当前位置:网站首页>Basic concepts of processor scheduling
Basic concepts of processor scheduling
2022-06-25 22:43:00 【loveCC_ orange】
The third chapter Processor scheduling and deadlock
- 3.1 The basic concept of processor scheduling
- 3.2 Scheduling algorithm
- 3.3 Real time scheduling
- 3.4 Scheduling in multiprocessor systems
- 3.5 Causes and necessary conditions of deadlock
- 3.6 Ways to prevent deadlocks
- 3.7 Deadlock detection and release
Key points of this chapter
- 1、 Master the basic concept and algorithm of processor scheduling
- 2、 Master the banker algorithm to avoid deadlock
3.1 The basic concept of processor scheduling
One 、 senior 、 Intermediate and low level scheduling
Two 、 Scheduling queue model
3、 ... and 、 Some criteria for selecting scheduling mode and scheduling algorithm
Jobs and processes

Scheduling of batch jobs
- Job scheduling :
Put jobs into main storage .
Jobs in backup status can be selected by job scheduling to enter memory for calculation on the premise that system resources are met . - Process scheduling :
Make the job process occupy the processor .
Only the job in the execution state can really constitute the opportunity for the process to obtain the calculation .
A batch job , Start by entering the system and residing on the backup queue of external memory , Until the job runs , The following three levels of scheduling may be required
- 1、 Advanced scheduling ( Job scheduling )
- 2、 Intermediate dispatch
- 3、 Low level scheduling ( Process scheduling )
1、 Advanced scheduling
For users , I always hope that the turnover time of my work is as little as possible , And for the system , The average turnaround time of the job is expected to be as little as possible , This is good for improving CPU Utilization and system throughput .
The main function :
According to some algorithm , Decide which jobs in the backup queue on the external memory will be transferred into the memory , Create processes for them , Allocate the necessary resources , And put them in the ready queue .
At each execution of the job ( senior ) When scheduling , Two decisions have to be made :
- How many assignments are accepted – How many jobs are admitted into memory each time , Depending on the degree of multiprogramming , That is, how many jobs are allowed to run in memory at the same time .
- Which assignments are accepted – Which jobs should be accepted to be transferred from external memory into memory , It depends on the scheduling algorithm . If first come, first serve , Short assignments are preferred , Later chapters will describe in detail .
In batch system , After the job enters the system, it first resides in the external memory , Therefore, job scheduling is required .
In order to achieve timely response in the time-sharing system , Commands or data are sent directly into memory , Therefore, job scheduling is not required .
In a real-time system , Generally, job scheduling is not required .
2、 Low level scheduling

1. Process scheduling ( Low level scheduling ) The function of

2. Three basic mechanisms of process scheduling
In order to realize process scheduling , It should have the following three basic mechanisms :
- (1) Queuer
- (2) Dispatcher ( Dispatchers )
- (3) Context switching mechanism
The following two scheduling methods can be adopted for process scheduling :
Non preemptive way
Way of seizing
1、 Non preemptive way
Once the processor is assigned to a process , Let the process continue , Until the process is completed or blocked by an event , To allocate the processor to other processes , Never allow a process to preempt an allocated processor .
evaluation : Implement a simple 、 Small overhead ; Suitable for most batch processing OS, But in the real-time system with strict requirements , This scheduling method is not suitable .
When non preemptive scheduling is adopted , Factors that may cause process scheduling are :
- 1、 Process execution complete , Or the execution cannot be continued due to an event
- 2、 The process in execution is due to I/O Request to suspend execution
- 3、 Performed some primitive operation : Such as P operation 、Block The original language
2、 Way of seizing

3、 Intermediate dispatch ( Exchange function )
- Also known as medium range scheduling . It is introduced to improve memory utilization and system throughput . The processes that cannot run temporarily should no longer occupy valuable memory resources , And transfer them to external storage to wait , The process state at this time is called ready external storage state or suspended state .
- When these processes are ready to run 、 And the memory is slightly free , The intermediate scheduling decides to put the ready processes with running conditions on the external memory , Redeploy to memory , And change its status to ready state , Hang on the ready queue and wait for process scheduling .
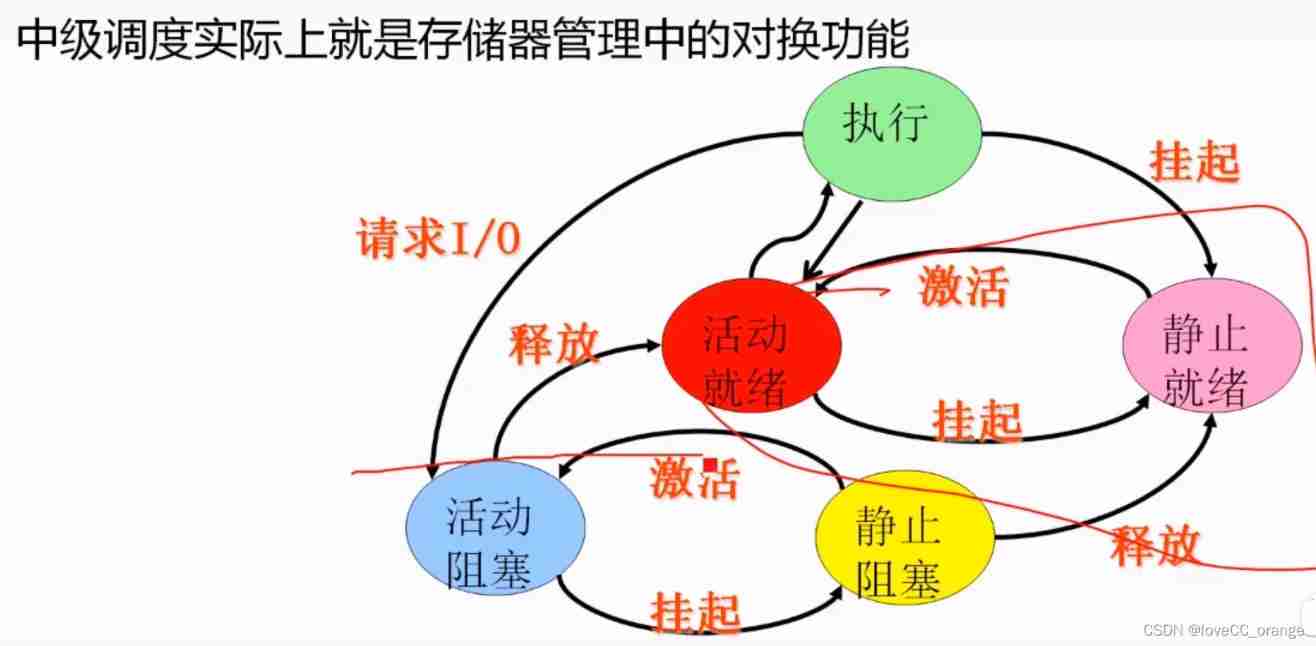
Comparison of three scheduling methods
- Process scheduling runs most frequently , In a time-sharing system, it is usually 10~100ms Process scheduling once , Therefore, the process scheduling algorithm should not be too complex , So as not to occupy too much CPU Time .
- Job scheduling occurs when a job finishes running , Exit the system , When a job needs to be rescheduled into memory , Therefore, the operation scheduling cycle is long , About every few minutes . Therefore, the job scheduling algorithm is allowed to spend more time .
- Operation frequency of intermediate dispatching , Between process scheduling and job scheduling .
Two 、 Scheduling queue model
No matter advanced 、 Intermediate or low-level scheduling , Both involve process queues , Thus, three types of scheduling queue models are formed :
- 1、 Scheduling queue model with only process scheduling
- 2、 Scheduling queue model with high-level and low-level scheduling
- 3、 Scheduling queue model with three-level scheduling at the same time
1、 Scheduling queue model with only process scheduling

- When the process is complete , Release CPU, Process scheduling will CPU Assigned to the next process in the ready queue
- When the time slice of process execution is over , Then release CPU, Put the process back on the ready queue , Begin to CPU Assigned to the next process in the ready queue , To perform .
- When a process encounters a wait event , The process will automatically block , Put in the blocking queue , take CPU Assigned to the next process in the ready queue , When waiting for an event to happen , The blocked process returns from the blocked queue to the ready queue .
2、 Queue model with high-level and low-level scheduling
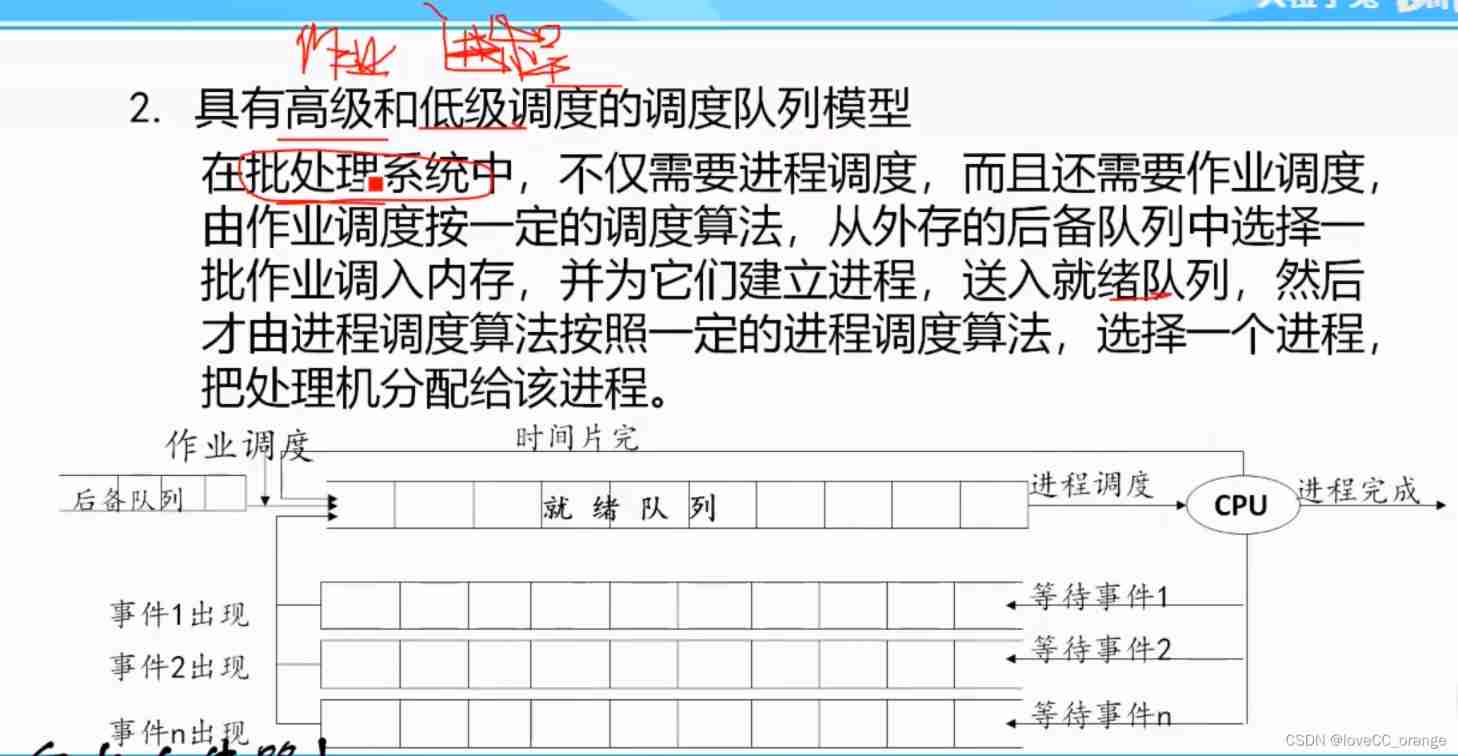
Job scheduling is added to the scheduling queue model with only process scheduling , At the same time, the number of blocking queues has also increased . Different blocking queues are established according to different waiting events .

The most commonly used is the highest priority first scheduling algorithm
- (1) In the previous model, we used FIFO Queue form
- (2) Make the blocking queue not too long , Thus, the operation efficiency of the blocking queue is improved
3、 Queue model with three-level scheduling

When intermediate scheduling is introduced into the system , The ready state of a process can be divided into memory ready and external memory ready , The blocking state is divided into memory blocking and external memory blocking .
Under the action of call out operation , It can change the process state from memory ready to external memory ready , From memory blocking to external memory blocking ; Under the function of intermediate dispatching , It can also turn external memory ready into memory ready .
3、 ... and 、 Some criteria for selecting scheduling mode and scheduling algorithm
In a OS In the design of , How to select the scheduling mode and algorithm , A lot depends on OS Types and goals of .
Such as in batch processing system 、 Time sharing system and real-time system , Usually, different scheduling methods and algorithms are used . Selected criteria , Some are user oriented , Some are system oriented .
1、 User oriented guidelines
Short turnaround time ( Evaluation index of batch processing system )
Turnaround time Average turnaround time
Turnaround time with rights Average weighted turnaround time
Fast response time : response time ( Indicators for evaluating time-sharing systems )
Guarantee of deadline : By the time ( Indicators for evaluating real-time systems )
Priority criteria
(1) Turnaround time

(2) Average turnaround time

Ti It means the i Job turnaround time for users
(3) Turnaround time with rights

(5) response time

(6) By the time
It refers to the latest time when a task must be started , Or the latest time that must be completed .
For strict real-time systems , Its scheduling method and algorithm must be able to guarantee this point , Otherwise, it may cause unpredictable consequences .
2、 System oriented guidelines
- High system throughput ( Evaluation index of batch processing system )
- Good processor utilization
- Balanced utilization of various resources
边栏推荐
- 2022-2028 global proton exchange membrane hydrogen electrolyzer industry survey and trend analysis report
- 2022-2028 global carbon fiber unidirectional tape industry research and trend analysis report
- 2022-2028 global web and browser isolation platform industry research and trend analysis report
- Openwrt (VIII) application layer development
- 2022giao考游记
- Beyond natural motion: exploring the discontinuity of video interpolation
- Pycharm 2022.1 EAP 2 release
- Development trend of China's power carrier communication industry and Research Report on the 14th five year plan 2022 ~ 2028
- 2022-2028 global industrial TFT LCD industry survey and trend analysis report
- Fujilai pharmaceutical has passed the registration: the annual revenue is nearly 500million yuan. Xiangyun once illegally traded foreign exchange
猜你喜欢

2022-2028 global vacuum jacket system industry survey and trend analysis report

Simple and easy-to-use cache library gcache

圖解棧幀運行過程

2022-2028 global SiC igniter industry research and trend analysis report

Nacos source code analysis 01 code structure

2022-2028 global industrial TFT LCD industry survey and trend analysis report

2022-2028 global TFT touch screen industry research and trend analysis report

SSH modifies grub in heiqunhui ds918+ system 7.0.1 cfg
Beyond natural motion: exploring the discontinuity of video interpolation

Where is win11 screen recording data saved? Win11 screen recording data storage location
随机推荐
Tlog helps Pangu framework realize microservice link log tracking
This 110 year old "longevity" enterprise has been planning for the next century
Evaluate the generalization performance of models and build integrated models using out of pocket prediction (oof)
Analysis of gpl3.0 license software copyright dispute cases
Simple and easy-to-use cache library gcache
Introduction to HLS content diversion and insert advertising specification
Obsidian基础教程
Zhihu Gaozan: what ability is important, but most people don't have it?
Mastering quantization technology is the key to video compression
2022giao考游记
记|一次exists关键字的学习记录
[invitation letter] on March 4, the platform enabled digital intelligence Innovation -- UFIDA BiP PAAS cloud platform IUAP digital intelligence hundred cities forum · Jinan Station
Dio encapsulated by the flutter network request (cookie management, adding interceptors, downloading files, exception handling, canceling requests, etc.)
China bed and mattress market status research analysis and development prospect forecast report (2022)
Hard liver! Super detailed basic introduction to Matplotlib!!!
Generic cmaf container for efficient cross format low latency delivery
Huawei cloud SMS has tested that many mobile phones prompt frequent sending
圖解棧幀運行過程
2022爱分析· IT运维厂商全景报告
Research Report on China's new energy technology and equipment market competition analysis and marketing strategy suggestions 2022-2028