送的等待队列。
// Signal to anyone trying to shrink our stack that we're about
// to park on a channel. The window between when this G's status
// changes and when we set gp.activeStackChans is not safe for
// stack shrinking.
atomic.Store8(&gp.parkingOnChan, 1)
//调用 gopark 方法挂起当前 goroutine(会记录执行位置),状态为 waitReasonChanSend,阻塞等待 channel。
gopark(chanparkcommit, unsafe.Pointer(&c.lock), waitReasonChanSend, traceEvGoBlockSend, 2)
// Ensure the value being sent is kept alive until the
// receiver copies it out. The sudog has a pointer to the
// stack object, but sudogs aren't considered as roots of the
// stack tracer.
//调用 KeepAlive 方法保证待发送的数据值是活跃状态,直到接收方将其复制出来。也就是分配在堆上,避免被 GC 回收。
KeepAlive(ep)
// 从这里开始唤醒,并恢复阻塞的发送操作
if mysg != gp.waiting {
throw("G waiting list is corrupted")
}
gp.waiting = nil
gp.activeStackChans = false
closed := !mysg.success
gp.param = nil
if mysg.releasetime > 0 {
blockevent(mysg.releasetime-t0, 2)
}
mysg.c = nil
releaseSudog(mysg)
if closed {
if c.closed == 0 {
throw("chansend: spurious wakeup")
}
panic(plainError("send on closed channel"))
}
return true
}
//至此完成所有类别的 channel 数据发送管理。
func full(c *hchan) bool {
// c.dataqsiz is immutable (never written after the channel is created)
// so it is safe to read at any time during channel operation.
if c.dataqsiz == 0 {
// Assumes that a pointer read is relaxed-atomic.
return c.recvq.first == nil
}
// Assumes that a uint read is relaxed-atomic.
return c.qcount == c.dataqsiz
}
send
send 方法承担向 channel 发送具体数据的功能:
func send(c *hchan, sg *sudog, ep unsafe.Pointer, unlockf func(), skip int) {
if raceenabled {
if c.dataqsiz == 0 {
racesync(c, sg)
} else {
// Pretend we go through the buffer, even though
// we copy directly. Note that we need to increment
// the head/tail locations only when raceenabled.
racenotify(c, c.recvx, nil)
racenotify(c, c.recvx, sg)
c.recvx++
if c.recvx == c.dataqsiz {
c.recvx = 0
}
c.sendx = c.recvx // c.sendx = (c.sendx+1) % c.dataqsiz
}
}
if sg.elem != nil {
sendDirect(c.elemtype, sg, ep)//调用 sendDirect 方法将待发送的数据直接拷贝到待接收变量的内存地址(执行栈)。
//例如:msg := <-ch 语句,也就是将数据从 ch 直接拷贝到了 msg 的内存地址。
sg.elem = nil
}
gp := sg.g//调用 sg.g 属性, 从 sudog 中获取等待接收数据的 goroutine,并传递后续唤醒所需的参数。
unlockf()
gp.param = unsafe.Pointer(sg)
sg.success = true
if sg.releasetime != 0 {
sg.releasetime = cputicks()
}
goready(gp, skip+1)//调用 goready 方法唤醒需接收数据的 goroutine,期望从 _Gwaiting 状态调度为 _Grunnable。
}
接收数据 runtime.chanrecv
发送和接受 channel 是相对的,也就是其核心实现也是相对的
func chanrecv(c *hchan, ep unsafe.Pointer, block bool) (selected, received bool) {
if debugChan {
print("chanrecv: chan=", c, "\n")
}
//若 channel 是 nil channel,且为阻塞接收则调用 gopark 方法挂起当前 goroutine。
//若 channel 是非阻塞模式,则直接返回。
if c == nil {
if !block {
return
}
gopark(nil, nil, waitReasonChanReceiveNilChan, traceEvGoStop, 2)
throw("unreachable")
}
//对于非阻塞模式的 channel 会进行快速失败检查,检测 channel 是否已经准备好接收。
//空检查
if !block && empty(c) {
//关闭检查
if atomic.Load(&c.closed) == 0 {
return
}
//通道不可逆地关闭。重新检查通道是否有任何待接收的数据,这些数据可能在上面的空检查和关闭检查之间到达。所以还要检查一次
//channel 已经关闭且不存在缓存数据了,则会清理 ep 指针中的数据并返回。
if empty(c) {
if raceenabled {
raceacquire(c.raceaddr())
}
if ep != nil {
typedmemclr(c.elemtype, ep)
}
return true, false
}
}
var t0 int64
if blockprofilerate > 0 {
t0 = cputicks()
}
//直接接收==》当发现 channel 上有正在阻塞等待的发送方时,则直接进行接收:
lock(&c.lock)
if c.closed != 0 && c.qcount == 0 {
if raceenabled {
raceacquire(c.raceaddr())
}
unlock(&c.lock)
if ep != nil {
typedmemclr(c.elemtype, ep)
}
return true, false
}
if sg := c.sendq.dequeue(); sg != nil {
recv(c, sg, ep, func() {
unlock(&c.lock) }, 3)
return true, true
}
//缓冲接收==》当发现 channel 的缓冲区中有元素时:
if c.qcount > 0 {
//调用 chanbuf 方法根据 recvx 的索引位置取出数据,找到要接收的元素进行处理。
qp := chanbuf(c, c.recvx)
if raceenabled {
racenotify(c, c.recvx, nil)
}
if ep != nil {
typedmemmove(c.elemtype, ep, qp)//若所接收到的数据和所传入的变量均不为空,则会调用 typedmemmove 方法将缓冲区中的数据拷贝到所传入的变量中。
}
typedmemclr(c.elemtype, qp)//最后数据拷贝完毕后,进行各索引项和队列总数的自增增减,并调用 typedmemclr 方法进行内存数据的清扫。
c.recvx++
if c.recvx == c.dataqsiz {
c.recvx = 0
}
c.qcount--
unlock(&c.lock)
return true, true
}
if !block {
unlock(&c.lock)
return false, false
}
//阻塞接收==》当发现 channel 上既没有待发送的 goroutine,缓冲区也没有数据时。将会进入到最后一个阶段阻塞接收:
gp := getg() //主体就是获取当前 goroutine
mysg := acquireSudog()
mysg.releasetime = 0
if t0 != 0 {
mysg.releasetime = -1
}
// No stack splits between assigning elem and enqueuing mysg
// on gp.waiting where copystack can find it.
mysg.elem = ep
mysg.waitlink = nil
gp.waiting = mysg
mysg.g = gp
mysg.isSelect = false
mysg.c = c
gp.param = nil
c.recvq.enqueue(mysg)//构建 sudog 结构保存当前待接收数据(发送方)的地址信息,并将 sudog 加入等待接收队列。
atomic.Store8(&gp.parkingOnChan, 1)
gopark(chanparkcommit, unsafe.Pointer(&c.lock), waitReasonChanReceive, traceEvGoBlockRecv, 2)//最后调用 gopark 方法挂起当前 goroutine,等待唤醒。
// 被唤醒后从此处开始
if mysg != gp.waiting {
throw("G waiting list is corrupted")
}
gp.waiting = nil
gp.activeStackChans = false
if mysg.releasetime > 0 {
blockevent(mysg.releasetime-t0, 2)
}
success := mysg.success
gp.param = nil
mysg.c = nil
releaseSudog(mysg)
return true, success
//被唤醒后,将恢复现场,回到对应的执行点,完成最后的扫尾工作。
}
recv
recv 方法承担在 channel 中接收具体数据的功能:
func recv(c *hchan, sg *sudog, ep unsafe.Pointer, unlockf func(), skip int) {
if c.dataqsiz == 0 {
if raceenabled {
racesync(c, sg)
}
if ep != nil {
//直接接收(不存在缓冲区):调用 recvDirect 方法,其作用与 sendDirect 方法相对,会直接从发送方的 goroutine 调用栈中将数据拷贝过来到接收方的 goroutine。
recvDirect(c.elemtype, sg, ep)
}
} else {
// Queue is full. Take the item at the
// head of the queue. Make the sender enqueue
// its item at the tail of the queue. Since the
// queue is full, those are both the same slot.
//缓冲接收(存在缓冲区):调用 chanbuf 方法,根据 recvx 索引的位置读取缓冲区元素,拷贝完毕后
qp := chanbuf(c, c.recvx)
if raceenabled {
racenotify(c, c.recvx, nil)
racenotify(c, c.recvx, sg)
}
//并将其拷贝到接收方的内存地址。
if ep != nil {
typedmemmove(c.elemtype, ep, qp)
}
// copy data from sender to queue
typedmemmove(c.elemtype, qp, sg.elem)
//对 sendx 和 recvx 索引位置进行调整。
c.recvx++
if c.recvx == c.dataqsiz {
c.recvx = 0
}
c.sendx = c.recvx // c.sendx = (c.sendx+1) % c.dataqsiz
}
//最后还是常规的 goroutine 调度动作,会调用 goready 方法来唤醒当前所处理的 sudog 的对应 goroutine。那么在下一轮调度时,既然已经接收了数据,自然发送方也就会被唤醒。
sg.elem = nil
gp := sg.g
unlockf()
gp.param = unsafe.Pointer(sg)
sg.success = true
if sg.releasetime != 0 {
sg.releasetime = cputicks()
}
goready(gp, skip+1)
}
关闭 closechan
func closechan(c *hchan) {
//前置处理==》基本检查和关闭标志设置,保证 channel 不为 nil 和未关闭,保证边界。
if c == nil {
panic(plainError("close of nil channel"))
}
lock(&c.lock)
if c.closed != 0 {
unlock(&c.lock)
panic(plainError("close of closed channel"))
}
if raceenabled {
callerpc := getcallerpc()
racewritepc(c.raceaddr(), callerpc, abi.FuncPCABIInternal(closechan))
racerelease(c.raceaddr())
}
c.closed = 1
//释放接收方==》在完成了异常边界判断和标志设置后,会将接受者的 sudog 等待队列(recvq)加入到待清除队列 glist 中:
var glist gList
//所取出并加入的 goroutine 状态需要均为 _Gwaiting,以保证后续的新一轮调度。
for {
sg := c.recvq.dequeue()
if sg == nil {
break
}
if sg.elem != nil {
typedmemclr(c.elemtype, sg.elem)
sg.elem = nil
}
if sg.releasetime != 0 {
sg.releasetime = cputicks()
}
gp := sg.g
gp.param = unsafe.Pointer(sg)
sg.success = false
if raceenabled {
raceacquireg(gp, c.raceaddr())
}
glist.push(gp)
}
//释放发送方==》同样,与释放接收方一样。会将发送方也加入到到待清除队列 glist 中:
for {
sg := c.sendq.dequeue()
if sg == nil {
break
}
sg.elem = nil
if sg.releasetime != 0 {
sg.releasetime = cputicks()
}
gp := sg.g
gp.param = unsafe.Pointer(sg)
sg.success = false
if raceenabled {
raceacquireg(gp, c.raceaddr())
}
glist.push(gp)
}
unlock(&c.lock)
//协程调度==》将所有 glist 中的 goroutine 状态从 _Gwaiting 设置为 _Grunnable 状态,等待调度器的调度:
// 后续所有的 goroutine 允许被重新调度后。若原本还在被动阻塞的发送方或接收方,将重获自由,后续该干嘛就去干嘛了,再跑回其所属的应用流程。
for !glist.empty() {
gp := glist.pop()
gp.schedlink = 0
goready(gp, 3)
}
}
他的数据结构就是带缓存的环形队列,再加上对称的 sendq、recvq 等双向链表的辅助属性,就能勾画出 channel 的基本逻辑流转模型。
在具体的数据传输上,都是围绕着 “边界上下限处理,上互斥锁,阻塞/非阻塞,缓冲/非缓冲,缓存出队列,拷贝数据,解互斥锁,协程调度” 在不断地流转处理。在基本逻辑上也是相对重合的,因为发送和接收,创建和关闭总是相对的。
参考资料
调试+图解 channel 的内部实现
参考资料
channal与csp
曹大
边栏推荐
- 用指南针交易股票安全吗?指南针是如何交易股票的,需要开户吗
- Wechat applet
- Redis6.0 new feature - ACL (permission control list) implements the restriction of user executable commands and keys
- 请指教同花顺软件究竟是什么?在线开户安全么?
- . Net7 miniapi (special part):preview5 optimizes JWT verification (Part 2)
- Simplex method (1)
- win32
- Cross server SQL connection configuration
- How to solve the problem that the iPhone 13 lock screen cannot receive the wechat notification prompt?
- What is the sudden power failure of iPhone and how to solve it?
猜你喜欢

ROS2+DDS+RTPS

Analytic hierarchy process

How do I take a screenshot of the iPad? 7 ways to take quick screenshots of iPad

Oracle连接问题以及解决方案
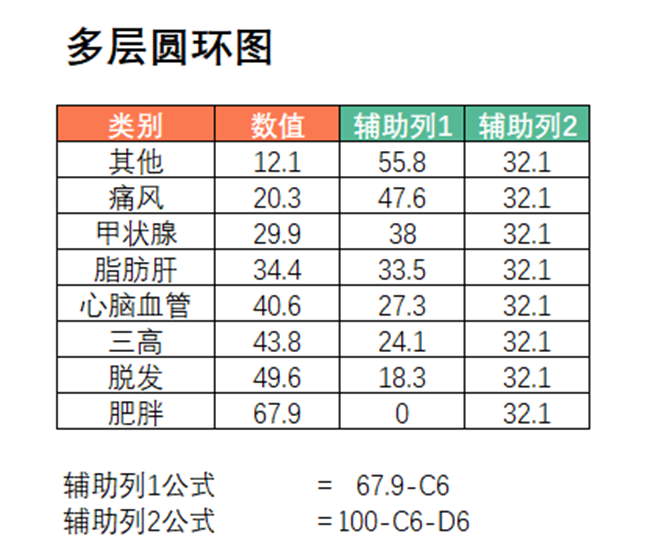
饼图变形记,肝了3000字,收藏就是学会!

为 ServiceCollection 实现装饰器模式

win32

Wechat launched a web version transmission assistant. Is it really easy to use?

MySQL必须掌握4种语言!
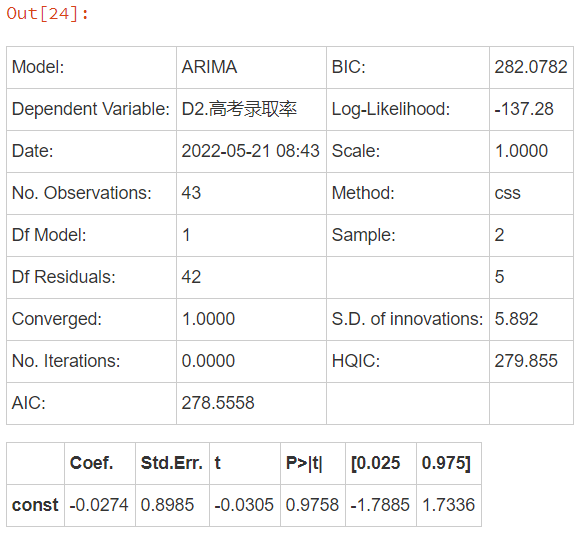
【机器学习】基于多元时间序列对高考预测分析案例
随机推荐
PyQt theme
win32
DF reports an error stale file handle
Breadth first traversal based on adjacency matrix
Blazor University (33) form - editcontext, fieldidentifiers
【图像过滤】基于matlab GUI图像过滤系统【含Matlab源码 1913期】
How did the thief unlock the password after the iPhone was stolen? After reading the long knowledge
【缺陷检测】基于matlab GUI印刷电路板自动缺陷检测【含Matlab源码 1912期】
MySQL必须掌握4种语言!
How to open a stock account? Is it safe to open an account online?
MySQL必須掌握4種語言!
The programmer's eight-year salary change has made netizens envious: you pay me one year's salary per month
OA process editing
Which securities company is better and safer to open a mobile stock account?
Wechat launched a web version transmission assistant. Is it really easy to use?
Google 推荐在 MVVM 架构中使用 Kotlin Flow
In depth good article: what is supernetting?
程序员的八年工资变动,令网友羡慕不已:你一个月顶我一年工资
Pointnet/pointnet++ learning
# 云原生训练营毕业总结