当前位置:网站首页>UEFI 源码学习4.1 - PciHostBridgeDxe
UEFI 源码学习4.1 - PciHostBridgeDxe
2022-06-23 09:12:00 【MyeDy】
文章目录
1. 数据结构
PciHostBridgeDxe中主要有三个数据结构:PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE, PCI_HOST_BRIDGE_INSTANCE,PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_INSTANCE。
PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE是一个记录信息的结构,主要包括Root Bridge的属性,IO和内存信息以及DevicePath。PciHostBridgeDxe以外的DXE不会用到这个数据结构。
typedef struct {
UINT32 Segment; ///< Segment number.
UINT64 Supports; ///< Supported attributes.
///< Refer to EFI_PCI_ATTRIBUTE_xxx used by GetAttributes()
///< and SetAttributes() in EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL.
UINT64 Attributes; ///< Initial attributes.
///< Refer to EFI_PCI_ATTRIBUTE_xxx used by GetAttributes()
///< and SetAttributes() in EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL.
BOOLEAN DmaAbove4G; ///< DMA above 4GB memory.
///< Set to TRUE when root bridge supports DMA above 4GB memory.
BOOLEAN NoExtendedConfigSpace; ///< When FALSE, the root bridge supports
///< Extended (4096-byte) Configuration Space.
///< When TRUE, the root bridge supports
///< 256-byte Configuration Space only.
BOOLEAN ResourceAssigned; ///< Resource assignment status of the root bridge.
///< Set to TRUE if Bus/IO/MMIO resources for root bridge have been assigned.
UINT64 AllocationAttributes; ///< Allocation attributes.
///< Refer to EFI_PCI_HOST_BRIDGE_COMBINE_MEM_PMEM and
///< EFI_PCI_HOST_BRIDGE_MEM64_DECODE used by GetAllocAttributes()
///< in EFI_PCI_HOST_BRIDGE_RESOURCE_ALLOCATION_PROTOCOL.
PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_APERTURE Bus; ///< Bus aperture which can be used by the root bridge.
PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_APERTURE Io; ///< IO aperture which can be used by the root bridge.
PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_APERTURE Mem; ///< MMIO aperture below 4GB which can be used by the root bridge.
PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_APERTURE MemAbove4G; ///< MMIO aperture above 4GB which can be used by the root bridge.
PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_APERTURE PMem; ///< Prefetchable MMIO aperture below 4GB which can be used by the root bridge.
PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_APERTURE PMemAbove4G; ///< Prefetchable MMIO aperture above 4GB which can be used by the root bridge.
EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL *DevicePath; ///< Device path.
} PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE;
PCI_HOST_BRIDGE_INSTANCE和PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_INSTANCE就比较重要,会对外暴露。其他的DXE可以通过gEfiPciHostBridgeResourceAllocationProtocolGuid获取PCI_HOST_BRIDGE_INSTANCE对象,然后通过PCI_HOST_BRIDGE_INSTANCE拿到挂在其下面的PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_INSTANCE对象。同时也可以根据gEfiPciRootBridgeIoProtocolGuid拿到PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_INSTANCE。其数据结构组织如下,一个PCI_HOST_BRIDGE_INSTACE挂了两个PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_INSTANCE。当然大部分系统中只有一个PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_INSTACE, OVMF中就只有一个Root Bridge。
typedef struct {
UINTN Signature; --> 签名
EFI_HANDLE Handle; --> 对象句柄
LIST_ENTRY RootBridges; --> 挂接的Root Bridge链表
BOOLEAN CanRestarted; --> 标识Host Bridge是否能restart
EFI_PCI_HOST_BRIDGE_RESOURCE_ALLOCATION_PROTOCOL ResAlloc;
} PCI_HOST_BRIDGE_INSTANCE;
struct _EFI_PCI_HOST_BRIDGE_RESOURCE_ALLOCATION_PROTOCOL {
/// PCI枚举软件调用这个接口通知Host Bridge进入某一个枚举阶段
EFI_PCI_HOST_BRIDGE_RESOURCE_ALLOCATION_PROTOCOL_NOTIFY_PHASE NotifyPhase;
/// 获取下一个Root Bridge的句柄
EFI_PCI_HOST_BRIDGE_RESOURCE_ALLOCATION_PROTOCOL_GET_NEXT_ROOT_BRIDGE GetNextRootBridge;
/// 获取PCI Root Bridge的allocation 属性
EFI_PCI_HOST_BRIDGE_RESOURCE_ALLOCATION_PROTOCOL_GET_ATTRIBUTES GetAllocAttributes;
/// 设置Pci Root Bridge用于开始Pci总线枚举。
EFI_PCI_HOST_BRIDGE_RESOURCE_ALLOCATION_PROTOCOL_START_BUS_ENUMERATION StartBusEnumeration;
///
/// 设置一个Root Bridge的Bus Number
EFI_PCI_HOST_BRIDGE_RESOURCE_ALLOCATION_PROTOCOL_SET_BUS_NUMBERS SetBusNumbers;
/// 提交一个PCI Root Bridge的ACPI 配置
EFI_PCI_HOST_BRIDGE_RESOURCE_ALLOCATION_PROTOCOL_SUBMIT_RESOURCES SubmitResources;
/// 返回Pci Root Bridge的配置和资源
EFI_PCI_HOST_BRIDGE_RESOURCE_ALLOCATION_PROTOCOL_GET_PROPOSED_RESOURCES GetProposedResources;
///
/// Provides hooks from the PCI bus driver to every PCI controller
/// (device/function) at various stages of the PCI enumeration process that
/// allow the host bridge driver to preinitialize individual PCI controllers
/// before enumeration.
///
EFI_PCI_HOST_BRIDGE_RESOURCE_ALLOCATION_PROTOCOL_PREPROCESS_CONTROLLER PreprocessController;
};
typedef struct {
UINT32 Signature; --> 签名
LIST_ENTRY Link; --> 用于链接在Host Bridge下面的
EFI_HANDLE Handle; --> 对象句柄
UINT64 AllocationAttributes; --> 属性
UINT64 Attributes;
UINT64 Supports;
/* typedef struct { PCI_RESOURCE_TYPE Type; // // Base is a host address // UINT64 Base; UINT64 Length; UINT64 Alignment; RES_STATUS Status; } PCI_RES_NODE; */
PCI_RES_NODE ResAllocNode[TypeMax]; --> 记录每一种类型的资源信息,一共包括有 TypeIo, TypeMem32,TypePMem32,TypeMem64,TypePMem64,TypeBus几种类型
PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_APERTURE Bus; --> Bus地址信息
PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_APERTURE Io; --> IO地址信息
PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_APERTURE Mem; --> Mem地址信息
PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_APERTURE PMem;
PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_APERTURE MemAbove4G;
PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_APERTURE PMemAbove4G;
BOOLEAN DmaAbove4G; --> 是否DMA可以访问4G以上
BOOLEAN NoExtendedConfigSpace; --> 有没有Extended Config 空间
VOID *ConfigBuffer; --> 配置的buffer
EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL *DevicePath;
CHAR16 *DevicePathStr;
EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL RootBridgeIo; --> 操作Root Bridge的Protocol,这个Protocol提供了一系列操作Root Bridge的函数集
BOOLEAN ResourceSubmitted; --> 资源是否被提交了
LIST_ENTRY Maps;
} PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_INSTANCE;
2. 初始化
InitializePciHostBridge
- 调用PciHostBridgeGetRootBridges从PCD中获取Root Bridge的信息,并创建一个PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE数组实例RootBridges。OVMF中的HostBridge只有一个,所以RootBridges数组只有一个成员。
- 创建一个PCI_HOST_BRIDGE_INSTANCE类型的头节点HostBridge,用于链接所有的Root Bridge。
- 根据PCD中Root Bridge的个数循环创建PCI_HOST_BRIDGE_INSTANCE对象RootBridge,设置其属性,并插入到HostBridge数组中。
- 为RootBridge向GCD分配内存和IO空间。
- 设置HostBridge的Resource Allocation Protocol的函数,并安装Protocol gEfiPciHostBridgeResourceAllocationProtocolGuid
- 遍历RootBridge中每一个对象为其安装gEfiPciRootBridgeIoProtocolGuid和gEfiDevicePathProtocolGuid。
EFI_STATUS
EFIAPI
InitializePciHostBridge (
IN EFI_HANDLE ImageHandle,
IN EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *SystemTable
)
{
...
//1. 调用PciHostBridgeGetRootBridges从PCD中获取Root Bridge的信息,并创建一个PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE数组实例**RootBridges**。OVMF中的HostBridge只有一个,所以**RootBridges**数组只有一个成员。
RootBridges = PciHostBridgeGetRootBridges (&RootBridgeCount);
// Most systems in the world including complex servers have only one Host Bridge.
// 2. 创建一个PCI_HOST_BRIDGE_INSTANCE类型的头节点**HostBridge**,用于链接所有的Root Bridge。
HostBridge = AllocateZeroPool (sizeof (PCI_HOST_BRIDGE_INSTANCE));
HostBridge->Signature = PCI_HOST_BRIDGE_SIGNATURE;
HostBridge->CanRestarted = TRUE;
InitializeListHead (&HostBridge->RootBridges);
ResourceAssigned = FALSE;
//
// Create Root Bridge Device Handle in this Host Bridge
//3. 根据PCD中Root Bridge的个数循环创建PCI_HOST_BRIDGE_INSTANCE对象**RootBridge**,设置其属性,并插入到**HostBridge**数组中。
for (Index = 0; Index < RootBridgeCount; Index++) {
//
// Create Root Bridge Handle Instance
//
RootBridge = CreateRootBridge (&RootBridges[Index]);
...
//为**RootBridge**向GCD分配内存和IO空间。
if (RootBridges[Index].Io.Base <= RootBridges[Index].Io.Limit) {
//
// Base and Limit in PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_APERTURE are device address.
// For GCD resource manipulation, we need to use host address.
//
HostAddress = TO_HOST_ADDRESS (
RootBridges[Index].Io.Base,
RootBridges[Index].Io.Translation
);
Status = AddIoSpace (
HostAddress,
RootBridges[Index].Io.Limit - RootBridges[Index].Io.Base + 1
);
ASSERT_EFI_ERROR (Status);
if (ResourceAssigned) {
Status = gDS->AllocateIoSpace (
EfiGcdAllocateAddress,
EfiGcdIoTypeIo,
0,
RootBridges[Index].Io.Limit - RootBridges[Index].Io.Base + 1,
&HostAddress,
gImageHandle,
NULL
);
ASSERT_EFI_ERROR (Status);
}
}
//
// Add all the Mem/PMem aperture to GCD
// Mem/PMem shouldn't overlap with each other
// Root bridge which needs to combine MEM and PMEM should only report
// the MEM aperture in Mem
//
MemApertures[0] = &RootBridges[Index].Mem;
MemApertures[1] = &RootBridges[Index].MemAbove4G;
MemApertures[2] = &RootBridges[Index].PMem;
MemApertures[3] = &RootBridges[Index].PMemAbove4G;
for (MemApertureIndex = 0; MemApertureIndex < ARRAY_SIZE (MemApertures); MemApertureIndex++) {
if (MemApertures[MemApertureIndex]->Base <= MemApertures[MemApertureIndex]->Limit) {
//
// Base and Limit in PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_APERTURE are device address.
// For GCD resource manipulation, we need to use host address.
//
HostAddress = TO_HOST_ADDRESS (
MemApertures[MemApertureIndex]->Base,
MemApertures[MemApertureIndex]->Translation
);
Status = AddMemoryMappedIoSpace (
HostAddress,
MemApertures[MemApertureIndex]->Limit - MemApertures[MemApertureIndex]->Base + 1,
EFI_MEMORY_UC
);
ASSERT_EFI_ERROR (Status);
Status = gDS->SetMemorySpaceAttributes (
HostAddress,
MemApertures[MemApertureIndex]->Limit - MemApertures[MemApertureIndex]->Base + 1,
EFI_MEMORY_UC
);
if (EFI_ERROR (Status)) {
DEBUG ((DEBUG_WARN, "PciHostBridge driver failed to set EFI_MEMORY_UC to MMIO aperture - %r.\n", Status));
}
if (ResourceAssigned) {
Status = gDS->AllocateMemorySpace (
EfiGcdAllocateAddress,
EfiGcdMemoryTypeMemoryMappedIo,
0,
MemApertures[MemApertureIndex]->Limit - MemApertures[MemApertureIndex]->Base + 1,
&HostAddress,
gImageHandle,
NULL
);
ASSERT_EFI_ERROR (Status);
}
}
}
//
// Insert Root Bridge Handle Instance
//把RootBridge插入到HostBridge数组中。
InsertTailList (&HostBridge->RootBridges, &RootBridge->Link);
}
//
// When resources were assigned, it's not needed to expose
// PciHostBridgeResourceAllocation protocol.
//设置**HostBridge**的Resource Allocation Protocol的函数,并安装Protocol gEfiPciHostBridgeResourceAllocationProtocolGuid
if (!ResourceAssigned) {
HostBridge->ResAlloc.NotifyPhase = NotifyPhase;
HostBridge->ResAlloc.GetNextRootBridge = GetNextRootBridge;
HostBridge->ResAlloc.GetAllocAttributes = GetAttributes;
HostBridge->ResAlloc.StartBusEnumeration = StartBusEnumeration;
HostBridge->ResAlloc.SetBusNumbers = SetBusNumbers;
HostBridge->ResAlloc.SubmitResources = SubmitResources;
HostBridge->ResAlloc.GetProposedResources = GetProposedResources;
HostBridge->ResAlloc.PreprocessController = PreprocessController;
Status = gBS->InstallMultipleProtocolInterfaces (
&HostBridge->Handle,
&gEfiPciHostBridgeResourceAllocationProtocolGuid,
&HostBridge->ResAlloc,
NULL
);
ASSERT_EFI_ERROR (Status);
}
//遍历**RootBridge**中每一个对象为其安装gEfiPciRootBridgeIoProtocolGuid和gEfiDevicePathProtocolGuid。
for (Link = GetFirstNode (&HostBridge->RootBridges)
; !IsNull (&HostBridge->RootBridges, Link)
; Link = GetNextNode (&HostBridge->RootBridges, Link)
)
{
RootBridge = ROOT_BRIDGE_FROM_LINK (Link);
RootBridge->RootBridgeIo.ParentHandle = HostBridge->Handle;
Status = gBS->InstallMultipleProtocolInterfaces (
&RootBridge->Handle,
&gEfiDevicePathProtocolGuid,
RootBridge->DevicePath,
&gEfiPciRootBridgeIoProtocolGuid,
&RootBridge->RootBridgeIo,
NULL
);
ASSERT_EFI_ERROR (Status);
}
PciHostBridgeFreeRootBridges (RootBridges, RootBridgeCount);
if (!EFI_ERROR (Status)) {
mIoMmuEvent = EfiCreateProtocolNotifyEvent (
&gEdkiiIoMmuProtocolGuid,
TPL_CALLBACK,
IoMmuProtocolCallback,
NULL,
&mIoMmuRegistration
);
}
return Status;
}
PciHostBridgeGetRootBridges
PciHostBridgeGetRootBridges 的实现不同的平台有不同的实现方式。OVMF用的是OvmfPkg/Library/PciHostBidgeLib/PciHostBridgeLib.c 中的实现。这里面的实现通过PCD获取root bridge的属性Attributes 以及IO和内存的地址信息:MemAbove4G,Mem,IO, 然后将这些参数传给PciHostBridgeUtilityGetRootBridges创建一个Root Bridge的实例。
PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE *
EFIAPI
PciHostBridgeGetRootBridges (
UINTN *Count
)
{
...
//hardcode的Atrributes
Attributes = EFI_PCI_ATTRIBUTE_IDE_PRIMARY_IO |
EFI_PCI_ATTRIBUTE_IDE_SECONDARY_IO |
EFI_PCI_ATTRIBUTE_ISA_IO_16 |
EFI_PCI_ATTRIBUTE_ISA_MOTHERBOARD_IO |
EFI_PCI_ATTRIBUTE_VGA_MEMORY |
EFI_PCI_ATTRIBUTE_VGA_IO_16 |
EFI_PCI_ATTRIBUTE_VGA_PALETTE_IO_16;
AllocationAttributes = EFI_PCI_HOST_BRIDGE_COMBINE_MEM_PMEM;
//根据PCD获取MemAbove4G信息
if (PcdGet64 (PcdPciMmio64Size) > 0) {
AllocationAttributes |= EFI_PCI_HOST_BRIDGE_MEM64_DECODE;
MemAbove4G.Base = PcdGet64 (PcdPciMmio64Base);
MemAbove4G.Limit = PcdGet64 (PcdPciMmio64Base) +
PcdGet64 (PcdPciMmio64Size) - 1;
} else {
CopyMem (&MemAbove4G, &mNonExistAperture, sizeof (mNonExistAperture));
}
//根据PCD获取Mem和IO信息
Io.Base = PcdGet64 (PcdPciIoBase);
Io.Limit = PcdGet64 (PcdPciIoBase) + (PcdGet64 (PcdPciIoSize) - 1);
Mem.Base = PcdGet64 (PcdPciMmio32Base);
Mem.Limit = PcdGet64 (PcdPciMmio32Base) + (PcdGet64 (PcdPciMmio32Size) - 1);
return PciHostBridgeUtilityGetRootBridges (
Count,
Attributes,
AllocationAttributes,
FALSE,
PcdGet16 (PcdOvmfHostBridgePciDevId) != INTEL_Q35_MCH_DEVICE_ID,
0,
PCI_MAX_BUS,
&Io,
&Mem,
&MemAbove4G,
&mNonExistAperture,
&mNonExistAperture
);
}
PciHostBridgeUtilityGetRootBridges
- 分配一个PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE 的对象**Bridges **。
- 根据qemu cfg来获取root bridge的个数,在OVMF中root bridge只有一个,所以他走到的是ExtraRootBridges =0这条路。
- 调用PciHostBridgeUtilityInitRootBridge 把内存,IO,属性等参数填到Bridges 的各个成员中。
- 向上层返回root bridge的count为一个root bridge。
PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE *
EFIAPI
PciHostBridgeUtilityGetRootBridges (
OUT UINTN *Count,
IN UINT64 Attributes,
IN UINT64 AllocationAttributes,
IN BOOLEAN DmaAbove4G,
IN BOOLEAN NoExtendedConfigSpace,
IN UINTN BusMin,
IN UINTN BusMax,
IN PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_APERTURE *Io,
IN PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_APERTURE *Mem,
IN PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_APERTURE *MemAbove4G,
IN PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_APERTURE *PMem,
IN PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_APERTURE *PMemAbove4G
)
{
...
PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE *Bridges;
UINTN Initialized;
...
*Count = 0;
ExtraRootBridges = 0;
Bridges = AllocatePool ((1 + (UINTN)ExtraRootBridges) * sizeof *Bridges);
Status = QemuFwCfgFindFile ("etc/extra-pci-roots", &FwCfgItem, &FwCfgSize);
if (EFI_ERROR (Status) || (FwCfgSize != sizeof ExtraRootBridges)) {
ExtraRootBridges = 0;
} else {
QemuFwCfgSelectItem (FwCfgItem);
QemuFwCfgReadBytes (FwCfgSize, &ExtraRootBridges);
}
LastRootBridgeNumber = BusMin;
for (RootBridgeNumber = BusMin + 1;
RootBridgeNumber <= BusMax && Initialized < ExtraRootBridges;
++RootBridgeNumber)
{
...
}
...
Status = PciHostBridgeUtilityInitRootBridge (
Attributes,
Attributes,
AllocationAttributes,
DmaAbove4G,
NoExtendedConfigSpace,
(UINT8)LastRootBridgeNumber,
(UINT8)BusMax,
Io,
Mem,
MemAbove4G,
PMem,
PMemAbove4G,
&Bridges[Initialized]
);
++Initialized;
*Count = Initialized;
return Bridges;
...
}
CreateRootBridge
这个函数根据传入PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE 对象生成PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_INSTANCE对象。
- AllocateZeroPool分配一个PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_INSTANCE对象**RootBridge **。
- 把PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE 的参数全部复制给**RootBridge **,包括属性,内存IO空间资源等。
- 把一堆RootBridgeIoProtocol赋值给RootBridge->RootBridgeIo。
PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_INSTANCE *
CreateRootBridge (
IN PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE *Bridge
)
{
PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_INSTANCE *RootBridge;
PCI_RESOURCE_TYPE Index;
CHAR16 *DevicePathStr;
PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_APERTURE *Aperture;
DevicePathStr = NULL;
...
//1. AllocateZeroPool分配一个PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_INSTANCE对象**RootBridge **。
RootBridge = AllocateZeroPool (sizeof (PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_INSTANCE));
//2. 把PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE 的参数全部复制给**RootBridge **,包括属性,内存IO空间资源等。
RootBridge->Signature = PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_SIGNATURE;
RootBridge->Supports = Bridge->Supports;
RootBridge->Attributes = Bridge->Attributes;
RootBridge->DmaAbove4G = Bridge->DmaAbove4G;
RootBridge->NoExtendedConfigSpace = Bridge->NoExtendedConfigSpace;
RootBridge->AllocationAttributes = Bridge->AllocationAttributes;
RootBridge->DevicePath = DuplicateDevicePath (Bridge->DevicePath);
RootBridge->DevicePathStr = DevicePathStr;
RootBridge->ConfigBuffer = AllocatePool (
TypeMax * sizeof (EFI_ACPI_ADDRESS_SPACE_DESCRIPTOR) + sizeof (EFI_ACPI_END_TAG_DESCRIPTOR)
);
InitializeListHead (&RootBridge->Maps);
CopyMem (&RootBridge->Bus, &Bridge->Bus, sizeof (PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_APERTURE));
CopyMem (&RootBridge->Io, &Bridge->Io, sizeof (PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_APERTURE));
CopyMem (&RootBridge->Mem, &Bridge->Mem, sizeof (PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_APERTURE));
CopyMem (&RootBridge->MemAbove4G, &Bridge->MemAbove4G, sizeof (PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_APERTURE));
CopyMem (&RootBridge->PMem, &Bridge->PMem, sizeof (PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_APERTURE));
CopyMem (&RootBridge->PMemAbove4G, &Bridge->PMemAbove4G, sizeof (PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_APERTURE));
for (Index = TypeIo; Index < TypeMax; Index++) {
switch (Index) {
case TypeBus:
Aperture = &RootBridge->Bus;
break;
case TypeIo:
Aperture = &RootBridge->Io;
break;
case TypeMem32:
Aperture = &RootBridge->Mem;
break;
case TypeMem64:
Aperture = &RootBridge->MemAbove4G;
break;
case TypePMem32:
Aperture = &RootBridge->PMem;
break;
case TypePMem64:
Aperture = &RootBridge->PMemAbove4G;
break;
default:
ASSERT (FALSE);
Aperture = NULL;
break;
}
RootBridge->ResAllocNode[Index].Type = Index;
if (Bridge->ResourceAssigned && (Aperture->Limit >= Aperture->Base)) {
//
// Base in ResAllocNode is a host address, while Base in Aperture is a
// device address.
//
RootBridge->ResAllocNode[Index].Base = TO_HOST_ADDRESS (
Aperture->Base,
Aperture->Translation
);
RootBridge->ResAllocNode[Index].Length = Aperture->Limit - Aperture->Base + 1;
RootBridge->ResAllocNode[Index].Status = ResAllocated;
} else {
RootBridge->ResAllocNode[Index].Base = 0;
RootBridge->ResAllocNode[Index].Length = 0;
RootBridge->ResAllocNode[Index].Status = ResNone;
}
}
//3. 把一堆RootBridgeIoProtocol赋值给**RootBridge->RootBridgeIo**。
RootBridge->RootBridgeIo.SegmentNumber = Bridge->Segment;
RootBridge->RootBridgeIo.PollMem = RootBridgeIoPollMem;
RootBridge->RootBridgeIo.PollIo = RootBridgeIoPollIo;
RootBridge->RootBridgeIo.Mem.Read = RootBridgeIoMemRead;
RootBridge->RootBridgeIo.Mem.Write = RootBridgeIoMemWrite;
RootBridge->RootBridgeIo.Io.Read = RootBridgeIoIoRead;
RootBridge->RootBridgeIo.Io.Write = RootBridgeIoIoWrite;
RootBridge->RootBridgeIo.CopyMem = RootBridgeIoCopyMem;
RootBridge->RootBridgeIo.Pci.Read = RootBridgeIoPciRead;
RootBridge->RootBridgeIo.Pci.Write = RootBridgeIoPciWrite;
RootBridge->RootBridgeIo.Map = RootBridgeIoMap;
RootBridge->RootBridgeIo.Unmap = RootBridgeIoUnmap;
RootBridge->RootBridgeIo.AllocateBuffer = RootBridgeIoAllocateBuffer;
RootBridge->RootBridgeIo.FreeBuffer = RootBridgeIoFreeBuffer;
RootBridge->RootBridgeIo.Flush = RootBridgeIoFlush;
RootBridge->RootBridgeIo.GetAttributes = RootBridgeIoGetAttributes;
RootBridge->RootBridgeIo.SetAttributes = RootBridgeIoSetAttributes;
RootBridge->RootBridgeIo.Configuration = RootBridgeIoConfiguration;
return RootBridge;
}
3. Root Bridge Io Protocol
Root Bridge Io Protocol提供了操作Root Bridge的一些函数集。其定义如下。
struct _EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL {
///
/// The EFI_HANDLE of the PCI Host Bridge of which this PCI Root Bridge is a member.
///
EFI_HANDLE ParentHandle; --> PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_INSTANCE的句柄
EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL_POLL_IO_MEM PollMem; --> 阻塞式访问memory,超时会timeout
EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL_POLL_IO_MEM PollIo; --> 阻塞式访问IO, 超市会timeout
EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL_ACCESS Mem; --> 读写memory
EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL_ACCESS Io; --> 读写IO
EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL_ACCESS Pci; --> 读写Pci配置空间
EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL_COPY_MEM CopyMem; --> 复制memory
EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL_MAP Map; --> 用于映射DMA地址 到system memory地址
EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL_UNMAP Unmap; --> 用于映射system memory地址到DMA地址
EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL_ALLOCATE_BUFFER AllocateBuffer; --> 分配一个buffer
EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL_FREE_BUFFER FreeBuffer; --> 释放一个buffer
EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL_FLUSH Flush; --> Flush一个buffer
EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL_GET_ATTRIBUTES GetAttributes; --> 获取Root Bridge的属性
EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL_SET_ATTRIBUTES SetAttributes; --> 设置Root Bridge的属性
EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL_CONFIGURATION Configuration; --> 获取Root Bridge的ACPI描述符
///
/// The segment number that this PCI root bridge resides.
///
UINT32 SegmentNumber;
};
对于其他DXE来讲最常用就是IO,Mem以及Pci配置空间的读写访问。函数太多,后面就分析这两个实现。
3.1 RootBridgeIoPciRead/Write
RootBridgeIoPciRead/Write实现了EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL_ACCESS Pci接口。用于访问Pci的配置空间。读和写最终都是调用RootBridgeIoPciAccess,只是第二个参数不同,第二个参数为TRUE则为读,为FALSE为写
EFI_STATUS
EFIAPI
RootBridgeIoPciRead (
IN EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
IN EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL_WIDTH Width,
IN UINT64 Address,
IN UINTN Count,
IN OUT VOID *Buffer
)
{
return RootBridgeIoPciAccess (This, TRUE, Width, Address, Count, Buffer);
}
EFI_STATUS
EFIAPI
RootBridgeIoPciWrite (
IN EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
IN EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL_WIDTH Width,
IN UINT64 Address,
IN UINTN Count,
IN OUT VOID *Buffer
)
{
return RootBridgeIoPciAccess (This, FALSE, Width, Address, Count, Buffer);
}
RootBridgeIoPciAccess 在一个循环里调用PciSegmentReadBuffer 或者PciSegmentWriteBuffer 访问PCI配置空间。
EFI_STATUS
EFIAPI
RootBridgeIoPciAccess (
IN EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
IN BOOLEAN Read,
IN EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL_WIDTH Width,
IN UINT64 Address,
IN UINTN Count,
IN OUT VOID *Buffer
)
{
...
for (Uint8Buffer = Buffer; Count > 0; Address += InStride, Uint8Buffer += OutStride, Count--) {
if (Read) {
PciSegmentReadBuffer (Address, Size, Uint8Buffer);
} else {
PciSegmentWriteBuffer (Address, Size, Uint8Buffer);
}
}
...
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
PciSegmentReadBuffer j将根据地址进行不同对齐形式的访问。
- 如果传入数据是8 bit对齐,比如0x1231,那么会先调用PciSegmentRead8 读掉第1个byte的数据,并把地址加到0x1232
- 如果数据是16 bit 对齐,比如0x1232,那么会调用PciSegmentRead16 读出第2和第3个byte的数据,并把地址加到0x1234,此时地址是32 bit对齐
- 接着就是循环读32 bit对齐的数据,当然如果最后尾巴还剩下一点非对齐的地址,就会调用PciSegmentRead16 和PciSegmentRead8 把数据读出来。
UINTN
EFIAPI
PciSegmentReadBuffer (
IN UINT64 StartAddress,
IN UINTN Size,
OUT VOID *Buffer
)
{
UINTN ReturnValue;
...
ReturnValue = Size;
if ((StartAddress & BIT0) != 0) {
//
// Read a byte if StartAddress is byte aligned
//
*(volatile UINT8 *)Buffer = PciSegmentRead8 (StartAddress);
StartAddress += sizeof (UINT8);
Size -= sizeof (UINT8);
Buffer = (UINT8 *)Buffer + 1;
}
if ((Size >= sizeof (UINT16)) && ((StartAddress & BIT1) != 0)) {
//
// Read a word if StartAddress is word aligned
//
WriteUnaligned16 (Buffer, PciSegmentRead16 (StartAddress));
StartAddress += sizeof (UINT16);
Size -= sizeof (UINT16);
Buffer = (UINT16 *)Buffer + 1;
}
while (Size >= sizeof (UINT32)) {
//
// Read as many double words as possible
//
WriteUnaligned32 (Buffer, PciSegmentRead32 (StartAddress));
StartAddress += sizeof (UINT32);
Size -= sizeof (UINT32);
Buffer = (UINT32 *)Buffer + 1;
}
if (Size >= sizeof (UINT16)) {
//
// Read the last remaining word if exist
//
WriteUnaligned16 (Buffer, PciSegmentRead16 (StartAddress));
StartAddress += sizeof (UINT16);
Size -= sizeof (UINT16);
Buffer = (UINT16 *)Buffer + 1;
}
if (Size >= sizeof (UINT8)) {
//
// Read the last remaining byte if exist
//
*(volatile UINT8 *)Buffer = PciSegmentRead8 (StartAddress);
}
return ReturnValue;
}
PciSegmentRead8 调用了PciRead8来读数据。
UINT8
EFIAPI
PciSegmentRead8 (
IN UINT64 Address
)
{
ASSERT_INVALID_PCI_SEGMENT_ADDRESS (Address, 0);
return PciRead8 (PCI_SEGMENT_TO_PCI_ADDRESS (Address));
}
这里看440FX的PciRead8的实现,最终调用到PciCf8Read8 来操作硬件。PciCf8Read8 会把地址写到PCI_CONFIGURATION_ADDRESS_PORT中,把数据从PCI_CONFIGURATION_DATA_PORT 读出来。我们知道在x86上这两个寄存器就是用来访问PCI的配置空间。在EDK2中可以看到这两个寄存器的地址定义。
#define PCI_CONFIGURATION_ADDRESS_PORT 0xCF8
#define PCI_CONFIGURATION_DATA_PORT 0xCFC
UINT8
EFIAPI
PciRead8 (
IN UINTN Address
)
{
return mRunningOnQ35 ?
PciExpressRead8 (Address) :
PciCf8Read8 (Address);
}
UINT8
EFIAPI
PciCf8Read8 (
IN UINTN Address
)
{
BOOLEAN InterruptState;
UINT32 AddressPort;
UINT8 Result;
ASSERT_INVALID_PCI_ADDRESS (Address, 0);
InterruptState = SaveAndDisableInterrupts ();
AddressPort = IoRead32 (PCI_CONFIGURATION_ADDRESS_PORT);
IoWrite32 (PCI_CONFIGURATION_ADDRESS_PORT, PCI_TO_CF8_ADDRESS (Address));
Result = IoRead8 (PCI_CONFIGURATION_DATA_PORT + (UINT16)(Address & 3));
IoWrite32 (PCI_CONFIGURATION_ADDRESS_PORT, AddressPort);
SetInterruptState (InterruptState);
return Result;
}
所以一个DXE通过RootBridgeIoProtocol访问PCI配置空间的函数调用如下
RootBridgeIoProtocol->Pci.Read
RootBridgeIoPciRead
RootBridgeIoPciAccess
PciSegmentReadBuffer
PciSegmentRead8/16/32
PciRead8/16/32
PciCf8Read8/16/32 --> 最终写入硬件寄存器0xCF8和0xCFC的地方
3.2 RootBridgeIoMemRead/Write
PCI Memory和IO空间的读写相比配置空间就简单很多。 在PCI设备完成枚举后,软件为PCI设备配置BAR空间后就能通过memory map方式访问PCI的Memroy空间。所以实现上也很简单,RootBridgeIoMemRead/Write最终就是直接读写内存。看似是调用了 mCpuIo->Mem.Read,实际上CpuIo底层实现就是直接读写一个内存而已。
EFI_STATUS
EFIAPI
RootBridgeIoMemRead (
IN EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
IN EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL_WIDTH Width,
IN UINT64 Address,
IN UINTN Count,
OUT VOID *Buffer
)
{
EFI_STATUS Status;
PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_INSTANCE *RootBridge;
UINT64 Translation;
...
RootBridge = ROOT_BRIDGE_FROM_THIS (This);
Status = RootBridgeIoGetMemTranslationByAddress (RootBridge, Address, &Translation);
...
// Address passed to CpuIo->Mem.Read needs to be a host address instead of
// device address.
return mCpuIo->Mem.Read (
mCpuIo,
(EFI_CPU_IO_PROTOCOL_WIDTH)Width,
TO_HOST_ADDRESS (Address, Translation),
Count,
Buffer
);
}
EFI_STATUS
EFIAPI
RootBridgeIoMemWrite (
IN EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
IN EFI_PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_IO_PROTOCOL_WIDTH Width,
IN UINT64 Address,
IN UINTN Count,
IN VOID *Buffer
)
{
EFI_STATUS Status;
PCI_ROOT_BRIDGE_INSTANCE *RootBridge;
UINT64 Translation;
...
RootBridge = ROOT_BRIDGE_FROM_THIS (This);
Status = RootBridgeIoGetMemTranslationByAddress (RootBridge, Address, &Translation);
return mCpuIo->Mem.Write (
mCpuIo,
(EFI_CPU_IO_PROTOCOL_WIDTH)Width,
TO_HOST_ADDRESS (Address, Translation),
Count,
Buffer
);
}
4. Resource Allocation Protocol (TODO)
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

Flink error --caused by: org apache. calcite. sql. parser. SqlParseException: Encountered “time“

Learn SCI thesis drawing skills (E)
Redis learning notes - single key management

点击添加下拉框

学习SCI论文绘制技巧(F)
GeoServer adding mongodb data source

【云原生 | Kubernetes篇】Kubernetes原理与安装(二)

什么是闭包函数

Click Add drop-down box
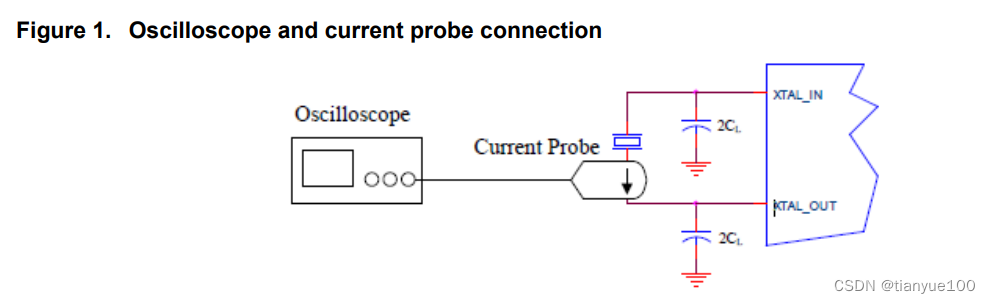
Quartz Crystal Drive Level Calculation
随机推荐
三层架构与SSM之间的对应关系
528. Random Pick with Weight
ARM中常见的英文解释
Cookie和Session入门
3、 System analysis and design
文件的打开新建与存储
Utilisation du cookie du module de demande de noeud
438. Find All Anagrams in a String
Redis学习笔记—主从复制
node request模块cookie使用
ionic5錶單輸入框和單選按鈕
在小程序中实现视频通话及互动直播的一种方法
Vue3表单页面利用keep-alive缓存数据的一种思路
[cloud native | kubernetes] kubernetes principle and installation (II)
[qnx hypervisor 2.2 user manual]6.1 using the QNX hypervisor system
Redis学习笔记—redis-cli详解
New engine, new capability, new experience, Tencent host security flagship release
[learning resources] understand and love mathematics
A method of realizing video call and interactive live broadcast in small programs
"Coach, I want to play basketball" -- AI Learning Series booklet for students who are making systems
