当前位置:网站首页>Implementing DNS requester with C language
Implementing DNS requester with C language
2022-06-24 21:35:00 【qq_ forty-two million one hundred and twenty thousand eight hun】
C Language implementation DNS Requester
List of articles
- C Language implementation DNS Requester
- Project introduction
- Pre knowledge
- Technical points
- Program execution flow
- Programming process
- Code analysis
- Full source code
- problem
Project introduction
This procedure completes the request corresponding to the given specified domain name ip Address function , Be similar to win and linux Next nslookup The function of
Pre knowledge
DNS Introduce
The domain name system ( english :Domain Name System , abbreviation DNS ) Is a service of the Internet . It is used to IP A distributed database with address mapping , Make it easier for people to access the Internet . DNS Use TCP and UDP port 53 . At present , The limit for the length of each level of domain name is 63 Characters , The total length of the domain name cannot exceed 253 Characters . The domain name system ( english :Domain Name System , abbreviation DNS The function of is to translate human readable domain names such as , www.example.com) Convert to machine-readable IP Address Such as , 192.0.2.44) .
DNS The layered
The domain name system is hierarchical .
In the hierarchy of the domain name system , All kinds of domain names are subordinate to the root domain of the domain name system . The first level of domain name is the top level domain , It includes common top-level domains , for example .com 、 .net and .org ; And national and regional top-level domains , for example .us 、 .cn and .tk . The next level of the top-level domain name is the secondary domain name , Step by step down . These domain names provide people with registration services , People can use it to create public Internet resources or run websites . The management service of the top-level domain name is provided by the corresponding Domain name registration The governing body ( Domain name registry ) be responsible for , The registration service is usually the responsibility of the domain name registrar .

Domain name resolution
Host name to IP There are two ways to map addresses :
Static mapping Configure the domain name and on this computer IP Mapping , Designed for use on this machine . Windows and Linux Of hosts The contents of the file belong to static mapping .
Dynamic mapping Set up a domain name resolution system ( DNS ), Only in specialized DNS Configure the host on the server to IP Address mapping , Devices on the network that need to communicate using a host name , First of all, we need to go to DNS The server queries the corresponding IP Address . Query the domain name server through the domain name , obtain IP The process of address is called domain name resolution . In resolving domain names , Generally, first static domain name resolution , Then dynamically resolve the domain name . Sure Put some common domain names into the static domain name resolution table , This can greatly improve the efficiency of domain name resolution .
Recursive queries and iterative queries
- recursive Inquire about : This machine sends a query request to the local domain name server , Just Waiting for the final result . If the local domain name server cannot resolve , I'll take DNS The identity of the client is queried from other domain name servers , Until the final IP Address to local .
- iteration Inquire about : Local domain name server queries root domain name server ,** The root domain server tells it where to go next , And then it checks ,** Every time it is a client Go to each server to query the identity
DNS Protocol message format

Head (Header)

Queries( Query question area )

domain name ( 2 Byte or indefinite length ): Its format and Queries The query name field of the region is the same . A little bit
The difference is , When the domain name in the message appears repeatedly , This field uses 2 Byte offset pointer . Than
Such as , stay In the resource record , The domain name is usually the repetition of the domain name in the query problem part , So with 2 A pointer to bytes
in , The first two bits are 11(0xC0), Used to identify the pointer . The rest 14 From DNS Opening of message
Start count ( from 0 Start ), Indicates the corresponding number of bytes in the message . A typical example ,
C00C(11 00 000000001100, 12 ( byte ) Exactly the length of the head , It just points to Queries Query name field of area .
Query type (Type): Indicates the type of resource record .
Query class (Class): about Internet Information , Always IN
Time to live ( TTL In seconds , Represents the lifecycle of a resource record , Generally used when the address resolution process
After the sequence fetches the resource record, it determines the time to save and use the cached data , It can also indicate the stability of the resource record
To a certain extent , Extremely stable information will Assigned a large value ( such as 86400 , This is the seconds of the day ).
Resource data : This field is a variable length field , Represents the number of related resource records returned according to the requirements of the query segment
According to the .** It can be Address ( Indicates that the desired response of the query message is a IP Address )** perhaps CNAME ( Indicates that the query
** The desired response of the message is a canonical hostname )** etc. .
wireshark analysis DNS Request and response messages

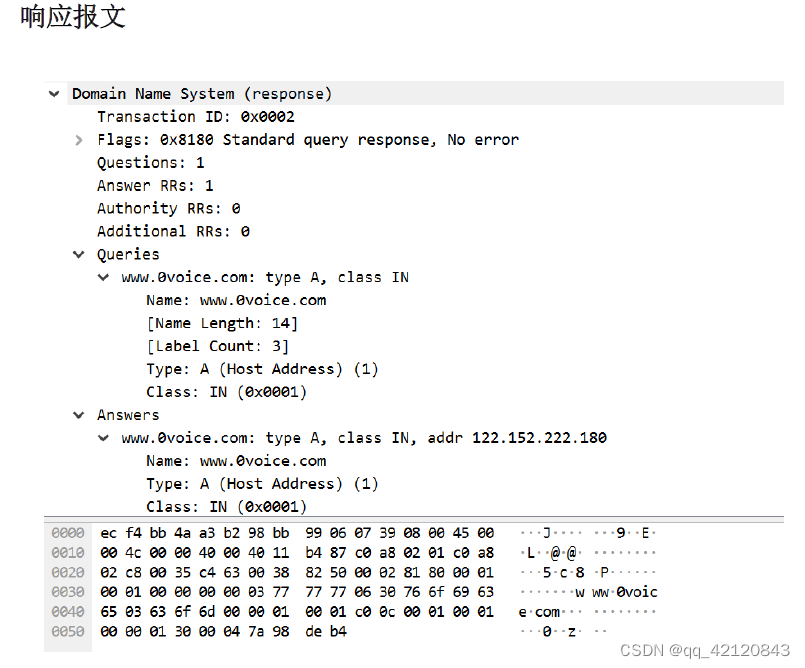
Technical points
- Use The transport layer UDP Socket Programming
- The application layer of the DNS Message format
Program execution flow

Programming process
- DNS The structure definition of the request header and body part
- DNS header Data filling
- DNS question Data filling
- Merge DNS header and question part (build_requestion)
- adopt UDP Socket Send request message and receive response message
- Analyze the relevant data of the response message
Code analysis
DNS header and question Part of the structure implements
contrast DNS The message format can be realized
//dns message Header Some data structures
struct dns_header{
unsigned short id; //2 byte (16 position )
unsigned short flags;
unsigned short questions; // Number of questions
unsigned short answer; // Number of answers
unsigned short authority;
unsigned short additional;
};
//dns message Queries Part of the data structure
struct dns_question{
int length; // Length of host name , I added , Easy to operate
unsigned short qtype;
unsigned short qclass;
// The query name is a combination of length and domain name
// Such as www.0voice.com ==> 60voice3com0
// The reason for this is that the domain name query is generally a tree structure query ,com Top-level domain ,0voice The secondary domain
unsigned char *name; // Host name ( The length is uncertain )
};
//dns Data in response message ( Domain name and ip) The structure of the body
struct dns_item{
char *domain;
char *ip;
};
DNS header Data filling
We just fill in 3 A field :Transaction ID、Flags、Questions. The session ID is randomly generated , The number of signs and questions should be Host byte order to network byte order Transformation :
// take header Some fields are filled with data
int dns_create_header(struct dns_header *header)
{
if(header == NULL)
return -1;
memset(header, 0x00, sizeof(struct dns_header));
//id With random numbers , For seed time(NULL), Indicates the range in which random numbers are generated
srandom(time(NULL)); // Thread unsafe
header->id = random();
// Network byte order ( Big end ): Address low bit stores data high bit ; The host byte order is the opposite
// host (host) Byte sequence to network (net) Byte order
header->flags = htons(0x0100);
header->questions = htons(1);
return 0;
}
DNS Queries Partial data filling
In the comparison message Queries Fill the part of
int dns_create_question(struct dns_question *question, const char *hostname)
{
if(question == NULL || hostname == NULL)
return -1;
memset(question, 0x00, sizeof(struct dns_question));
// Memory space length :hostname length + ending \0 Give one more space
question->name = (char *)malloc(strlen(hostname) + 2);
if(question->name == NULL)
{
return -2;
}
question->length = strlen(hostname) + 2;
// Query type 1 Indicates acquisition IPv4 Address
question->qtype = htons(1);
// Query class 1 Express Internet data
question->qclass = htons(1);
//【 major measure 】
// Name store :www.0voice.com -> 3www60voice3com
const char delim[2] = ".";
char *qname = question->name; // A pointer used to fill in content
//strdup Start with size and hostname Same memory , And then hostname The characters are copied to the developed memory
char *hostname_dup = strdup(hostname); // Copy string , call malloc
// Will be in accordance with the delim Split the string array , Returns the first string
char *token = strtok(hostname_dup, delim);
while(token != NULL)
{
//strlen The length of the returned string does not contain '\0'
size_t len = strlen(token);
*qname = len;// Of length ASCII code
qname++;
// take token The indicated string is copied to qname On the memory referred to , Copy at most len + 1 length
//len+1 Make the last string put \0 Copy in
strncpy(qname, token, len + 1);
qname += len;
// Fixed writing , At this point, the next split string will be returned internally (strtok Will depend on the results of the last run )
token = strtok(NULL, delim); // Rely on the last result , Thread unsafe
}
free(hostname_dup);
}
Merge DNS header and question part
take header Some data and question Part of the data is merged into the character array .
// take header and question Merge into request in
//header [in]
//question [in]
//request [out]
//rlen: representative request Size
int dns_build_requestion(struct dns_header *header, struct dns_question *question, char *request, int rlen)
{
if (header == NULL || question == NULL || request == NULL)
return -1;
memset(request, 0, rlen);
//header -> request
memcpy(request, header, sizeof(struct dns_header));
int offset = sizeof(struct dns_header);
//Queries Some fields are written to request in ,question->length yes question->name The length of
memcpy(request + offset, question->name, question->length);
offset += question->length;
memcpy(request + offset, &question->qclass, sizeof(question->qclass));
offset += sizeof(question->qclass);
memcpy(request + offset, &question->qtype, sizeof(question->qtype));
offset += sizeof(question->qtype);
return offset; // return request The actual length of the data
}
UDP Socket Programmed transmission DNS Request and receive DNS Respond to
UDP Socket The basic programming process and function call sequence are basically the same ,
Code flow :
- establish UDP Socket
- Fill in the server address Data of structure (struct sockaddr_in)
- Connect To ensure as reliable as possible (connect)
- DNS message Data filling (dns_create_header、dns_build_requestion)
- adopt socket send out DNS Request message (sendto)
- Accept DNS response message (recvfrom)
- analysis response message
int dns_client_commit(const char *domain)
{
// The following process is a routine that is basically dead
//1. establish UDP socket
// The network layer ipv4, For transport layer udp
int sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
if(sockfd < 0)
{
return -1;
}
//2. Structure filling data
struct sockaddr_in servaddr;
bzero(&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr)); // Empty the structure array
servaddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
servaddr.sin_port = htons(DNS_SERVER_PORT);
// A binary number used to convert a dotted decimal address into a network Replace inet_pton
//servaddr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(DNS_SERVER_IP);
inet_pton(AF_INET, DNS_SERVER_IP, &servaddr.sin_addr.s_addr);
//UDP Not necessarily connect, It just increases the probability of successfully sending the request
connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr));
//3.dns Data filling of message
struct dns_header header = {
0};
dns_create_header(&header);
struct dns_question question = {
0};
dns_create_question(&question, domain);
char request[1024] = {
0};
int len = dns_build_requestion(&header, &question, request, 1024);
//4. adopt sockfd send out DNS Request message
int slen = sendto(sockfd, request, len, 0, (struct sockaddr *)&servaddr, sizeof(struct sockaddr));
char response[1024] = {
0};
struct sockaddr_in addr;
size_t addr_len = sizeof(struct sockaddr_in);
//5. Accept DNS Server response message
//addr and addr_len It's the output parameter
int n = recvfrom(sockfd, response, sizeof(response), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&addr, (socklen_t *)&addr_len);
struct dns_item *dns_domain = NULL;
//6. Parse response
dns_parse_response(response, &dns_domain);
free(dns_domain);
return n; // Returns the length of the received response message
}
Analyze the relevant data of the response message
The function that parses the response
//struct dns_item** It's because of dang struct dns_item * by NULL The value needs to be changed
static int dns_parse_response(char *buffer, struct dns_item **domains)
{
int i = 0;
unsigned char *ptr = buffer;
ptr += 4; // ptr forward 4 byte , Point to Questions( Number of questions ) Field starts with
int querys = ntohs(*(unsigned short *)ptr);
ptr += 2; //ptr forward 2 byte , Point to Answer RR Start with the answer number
int answers = ntohs(*(unsigned short *)ptr); // A domain name may correspond to more than one ip
ptr += 6; //ptr forward 6 byte , Point to Queries( Query question area )Name The beginning of the field
for(i = 0;i < querys; i++)
{
// For example, the inquiry website is www.0voice, be Name = 3www60voice3com0
while(1)
{
//flag Is the length of the subsequent string
int flag = (int)ptr[0];
ptr += (flag + 1);
if(flag == 0) break;
}
ptr += 4; // Point to next query name Name The beginning of the field
// The last loop is to skip Type and Class Field
}
char cname[128], aname[128], ip[20], netip[4];
int len, type, ttl, datalen;
int cnt = 0;
// An array that dynamically allocates memory
// Distribute answers individual dns_item Of memory , And set all to 0, Returns a pointer to a position
struct dns_item *list = calloc(answers, sizeof(struct dns_item));
if(list == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
// It is concluded that Answers( Answer area ) The content of
for(int i = 0;i < answers;++i)
{
bzero(aname, sizeof(aname));
len = 0;
// from buffer in ptr Resolve the domain name to the location pointed to aname in , And write the length to len in
dns_parse_name(buffer, ptr, aname, &len);
ptr += 2; //???
type = htons(*(unsigned short *)ptr);
ptr += 4;
ttl = htons(*(unsigned short *)ptr);
ptr += 4;
datalen = ntohs(*(unsigned short *)ptr);
ptr += 2;
if(type == DNS_CNAME)
{
bzero(cname, sizeof(cname));
len = 0;
from buffer Of ptr The position starts to parse the content to cname in ,len Used to accept the parsed content length
dns_parse_name(buffer, ptr, cname, &len);
ptr += datalen;
}
else if(type == DNS_HOST)
{
bzero(ip, sizeof(ip));
//ipv4 by 4 byte
if(datalen == 4)
{
memcpy(netip, ptr, datalen);
// Binary network byte order netip Convert to dotted decimal address and save to ip
inet_ntop(AF_INET, netip, ip, sizeof(struct sockaddr));
printf("%s has address %s\n", aname, ip);
printf("\t Time to live : %d minutes, %d seconds\n",ttl / 60, ttl % 60);
list[cnt].domain = (char *)calloc(strlen(aname) + 1, 1);
memcpy(list[cnt].domain, aname, strlen(aname));
list[cnt].ip = (char *)calloc(strlen(ip) + 1, 1);
memcpy(list[cnt].ip, ip, strlen(ip));
cnt++;
}
ptr += datalen;
}
}
*domains = list;
ptr += 2; //????
return cnt;
}
The function that resolves the domain name
domain name ( 2 Byte or indefinite length ): Its format and Queries The query name field of the region is the same . A little bit
The difference is , When the domain name in the message appears repeatedly , This field uses 2 Byte offset pointer . Than
Such as , stay In the resource record , The domain name is usually the repetition of the domain name in the query problem part , So with 2 A pointer to bytes
in , The first two bits are 11(0xC0), Used to identify the pointer . The rest 14 From DNS Opening of message
Start count ( from 0 Start ), Indicates the corresponding number of bytes in the message . A typical example ,
C00C(11 00 000000001100, 12 ( byte ) Exactly the length of the head , It just points to Queries Query name field of area .
For the first time, some Name( domain name )

The second time the same domain name appears , Only two bytes (C0 0C = 1100 0000 0000 1100), high 2 The bit representation is a pointer , low 14 Bit indicates the offset of the domain name for the first time (12 byte )

// from chunk Of ptr Start to resolve the name at the position pointed to , Length write len
static void dns_parse_name(unsigned char* chunk, unsigned char *ptr, char *out, int *len)
{
int flag = 0, n = 0, alen = 0;
//pos The memory pointed to is used to store the parsed results
char *pos = out + (*len); // Incoming *len = 0
while(1)
{
flag = (int)ptr[0];
if(flag == 0) break;
// If a pointer indicates that Name Repeated , This field only occupies 2 byte
if(is_pointer(flag))
{
n = (int)ptr[1]; // Get the first Name The resulting offset
ptr = chunk + n;
dns_parse_name(chunk, ptr, out, len);
break;
}
else // It's not a pointer , Indicates that it is the first time Name The place of , here flag Represents the length of the subsequent string
{
ptr++;
memcpy(pos, ptr, flag);
pos += flag;
ptr += flag;
*len += flag;
if((int)ptr[0] != 0)
{
memcpy(pos, ".", 1);
pos += 1;
(*len) += 1;
}
}
}
}
static int is_pointer(int in)
{
//0xC0 : 1100 0000
return ((in & 0xC0) == 0xC0);
}
Full source code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#define DNS_SERVER_PORT 53
#define DNS_SERVER_IP "114.114.114.114"
#define DNS_HOST 0x01
#define DNS_CNAME 0x05
//dns message Header Some data structures
struct dns_header{
unsigned short id; //2 byte (16 position )
unsigned short flags;
unsigned short questions; // Number of questions
unsigned short answer; // Number of answers
unsigned short authority;
unsigned short additional;
};
//dns message Queries Part of the data structure
struct dns_question{
int length; // Length of host name , I added , Easy to operate
unsigned short qtype;
unsigned short qclass;
// The query name is a combination of length and domain name
// Such as www.0voice.com ==> 60voice3com0
// The reason for this is that the domain name query is generally a tree structure query ,com Top-level domain ,0voice The secondary domain
unsigned char *name; // Host name ( The length is uncertain )
};
//dns Data in response message ( Domain name and ip) The structure of the body
struct dns_item{
char *domain;
char *ip;
};
// take header Some fields are filled with data
int dns_create_header(struct dns_header *header)
{
if(header == NULL)
return -1;
memset(header, 0x00, sizeof(struct dns_header));
//id With random numbers , For seed time(NULL), Indicates the range in which random numbers are generated
srandom(time(NULL)); // Thread unsafe
header->id = random();
// Network byte order ( Big end ) Address low bit stores data high bit
// host (host) Byte sequence to network (net) Byte order
header->flags = htons(0x0100);
header->questions = htons(1);
return 0;
}
// take Queries Some fields are filled with data
int dns_create_question(struct dns_question *question, const char *hostname)
{
if(question == NULL || hostname == NULL)
return -1;
memset(question, 0x00, sizeof(struct dns_question));
// Memory space length :hostname length + ending \0 Give one more space
question->name = (char *)malloc(strlen(hostname) + 2);
if(question->name == NULL)
{
return -2;
}
question->length = strlen(hostname) + 2;
// Query type 1 Indicates acquisition IPv4 Address
question->qtype = htons(1);
// Query class 1 Express Internet data
question->qclass = htons(1);
//【 major measure 】
// Name store :www.0voice.com -> 3www60voice3com
const char delim[2] = ".";
char *qname = question->name; // A pointer used to fill in content
//strdup Start with size and hostname Same memory , And then hostname The characters are copied to the developed memory
char *hostname_dup = strdup(hostname); // Copy string , call malloc
// Will be in accordance with the delim Split the string array , Returns the first string
char *token = strtok(hostname_dup, delim);
while(token != NULL)
{
//strlen The length of the returned string does not contain '\0'
size_t len = strlen(token);
*qname = len;// Of length ASCII code
qname++;
// take token The indicated string is copied to qname On the memory referred to , Copy at most len + 1 length
//len+1 Make the last string put \0 Copy in
strncpy(qname, token, len + 1);
qname += len;
// Fixed writing , At this point, the next split string will be returned internally (strtok Will depend on the results of the last run )
token = strtok(NULL, delim); // Rely on the last result , Thread unsafe
}
free(hostname_dup);
}
// take header and question Merge into request in
//request Are incoming and outgoing parameters
int dns_build_requestion(struct dns_header *header, struct dns_question *question, char *request, int rlen)
{
if (header == NULL || question == NULL || request == NULL)
return -1;
memset(request, 0, rlen);
//header -> request
memcpy(request, header, sizeof(struct dns_header));
int offset = sizeof(struct dns_header);
//Queries Some fields are written to request in ,question->length yes question->name The length of
memcpy(request + offset, question->name, question->length);
offset += question->length;
memcpy(request + offset, &question->qclass, sizeof(question->qclass));
offset += sizeof(question->qclass);
memcpy(request + offset, &question->qtype, sizeof(question->qtype));
offset += sizeof(question->qtype);
return offset; // return request The actual length of the data
}
static int is_pointer(int in)
{
//0xC0 : 1100 0000
return ((in & 0xC0) == 0xC0);
}
// from chunk Of ptr Start to resolve the name at the position pointed to , Length write len
static void dns_parse_name(unsigned char* chunk, unsigned char *ptr, char *out, int *len)
{
int flag = 0, n = 0, alen = 0;
//pos The memory pointed to is used to store the parsed results
char *pos = out + (*len); // Incoming *len = 0
//???
while(1)
{
flag = (int)ptr[0]; // ???
if(flag == 0) break;
if(is_pointer(flag))
{
n = (int)ptr[1];
ptr = chunk + n;
dns_parse_name(chunk, ptr, out, len);
break;
}
else // It's not a pointer , Indicates that it is the first time Name The place of
{
ptr++;
memcpy(pos, ptr, flag);
pos += flag;
ptr += flag;
*len += flag;
if((int)ptr[0] != 0)
{
memcpy(pos, ".", 1);
pos += 1;
(*len) += 1;
}
}
}
}
// Parse response
//struct dns_item** It's because of dang struct dns_item * by NULL The value needs to be changed
static int dns_parse_response(char *buffer, struct dns_item **domains)
{
int i = 0;
unsigned char *ptr = buffer;
ptr += 4; // ptr forward 4 byte , Point to Questions( Number of questions ) Field starts with
int querys = ntohs(*(unsigned short *)ptr);
ptr += 2; //ptr forward 2 byte , Point to Answer RR Start with the answer number
int answers = ntohs(*(unsigned short *)ptr); // A domain name may correspond to more than one ip
ptr += 6; //ptr forward 6 byte , Point to Queries( Query question area )Name The beginning of the field
for(i = 0;i < querys; i++)
{
// For example, the inquiry website is www.0voice, be Name = 3www60voice3com0
while(1)
{
int flag = (int)ptr[0];
ptr += (flag + 1); //???
if(flag == 0) break;
}
ptr += 4; // Point to next query name Name Start of field or skip Type and Class Field
}
char cname[128], aname[128], ip[20], netip[4];
int len, type, ttl, datalen;
int cnt = 0;
// An array that dynamically allocates memory
// Distribute answers individual dns_item Of memory , And set all to 0, Returns a pointer to a position
struct dns_item *list = calloc(answers, sizeof(struct dns_item));
if(list == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
for(int i = 0;i < answers;++i)
{
bzero(aname, sizeof(aname));
len = 0;
// Resolve the domain name
dns_parse_name(buffer, ptr, aname, &len);
ptr += 2;
type = htons(*(unsigned short *)ptr);
ptr += 4;
ttl = htons(*(unsigned short *)ptr);
ptr += 4;
datalen = ntohs(*(unsigned short *)ptr);
ptr += 2;
if(type == DNS_CNAME)
{
bzero(cname, sizeof(cname));
len = 0;
// guess : from buffer Of ptr The position starts to parse the content to cname in ,len Used to accept the parsed content length
dns_parse_name(buffer, ptr, cname, &len);
ptr += datalen;
}
else if(type == DNS_HOST)
{
bzero(ip, sizeof(ip));
//ipv4 by 4 byte
if(datalen == 4)
{
memcpy(netip, ptr, datalen);
// Binary network byte order netip Convert to dotted decimal address and save to ip
inet_ntop(AF_INET, netip, ip, sizeof(struct sockaddr));
printf("%s has address %s\n", aname, ip);
printf("\t Time to live : %d minutes, %d seconds\n",ttl / 60, ttl % 60);
list[cnt].domain = (char *)calloc(strlen(aname) + 1, 1);
memcpy(list[cnt].domain, aname, strlen(aname));
list[cnt].ip = (char *)calloc(strlen(ip) + 1, 1);
memcpy(list[cnt].ip, ip, strlen(ip));
cnt++;
}
ptr += datalen;
}
}
*domains = list;
ptr += 2; // After testing, this line is OK without adding
return cnt;
}
// Client to dns The server sends the request
int dns_client_commit(const char *domain)
{
// The following process is a routine that is basically dead
//1. establish UDP socket
// The network layer ipv4, For transport layer udp
int sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
if(sockfd < 0)
{
return -1;
}
//2. Structure filling data
struct sockaddr_in servaddr;
bzero(&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr)); // Empty the structure array
servaddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
servaddr.sin_port = htons(DNS_SERVER_PORT);
// A binary number used to convert a dotted decimal address into a network Replace inet_pton
//servaddr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(DNS_SERVER_IP);
inet_pton(AF_INET, DNS_SERVER_IP, &servaddr.sin_addr.s_addr);
//UDP Not necessarily connect, It just increases the probability of successfully sending the request
connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr));
//3.dns Data filling of message
struct dns_header header = {
0};
dns_create_header(&header);
struct dns_question question = {
0};
dns_create_question(&question, domain);
char request[1024] = {
0};
int len = dns_build_requestion(&header, &question, request, 1024);
//4. adopt sockfd send out DNS Request message
int slen = sendto(sockfd, request, len, 0, (struct sockaddr *)&servaddr, sizeof(struct sockaddr));
char response[1024] = {
0};
struct sockaddr_in addr;
size_t addr_len = sizeof(struct sockaddr_in);
//5. Accept DNS Server response message
//addr and addr_len It's the output parameter
int n = recvfrom(sockfd, response, sizeof(response), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&addr, (socklen_t *)&addr_len);
struct dns_item *dns_domain = NULL;
//6. Parse response
dns_parse_response(response, &dns_domain);
free(dns_domain);
return n; // Returns the length of the received response message
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if(argc < 2) return -1;
dns_client_commit(argv[1]);
return 0;
}
Compile and execute

problem
dns_parse_responseThe following part of the functionfor(int i = 0;i < answers;++i) { bzero(aname, sizeof(aname)); len = 0; // Resolve the domain name dns_parse_name(buffer, ptr, aname, &len); ptr += 2;// ??????? Why? ptr Just move the pointer 2 Bytes , instead of len,aname Isn't it changeable , Only skip aname The actual length will reach Type Field .
边栏推荐
- Call process of package receiving function
- how to install clustershell
- Role of wait function
- JMeter implementation specifies concurrent loop testing
- [Web Security Basics] some details
- 使用 Go 编程语言 66 个陷阱:Golang 开发者的陷阱和常见错误指北
- database/sql
- Decoration home page custom full screen video playback effect GIF dynamic picture production video tutorial playback code operation settings full screen center Alibaba international station
- Learn to use a new technology quickly
- Functional analysis of ebpf tracepoint
猜你喜欢

memcached全面剖析–5. memcached的应用和兼容程序

CondaValueError: The target prefix is the base prefix. Aborting.

基于STM32的物联网下智能化养鱼鱼缸控制控制系统

VirtualBox virtual machine installation win10 Enterprise Edition

Volcano becomes spark default batch scheduler

Oauth2.0 introduction
基于C语言实现的足球信息查询系统 课程报告+项目源码+演示PPT+项目截图

123. 买卖股票的最佳时机 III

Pattern recognition - 9 Decision tree

Read all text from stdin to a string
随机推荐
Learn to use a new technology quickly
Tso hardware sharding is a header copy problem
BPF_ PROG_ TYPE_ SOCKET_ Filter function implementation
Call process of package receiving function
Auto. JS to automatically authorize screen capture permission
Football information query system based on C language course report + project source code + demo ppt+ project screenshot
TCP Jprobe utilization problem location
66 pitfalls in go programming language: pitfalls and common errors of golang developers
Blender's landscape
升哲科技 AI 智能防溺水服务上线
Use of kubernetes storage volumes
一文理解OpenStack网络
Pyaudio audio recording
Web automation: summary of special scenario processing methods
Summary of message protocol problems
Markdown use
使用 Go 编程语言 66 个陷阱:Golang 开发者的陷阱和常见错误指北
[cloud native learning notes] kubernetes practice command
XTransfer技术新人进阶秘诀:不可错过的宝藏Mentor
Network flow 24 questions (round table questions)