当前位置:网站首页>Four data interaction modes of go grpc
Four data interaction modes of go grpc
2022-07-24 08:28:00 【micro_ cloud_ fly】
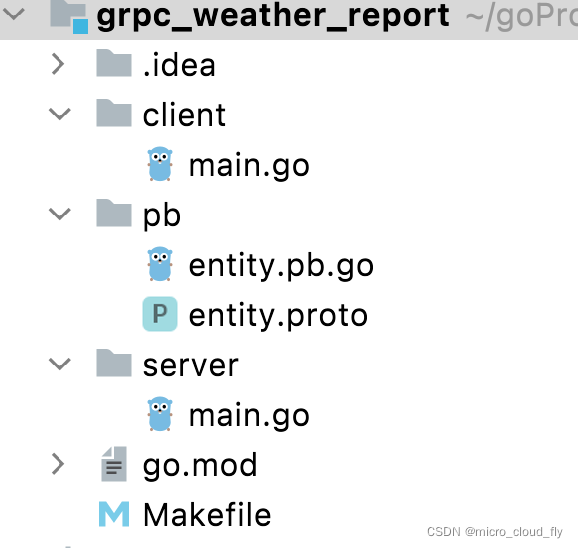
Directory structure of the project
.
├── Makefile
├── client
│ └── main.go
├── go.mod
├── go.sum
├── pb
│ ├── entity.pb.go
│ └── entity.proto
└── server
└── main.go
proto The file is introduced
syntax = "proto3";
option go_package = "../pb";
package pb;
service Query{
// Get weather forecast details by city name , This is the most common way of data transmission , One question and one answer
// The client sends the request , Only when the server returns , The client can continue to send the second request , Blocking type
rpc GetByName(WeatherRequest) returns(WeatherResponse);
// Through the city id Get the weather forecast , ditto
rpc GetById(WeatherRequest) returns(WeatherResponse);
// The client sends data through streaming , The server waits until the client's request is sent
// Return data to the client at one time , At this time, the server needs to read from the client's stream circularly
// Data sent by the client , Until the signal sent by the client is received , Only one-time return data
rpc GetByStream(stream WeatherRequest) returns(StreamResp);
// The client sends a normal request , But the server returns data in a stream
// Such usage scenarios are as : Users send a city ID, The server needs to return to
// All information of all county-level cities , The server processes the information of one county and city at a time , After each treatment
// A county-level city , Immediately back to the client , At this time, when the client reads the return of the server
// You need to read the return data circularly from the stream on the server , Until receiving the signal that the server has returned
// after , Just stop receiving the returned data
rpc ReturnByStream(CityRequest) returns(stream CityResp);
// Two-way flow , The client constantly sends goods to the server through streaming id
// Every time the server receives a product ID after , Check product details now , After finding it, it will be returned to the client by stream
// At this time, the client needs to constantly send data to the server , The server needs to constantly read the request data from the client stream
// Processing request data at the same time , Return immediately after each request is processed , At this time, the client also needs to continuously stream from the server
// Read the return data in
rpc BidirectionalStream(stream Product) returns(stream Product);
}
// goods
message Product {
int64 id = 1;// goods id
string name = 2;// Name of commodity
}
// Return to the weather by flow
message StreamResp{
repeated WeatherResponse results = 1;
}
// City request body
message CityRequest{
string province = 1;
}
// Urban returnees
message CityResp{
string cityname = 1;
}
// The weather forecast result Field
message Result{
string city = 1;
Realtime realtime = 2;
repeated Future future = 3;
}
// Real time field of weather forecast
message Realtime{
string temperature = 1;
string humidity = 2;
string info = 3;
string wid = 4;
string direct = 5;
string power = 6;
string aqi = 7;
}
message Wid {
string day = 1;
string night = 2;
}
// Weather forecast future forecast
message Future{
string date = 1;
string temperature = 2;
string weather = 3;
Wid wid = 4;
string direct = 5;
}
// Weather forecast return entity
message WeatherResponse {
string reason = 1;
Result result = 2;
int64 error_code = 3;
}
// Weather forecast request entity
message WeatherRequest{
string city = 1;
string key = 2;
string province = 3;
}
Generated server code
package main
import (
"context"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"io"
"io/ioutil"
"juhe.cn.weather_report/pb"
"log"
"net"
"net/http"
"strconv"
"time"
)
const key = "2d1b16a202************"
func main() {
listen, err := net.Listen("tcp", ":8080")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to listen:%v", err)
}
s := grpc.NewServer()
pb.RegisterQueryServer(s, &weatherServer{
})
log.Printf("server listening at %v", listen.Addr())
if err := s.Serve(listen); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to server:%v", err)
}
}
/** * @author micro.cloud.fly * @date 2022/3/25 3:08 Afternoon * @desc Weather forecast server */
type weatherServer struct {
pb.UnimplementedQueryServer
}
type WeaResp struct {
Reason string `json:"reason"`
Result struct {
City string `json:"city"`
Realtime struct {
Temperature string `json:"temperature"`
Humidity string `json:"humidity"`
Info string `json:"info"`
Wid string `json:"wid"`
Direct string `json:"direct"`
Power string `json:"power"`
Aqi string `json:"aqi"`
} `json:"realtime"`
Future []struct {
Date string `json:"date"`
Temperature string `json:"temperature"`
Weather string `json:"weather"`
Wid struct {
Day string `json:"day"`
Night string `json:"night"`
} `json:"wid"`
Direct string `json:"direct"`
} `json:"future"`
} `json:"result"`
ErrorCode int64 `json:"error_code"`
}
// The client sends data through streaming , At this time, the server , You need to constantly read the data sent by the client
// The data of , When all are received , One row returns data to the client
func (ws *weatherServer) GetByStream(qgs pb.Query_GetByStreamServer) error {
var respArr []*pb.WeatherResponse
for {
recv, err := qgs.Recv()
if err == io.EOF {
return qgs.SendAndClose(&pb.StreamResp{
Results: respArr})
}
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return err
}
// Constantly obtain data sent from the client , Keep calling the interface
log.Println(" received :", recv.GetCity())
resp := httpGet(recv.GetCity())
log.Println(" Aggregate return :", resp)
var weaResp WeaResp
_ = json.Unmarshal([]byte(resp), &weaResp)
respArr = append(respArr, &pb.WeatherResponse{
Reason: weaResp.Reason,
Result: &pb.Result{
City: weaResp.Result.City,
Realtime: &pb.Realtime{
Aqi: weaResp.Result.Realtime.Aqi},
},
ErrorCode: weaResp.ErrorCode,
})
}
}
func (ws *weatherServer) GetByName(ctx context.Context, weaRequest *pb.WeatherRequest) (*pb.WeatherResponse, error) {
log.Println(" received :", weaRequest.City)
resp := httpGet(weaRequest.GetCity())
var weaResp WeaResp
err := json.Unmarshal([]byte(resp), &weaResp)
fu := &pb.Future{
Date: weaResp.Result.Future[0].Date,
Temperature: weaResp.Result.Future[0].Temperature,
Weather: weaResp.Result.Future[0].Weather,
Direct: weaResp.Result.Future[0].Direct,
}
fuArr := []*pb.Future{
fu}
return &pb.WeatherResponse{
Reason: weaResp.Reason,
Result: &pb.Result{
City: weaResp.Result.City,
Realtime: &pb.Realtime{
Aqi: weaResp.Result.Realtime.Aqi},
Future: fuArr,
},
ErrorCode: weaResp.ErrorCode,
}, err
}
// The client sends the name of one province at a time , The service side flows , Every time I find a city in this province , Just write to the stream
// Return to the client
func (ws *weatherServer) ReturnByStream(request *pb.CityRequest, qrs pb.Query_ReturnByStreamServer) error {
// Take out the province name sent by the client
jiangsu_city := []string{
" xuzhou ", " Suzhou ", " nanjing ", " zhenjiang "}
zhejiang_city := []string{
" ningbo ", " zhoushan ", " Hangzhou ", " wenzhou "}
if request.GetProvince() == " jiangsu " {
for _, s := range jiangsu_city {
err := qrs.Send(&pb.CityResp{
Cityname: s})
if err != nil {
return err
}
time.Sleep(time.Second * 2)
}
} else {
for _, s := range zhejiang_city {
err := qrs.Send(&pb.CityResp{
Cityname: s})
if err != nil {
return err
}
time.Sleep(time.Second * 2)
}
}
return nil
}
// Both client and server use streams , The client sends one , The server will return a , Until the end
func (ws *weatherServer) BidirectionalStream(stream pb.Query_BidirectionalStreamServer) error {
for {
req, err := stream.Recv()
if err == io.EOF {
// At this point, it means that the client sending is over
return nil
}
if err != nil {
// At this point, it means that there is really a mistake
return err
}
// At this time, a request is received , The server will return a request
fmt.Println(" Receive a request :",req.Id)
err = stream.Send(&pb.Product{
Id: req.Id,
Name: strconv.Itoa(int(req.Id)) + "name",
})
fmt.Println(" Reply client :",req.Id)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
time.Sleep(time.Second * 5)
}
return nil
}
func (ws *weatherServer) GetById(ctx context.Context, weaRequest *pb.WeatherRequest) (*pb.WeatherResponse, error) {
log.Println(" received :", weaRequest.GetCity())
resp := httpGet(weaRequest.GetCity())
log.Println(" Aggregate return :", resp)
var weaResp WeaResp
err := json.Unmarshal([]byte(resp), &weaResp)
fu := &pb.Future{
Date: weaResp.Result.Future[0].Date,
Temperature: weaResp.Result.Future[0].Temperature,
Weather: weaResp.Result.Future[0].Weather,
Direct: weaResp.Result.Future[0].Direct,
}
fuArr := []*pb.Future{
fu}
return &pb.WeatherResponse{
Reason: weaResp.Reason,
Result: &pb.Result{
City: weaResp.Result.City,
Realtime: &pb.Realtime{
Aqi: weaResp.Result.Realtime.Aqi},
Future: fuArr,
},
ErrorCode: weaResp.ErrorCode,
}, err
}
func httpGet(cityName string) string {
url := "http://apis.juhe.cn/simpleWeather/query?key=" + key + "&city=" + cityName
log.Println(url)
res, _ := http.Get(url)
defer res.Body.Close()
body, _ := ioutil.ReadAll(res.Body)
return string(body)
}
Four client codes
Simple mode
simple_rpc.go
package main
import (
"context"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"juhe.cn.weather_report/pb"
"log"
)
/** * @author micro.cloud.fly * @date 2022/3/25 3:54 Afternoon * @desc */
func main() {
dial, err := grpc.Dial("localhost:8080", grpc.WithInsecure())
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer dial.Close()
client := pb.NewQueryClient(dial)
/* The client and server are synchronized */
//--------| client |----------| Server side |
//-------| One time transmission |---------| Sync back |
pinyin, err := client.GetById(context.Background(), &pb.WeatherRequest{
City: " Beijing ",
Key: "",
})
log.Println(" return :", pinyin)
log.Println(" error :", err)
}
Client segment flow mode
client_side_stream_rpc.go
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"juhe.cn.weather_report/pb"
"log"
"time"
)
/** * @author micro.cloud.fly * @date 2022/3/25 3:54 Afternoon * @desc */
func main() {
dial, err := grpc.Dial("localhost:8080", grpc.WithInsecure())
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer dial.Close()
client := pb.NewQueryClient(dial)
/* The client is a stream , The service is a one-time return */
//--------| client |----------| Server side |
//-------| flow |----------- | After receiving one synchronization, return |
// The client sends three data through streaming ----start
names, err := client.GetByStream(context.Background())
city := []string{
" Suzhou ", " Shanghai ", " Qingdao "}
for i := 0; i < 3; i++ {
if err := names.Send(&pb.WeatherRequest{
City: city[i],
Key: "",
}); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
time.Sleep(time.Second * 2)
}
// Turn off sending , Let the server know that the client has finished sending
recv, err := names.CloseAndRecv()
fmt.Println(recv, err)
//----------------end-------
}
Server stream mode
server_side_stream_rpc.go
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"io"
"juhe.cn.weather_report/pb"
"log"
)
/** * @author micro.cloud.fly * @date 2022/3/25 3:54 Afternoon * @desc */
func main() {
dial, err := grpc.Dial("localhost:8080", grpc.WithInsecure())
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer dial.Close()
client := pb.NewQueryClient(dial)
/* The client sends past data at one time , The server returns through flow */
//--------| client |----------| Server side |
//--------| One time transmission |-----------| Stream return |
// The client sends one province at a time , The server returns to all cities in this province by streaming
stream, err := client.ReturnByStream(context.Background(), &pb.CityRequest{
Province: " jiangsu "})
// Because the server returns data in a stream , So at this time, you need to read the return data from the stream circularly
var city []string
for {
recv, err := stream.Recv()
if err == nil {
fmt.Println(" Server return :", recv.Cityname)
city = append(city, recv.Cityname)
}
if err == io.EOF {
fmt.Println(" The server has all returned , The client accepts !")
break
}
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
log.Println(" All cities in Jiangsu are :", city)
}
Two way flow mode
bidirectional_stream.go
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"io"
"juhe.cn.weather_report/pb"
"log"
)
/** * @author micro.cloud.fly * @date 2022/3/25 3:54 Afternoon * @desc */
func main() {
dial, err := grpc.Dial("localhost:8080", grpc.WithInsecure())
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer dial.Close()
client := pb.NewQueryClient(dial)
stream, err := client.BidirectionalStream(context.Background())
if err!=nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
for i := 0; i < 5; i++ {
err := stream.Send(&pb.Product{
Id: int64(i)})
if err!=nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Println(" Send goods :",i)
recv, err := stream.Recv()
if err==io.EOF {
// Indicates the end of receiving this stream
break
}
if err!=nil {
log.Fatal(err)
continue
}
fmt.Println(" Goods received :",recv.GetId(),recv.GetName())
}
}
边栏推荐
- Adaptive problem of img aspect ratio scaling in flex layout in Safari
- JMX Console 未授权访问漏洞
- The code is tired. Stop and enjoy the top color matching~
- Enterprises love hybrid app development, and applet container technology can improve efficiency by 100%
- 【游戏合集】手机都要被塞爆了,6款优质Pygame游戏合集降临~(附源码)
- [Yum] configuration and use of Yum source
- From starfish OS' continued deflationary consumption of SFO, the value of SFO in the long run
- How to write your FAQ page?
- [multithreading] five communication modes between multithreads
- 基于thinkphp将execle表格上传并插入数据库
猜你喜欢
Cososcreator upgrade gradle version
![[wechat applet development (III)] realize the stacking and sliding of cards](/img/6c/4ebd60a2106b56b8bf3a6bf17d11f9.png)
[wechat applet development (III)] realize the stacking and sliding of cards

Look at the most influential infrastructure m-dao of Web3 through the current situation of Dao

The code is tired. Stop and enjoy the top color matching~

【MySQL】08:聚合函数

MySQL日期格式化

Wechat applet file types and functions

Web3≠NFT? A digital Renaissance?
JMX Console 未授权访问漏洞

DGL库中一些函数或者方法的介绍
随机推荐
Web3≠NFT? A digital Renaissance?
Dao race track is booming. What are the advantages of m-dao?
「题解」火神之友
[database] complete SQL statement
Limited and unlimited Games: crypto
Is it safe to open an account online in Beijing
Group by group and get the first data
Summary of points management system project
Saining Techtalk attack and defense drill: attack combination fist "stable, accurate and ruthless" penetration
[wechat applet development (IV)] applet fast actual combat classic problem navigation
3587. 连通图(吉林大学考研机试题)
「题解」零钱兑换
Assemble | find the maximum and minimum values
DGL库中一些函数或者方法的介绍
Go: how to gracefully time out
[JDBC] classic interview questions of JDBC, constantly updating
Bit.store, which has attracted much attention, is at a glance of the latest developments
[golang from introduction to practice] student achievement management system
【golang从入门到实践】学生成绩管理系统
Aquanee: the true meaning of "p2e"