当前位置:网站首页>Implementation of dynamic and static libraries (packaging dynamic and static libraries for others to use)
Implementation of dynamic and static libraries (packaging dynamic and static libraries for others to use)
2022-07-26 12:15:00 【Rabbit 7】


Hello everyone , I am a rabbit 7 , A hard-working C++ Bloggers ~
If there is something wrong with the knowledge of the article , Please correct me. ! Learn with you , Progress together
If you have not understand , You can always ask me questions , I will try my best to explain ~
If you feel the blogger's article is good , I want you to pay attention 、 give the thumbs-up 、 Collect three companies to support bloggers ~!
Your support is the driving force of my creation !
🧸 I believe the hard work now , Are the best witness for the future !
🧸 People's attitude determines posture !
This article CSDN First episode !
Catalog
Preface
This blog is the information that bloggers will review in the future , So you can rest assured to learn , It's very comprehensive , Each piece of code has been sent to everyone , If you have any questions, you can try debugging .
We must look at the pictures carefully , The words in the picture are all essence , Many details are shown in the picture 、 It's written out , So we must be careful ~
Thank you for your support , Thank you for your love , rabbit 7 I wish you all a smooth journey in your study , Everything goes well on the way of life ~!
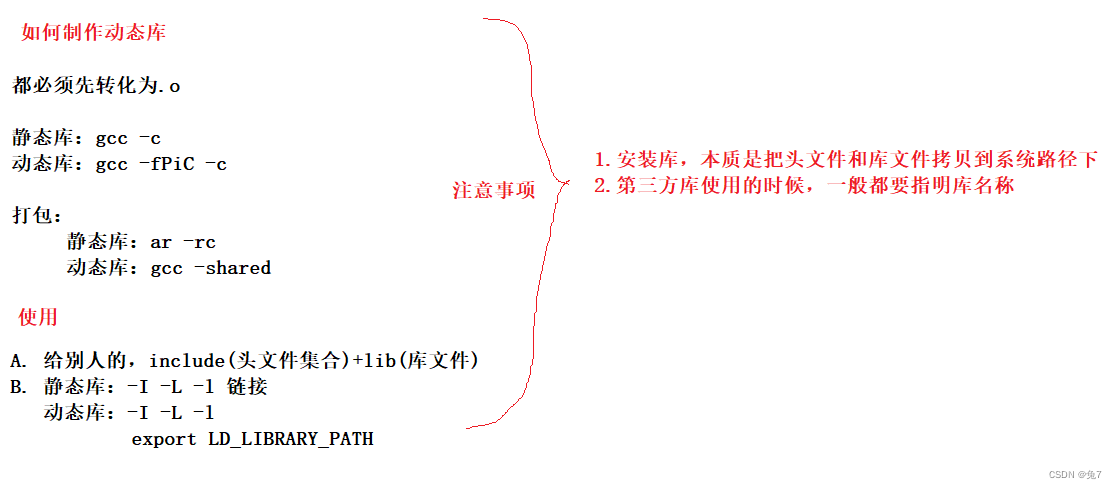
Dynamic and static libraries
- Static library (.a): When compiling the link, the program links the code of the library to the executable file . The static library will no longer be needed when the program runs .
- Dynamic library (.so): When the program is running, it links the code of the dynamic library , Multiple programs share code that uses the library .
- An executable linked to the dynamic library only contains a table of the function entry address it uses , Instead of the entire machine code of the target file where the external function is located .
- Before the executable starts running , The machine code of the external function is copied from the dynamic library on disk to memory by the operating system , This process is called dynamic linking (dynamic linking).
- Dynamic libraries can be shared among multiple programs , So dynamic linking makes the executable smaller , Save disk space . The operating system uses the virtual memory mechanism to allow a dynamic library in physical memory to be shared by all processes that need to use the library , Save memory and disk space .
Actually Dynamic and static libraries are essentially executable programs " Partially Prepared Products ".
printf,scanf,abs ... ... These interfaces , As long as users can use it , Where are the specific implementations of these interface functions ?
First of all, these functions must be written in code , Since it's code , Must be compiled , As long as it is to be compiled , Will be C The text code in the program is translated into an executable program , That is, the process of translating text into binary files . But not to printf,scanf,abs ... ... These functions form executable programs , Instead, these basic functional programming modules should be used by others .


In fact, we are finishing printf It's not just because we call printf , Among them is our Linux When compiling programs at its system level, the library is also connected . Of course , We can also have a look at :

So where are all my enclosed documents ? Of course, we can find :
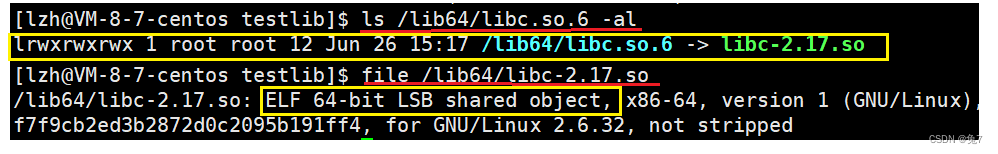
What you see in the second line is soft connection ! Of course, we can also find the linked file , You can see that this is a library file , That is, the object file after assembly (.o).

Next, let's talk about the characteristics of dynamic and static libraries :

1. Static library
Generate static libraries
The tool for generating static libraries is ar .



In this way, we form a static library , If the top Makefile Still can't understand , In fact, it is the same as the following operation :

Package it for others
First of all, we need the above Makefile add :


We can see that a mathlib The file of , This shape is inside :

This is the time , We just need to mathlib To others , Others can use .
How to use
We first write a program to call it :

When we run , Found it didn't find add.h This file .
as for stdio.h Why can I find , Because of this stdio.h This header file is in the system /usr/include/stdio.h This library directory , So the compiler can be found , And ours add.h This header file is in our current directory include in , It's our custom , So it can't find , So in order to find :

We can see , Although there is still a mistake here , But the report is not missing add.h This document , So it was found .
But it still says my_add It doesn't exist , Because we didn't tell the compiler my_add It's a method , Although the header file was found , But the function does not . Because the header file only declares , The specific implementation does not give . So we need to find that library !
Then why did we compile C It was not specified when ?
Because C The library itself is under the corresponding path , These paths are system paths , Compilers can be found , And we wrote , The compiler cannot be found , So we need to add .


We found that the error was still not reported , In fact, it's because although we here mathlib/lib There is only one library , But what if there are multiple ? So which link is the problem , So we must specify which library to link ! As I said before , The name of the library is to remove the prefix , Remove the suffix , The rest is the library name !

We found that , Finally, it is generated a.out This executable program .
therefore , We give our library to others , What you give others is a set of header files , A group of lib , This header file only contains the function declaration .

So it's ok if we don't want to use so many options .
The reason why we use so many options is that the header files and libraries we implement are not in the system , If you copy our header files and libraries to the system path , Then we don't need to bring those options :

First, we copy to the system path through the above two commands , Run after copying , I found something wrong with the header file , Still no definition my_add , This is because although there is no need to specify the library path and header file path , Because it has been under the system path , But we also need to specify the library name , That is to say, I have to bring -l .
As for why C Language doesn't need , It's because we compiled C Language , By default, the compiler is looking for C The library , So it knows C What is the library , It compiles by default , But here it doesn't know , So you have to bring -l .

So we just The process of copying is actually the process of installing the Library .
For example, if we package the static library , If you want to give it to others , Then add an installation script , In fact, just copy the file to the system path .
Of course , This is still very bad , Because I don't know what kind of code I wrote for a long time , And don't pollute others' libraries , So we need to delete the added :

Be careful not to make mistakes , Actually we The process of deleting is the process of uninstalling the Library .
2 Dynamic library
Generate dynamic library
There is no need to generate dynamic libraries ar 了 , It's just gcc perhaps g++ .
- shared: Represents the format for generating shared libraries
- fPIC: Generate location independent code (position independent code)
- Library name rule :libxxx.so
Here's an explanation Generate location independent code :
Static libraries copy code directly into executable programs , Load into memory , Then it can be used directly in the process .
The dynamic library requires your program and the library program to produce a secondary interaction process . Then your program must be able to find the corresponding library , But where is the library loaded in memory , It is uncertain to map to which region , So we must make the address of the library generate location independent addresses , In this way, you can map anywhere or generate associations .
Pack it for others
Next, let's operate :

We can see that the corresponding dynamic library is generated .
So if we want to package dynamic libraries for others , You also need to provide others with a set of header files and a library file , It is the same as static library !
How to use
We still want to put the header file into include in , libcal.so Put it in lib in , Then compile it :

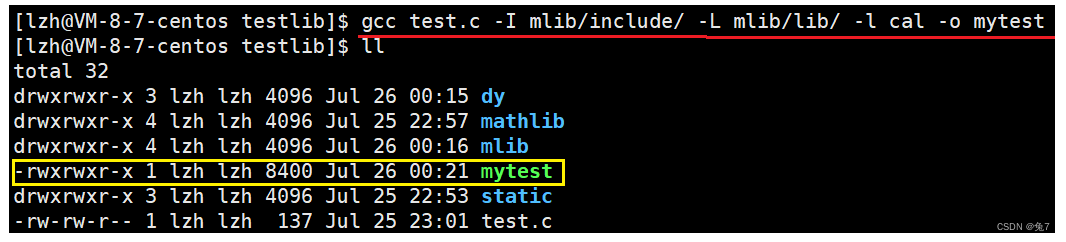
We can find out , Successfully formed mytest This executable program .

But dynamic libraries are still a little different , We can see , If we go straight ./mytest This executable program , As a result, it doesn't work .
as a result of : When loading this dynamic library , This file was not found .
Because the one in front of us -I -L -l It tells the compiler where the header file and library are and which library it is during compilation , But when the compilation is successful, the executable program already exists .
When ./mytest Turn executable into process , But to turn an executable into a process, you must load the current code into memory , But when it is loaded into memory , The associated dynamic library synchronized with it cannot be found , This time the operating system cannot be found . Because the operating system finds that this executable depends on a library , But Ku doesn't know which .
Of course, it can also prove this statement :

So that's what I said above , Although I told the compiler when compiling , But when the program is running, it has nothing to do with the compiler , At this time, the system cannot find it .
There are three ways :
- Put this libcal.so Copy this library to the system path ( Not recommended )
- Configure in the system (ldconfig To configure /etc/ld.so.conf.d/,ldconfig to update )
- Export an environment variable LD_LIBRARY_PATH , It represents the program runtime , The path to search when dynamically finding the Library .
Next, I will use method 3 to operate :

After importing environment variables, we found that LD_LIBRARY_PATH You can find the dynamic library in !

At this time ldd , You can find libcal.so You can find .

After finding it, you will find that it can run directly !
3 summary
In fact, the above method 2 can also be used .

We can see that this configuration file is actually a path .
Next, I'll do the configuration :


We found that , Finally, it runs successfully .
But in fact, the most commonly used later is to copy the library to the directory .
4 Using external libraries
There are actually many libraries in the system , They usually consist of a set of interrelated functions used to complete a common task . For example, the function used to process the screen display (ncurses library )

In fact, direct compilation can run , There is no concept of introducing mathematical library , The reason is that the current header file contains a compiler that automatically helps us find , So there's no problem .
But we can also find it ourselves :

You can see this m Come out . And then we ./a.out It works .

That's it Dynamic and static library All the knowledge of , If you like reading this article and have some harvest , You can support rabbit 7 , to rabbit 7 Pay more attention for three times , Your attention is my greatest encouragement , It is also my creative motivation ~!
Thank you again for watching , Thank you for your support !
边栏推荐
- Flutter's learning path
- Sword finger offer 25. merge two sorted linked lists
- Pytest interface automation test framework | execute use cases through markup expressions
- 儿童玩乐场所如何运营?
- pytest接口自动化测试框架 | pytest之fixture介绍
- pytest接口自动化测试框架 | pytest常用插件
- Sunflower senior product director technology sharing: how to apply in AD domain environment
- Who is responsible for the problems of virtual idol endorsement products? And listen to the lawyer's analysis
- Pytest interface automation test framework | setup and teardown functions of pytest
- pytest接口自动化测试框架 | fixture调用fixture
猜你喜欢

DS-112时间继电器
RFID的工作原理

Understand the string class

SSJ-21B时间继电器

网络协议:TCP/IP协议

Is it easy to find a job after programmer training?
On the construction and management of low code technology in logistics transportation platform

Sword finger offer 25. merge two sorted linked lists

羽毛球馆的两个基础设施你了解多少?
海外APP推送(下篇):海外厂商通道集成指南
随机推荐
大佬们,cdc oracle 怎么设置从指定scn号开始读取,或是怎么设置只读全量的归档,不去读取快
Understand the string class
Li Kai: the interesting and cutting-edge audio and video industry has always attracted me
以太网驱动详解之RMII、SMII、GMII、RGMII接口
Introduction to FPGA (II) - one out of two selector
Fineos announced the open registration of grouptech connect activities in 2022
什么是Per-Title编码?
You Yuxi recommends vite to beginners [why use vite]
【2243】module_ param.m
Pytest interface automation test framework | use decorators to decorate the use cases that need to be run
大佬们,请教一下,我按照文档配了cdc连接oracle,总是运行报错找不到类 ValidstionE
QT入门引导 及其 案例讲解
14.2字节流学习
uniapp h5、app引用外部在线js
代码实例详解【可重入锁】和【不可重入锁】区别?
Overseas app push (Part 2): Channel Integration Guide for overseas manufacturers
Beauty salon management system unified management system?
Sword finger offer 25. merge two sorted linked lists
Pytoch deep learning quick start tutorial -- mound tutorial notes (II)
Pytest interface automation test framework | rerun failed cases