当前位置:网站首页>[Inter-process communication]: pipe communication/named/unnamed
[Inter-process communication]: pipe communication/named/unnamed
2022-08-02 16:04:00 【white U】
进程间通信的方式:
- 管道 (半双工(Can only receive or send,不能同时) ,全双工(同步进行,同发同收)
- 信号量
- 共享内存
- 消息队列
- 套接字
- 管道: 有名管道和无名管道
有名管道:可以在任意进程间通信
无名管道:Only communicate between parent and child processes - 定义:
Link data flow from one process to another
说人话:The output of one process is passed through some medium as the input of another process
This medium is the pipe.This is also why pipes are needed.
命令的写法:cmd1 | cmd2
比如shell Have both standard input and standard output piped to the terminal screen:
cmd1 standard input command(键盘)
cmd1 Standard output is passed to cmd2 ,作为cmd2的标准输入
cmd2 标准输出到屏幕
如下图: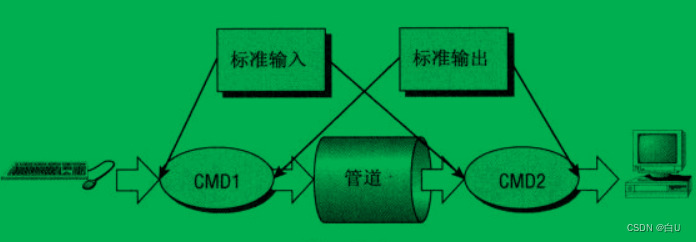
- 管道通信:Program implementation if required,需要两个函数(popen()和pclose())to transfer data between two processes.
command :The name of the program to run and the corresponding parameters
open_mode:r / w 权限
r : The exported program can be used by the exporting program,Output program usepopen返回的FILE*文件流指针,使用freadto read the output of the exported program.
w: The output program passesfwrite Send data to the output program.Instead, the output program reads data from standard input.【It doesn't know that the meal has just been spit out of someone else's mouth.放在盘子里.】
【接盘侠,It can be understood as getting a second-hand product that someone else spit out from a matchmaking agency】
#include<stdio.h>
FILE *popen(const char* command,const char* open_mode);
int pclose(FILE *stream_to_close);
popen() :Allows a program to start another program as a new process.
That is, the output command of one program is used as the input of another program
pclose() : 只在popenReturns when the started process ends.The return value is the exit code of the process in which the closed file stream resides.If the parent process obtains the exit code of the process in advance,Then the process and its resources are reclaimed.其返回值为-1或error.
也就是pcloseMust execute before the parent process gets the process exit code.
例如:ps -ef 输出 | 输入grep “main”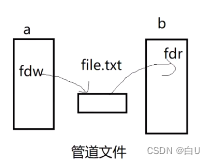
出现一下问题:
1. Pipes must read and write processes at the same time open,否则会阻塞
2. 如果管道没有数据,那么read ,阻塞
3. 管道的写端关闭,读read返回值为0
4. 管道的读端关闭,Writing will generate an exception(发送SIGPIPE)
(Girlfriend hangs up,What's the use of you keep talking?)
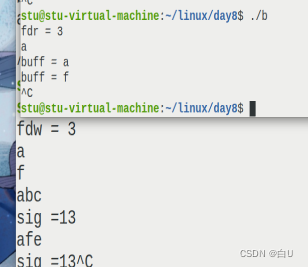
#include<signal.h>
void fun(int sig)
{
printf("sig =%d",sig);
}
int main()
{
signal(SIGPIPE,fun);
- 创建有名管道
mkfifo FIFO (fifo 可以随便起)
touch a.c b.c
特殊之处:Open the filepipe file,会在内存中开辟一片空间,The written data will be written to memory.No matter the named pipe or the unnamed pipe
- a.c文件
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
int main()
{
int fdw = open("fifo", O_WRONLY);
if (fdw == -1)
{
exit(-1);
}
char buff[128] = {
0 };
fgets(buff, 128, stdin);
write(fdw, buff, strlen(buff) - 1);
close(fdw);
exit(0);
}
- b.c文件
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
int main()
{
int fdr = open("fifo", O_RDONLY);
if (fdr == -1)
{
exit(1);
}
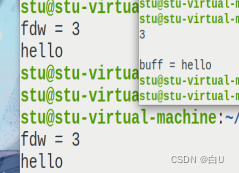
printf("fdr =%d\n", fdr);
char buff[128] = { 0 };
int num = read(fdr, buff, 127);
printf("buff =%s\n", buff);
close(fdr);
exit(0);
}
- 改进:(连续发送数据,和接收数据)
No data in the pipe will block(Just don't close the pipe)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
int main()
{
int fdw = open("fifo", O_WRONLY);
if (fdw == -1)
{
exit(-1);
}
while(1){
char buff[128] = {
0 };
fgets(buff, 128, stdin);
if(strncmp(buff,"end",3)==0 )
{
break;
}
write(fdw, buff, strlen(buff) - 1);
}
close(fdw);
exit(0);
}
- b.c文件
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
int main()
{
int fdr = open("fifo", O_RDONLY);
if (fdr == -1)
{
exit(1);
}
printf("fdr =%d\n", fdr);
while(1){
char buff[128] = { 0 };
int num = read(fdr, buff, 127);
if(num == 0) //读到的数据为0
{
break;
}
printf("buff =%s\n", buff);
}
close(fdr);
exit(0);
}
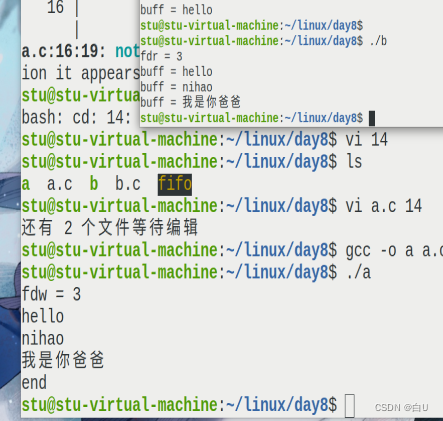
无名管道创建
man pipe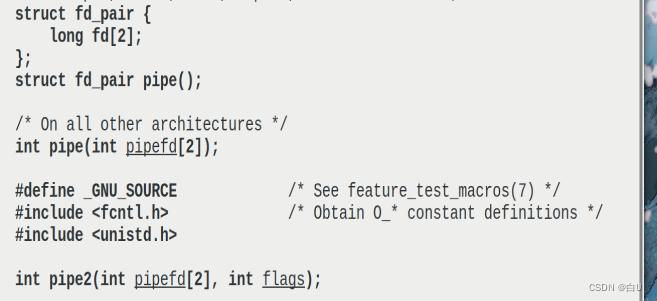
通过pipe打开管道文件,Return the file descriptor of the pipe directly
会用fork()产生一个子进程,(So the parent process is responsible for writing,The child process is responsible for reading)
Both parent and child processes must be closed,The file is closedca.(The last person left in the classroom,才算真的关闭)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
int main()
{
int fd[2];
if (pipe(fd) == -1) //fd[0] 读,fd[1]写
{
exit(1);
}
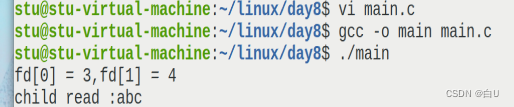
printf("fd[0] = %d,fd[1] = %d\n", fd[0], fd[1]);
pid_t pid =fork();
if(pid == -1)
{
exit(0);
}
if(pid == 0)
{
close(fd[1]);
char buff[128] ={
0};
read(fd[0],buff,127);
printf("child read :%s\n",buff);
close(fd[0]);
}
else
{
close(fd[0]);
write(fd[1],"abc",3);
close(fd[1]);
}
exit(0);
}
- 面试会问:
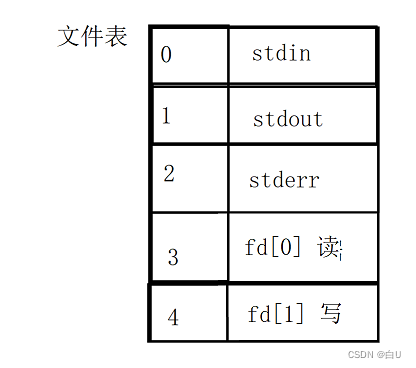
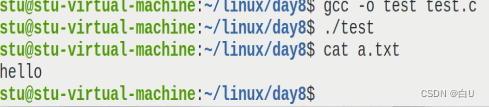
dup(3,1)将3file descriptor to copy to1的位置ls>a.test文件重定向 (append and overwrite)
Because standard input and output have already been useda.txt 覆盖,So there is no standard output and standard input.因此hello打印再a.txt中
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
int main()
{
int fd = open("a.txt", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT, 0600)
{
if (fd == -1)
{
printf("open a.txt filed\n");
exit(1);
}
dup2(fd, 1);
dup2(fd, 2);
}
printf("hello\n"); //Because standard input and output have already been useda.txt 覆盖,So there is no standard output and standard input.因此hello打印再a.txt中
exit(0);
}
管道的实现: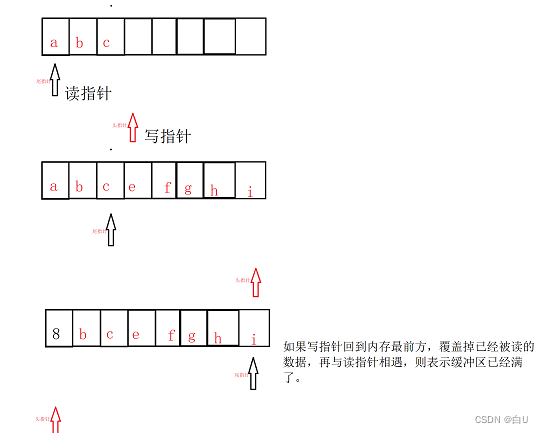
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Qt | 串口通信 QSerialPort
HCIE学习记录——数据封装与常用协议(TCP/UDP)
Litestar 4D – WebCatalog 7:全自动数据管理
Unity-3D数学
双链表(普通迭代器和常性迭代器)
光学好书推荐
net start mysql 服务名无效。
内存和硬盘、磁盘的区别
TypeScript
PostgreSQL 协议数据样例
Test case exercises
从FAST TCP到POWERTCP
unity-shader(入门)
饥荒联机版Mod开发——配置代码环境(二)
分布式一致性协议-Paxos
【线程安全】用户级,内核级,组合级线程|线程同步的处理(条件变量)|strtok_r(可冲入函数)
Oauth2.0 resource server construction
Apache ShardingSphere 5.1.1 正式发布
mininet multihomed topology
UnityAPI-Ray-Physics