当前位置:网站首页>JVM | virtual machine stack (local variable table; operand stack; dynamic link; method binding mechanism; method call; method return address)
JVM | virtual machine stack (local variable table; operand stack; dynamic link; method binding mechanism; method call; method return address)
2022-06-11 21:28:00 【z754916067】
Catalog
Heap and stack in memory
The stack is function Time unit , And the pile is Storage The unit of .
namely : The stack solves the running problem of the program , That is, how the program is executed , Or how to deal with the data .
Heap solves the problem of data storage , How to put the data , Where to put it .
Virtual machine stack
- Because of the cross platform design ,Java The instructions of are designed according to the stack , Different platforms CPU Different architectures , So it can't be designed as register based .
- The data in the stack exists in the format of stack frame , Each method being executed on the thread corresponds to a stack frame .
- Stack frame is a memory block , Is a dataset , It maintains all kinds of data information in the process of method execution .
advantage : Cross platform , Instruction set is small , The compiler is easy to implement .
shortcoming : Performance degradation , More instructions are needed to implement the same function .
Definition
- Java Virtual machine stack is also called Java Stack , Each thread creates a virtual machine stack when it is created , It stores stack frames one by one , Corresponding to time and again Java Method call .
- Its life cycle is the same as thread .
effect
executive director Java Program operation , It saves the of the method local variable (8 Basic data types , Object reference address ), Part of the result , And participate in the method call and return .
characteristic
- Access speed is second only to the program counter .
- JVM Direct pair Java There are only two operations on the stack :1. Each method executes , Along with the stack ( Push )2. After the execution of the stack work .
- There is no garbage collection problem for the stack .
Common exceptions of virtual machine stack
- If the virtual machine stack size is fixed , At this time, the thread requests to allocate more stack capacity than Java Maximum capacity allowed by virtual machine stack ,Java The virtual machine will throw a StackOverflowError abnormal .
- If the virtual machine stack can be expanded dynamically , And did not request enough memory when trying to expand , Or when creating a new thread, there is not enough memory to create the corresponding virtual machine stack , take Java The virtual machine will throw a OutOfMemoryError abnormal .
Stack frame
Storage
- Local variable table
- The stack of operands
- Dynamic links ( Or a method reference to the runtime constant pool )
- Method return address
- Some additional information
Local variable table
Definition
- An array of numbers , It is mainly used to store method parameters and local variables defined in the method body . The data types include eight basic data types , Object reference , as well as ReturnAddress class .
- There are no data security issues , Because the local variable table is built on the thread stack , It's the thread's private data .
- The size of the local variable table is determined at compile time , It will not change during operation .
- The basic storage unit is Slot( Variable slot )
- Variables in the local variable table are also important garbage collection root nodes , As long as the objects directly or indirectly referenced in the local variable table are not recycled .
Storage of basic data types
- long and double Take two slot, The rest occupy only one slot
- byte short char Converted to before storage int,boolean Also converted to int,0 Express false, Not 0 Express true.
The destruction
Variables in the local variable table are only valid in the current method call , When the method executes , Virtual machine completes the transfer process from parameter value to parameter variable list by using local variable table .
When the method call ends , With the destruction of method stack frames , The local variable table will also be destroyed .
Slot
- JVM For each of the local variable tables Slot All assigned an access index , Through this index, the local variable values specified in the local variable table can be accessed successfully .
- If you need to access one of the local variables table 64 Local variable value of bit , Just use the previous index .
- If the current frame is created by a constructor or instance method , Then the object references this Will be stored in index by 0 Of slot It's about , The rest of the parameters continue to be arranged in parameter table order .
Classification of variables
According to the data type : Basic data types and reference data types
According to the position declared in the class :
- Member variables : The default initialization assignment has been experienced before use , It is divided into the following two categories
Class variables : use static modification , stay Linking Phase default assignment ,intial Stage assigns explicit values to class variables, i.e. static code block assignment .
Instance variables : As the object is created, the instance variable space is allocated in the heap space , And default assignment . - local variable : Before using , Must be explicitly assigned , Otherwise, the compilation fails .
The stack of operands
It can also be called an expression stack , Mainly in the process of method execution , Write data to the stack or extract data according to bytecode instructions , That's the stack / Out of the stack .
So-called Java The interpretation engine of virtual machine is stack based execution engine , The stack refers to the operand stack .
effect
It is mainly used to save intermediate results in the calculation process , At the same time, it serves as the temporary storage space for variables in the calculation process .
Be born
When a method starts executing , A new stack frame will also be created , The operand stack of this method is empty .
Storage
Each stack of operands has a clear stack depth for storing values , The maximum depth required is defined in the compiler .
Any element in the stack can be arbitrary Java data type , among 32bit The type occupies a stack unit depth ,64bit The type of the stack occupies two stack units of depth .
Stack top caching technology
Because the stack structure of the virtual machine used by the zero address instruction is more compact , But to complete an operation, you must use more stack in and stack out instructions , It also means that more instruction allocations and memory reads and writes will be required .
Because the operands are stored in memory , Therefore, frequent memory read and write operations will inevitably affect the execution speed , To solve this problem , Put forward Stack top caching technology
That is to cache all the elements on the top of the stack in physics CPU In the register of , In order to reduce the number of times to read and write memory , Improve the execution efficiency of the execution engine .
Dynamic links
Definition
Point to the runtime constant pool ( It is in the method area ) Reference to the method to which the stack frame belongs , The purpose of including this reference is that the code that supports the current method can realize dynamic linking .
When Java When the source file is compiled into a bytecode file , All variable and method references are stored as symbolic references in class In the constant pool of files , such as : Describe when a method calls another method , It is represented by a symbolic reference to a method in the constant pool , The purpose of dynamic linking is to convert these symbolic references into direct references of calling methods .
effect
Stack frame as a method , Store only references, not variables and methods themselves , Because different methods can call the same variable or method , If you put these in the stack frame , It takes up a large and complicated space , So save the reference .
Method binding mechanism
binding
Binding is a field , Methods or classes are replaced by direct references in symbolic references , Only once .
Static links
When a bytecode file is loaded into JVM On the inside , If the called The target method is known at compile time , And the operation period remains unchanged , In this case, the process of converting the symbolic reference of the calling method into a direct reference is called static linking .
Dynamic links
If The called method cannot be determined at compile time , That is to say, the symbolic reference of the calling method can only be converted into a direct reference during the program run time , Because of the dynamic nature of this reference conversion process , It is called dynamic link .
Early binding
Refers to the called target method, if known at compile time , And the operation period remains unchanged , You can bind this method to the type it belongs to , Therefore, since it is clear which target method is called , You can use static links to convert symbolic references to direct references .
Late binding
If the called method cannot be determined at compile time , You can only bind related methods according to the actual type during the program run time , This method is called late binding .
Method call
Non virtual method
If the method determines the specific calling version at compile time , This version is immutable at run time . Such a method is called non virtual method .( That is, you cannot rewrite )
Static methods , Private method ,final Method , Instance builder , Parent methods are non virtual methods .
Other methods are called virtual methods .
Call instruction
Normal call instructions :
- invokestatic: Call static methods , The parsing phase determines the unique method version .( The method called is called a non virtual method )
- invokespecial: call < init> Method , Private and superclass methods , The parsing phase determines the unique method version .( The method called is called a non virtual method )
- invokevirtual: Call all virtual methods
- invokeinterface: Call interface method
Call instructions dynamically : - invokedynamic: Dynamically resolve the method to be called , And then execute .
invokedynamic
invokedynamic yes Java In order to achieve 【 Dynamic type language 】 And do a hurry , Can pass Java8 Of Lambda expression Direct generation .
Dynamically typed languages and statically typed languages
Static type language is to judge the type information of variable itself , Dynamic type language is to judge the type information of variable value , The variable itself has no type information , Only variable values have type information .
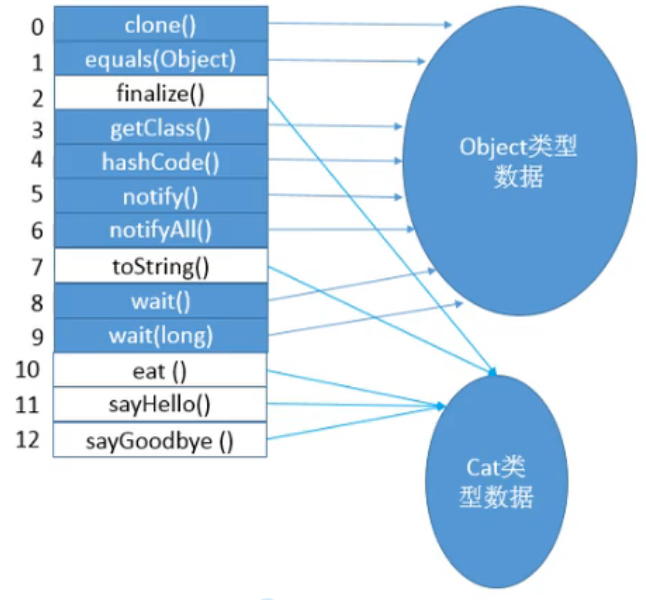
Virtual method table
- Each class has a virtual method table , The table contains the actual entries for each method .
- The virtual method table is created and initialized during the link phase of class loading , After the initial value of the class variable is ready ,JVM The method table of this class will also be initialized .
- With the virtual method table , You don't need to look up who implemented a method every time .
- Pictured ,Cat Class overridden :finalize() toString() eat() sayHello() sayGoodbye() Other methods .
Method return address
To store the call to the method pc Register value .
The end of a method , There are two ways :1. Normal execution complete 2. An unhandled exception occurred , Abnormal exit .
After the method exits, it will return to the location where the method was called , When the method exits normally , Of the caller pc The value of the counter is used as the return address ,** That is, the address of the next instruction that calls the method .** But through the exception , The return address should be determined through the exception table , This part of information will not be saved in stack frame .
Return instruction
When the execution engine encounters the bytecode instruction returned by any method , There will be a return value passed to the upper level method caller , namely Complete the exit normally .
Bytecode instructions contain :
- ireturn( The return value is boolean byte char short int)
- lreturn (long)
- freturn (float)
- dreturn (double)
- areturn ( Reference type )
- return (void)
Exception handling table
The exception handling when an exception is thrown during method execution will be stored in an exception handling table , It is convenient to find the code to handle the exception when an exception occurs .
That is, if Bytecode file pass the civil examinations 4 Go to the first place 16 The line is abnormal , Just from 19 Line to process .
Exception table:
from to target type
4 16 19 any
19 21 19 any
Some additional information
Stack frames are also allowed to carry with Java Some additional information about virtual machine implementation , for example : Information to support program debugging .
Test questions
For example, stack overflow ?
Can pass -Xss Set the stack size , Fixed if insufficient , Will be submitted to the StackOverflowError error . If the whole space is not enough , Will be submitted to the OOMWill garbage collection involve virtual machine stacks ?
Can'tHow to define thread safety
If only one thread can manipulate this data , So this data is thread safe .
If a variable is internally generated , Internal demise , So it can be called thread safety , If there is an operation such as being returned , It's not safe .
边栏推荐
- 12 golden rules of growth
- I haven't blogged for two months. I sent an article to prove that my account is still alive
- 【C语言进阶】整型在内存中的存储
- Game client performance (memory) [previous]
- JVM heap
- Release of version 5.6 of rainbow, add multiple installation methods, and optimize the topology operation experience
- Iros 2021 | new idea of laser vision fusion? Lidar intensity diagram +vpr
- 为什么需要微服务
- Website online customer service system Gofly source code development log - 2 Develop command line applications
- Diary at 16:29:41 on June 9, 2022
猜你喜欢

LeetCode-129-求根节点到叶节点数字之和

LeetCode-155-最小栈

Jenkins+allure integrated report construction

ORA-04098: trigger ‘xxx. xxx‘ is invalid and failed re-validation

LeetCode-110-平衡二叉树

如何利用RPA机器人开启货代行业数字化转型第一步?

LabVIEW Arduino electronic weighing system (project Part-1)
Cs144 lab0 lab1 record
Tensorflow 2. X Getting Started tutorial
LabVIEW控制Arduino实现红外测距(进阶篇—6)
随机推荐
Release of version 5.6 of rainbow, add multiple installation methods, and optimize the topology operation experience
Realize the same length of tablayout subscript and text, and change the selected font size
JVM object allocation policy TLAB
二分图King
Redis data type (string)
How to import workflows provided on SAP API hub to sap BTP
Online excel file parsing and conversion to JSON format
[Part 16] copyonwritearraylist source code analysis and application details [key]
Codeforces Round #742 (Div. 2) F. One-Four Overload
[Part 14] source code analysis and application details of completionservice class [key]
LeetCode-32-最长有效括号
[Game Theory - introduction]
Solve the problem of img 5px spacing
JS performs non empty judgment on various data types of the returned data.
JVM之堆区
Tensorflow 2. X Getting Started tutorial
Flutter implements the JD address selection component
Why microservices are needed
AC automata
焕新升级 | 创新,从云商店开始