当前位置:网站首页>案例驱动 :从入门到掌握Shell编程详细指南
案例驱动 :从入门到掌握Shell编程详细指南
2022-06-28 11:35:00 【华为云】
@TOC
一、概述
Shell是一个命令行解释器,接收应用程序用户命令,去调用操作系统的内核。它又是一种程序设计语言。作为命令语言,它交互式解释和执行用户输入的命令或者自动地解释和执行预先设定好的一连串的命令。它的特点是易编写、非常灵活。
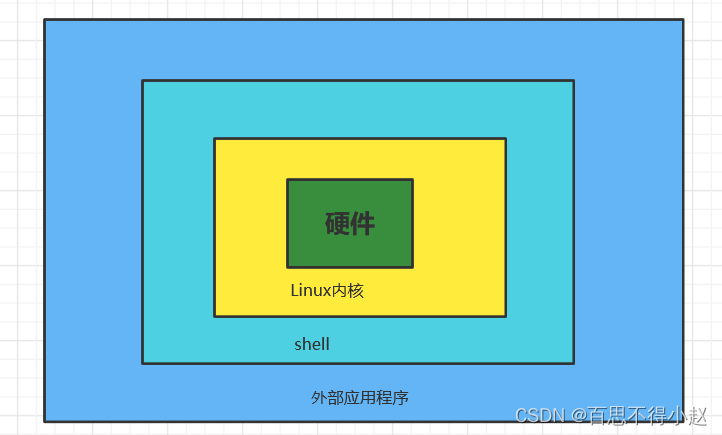
Shell解析器
Linux提供的Shell解析器有如下几种:
cat /etc/shells 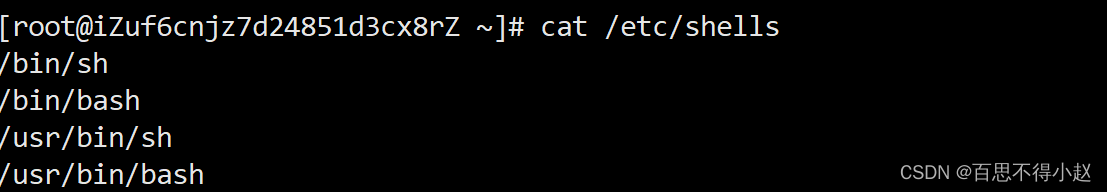
在centOS中默认的解析器为bash
echo $SHELL
二、入门案例
shell 脚本以#!/bin/bash开头(指定解析器)
案例:创建一个Shell脚本,输出hello shell
第一步:编写shell脚本
首先创建一个helloShell.sh脚本文件,然后输入如下内容
#!/bin/bashecho "hellom shell"

第二步:运行shell脚本
- 第一种:采用bash或sh+脚本的相对路径或绝对路径(不用赋予脚本权限)
sh helloShell.sh bash helloShell.shsh /root/Test/helloShell.sh bash /root/Test/helloShell.sh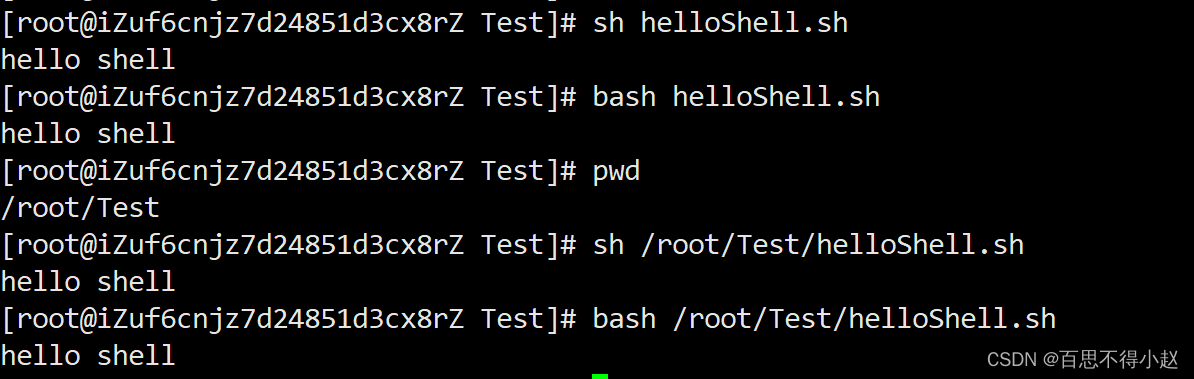
- 第二种:采用输入脚本的绝对路径或相对路径执行脚本(必须具有可执行权限)(没有给权限就会出现如下错误)

首先要赋予helloworld.sh 脚本的+x权限
chmod 777 helloShell.sh 然后重新运行
./helloShell.sh 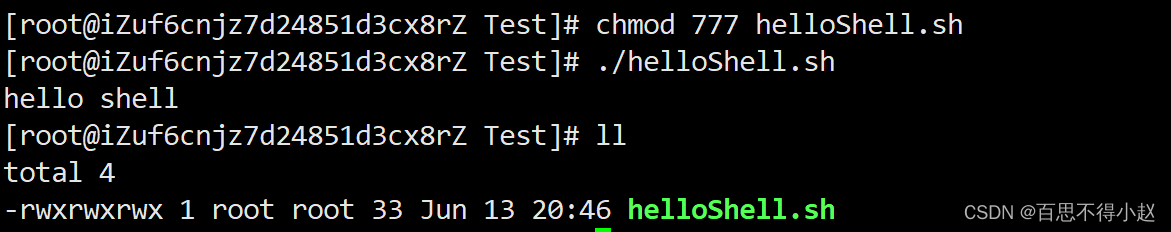
案例:在
/root/Test路径下创建一个zhangsan.txt的文件,然后给文件中增加“ I love shell”.
具体实现如下:
[[email protected] Test]# > demo1.sh[[email protected] Test]# vi demo1.sh 在demo1.sh中输入如下内容#!/bin/bashcd /root/Testtouch zhangsan.txtecho "I love shell" >>zhangsan.txt测试运行成功:
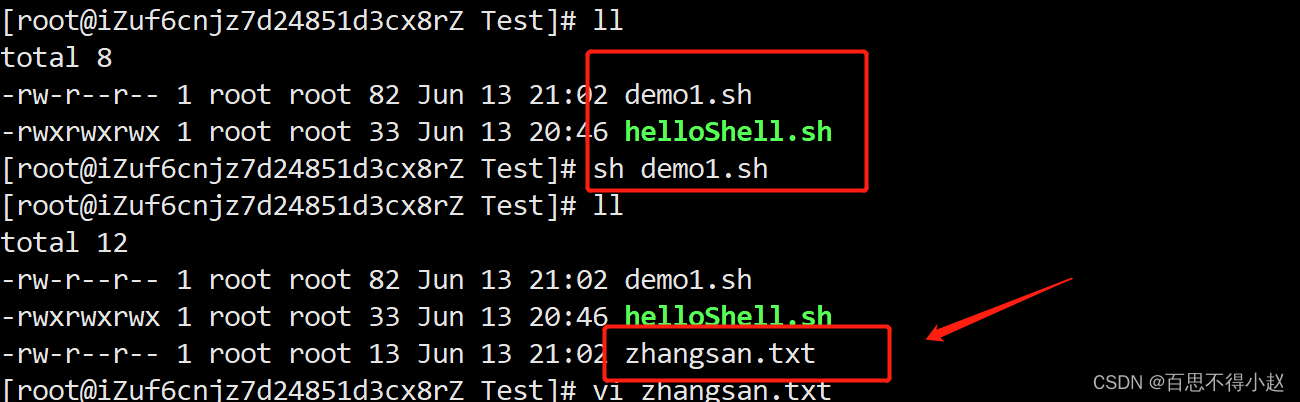

三、Sell中的变量
系统变量
常用系统变量$HOME、$PWD、$SHELL、$USER等
查看系统变量的值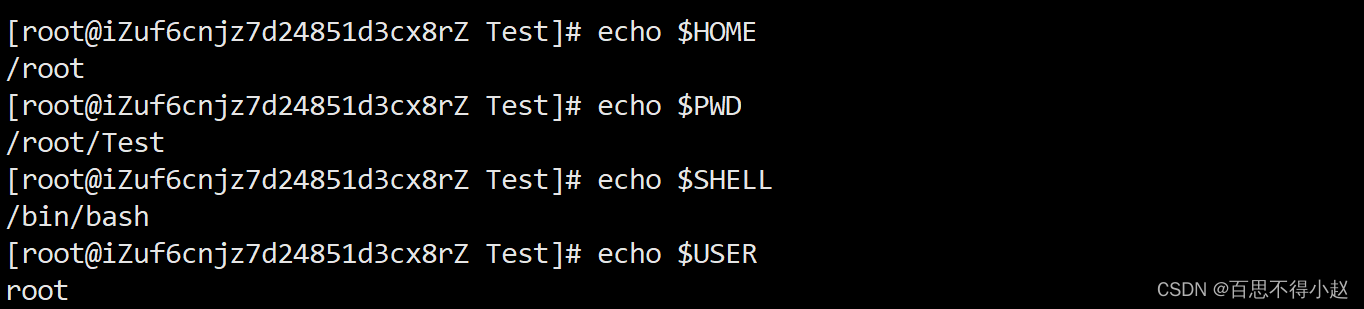
自定义变量
基本语法
- 定义变量:
变量=值 - 撤销变量:
unset 变量 - 声明静态变量:
readonly变量,注意:不能unset
其他说明
变量名称可以由字母、数字和下划线组成,但是不能以数字开头,环境变量名建议大写。
等号两侧不能有空格
在bash中,变量默认类型都是字符串类型,无法直接进行数值运算
变量的值如果有空格,需要使用双引号或单引号括起来
案例:
1、定义变量S
2、撤销变量S
3、声明静态的变量A=2
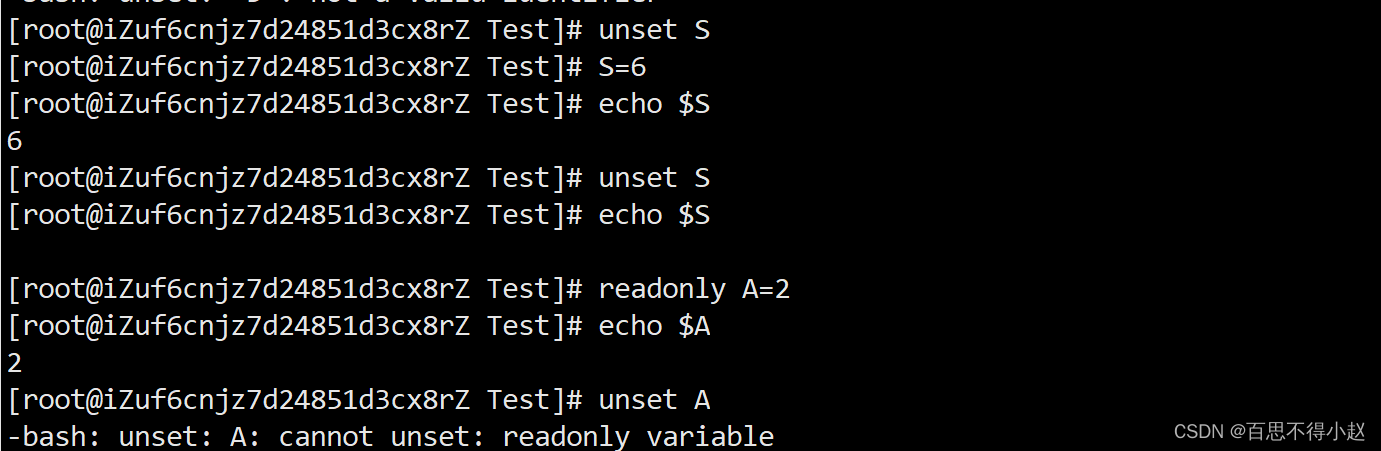
补充:把变量提升为全局环境变量,可供其他Shell程序使用。
语法:export 变量名
案例:使用shell脚本输出变量B
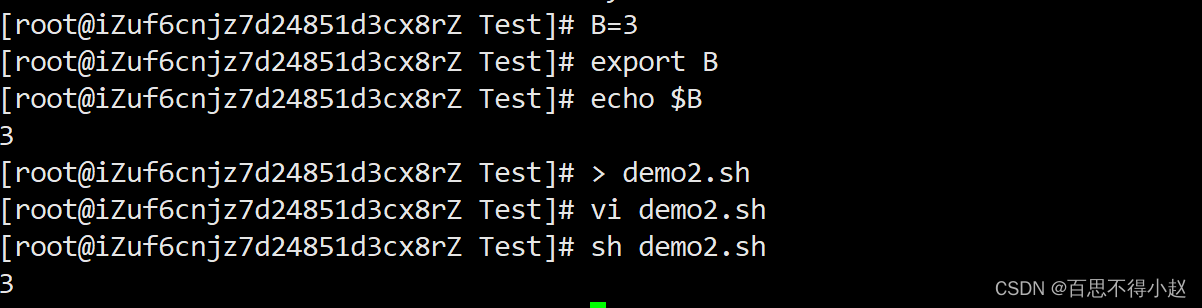

特殊变量
$n
$n(功能描述:n为数字,$0代表该脚本名称,$1-{10})
案例:输出该脚本文件名称、输入参数1和输入参数2 的值
#!/bin/bashecho "$0 $1 $2 "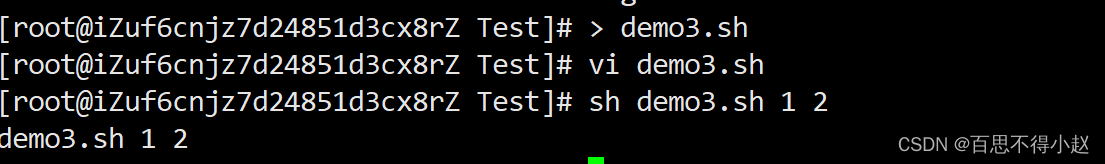
$#
$# (功能描述:获取所有输入参数个数,常用于循环)
案例:获取输入参数的个数
#!/bin/bashecho $#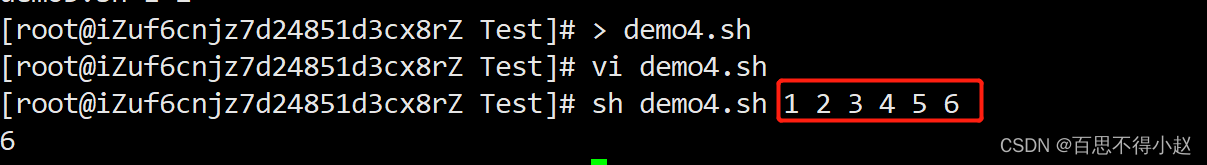
$*、[email protected]
$*(功能描述:这个变量代表命令行中所有的参数,$*把所有的参数看成一个整体)
[email protected](功能描述:这个变量也代表命令行中所有的参数,不过[email protected]把每个参数区分对待)
案例:打印输入的所有参数
#!/bin/bashecho $*echo [email protected]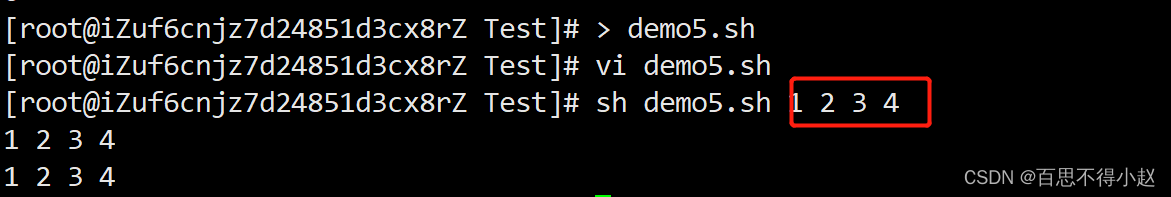
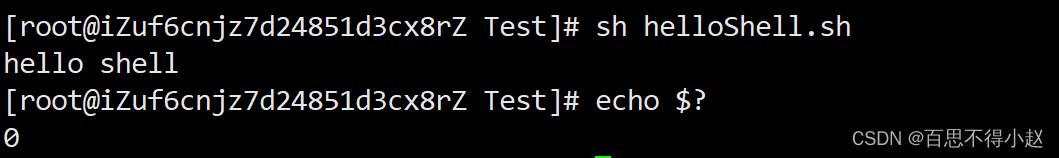
$?
$? (功能描述:最后一次执行的命令的返回状态。如果这个变量的值为0,证明上一个命令正确执行;如果这个变量的值为非0(具体是哪个数,由命令自己来决定),则证明上一个命令执行不正确了。)
案例:判断helloShell.sh脚本是否正确执行
四、运算符和条件判断
运算符
基本语法
“$((运算式))”或“$[运算式]”- expr + , - , *, /, % 。==注意:expr运算符间要有空格==
案例:使用
expr
1、计算3+2的值
expr 2 + 3
2、计算2+3x4
expr `expr 2 + 3` \* 4
案例:使用$符号
计算2+3乘4
S=$[ (2+3) *4 ]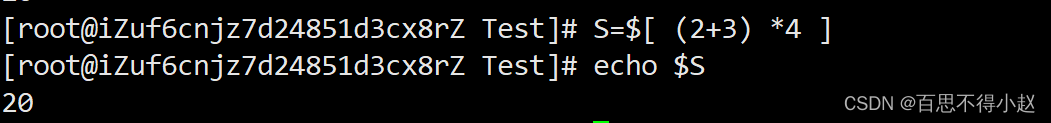
条件判断
基本语法
[ condition ](注意condition前后要有空格)条件非空即为true,[ lisi ]返回true,[] 返回false。常用判断条件
- 两个整数之间比较

案例:比较 2 大于 1
[ 2 -gt 1 ]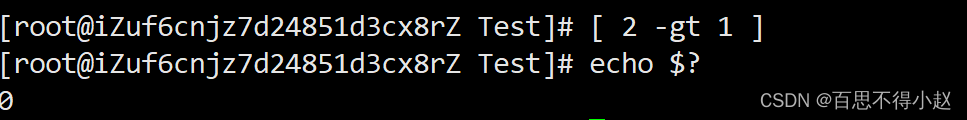
- 按照文件权限进行判断

案例:helloShell.sh是否具有写权限
[ -w helloShell.sh ]
- 按照文件类型进行判断

案例:
/root/Test/helloShell.sh目录中的文件是否存在
[ -e /root/Test/helloShell.sh ]
五、流程控制
if
基本语法
if [ 条件判断式 ];then 程序 fi if [ 条件判断式 ] then 程序 fi注意事项:
- [ 条件判断式 ],中括号和条件判断式之间必须有空格
- if后要有空格
案例:输入一个数字,如果是1,则输出the number is 1,如果是2,则输出the number is 2,如果是其它,什么也不输出。
#!/bin/bashif [ $1 -eq "1" ]then echo "the number is 1"elif [ $1 -eq "2" ]then echo "the number is 2"fi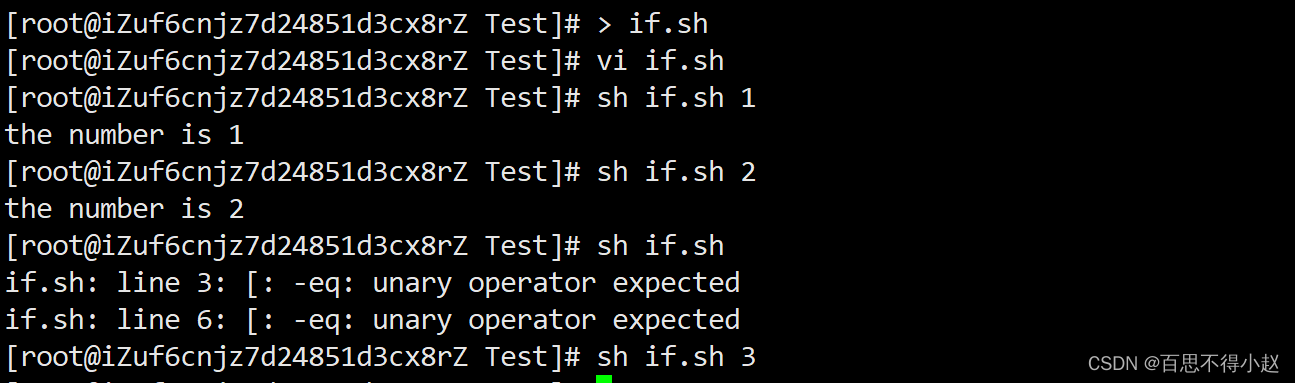
case
基本语法
case $变量名 in "值1") 如果变量的值等于值1,则执行程序1 ;; "值2") 如果变量的值等于值2,则执行程序2 ;; …省略其他分支… *) 如果变量的值都不是以上的值,则执行此程序 ;; esac注意事项:
- case行尾必须为单词“in”,每一个模式匹配必须以右括号“)”结束。
- 双分号“;;”表示命令序列结束,相当于java中的break。
- 最后的“*)”表示默认模式,相当于java中的default。
案例:输入一个数字,如果是1,则输出the number is 1,如果是2,则输出the number is 2,如果是其它,输出 other number。
#!/bin/bashcase $1 in "1") echo "the number is 1";;"2") echo "the number is 2";;*) echo "other number";;esac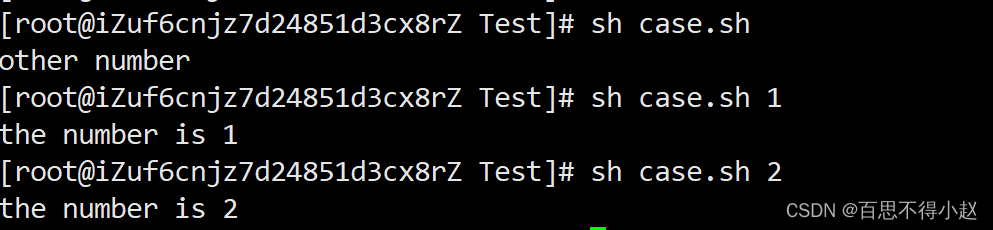
while
基本语法
while [ 条件判断式 ] do 程序 done案例:从1加到100
#!/bin/bashs=0i=1while [ $i -le 100 ]do s=$[$s+$i] i=$[$i+1]doneecho $s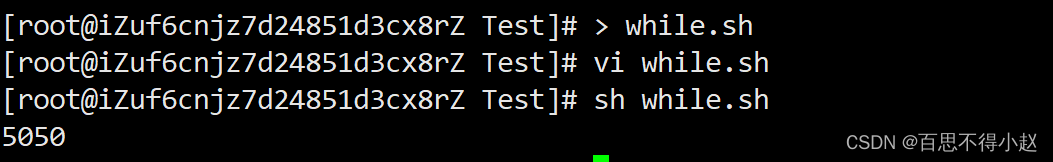
for
for (( 初始值;循环控制条件;变量变化 )) do 代码 done for 变量 in 值1 值2 值3… do 程序 done案例:
1、打印所有输入参数
#!/bin/bashfor i in $*do echo "value is : $i"done 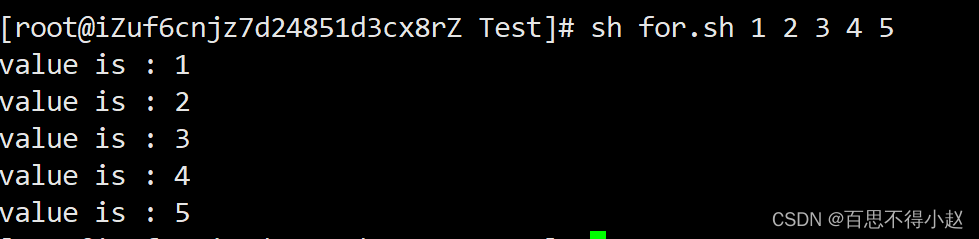
2、从1加到100
#!/bin/bashs=0for((i=0;i<=100;i++))do s=$[$i+$s]doneecho $s
六、读取控制台输入内容
基本语法
read(选项)(参数) - 选项: - `-p:指定读取值时的提示符;` `-t:指定读取值时等待的时间(秒)`参数 变量:指定读取值的变量名案例:提示5秒内,读取控制台输入的名称
#!/bin/bashread -t 5 -p "input your name" NAMEecho $NAME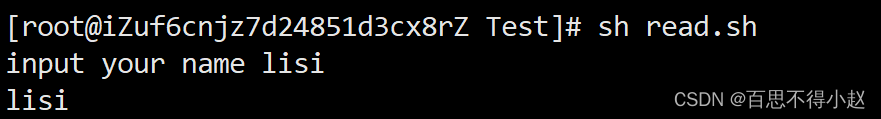
七、函数
系统函数
basename基本语法
basename [string / pathname] [suffix] 功能描述:basename命令会删掉所有的前缀包括最后一个(‘/’)字符,然后将字符串显示出来。选项:suffix为后缀,如果suffix被指定了,basename会将pathname或string中的suffix去掉。案例:截取该
/root/Test/helloShell.sh路径的文件名称
basename /root/Test/helloShell.sh 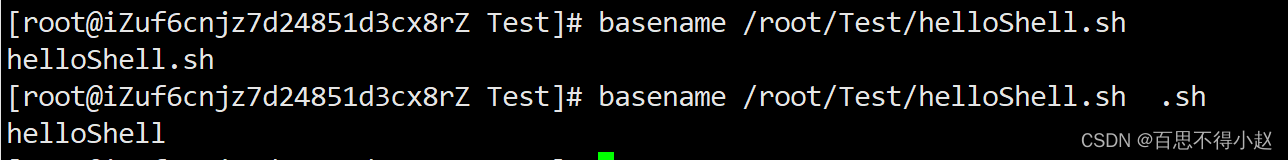
dirname基本语法
dirname 文件绝对路径 功能描述:从给定的包含绝对路径的文件名中去除文件名(非目录的部分),然后返回剩下的路径(目录的部分)案例:获取
helloShell.sh文件的路径
dirname /root/Test/helloShell.sh 
自定义函数
基本语法
[ function ] funname[()]{ Action; [return int;]}funname补充说明:
- 必须在调用函数地方之前,先声明函数,shell脚本是逐行运行。不会像其它语言一样先编译。
- 函数返回值,只能通过$?系统变量获得,可以显示加:return返回,如果不加,将以最后一条命令运行结果,作为返回值。return后跟数值n(0-255)
案例:计算两个输入参数的和
#!/bin/bashfunction sum(){ s=0 s=$[ $1 + $2 ] echo $s}read -p "input first number: " N1read -p "input second number: " N2sum $N1,$N2;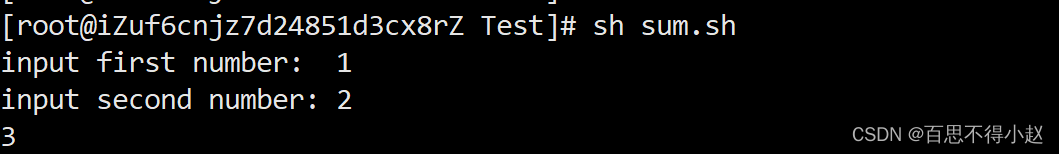

边栏推荐
- Mutual conversion between mytipartfile and file
- Database Series: is there any way to seamlessly upgrade the business tables of the database
- Chendanqi, Fang Fei, guquanquan and Li Bo won the prize, and the list of Sloan research award in 2022 was released
- Apache2配置对目录拒绝访问,但是可以访问里面文件的设置
- 来吧元宇宙,果然这热度一时半会儿过不去了
- 零基础C语言(一)
- 【无标题】虚拟机vmnet0找不到且报错:没有未桥接的主机网络适配器
- [sciter]: how sciter uses i18 to realize multi language switching of desktop applications and its advantages and disadvantages
- MapReduce项目案例1
- Unity屏幕截图功能
猜你喜欢

Day29 JS notes 2021.09.23

New listing of operation light 3.0 - a sincere work of self subversion across the times!

Tidb v6.0.0 (DMR): initial test of cache table - tidb Book rush

《运营之光3.0》全新上市——跨越时代,自我颠覆的诚意之作!
day32 js笔记 事件(上)2021.09.27

水果FL Studio/Cubase/Studio one音乐宿主软件对比

day33 js笔记 事件(下)2021.09.28

day31 js笔记 DOM下 2021.09.26

一套十万级TPS的IM综合消息系统的架构实践与思考

Practice and Thinking on the architecture of a set of 100000 TPS im integrated message system
随机推荐
Dongyuhui, New Oriental and Phoenix Satellite TV
The development and principle of the metacosmic system
day32 js笔记 事件(上)2021.09.27
Database Series: is there any way to seamlessly upgrade the business tables of the database
SoapUI rookie tutorial
【无标题】虚拟机vmnet0找不到且报错:没有未桥接的主机网络适配器
fatal: unsafe repository (‘/home/anji/gopath/src/gateway‘ is owned by someone else)
建立自己的网站(18)
JS foundation 10
Come on, yuanuniverse. Sure enough, the heat won't pass for a while
Apache2配置对目录拒绝访问,但是可以访问里面文件的设置
Ali three sides: what is the difference between using on or where in the left join associated table and the condition
If you want to change to software testing, how can you package your resume as a test engineer with 1 year of work experience
Web3安全连载(3) | 深入揭秘NFT钓鱼流程及防范技巧
《运营之光3.0》全新上市——跨越时代,自我颠覆的诚意之作!
太阳能无线LED显示屏的特点
Characteristics of solar wireless LED display
Packaging and publishing application of jetpack compose desktop version
Day23 JS notes 2021.09.14
Chapter 2 do you remember the point, line and surface (2)