当前位置:网站首页>Leetcode: 102. Sequence traversal of binary tree
Leetcode: 102. Sequence traversal of binary tree
2022-07-26 03:45:00 【uncle_ ll】
102. Sequence traversal of binary tree
source : Power button (LeetCode)
link : https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/
Give you the root node of the binary tree root , Returns the Sequence traversal . ( That is, layer by layer , Access all nodes from left to right ).

Example 1:
Input :root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output :[[3],[9,20],[15,7]]
Example 2:
Input :root = [1]
Output :[[1]]
Example 3:
Input :root = []
Output :[]
Tips :
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 2000] Inside
-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
solution
- recursive : A given node And layer , Judge whether the number of layers is the same as the length of the result , If it's the same , Explain the node It should be placed in this layer , Attention is from the 0 Layer start .
- BFS: Sequence traversal , Use a list to maintain the nodes of the current layer . The length of the current layer controls the number of iterations , If there are left and right child nodes , Add it to the list ;
Code implementation
recursive
python Realization
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def levelOrder(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[List[int]]:
if not root:
return []
levels = []
def helper(node, level):
if len(levels) == level:
levels.append([])
levels[level].append(node.val)
if node.left:
helper(node.left, level+1)
if node.right:
helper(node.right, level+1)
helper(root, 0)
return levels
c++ Realization
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */
class Solution {
vector<vector<int>> res;
public:
void helper(TreeNode* node, int level) {
if (res.size() == level)
res.push_back({
});
res[level].push_back(node->val);
if (node->left)
helper(node->left, level+1);
if (node->right)
helper(node->right, level+1);
}
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return res;
helper(root, 0);
return res;
}
};
Complexity analysis
- Time complexity : O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
- Spatial complexity : O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
BFS
python Realization
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def levelOrder(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[List[int]]:
# bfs
if not root:
return []
queue = []
res = []
queue.append(root)
while queue:
level_res = []
for i in range(len(queue)):
node = queue.pop(0)
level_res.append(node.val)
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
res.append(level_res)
return res
c++ Realization
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return {
};
queue<TreeNode*> q;
vector<vector<int>> res;
q.push(root);
while (q.size() != 0) {
vector<int> tmp;
int level_wide = q.size();
for(int i=0; i<level_wide; i++) {
TreeNode* node = q.front();
q.pop();
tmp.push_back(node->val);
if(node->left != nullptr)
q.push(node->left);
if (node->right != nullptr)
q.push(node->right);
}
res.push_back(tmp);
}
return res;
}
};
Complexity analysis
- Time complexity : O ( n ) O(n) O(n) , Enter and leave the team at each point , Therefore, the asymptotic time complexity is O(n)
- Spatial complexity : O ( n ) O(n) O(n), The number of elements in the queue does not exceed n individual , So the asymptotic space complexity is O(n)
边栏推荐
- ext4、ntfs、xfs、btrfs、zfs、f2fs和reiserFS性能对比
- [class and object instances in kotlin]
- ELS message loop
- 中国数据库 OceanBase 入选 Forrester Translytical 数据平台报告
- Completion report of communication software development and Application
- C language functions (2)
- ASEMI整流桥GBU1510参数,GBU1510规格,GBU1510封装
- [stl] priority queue priority_ queue
- Dtcloud the next day
- MPLS basic experiment configuration
猜你喜欢
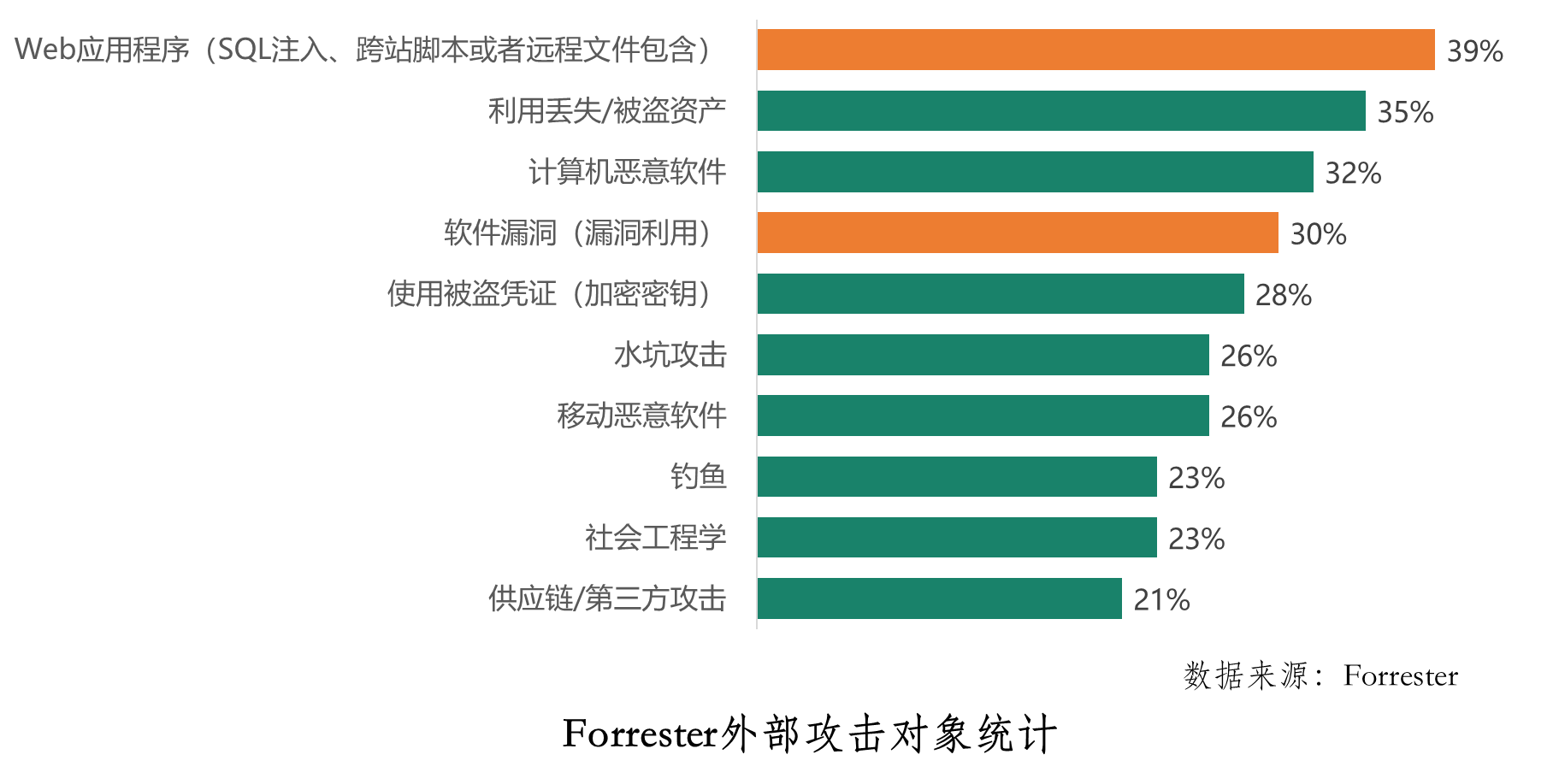
想要做好软件测试,可以先了解AST、SCA和渗透测试

Course selection information management system based on SSM

Hcip day 14

Visio:甘特图如何合并单元格?解决方案:覆盖单元格
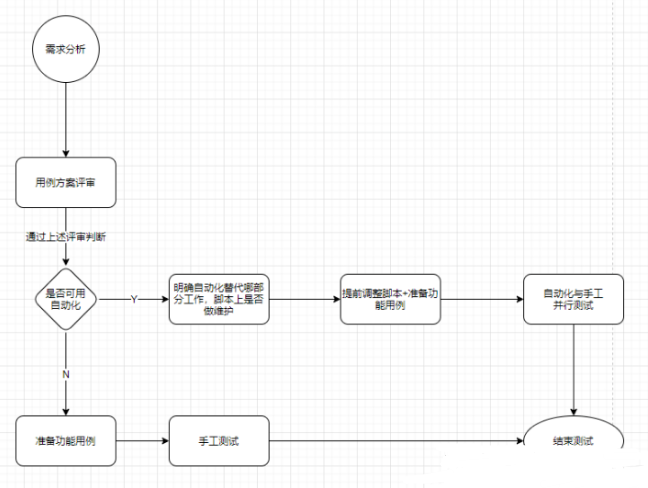
6年从零开始的自动化测试之路,开发转测试我不后悔...

DDD landing is called an advanced
![[mathematical modeling - Summary of planning model] | matlab solution](/img/b0/a4d33d7d7b605b7cc6149b59b55fb8.png)
[mathematical modeling - Summary of planning model] | matlab solution

KBPC1510-ASEMI大芯片15A整流桥KBPC1510

文件上传报错:Current request is not a multipart request

What are you interviewing for in a big factory? It's worth watching (I)
随机推荐
[mathematical modeling - Summary of planning model] | matlab solution
ext4、ntfs、xfs、btrfs、zfs、f2fs和reiserFS性能对比
redis集群的三种方式
Hurry in!!! Write a number guessing game with dozens of lines of code based on the basic knowledge of C language
waf详解
booking.com缤客上海面经
Network model and protocol
JS Base64 encoding and decoding
How Lora wireless gateway can quickly realize end-to-cloud transmission
Experimental reproduction of image classification (reasoning only) based on caffe resnet-50 network
Bracket nesting problem (recommended Collection)
想要做好软件测试,可以先了解AST、SCA和渗透测试
Visio:甘特图如何合并单元格?解决方案:覆盖单元格
文件上传报错:Current request is not a multipart request
ELS modify cursor, modify Icon
容器跑不动?网络可不背锅
Let Baidu collect, crawler own website
Aike AI frontier promotion (7.18)
Completion report of communication software development and Application
DDD landing is called an advanced