
supporting BMTrain The outstanding performance is the adoption of multiple distributed training optimization technologies , Together, they solve the problem of Memory occupation problem . In order to deeply understand this key problem , We might as well analyze the memory occupation during model training .
The memory occupation in model training mainly includes : Model parameters 、 Model gradient 、 Optimizer status 、 Operation intermediate variable . The following is an example , The memory occupation in the training process includes a model parameter and a corresponding gradient , More commonly used Adam Optimizer parameters that retain twice the number of parameters , In addition, there are intermediate variables of some operations .
According to the above analysis , For a large model with 10 billion parameters , The model parameters are about 20G, During the training process, the memory used will exceed 80G, Maintain these contents completely in every graphics card , Video memory is not enough . This requires us to adopt relevant distributed training technology , Video memory optimization for model training . To solve this key problem , stay BMTrain in , We go through Data parallelism Reduce the proportion of video memory of intermediate variables in operation 、 Increase throughput , adopt ZeRO Reduce model parameters 、 Model gradient 、 Proportion of video memory in optimizer state , adopt Optimizer Offload Unload optimizer state into memory , adopt Checkpointing and Operator fusion Avoid storing intermediate variables for operations , Finally using Communication computation overlaps Further reduce the time cost of the whole system . Use these technologies together ,BMTrain Can achieve Single consumer graphics card full parameter tuning BERT-Large,8 platform A100 Small group training GPT-3, In the super large-scale model training scenario and DeepSpeed And other frameworks 90% Calculation cost of . Want to know the specific details of these technologies ? This article takes you to find out !
 Background knowledge
Background knowledge
The core spirit of distributed training is cutting , Put the data 、 Parameters and other elements are cut into different calculation nodes for operation . Where there is cutting, there is merging , Different nodes communicate frequently to synchronize and summarize the calculation results . Here we briefly introduce 5 A basic communication operator , This is an important foundation of the distributed training framework ( Take four graphics cards as an example , from rank0 To rank3 Express ):
01 Broadcast
The tensor is in a graphics card , After the broadcast , Every graphics card will get the same tensor .

02 Reduce
There is a tensor in each graphics card , Sum these tensors as 、 take max After calculation , The result is placed on a specified graphics card .

03 All Reduce
There is a tensor in each graphics card , The results of relevant calculations using them are placed on all graphics cards , The results obtained on each graphics card are the same . Each graphics card has a size of 4d Tensor , The calculated results between tensors are divided into 4 Share , The size of each serving is d, Put them separately in 4 On the graphics card . Each graphics card has a size of d Tensor , After collection , The result of tensor splicing ( The size is 4d) Placed on all graphics cards , The results obtained on each graphics card are the same .
![]()
 Distributed training
Distributed training
A typical distributed training method is to use data parallelism , However, for large models , It is not enough to optimize video memory only through data parallelism , We need to cut further . The technologies for further optimization mainly come from two major technical routes : Cutting at the operator level Model parallel 、 Pipeline parallel technology And cutting on the video memory ZeRO technology . stay BMTrain in , We used Data parallelism and ZeRO technology For distributed training of the model , Model parallelism and pipeline parallelism will be supported in succession .
Data parallelism
Data parallelism is achieved by reducing the processing time on each graphics card batch Size to reduce the running intermediate variables of the model . say concretely , Suppose there is n Zhang graphics card , Then each graphics card can only be processed batch_size / n The data of , Finally, the gradient calculated by each graphics card is summed ( all-reduce ) that will do . In this way , Each graphics card will get complete gradient information , Finally, the optimizer is executed on each graphics card step.

- Adopt data parallel strategy , The intermediate variables needed for the training of the original model are divided into different graphics cards . In the figure, the eight card combination is taken as an example , The following figures also use the same settings
Model parallel
Model parallel technology attempts to cut model computation . Take the full connection layer as an example , For computing  , By decomposing the parameter matrix into n A small matrix
, By decomposing the parameter matrix into n A small matrix  , Calculate on each graphics card
, Calculate on each graphics card  , And then through all-gather Complete results can be obtained through communication
, And then through all-gather Complete results can be obtained through communication  . Here Among the methods , Each graphics card processes the same batch of data , Cooperate in calculation .
. Here Among the methods , Each graphics card processes the same batch of data , Cooperate in calculation . 
- Adopt model parallel strategy , The model parameters are divided into different graphics cards
A solution similar to model parallelism is pipeline parallelism , It is also an attempt to segment the training calculation . Compared with the model parallel transformer The model performs longitudinal calculation segmentation , Pipeline parallelism will be different layers of transformer block The calculation is divided into different graphics cards .
ZeRO
In actual training , Optimizer ( Such as Adam ) States occupy more video memory than parameters and gradients combined , therefore ZeRO(Zero Redundancy Optimizer, Zero redundancy optimizer ) For the first time, the technology proposes to segment the optimizer state , Each graphics card is only responsible for updating some parameters corresponding to the optimizer status . Training strategy ,ZeRO Based on data parallelism , Different data is divided into different graphics cards for calculation . According to the optimizer status 、 gradient 、 Different degree of parameter division ,ZeRO Technology includes ZeRO-1/2/3 Three levels .
ZeRO-1
because ZeRO Based on data parallelism , First we need to pass all-gather Operation to obtain the complete model parameter update results , Then each graphics card completes the corresponding forward propagation and back propagation according to its own data and model parameters . In the whole process , The gradient and parameters are completely retained on each card , The gradient is then reduce-scatter, Each card calculates the model parameters of the corresponding part according to its divided optimizer state and gradient . 
- be based on ZeRO-1 Parallel with data , Optimizer state and operation intermediate variables are divided into different graphics cards
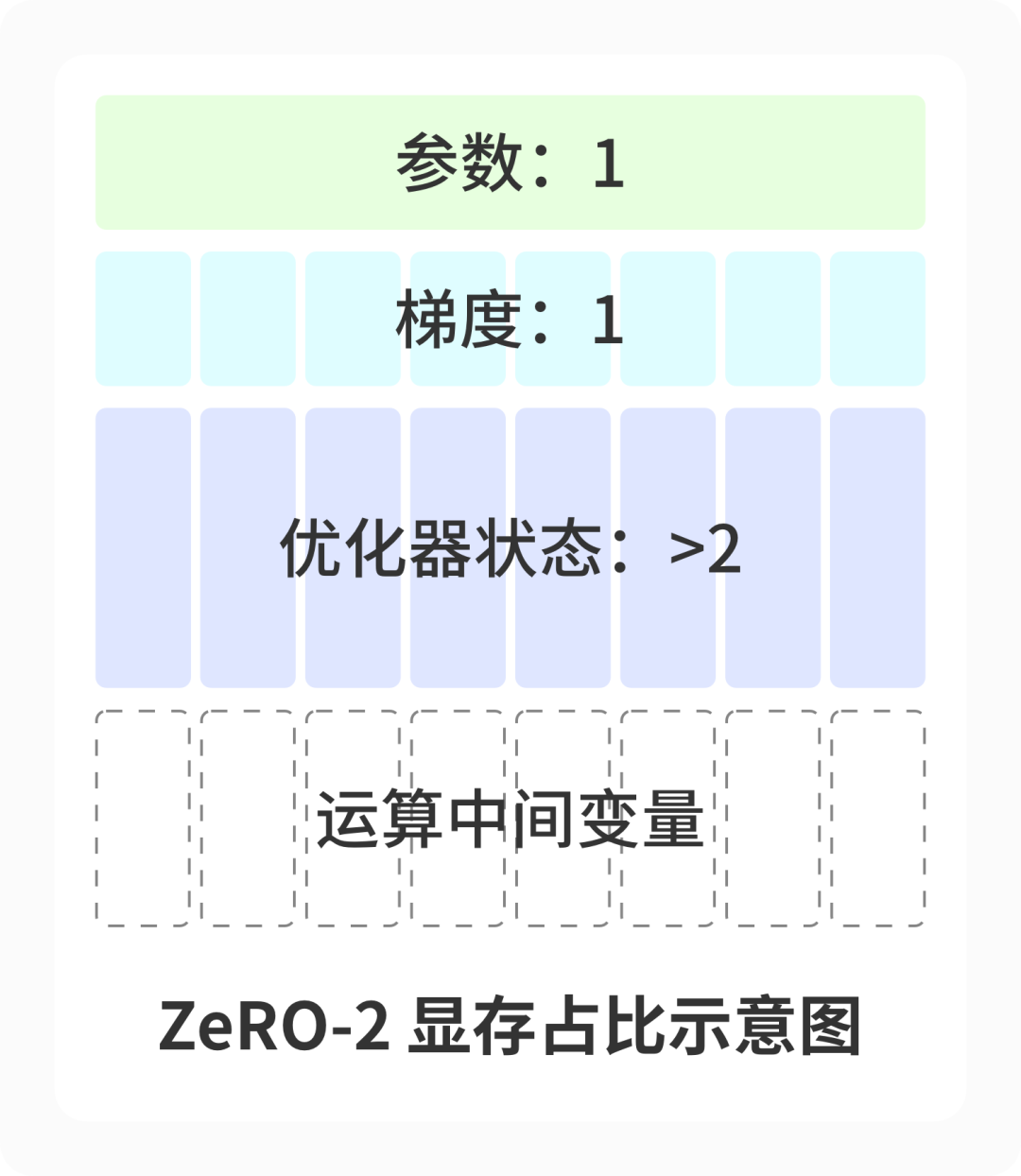
ZeRO-2
ZeRO-2 stay ZeRO-1 The gradient is further divided on the basis of . Be careful , Because in the process of reverse transmission , It is not necessary to always keep the complete gradient , When calculating the gradient of the current layer , Only the gradient input from the next layer is required . So in the process of reverse transmission , For gradients that do not participate in the subsequent reverse transfer calculation , You can immediately reduce-scatter Split into multiple cards , So in the process of training , Gradient memory usage on each card , It becomes the original 1/n 了 . After the reverse transmission , Each card then depends on the gradient of the part and the optimizer status , Calculate the updated model parameters , Finally, use the updated parameters all-gather Sync to other graphics cards .
- be based on ZeRO-2 Parallel with data , gradient 、 Optimizer state and operation intermediate variables are divided into different graphics cards
ZeRO-3
and ZeRO-3 technology , Is to further segment the model parameters . Since there is only a part of optimizer status per graphics card , Only part of the parameters are updated , A very intuitive idea is to maintain only the part of the parameters that the optimizer needs to update on each graphics card . However , During the calculation of the model , You still need complete model parameters . So in the ZeRO-3 in , Each module in the model is calculated before , All need to pass once all-gather The operation will restore the parameters to their integrity , And release the model parameters after the forward calculation . When performing reverse transmission , Reuse all-gather Get the parameters to calculate the gradient and use reduce-scatter Divide the gradient , Here's the picture .

By using ZeRO-3 Optimize , All training related information is shredded and distributed to different graphics cards , Reduce the memory occupation of each graphics card to the extreme , So that each graphics card can hold a larger batch_size, Make better use of the computing core , Bring greater model throughput , At the same time, the number of graphics cards required by the training model is minimized .
![]()
- be based on ZeRO-3 Parallel with data , Parameters 、 gradient 、 Optimizer state and operation intermediate variables are divided into different graphics cards
But in the ZeRO It is pointed out in the original paper that , ZeRO-3 An additional parameter communication time is added ( I.e. in the case of back propagation all-gather ), Therefore, additional communication overhead will be introduced , In some scenarios, the performance is not as good as ZeRO-2 Parallel with model . In order to reduce the efficiency loss caused by additional traffic , We also introduce the strategy of communication computation overlap , This will be introduced later to . According to our implementation , Experimental results show that ZeRO-3 stay NVLink+IB Training large-scale models under the environment of ZeRO-2 The scheme in parallel with the model will bring greater improvement in computing throughput .
![]()
 Memory optimization
Memory optimization
In addition to the above distributed training methods ,BMTrain And through Optimizer Offload and Checkpointing Technology further reduces redundant memory footprint , And at the expense of the least communication cost , It can still train efficiently under the extreme video memory optimization . Optimizer Offload
Optimizer Offload This refers to changing the optimizer state from GPU Uninstall to CPU On , So as to further save video memory . We use Adam Take the optimizer as an example to explain why the parameters of the optimizer need to be unloaded . stay Adam in , The optimizer needs to maintain the moving average of the gradient and the moving average of the square of the gradient : As shown above , Compared with model parameters , Adam The optimizer requires at least two copies of video memory , This is a very large cost in hybrid accuracy training . By using ZeRO-3 Gradient segmentation of , The gradient information to be processed on each computing card is greatly reduced , Put this part GPU Calculate unload to CPU The resulting communication requirements are small , meanwhile CPU It will not be particularly difficult to deal with the gradient after such segmentation . Accordingly , We paid a very small amount of extra cost to reduce the video memory cost to about half of the original .

- chart Optimizer Offload technology
Checkpointing
Checkpointing Technology has long been proposed , A method for optimizing graph overhead in neural network model training . This method Transformers In the model training of equal structure , Can play a very obvious role . At present, the mainstream Transformers The model consists of a large number of fully connected layers , We take the full connection layer as an example to analyze the video memory of the computing graph .
In order to be able to calculate the gradient in back propagation , The parameter matrix needs to be recorded during forward propagation  With the input
With the input  , These two parameters accumulate layer by layer with forward propagation , It consumes a lot of video memory . therefore , We use Checkpointing technology ( Also known as sub linear memory optimization ), The core way is to change space through time , We set checkpoints between the layers of the model , Only record the input vector of each layer of model . In back propagation , According to the latest checkpoint Recalculate the local calculation diagram of this layer .
, These two parameters accumulate layer by layer with forward propagation , It consumes a lot of video memory . therefore , We use Checkpointing technology ( Also known as sub linear memory optimization ), The core way is to change space through time , We set checkpoints between the layers of the model , Only record the input vector of each layer of model . In back propagation , According to the latest checkpoint Recalculate the local calculation diagram of this layer .
 Optimization of framework implementation
Optimization of framework implementation
In addition to the above video memory optimization techniques ,BMTrain It also optimizes the implementation , In order to get better acceleration effect .
Mixing accuracy
Traditional models use single precision parameters for training , In large model training , We can reduce the number of parameters and save the operation time by using half precision parameters . Specific implementation ,BMTrain In the process of forward propagation and back propagation, half precision is used for calculation , And maintain single precision model parameters and optimizer parameters in the optimizer .
Another advantage of using mixed precision is that it can make better use of the tensor core. Newer graphics cards in CUDA core outside , We also set up a core for tensor operation tensor core, utilize tensor core It will bring further performance improvement to the program . Using mixed accuracy training can make better use of tensor core characteristic , So as to further accelerate the training process .
Operator fusion
To further improve performance , We are CPU and GPU All levels are optimized at the operator level . stay CPU On , We use multithreading + SIMD( Single instruction stream multi data stream ) Of CPU programmatically , Yes Offload to CPU Calculated Adam Optimizer CPU Computing acceleration on , So that it will not become the performance bottleneck of the system . stay GPU On , We use operator fusion , take Softmax And NLLLoss Operators merge into one , Reduce the memory occupation of intermediate results .
Communication computation overlaps
As mentioned above ,ZeRO3 Technology will introduce additional communication time , We use the communication computing strategy to optimize the communication time . Take back propagation as an example , Due to the use of ZeRO-3 technology , It is necessary to temporarily reassemble the model shredded to each computing card ( Corresponds to Gather ); And in back propagation ( Corresponds to Calculate ) after , We also need to shred the obtained local gradient onto different computing cards ( Corresponds to Scatter ). We go through different CUDA stream Distinguish between different operations , Let computing and communication run at the same time , Hide the time cost of communication through a large amount of computing time .
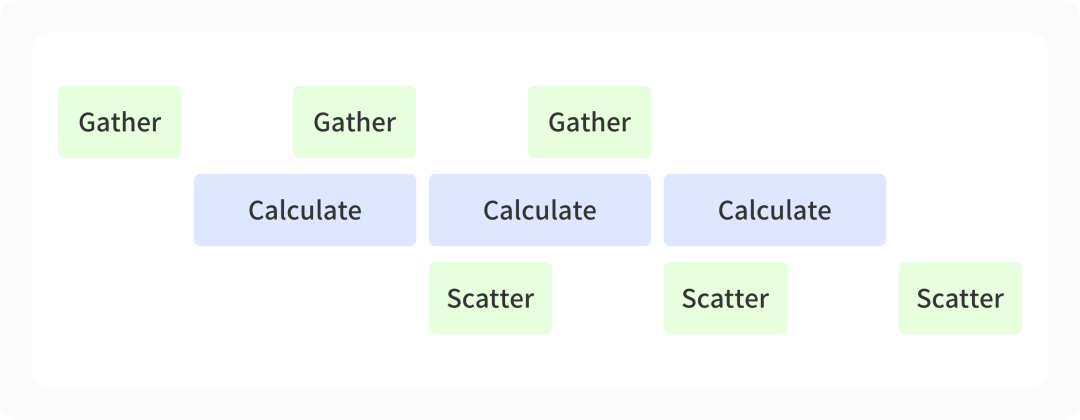
- chart Communication computation overlaps
 The performance show
The performance show
Comprehensive use of the above technologies ,BMTrain Excellent effect in large model training , It has good performance under the conditions of different scale computing power . In single card 2080Ti On ,BMTrain Can achieve transformers The library cannot implement 3 Million parameters BERT-Large fine-tuning . In single card V100 On ,BMTrain Training 3 Million parameters BERT-Large a transformers Implementation can improve about 20 times batch size,2.5 Double throughput . On stand-alone 8 card A100 In the environment ,BMTrain Training 130 Billion parameter GPT a Deepspeed / veGiantModel Implementation can improve about 4 times batch size,1.6 Double throughput . On multiple machines 8 card A100 In the environment ,BMTrain Less... Can be used GPU Training 1750 Billion parameter GPT-3, See the following table for performance :
Use BMTrain,64 Zhang A100 Run away GPT-3 Of 300B token Probably need 2 year , The rent of server and graphics card is about 900 About 10,000 RMB . According to our experimental estimation , Use 128 Zhang A100 when , Single card throughput can be improved 2.5 More than times ,6 You can run... In a month GPT-3, The server rent is about 500 About 10,000 RMB . Although trained GPT-3 The cost of is still high , But with GPT-3 Of 1200 Ten thousand dollars compared to , The cost remains Economize 90% above .
 Future outlook
Future outlook
In this chapter, we mainly introduce BMTrain The basic acceleration algorithm in , future BMTrain We will continue to focus on the efficient training and performance optimization of large models , And further optimize and upgrade the toolkit , Relevant technical reports will also be published publicly . meanwhile , We sincerely welcome interested researchers and developers to join our open source community , Participate in relevant research exchanges 、 Technical discussion and tool development , Together contribute to the landing and application of large models !
 Pay attention to our
Pay attention to our
Official website :https://www.openbmb.org communication QQ Group :735930538 Qizhi community :https://git.openi.org.cn/OpenBMB GitHub:https://github.com/OpenBMB Microblogging :http://weibo.cn/OpenBMB You know :https://www.zhihu.com/people/OpenBMB Twitter:https://twitter.com/OpenBMB

1. Samyam Rajbhandari, Jeff Rasley, Olatunji Ruwase, Yuxiong He. ZeRO: Memory Optimizations Toward Training Trillion Parameter Models.2. Zhengda Bian, Hongxin Liu, Boxiang Wang, et al. Colossal-AI: A Unified Deep Learning System For Large-Scale Parallel Training.3. Adam Paszke, Sam Gross, Francisco Massa, et al. PyTorch: An Imperative Style, High-Performance Deep Learning Library.4. Zhengyan Zhang, Xu Han, Hao Zhou, et al. CPM: A Large-scale Generative Chinese Pre-trained Language Model.5. Zhengyan Zhang, Yuxian Gu, Xu Han, et al. CPM-2: Large-scale Cost-efficient Pre-trained Language Models.6. Jacob Devlin, Ming-Wei Chang, Kenton Lee and Kristina Toutanova. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding.7. Colin Raffel, Noam Shazeer, Adam Roberts, et al. T5: Exploring the Limits of Transfer Learning with a Unified Text-to-Text Transformer.8. Alec Radford, Jeffrey Wu, Rewon Child, et al. GPT2: Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners.9. Ben Wang and Aran Komatsuzaki, et al. GPT-J from EleutherAI released in the repo mesh-transformer-jax.10. Diederik P. Kingma, Jimmy Ba. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization.11. Yang You, Jing Li, Sashank Reddi, et al. Large Batch Optimization for Deep Learning: Training BERT in 76 minutes.12. Hanlin Tang, Shaoduo Gan, Ammar Ahmad Awan, et al. 1-bit Adam: Communication Efficient Large-Scale Training with Adam's Convergence Speed.13. NCCL: https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/nccl/user-guide/docs/usage/collectives.html
For business cooperation, please contact


 Background knowledge
Background knowledge 




![]()
 Distributed training
Distributed training 
 , By decomposing the parameter matrix into n A small matrix
, By decomposing the parameter matrix into n A small matrix  , Calculate on each graphics card
, Calculate on each graphics card  , And then through all-gather Complete results can be obtained through communication
, And then through all-gather Complete results can be obtained through communication  . Here Among the methods , Each graphics card processes the same batch of data , Cooperate in calculation .
. Here Among the methods , Each graphics card processes the same batch of data , Cooperate in calculation .



![]()
 Memory optimization
Memory optimization 


 With the input
With the input  , These two parameters accumulate layer by layer with forward propagation , It consumes a lot of video memory .
, These two parameters accumulate layer by layer with forward propagation , It consumes a lot of video memory .
 Optimization of framework implementation
Optimization of framework implementation 
 The performance show
The performance show 
 Future outlook
Future outlook  Pay attention to our
Pay attention to our 










