当前位置:网站首页>[C language] dynamic memory allocation
[C language] dynamic memory allocation
2022-06-12 03:15:00 【Ordinary people 1】
Catalog
The introduction of dynamic memory function
Yes NULL Dereference operation of pointer
Use free Release a part of dynamic memory
Multiple releases of the same dynamic memory
Forget to release dynamic memory ( Memory leak )
Why dynamic memory allocation
There are two ways to use memory
1. Create a variable
2. Create an array
int a = 1;
int arr[10];But these two methods have some characteristics
1. Space is a fixed size , It won't change
2. You must know in advance how much space to open up , You must specify the length of the array .
But actually , The need for space , Sometimes , We don't know how much memory space to allocate , Sometimes you need to know when the program is running , For example, use an array to store the age of students in the class , We don't know how many students , I don't know how much space is needed , And the compiler does not support variable length arrays , Constant expression expected . Now , Using arrays to allocate fixed space is not suitable .
To better allocate memory space , At this time, we need our dynamic memory allocation .
When it comes to memory , We know that memory is divided into 3 Regions , The stack area , Heap area , Static zone .
The stack area —— local variable , Function parameter
Heap area —— Dynamic memory allocation
Static zone —— Global variables , Static variables ( Such as static int a = 10)

The introduction of dynamic memory function
malloc
void *malloc( size_t size ); A function opens up a continuous space to the heap , Return the starting address of the space .
● It's a success , Return a pointer to the opened space
● Failed to open up , return NULL The pointer , So check whether the development is successful
● The type returned is void*, therefore malloc I don't know the type of development , Their own decisions
● If size by 0,malloc The standard of behavior is undefined , Depends on the compiler
● Remember to reference the header file #include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main()
{
int* p = (int*)malloc(10 * sizeof(int));
if (p == NULL)
{
// One way to print the cause of the error
printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));
}
else
{
// Normal use
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
*(p + i) = i;
}
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("%d ", *(p+i));
}
}
// Release
free(p);
p = NULL;
return 0;
}free
void free( void *memblock );
c Language provides a function free, Specially used for dynamic memory recovery and release
The header file is #include <stdlib.h>
Pay attention to some points. :
Memory for dynamic development , If not , that free Function behavior is undefined
If the pointer is NULL The pointer , Then the function does nothing
By free It's better to manually set the pointer after to NULL, Avoid wild pointer , Cause mistakes
free(p);
p=NULL;calloc
void *calloc( size_t num, size_t size );
calloc It is also used to dynamically open up space . The header file is also #include <stdlib.h>
And malloc The difference between :
● Different parameters
● And malloc The only difference is calloc Each byte of the requested space is initialized to... Before returning the address 0.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main()
{
//malloc(10*sizeof(int));
int*p = (int*)calloc(10, sizeof(int));
if (p == NULL)
{
printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));
}
else
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("%d ", *(p + i));
}
}
free(p);
p = NULL;
return 0;
}debugged , You can see that the memory is initialized to 0 了

According to the actual situation , If initialization is required, use calloc
realloc
void *realloc( void *ptr, size_t size );
Header files are also references #include <stdlib.h>
ptr Is the memory address to be adjusted
size New size after adjustment , Instead of increasing the size
The return value is the starting memory position after adjustment
realloc Functions make dynamic memory management more flexible
Sometimes we find that the application space is too small , Sometimes I feel that the application is too big , In order to allocate memory reasonably , We can flexibly adjust the size of memory ,realloc You can adjust the size of dynamic memory
matters needing attention
realloc There are two situations in adjusting memory
situation 1: There is enough space behind the original space
● If p There is enough memory to append after the space pointed to , Then... Is added directly , After the return p
situation 2: There is not enough space after the original space
● If p There is not enough memory space to append after the space pointed to , be realloc The function will find a new memory area again
Open up a space to meet the needs , And copy back the data in the original memory , Free up old memory space , Finally, return the newly opened memory space address
● You have to use a new variable to receive realloc The return value of

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main()
{
int* p = (int*)malloc(20);
if (p == NULL)
{
printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));
}
else
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
*(p + i) = i;
}
}
// In the use of malloc Opened up 20 Space
// Suppose here 20 One byte is not enough for our use
// I hope we can have 40 Bytes of space
// You can use realloc To adjust the dynamically opened memory
int* ptr = realloc(p, 40);
if (ptr != NULL)
{
p = ptr;
int i = 0;
for (i = 5; i < 10; i++)
{
*(p + i) = i;
}
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("%d ", *(p+ i));
}
}
free(p);
p = NULL;
return 0;
}Common mistakes
Yes NULL Dereference operation of pointer
int main()
{
int* p = (int*)malloc(INT_MAX/4);
*p = 20;// If p Is a null pointer , There will be problems ;
free(p);
return 0;
}A cross-border visit
int* p = (int*)malloc(40);
if (p == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
int i = 0;
// Transboundary
for (i = 0; i <= 10; i++)
{
*(p + i) = i;
}
free(p);
p = NULL;Should be i<10
For non dynamic memory free
int a = 10;
int* p = &a;
free(p);
p = NULL;Use free Release a part of dynamic memory
int* p = (int*)malloc(40);
if (p == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
*p++ = i;
}
free(p);
return 0; 
p Not at the starting point of dynamic memory development , We should redefine a pointer to remember the starting address
Multiple releases of the same dynamic memory
int* p = (int*)malloc(40);
if (p == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
free(p);
free(p);
Forget to release dynamic memory ( Memory leak )
Forget to free dynamically opened memory , Will cause memory leaks
while (1)
{
malloc(1);
Sleep(1000);
}Apply for memory without returning it , The memory of a computer is limited , Memory will run out
Conclusion
All right. , This time about c The knowledge of language dynamic memory is over , A great bai .
边栏推荐
- SSH public key login failed with error: Sign_ and_ send_ pubkey: no mutual signature supported
- [DFS "want" or "don't"] seek subsets; Seeking combination
- Special materials | household appliances, white electricity, kitchen electricity
- 无限循环判断方法;
- 【鸿蒙】 使用定时器做一个简单的抢红包小游戏
- Final summary of addition, deletion, modification and query - 2.2 (knowledge points in mapper.xml)
- Calculus review 2
- [high code file format API] downing provides you with the file format API set Aspose, which can create, convert and operate more than 100 file formats in just a few lines of code
- DbNull if statement - DbNull if statement
- 2020-12-06
猜你喜欢

Requirements and business model innovation - Requirements 12 - process oriented modeling

The idea of setting the flash memory management and resource size, and the quantitative relationship among parallelism, slot, and taskmanager quantity

Solutions to errors in ROM opening by MAME

cupp字典生成工具(同类工具还有crunch)

Cupp dictionary generation tool (similar tools include crunch)

Kubernetes affinity learning notes

2020-12-10
![Leetcode 6[finding rules] Z-transform the leetcode path of heroding](/img/c0/aca2eb185ce4b423df9ee171ee91e1.jpg)
Leetcode 6[finding rules] Z-transform the leetcode path of heroding

余压监控系统在高层民用建筑的应用
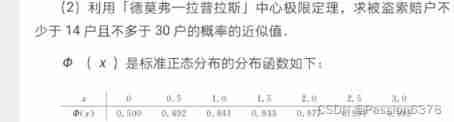
central limit theorem
随机推荐
Wechat applet project example - renju for two
Laravel 8 selects JWT for interface verification
The four pain points of enterprise digitalization are solved by low code platform
JSON and XML pros and cons
Computer common sense
Key points of code neatness (III)
Inverted string - two solutions
[digital signal processing] correlation function (energy signal | cross correlation function of energy signal | autocorrelation function of energy signal)
The road of global evolution of vivo global mall -- multilingual solution
GeForce GTX 2050/2080/3090/A6000自动安装nvidia显卡驱动
Unity3D中DrawCall、Batches、SetPassCall
Infinite loop judgment method;
Restful interface design specification [for reference only]
Comment prévenir les incendies électriques dans les centres commerciaux?
Comparaison de la taille des fractions
laravel 8 选用 jwt 进行接口验证
Go 语法 变量
Go recursive infinite classification
1186_ Accumulation of embedded hardware knowledge_ Triode and three electrodes
Application of ard3m motor protector in coal industry