当前位置:网站首页>Notes on C language learning of migrant workers majoring in electronic information engineering
Notes on C language learning of migrant workers majoring in electronic information engineering
2022-07-03 09:53:00 【Dream change】
List of articles
Preface
According to freshman C Language courses ( By Tan Haoqiang ) Summary of my studyOne 、 Beginner must know principle
1、 Code is a substitute for “ Human beings operate computers to execute instructions ” The information of this action shows , Code is a rule system readable by program apes ; A program is an instruction that a computer can recognize and execute , Generated by the code through the compiler ( code ) The executable of (.exe). edit (.c、.h)-> compile (.obj)-> Connect (.h、.obj)-> perform (.exe),1 byte = 8 Bit binary number .
2、 machine language : The binary code that the computer can recognize and accept constitutes machine instructions , The set of machine instructions is machine language .
assembly language : Computer low-level language , It cannot be used between different machines , The computer is efficient , But the amount of symbols is large , It's hard to learn , It is mainly used for machine control codes that need high efficiency .
3、C Language, like other languages, is a high-level language , But it is widely used in low-level development , Mainly process oriented .C Language can realize most of the functions of assembly language , Learn easy , Be able to learn other languages well after the concept is formed ( commonly C++ Compatible C Language grammar ).
4、 Study C Language common files (VS2019 Edition and VSCode edition ):
“.c”:C Language source file ;".cpp":C++ Source file ;".h":C Language /C++ The header file ;".sln":C Language solutions ;".obj": Binary object file ;".json"(JavaScript Object Notation): A lightweight data exchange format file
Two 、 Basic knowledge
1.“HELLO WORLD”
#: Identifier of precompiled processing
<xxx.h>: Angle brackets contain standard header files
“xxx.h”: Double quotes contain custom header files
stdio.h: Standard I/o header file
printf(“ Output content ”): Output statement , Output to the terminal 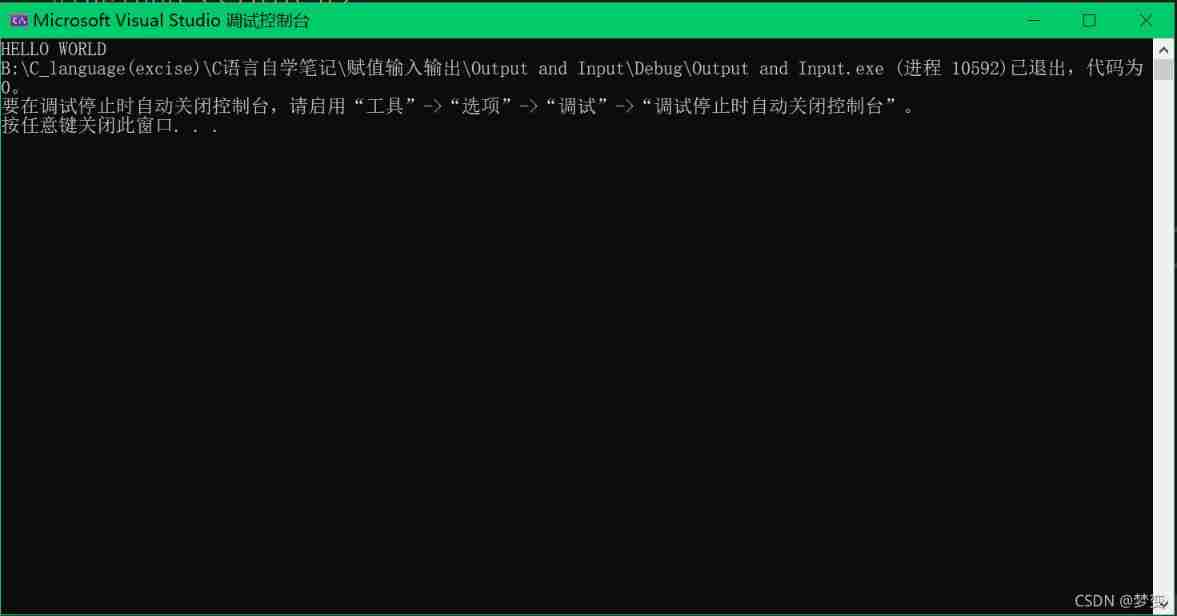
scanf(“ Input content ( Keyboard entry )”): Enter the assignment statement , Assign the input to the variable 
/**/、//: annotator , Comments do not take up memory space
2. data type
char:1 byte , Character type ,-128 ~ 127 example :‘a’,-128;
unsigned char:1 byte , The unsigned character type ,0 ~ 255 example :‘a’,255;
int: Common compiler 4 byte , Integer type ,-2147483648 ~ 2147483647;
unsigned int: Common compiler 4 byte , Unsigned integer type ,0 ~ 4294967295;
short(short int): No, the occupied space in the compiler is different , Short integer type ;
long(long int): No, the occupied space in the compiler is different , Short integer type ;
float:4 byte , Single precision floating point type , The absolute range of values is 0 as well as 1.2 x 10 Of -38 Power to 3.4 x 10 Of -38 Power ;
double:8 byte , Double precision floating point type , The absolute range of values is 0 as well as 2.3 x 10 Of -38 Power to 1.7 x 10 Of -38 Power ;
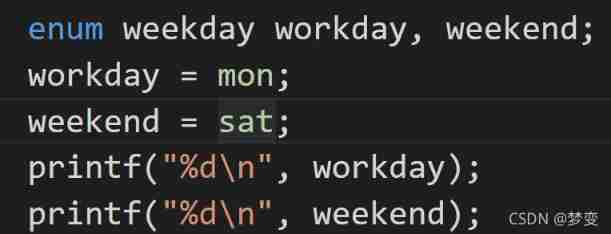
enum: Enumeration type , Variable values are only enumeration elements , Each element is constant ;
—> Enumeration type details 

#define Used for precompiled string substitution ,typedef Used to alias the data type after compilation
—>define And typedef The difference between
void: Empty type , It is often used to define that a function has no return value ;
struct: Type of structure , The structure element is composed of multiple basic types or pointer types , It is equivalent to an array with different data types ;
union: Type of community , The common body element is composed of multiple basic types or pointer types , It is equivalent to that elements in a structure only occupy one address , Every time an element variable is assigned, the value of the address is overwritten ;
Basic types Array name []: An array type , Used to store multiple values , The storage address is a continuous segment ;
Basic types *: Common compiler 4 byte , Pointer types , Used to store the address of the variable or function of this basic type ;
unsigned Represents an unsigned integer , The first binary number of each data type represents positive and negative , Unsigned is a binary number with sign bits representing positive numbers 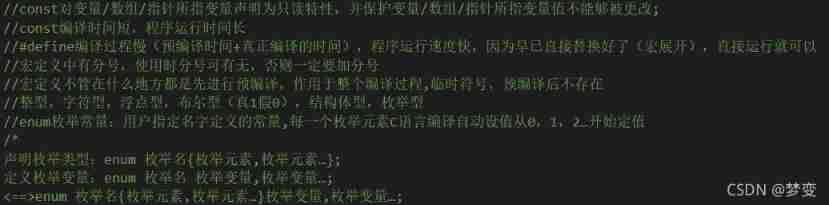
Floating point numbers can float between decimal points , Store in exponential form 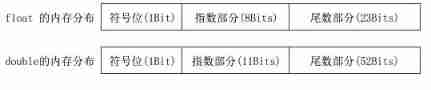 —> Floating point storage related explanations
—> Floating point storage related explanations
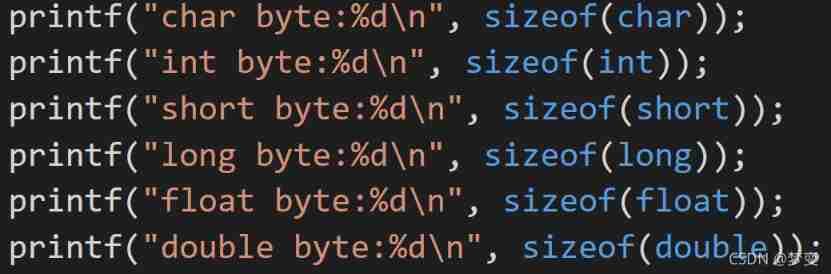
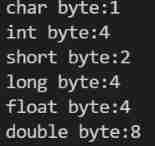
notes : This byte length standard is only a common standard in compilers , In case of any difference, the actual situation shall prevail
/*****************************************************/
Implicit conversion of data types :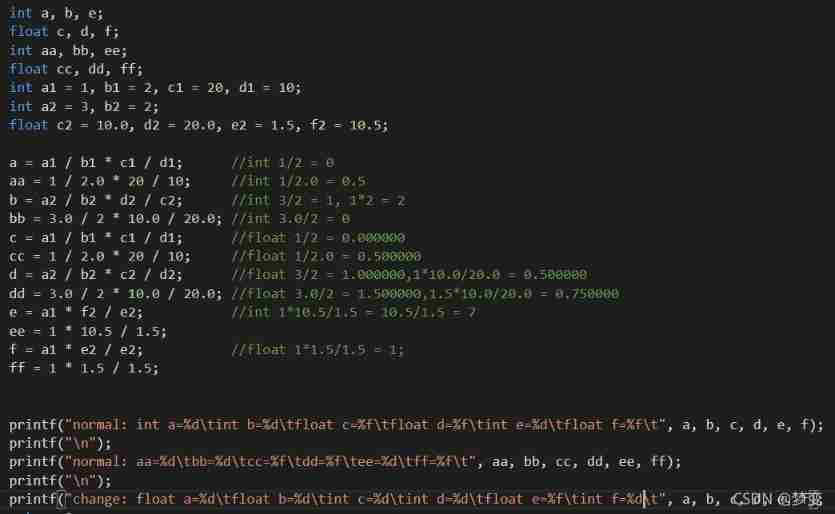
 When performing operations of different data types , Small types are converted to large types first , The final result type is the data type that occupies the largest space
When performing operations of different data types , Small types are converted to large types first , The final result type is the data type that occupies the largest space
Coercive transformation ( Display conversion ):
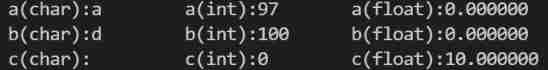
The assignment statement is marked with “( data type )” Cast the value on the right to this data type and assign it to the variable on the left
Be careful : When writing code, you need to pay attention to the implicit conversion of values , And force conversion with goto The sentence is the same , Don't use... When the result is unclear and unnecessary .
3. Operators and Expressions
“i++ and ++i”, Arithmetic operators take precedence over shift operators ,“->” Used to point to structure members
Be careful :“while and if Whether it is it+ still ++i, Execute the self increase or decrease in brackets first , Then execute the statement in braces ”
—> Operator details 
—> Operator considerations
There is a detailed summary in the reference link , You need to remember each operator and priority , Beginners especially need to pay attention to the mistakes . The above content is my own fallibility , For reference only .
3.C sentence
1、C sentence :
One line of preprocessing cannot be written : Write a preprocessing instruction as multiple lines “\” Line continuation , Because by definition , A preprocessing instruction can only consist of one logical line of code .
One line of normal program cannot be written : hold C If you write multiple lines of code, you don't have to use line continuation , Because the linefeed is C The code is nothing more than a blank character , Doing grammar parsing ( Syntax analysis ) All white space characters are discarded .
String constants span lines : \n It can only work in one line ,\ You can write across lines , But you can't wrap lines , It can only serve as a connection , You can write across lines , however \n And \ When used together, you can both wrap lines and write across lines .
2、 Conditional statements
if sentence : Conditions use relational operators , Be careful ‘==’ Don't ‘=’, Otherwise, only assignment operation will be performed , Whether to carry out if The statement in depends on whether the value in brackets is non-zero 1. General form : Use non 0 A value indicates true , use 0 Said the false ,if(flag) amount to if(1 == flag), Floating point numbers cannot be compared with 0 Compare , Only approximate values can be used to compare ;
—> if Statement explanation
3、 Loop statement
for sentence : Be careful for The contents and execution order of the three statements in the parentheses of the statement .
—> for Statement explanation
while Statement and do…while sentence : Notice the conditions that jump out of the loop in parentheses ,do…while Statement ratio while The statement executes the content once before judging the condition .
—> while Statement explanation And —> do…while Statement benefits
4、 Select statement
goto、break、continue sentence : It is unnecessary to use goto sentence ;break Statement is used to directly jump out of the loop body ;continue Statement is used to end this cycle and enter the next cycle .
—> goto、break、continue Statement explanation
—>goto、break、continue、rutern Statements and exit() The difference between functions 
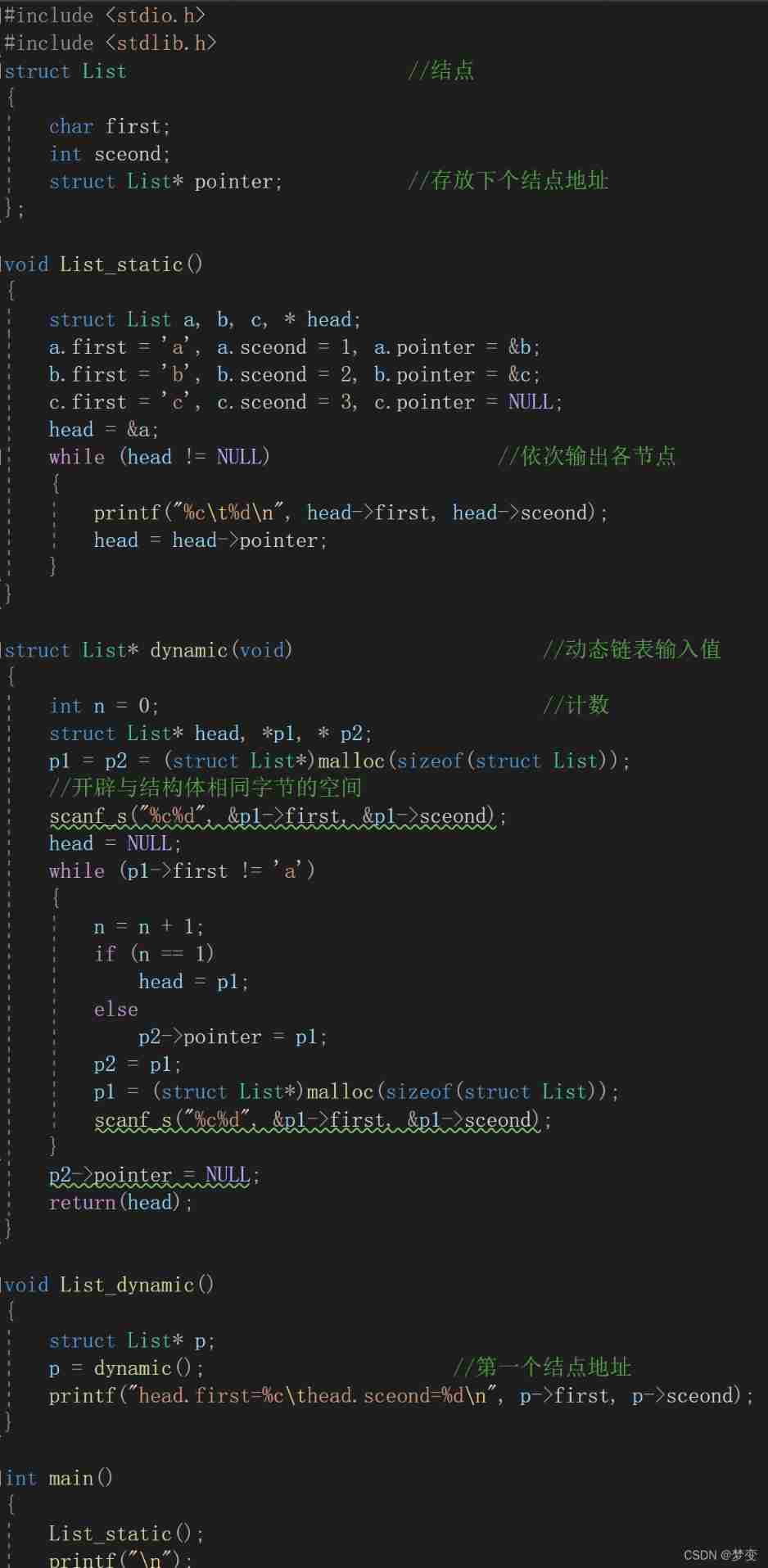
4. Array
1、 One dimensional array
Type character Array name [ Constant expression ]; Array elements are subscripted 0 Start , Character array ( character string ) The length is the number of characters + Terminator ;
—> Detailed explanation of one-dimensional array
2、 Multidimensional arrays
Approximate multiple one-dimensional arrays to form a multi array
—> Detailed explanation of multidimensional array 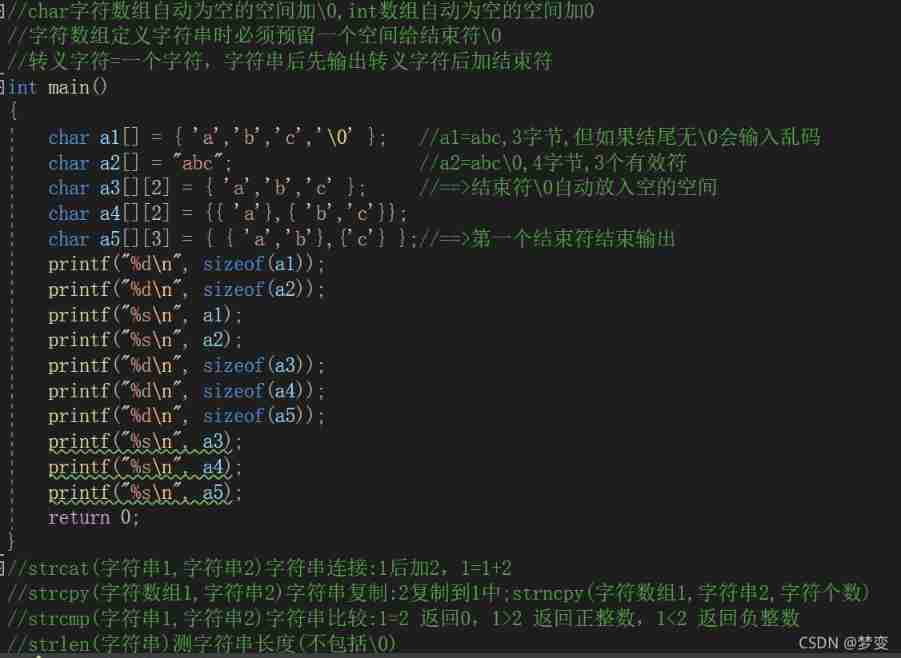
5. function
Definition : Type name Function name () / (void) / ( Parameters ) {}
—>C function
6. The pointer
7. Memory
Storage mode and lifetime of variables :
// Dynamic storage : Heap area : need malloc、calloc function (C Language ,stdlib.h) Apply voluntarily or new function (C++),free(C Language ,stdlib.h) or delete function (C++) Active release , At the end of the program, the system recycles , Slow speed ; The stack area : Store local variables ( Except static ) And formal parameters , First in, then out ( The variables used first are released at last ), Fast
// Static storage : Static storage area : Store global and static variables and external variables , Keep the value after the last operation , Until the end of the program
// Register storage : Stored in CPU In the register
//.c Source file ,.h The header file , The program can include multiple files ; external ( Outside the scope ): Outside parentheses , Function external , Outside the file
// Global variables : Keep the value after the last operation , Until the end of the program ; Global availability ; Only stored in static storage
// local variable : Dynamic local variable , Release... After the function ends , Valid within a function , Store in stack area ;static Static local variables , Stored in static storage area
//extern: Expand scope , External global variable declaration or external function declaration ,( Source file ) Declare the variable ( Used for global variables outside and below the function call function ) Or the scope of this function is extended to this location
// ( The header file ) Declare that the global variable or the function can be called by other functions
//static: Define static variables or static functions ( In the source file ),static Static local variables can retain the value of local variables of sub functions after operation , Stored in static storage area , Other documents ( Except for precompiled header files ) invisible
// static Static functions are not visible in other files
//regiter: Define register variables , Only dynamic local variables and formal parameters can be defined as register variables ,int、char、short Wait for the definition ,CPU The number of registers is limited
#include <stdio.h>
static int a1= 1; //a1 After the global variable is re assigned by the function call , Change the value of the global variable
int main()
{
static int a2 = 1; //a2 There is no return value after the local variable value is passed to other functions , Don't change
void Func1();
void Func2(int a2);
void Func3();
Func1();
Func2(a2);
Func3();
printf("a1=%d\n", a1);
printf("a2=%d\n", a2);
printf("\n");
Func1();
Func2(a2);
Func3();
printf("a1=%d\n", a1);
printf("a2=%d\n", a2);
return 0;
}
void Func1()
{
a1++;
printf("a1=%d\n", a1);
}
void Func2(int a2)
{
a2++;
printf("a2=%d\n", a2);
}
void Func3()
{
static int a3 = 1; // Static local variables a3 Keep the value after the last operation , Until the end of the program
a3++;
printf("a3=%d\n", a3);
}

8. File input and output
summary
C Language related blog network materials have been relatively complete , The above is only a summary of my knowledge , This article does not cover the knowledge points that have not been learned , The link URL is only for record , If there is infringement or content error , Please contact axzheng . If readers think this article is helpful for learning , Might as well Give a like,Respect!!!
边栏推荐
- Happy Dragon Boat Festival—— Zongzi written by canvas~~~~~
- Idea remote breakpoint debugging jar package project
- Stm32-hal library learning, using cubemx to generate program framework
- Leetcode daily question (2305. fair distribution of cookies)
- [csdn] C1 analyse des questions de formation Partie III Bar _ JS Foundation
- STM32 interrupt priority management
- Leetcode daily question (931. minimum falling path sum)
- numpy. Reshape() and resize() functions
- 要選擇那種語言為單片機編寫程序呢
- 1300. sum of varied array closed to target
猜你喜欢
![[22 graduation season] I'm a graduate yo~](/img/e2/5393b051e2d1cb4c307efdfb3f9148.png)
[22 graduation season] I'm a graduate yo~

Runtime.getRuntime().gc() 和 Runtime.getRuntime().runFinalization() 的区别

MySQL data manipulation language DML common commands

Definition and use of enum in C language

单片机学到什么程度能找到工作,这个标准不好量化

Uniapp realizes global sharing of wechat applet and custom sharing button style

NR technology -- MIMO
干单片机这一行的时候根本没想过这么多,只想着先挣钱养活自己

STM32 serial port usart1 routine

Runtime. getRuntime(). GC () and runtime getRuntime(). The difference between runfinalization()
随机推荐
When you need to use some functions of STM32, but 51 can't realize them, 32 naturally doesn't need to learn
UCI and data multiplexing are transmitted on Pusch - Part I
Stm32-hal library learning, using cubemx to generate program framework
MySQL的简单使用(增删改查)
Leetcode daily question (2232. minimize result by addressing parents to expression)
[graduation successful] [1] - tour [Student Management Information System]
Comment la base de données mémoire joue - t - elle l'avantage de la mémoire?
Error output redirection
Uniapp realizes global sharing of wechat applet and custom sharing button style
Successful graduation [2] - student health management system function development...
Getting started with JMX, MBean, mxbean, mbeanserver
Learn the contents of 5g toolbox supporting NR through the NR resources provided by MATLAB
All processes of top ten management in project management
The number of weak characters in the game (1996)
[CSDN] C1 training problem analysis_ Part II_ Web Foundation
Design and development of biological instruments
Electronic product design
307. Range Sum Query - Mutable
Nr-prach:prach format and time-frequency domain
SSB Introduction (PbCH and DMRs need to be supplemented)