当前位置:网站首页>Wavelet transform DB4 for four layer decomposition and signal reconstruction matlab analysis and C language implementation
Wavelet transform DB4 for four layer decomposition and signal reconstruction matlab analysis and C language implementation
2022-06-22 19:33:00 【xiaoweiwei99】
Wavelet transform db4 Four layer decomposition and signal reconstruction
- Preface
- One 、Matlab Correlation function of wavelet transform
- Two 、C Language to realize wavelet decomposition and reconstruction
- 3、 ... and 、 Results comparison
- summary
- Reference article
Preface
This article mainly analyzes matlab On the correlation function of wavelet transform :wavedec( For wavelet decomposition ) and wrcoef( For wavelet reconstruction ). By analyzing the actual actions of the two functions , Further use C Language to realize the decomposition and reconstruction of wavelet transform . Finally, we compare matlab The result of C Language results , Consistent result , Realized C Wavelet transform of language .
(*ps: This article is only for db4 wavelet , Analyze the four layer wavelet transform . The decomposition of other wavelets and different levels needs to change the program according to the actual situation .)
One 、Matlab Correlation function of wavelet transform
1. wavedec function
wavedec Function is a function used for wavelet decomposition , stay matlab The basic format used in is as follows :
[C,L] = wavedec(rawData,4,'db4');
Input :
name
significance
rawData
Raw data to be decomposed
4
Number of layers decomposed
‘db4’
Wavelet signals used
The raw data used for testing here is :
rawData = [24,34,49,48,25,17,34,50,64,71,64,54,53,55,56,60];
Output :
name
significance
C
Decomposed detail components of each layer cD And the approximate component of the last layer cA
L
And C Corresponding cA And cD The number of
C and L The specific meaning of the word is in matlab As explained below :
The above figure shows the result of three-level decomposition . Therefore, when the original data is decomposed into four layers ,C The data in should be :cA4 cD4 cD3 cD2 cD1. and L The result in is the length of each data .
Following pair wavedec Function :
By means of matlab The code of this function can be found in ,wavedec The core of the function is actually the discrete wavelet transform (dwt):
[x,d] = dwt(x,Lo_D,Hi_D);
It's here Lo_D and Hi_D Two quantities ,x Is the input raw data , that Lo_D and Hi_D What are the differences ? Take a closer look at the code , It can be found that these two quantities are actually the low-pass decomposition quantity and high-pass decomposition quantity of each wavelet signal . Different wavelet signals , The amount of decomposition is also different , But the decomposition value of each wavelet signal is fixed . Can be in matlab Pass through wfilters Function to obtain the decomposition amount of each wavelet signal , obtain ’db4’ The decomposition amount of wavelet is as follows :
[Lo_D,Hi_D,Lo_R,Hi_R]=wfilters('db4');
At this time, two quantities are introduced :Lo_R( Low pass reconfiguration ) and Hi_R( High pass reconfiguration ), Corresponding to the above decomposition amount , These two quantities are used for signal reconstruction , stay wrcoef Function will use .
The result is :
Lo_D =[ -0.0106,0.0329,0.0308,-0.1870,-0.0280,0.6309,0.7148,0.2304];
Hi_D =[-0.2304,0.7148,-0.6309,-0.0280,0.1870,0.0308,-0.0329,-0.0106];
Lo_R =[0.2304,0.7148,0.6309,-0.0280,-0.1870,0.0308,0.0329,-0.0106];
Hi_R =[-0.0106,-0.0329,0.0308,0.1870,-0.0280,-0.6309,0.7148,-0.2304];
Come here , analysis wavedec Function becomes analysis dwt function .
matlab Chinese vs dwt The structure of the function can be simply explained by the following figure :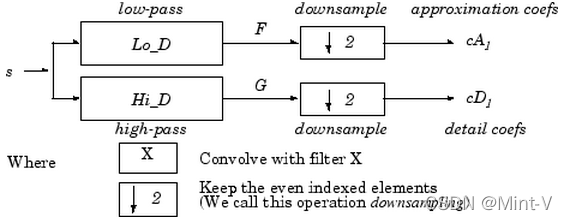
As you can see from the diagram , Implementation of discrete wavelet transform , First, the original signal is passed through a low-pass filter and a high pass filter respectively , Then, we can get by downsampling respectively cA And cD. there “ Through low pass filter and high pass filter ” It can be simply understood as the signal and the two decomposition quantities obtained before (Lo_D and Hi_D) Convolution , For specific meaning, please refer to : One of wavelet learning ( Single layer one-dimensional discrete wavelet transform DWT Of Mallat Algorithm C++ and MATLAB Realization ) — Reprint .
In this paper, the decomposition of single-layer one-dimensional discrete wavelet transform is explained in detail , And use C++ The wavelet decomposition and reconstruction are carried out , Can realize signal reconstruction , But the result of signal decomposition is similar to matlab There are discrepancies in the results of . Besides , On the basis of realizing single-layer wavelet decomposition and reconstruction , Our goal is to realize the decomposition and reconstruction of multi-layer signals . So based on the code in this article , The author changed it , Changing into C At the same time, the language version realizes the multi-layer decomposition and reconstruction of signals , Make the result consistent with matlab Consistent results .
In wavelet decomposition , The signal is decomposed layer by layer , The approximate component of each layer is decomposed to obtain the approximate component and detail component of the next layer , The principle is shown in the figure below . therefore , To achieve wavedec The function requires discrete wavelet transform for each layer (dwt).
Discrete wavelet transform is applied to the original signal (dwt) after , The approximate components obtained in turn (cA) Discrete wavelet transform is performed to obtain the decomposition amount of the next layer . Will each layer need cD And cA And the number of them can be summed up to get wavedec The result of the function C and L.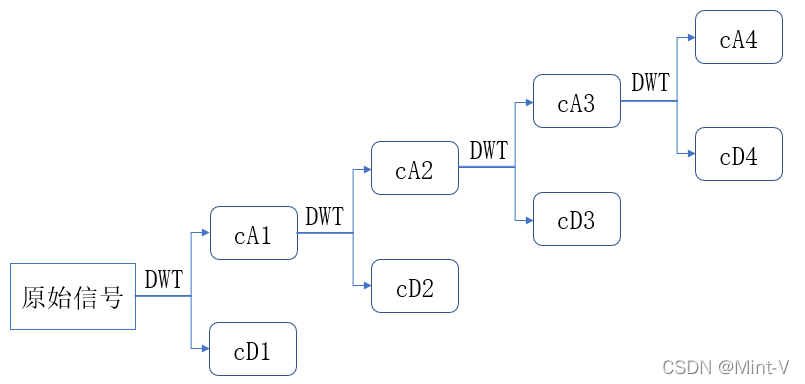
2. wrcoef function
wrcoef Function is used to reconstruct the decomposed signal , stay matlab The methods used in are as follows :
[d1] = wrcoef('d',C,L,'db4',1);
[d2] = wrcoef('d',C,L,'db4',2);
[d3] = wrcoef('d',C,L,'db4',3);
[d4] = wrcoef('d',C,L,'db4',4);
[a4] = wrcoef('a',C,L,'db4',4);
Input :
name
significance
‘d’ / ‘a’
For details (cD) restructure / For approximate components (cA) restructure
C
from wavedec The result , Including approximate component and detail component
L
from wavedec The result , The number of approximate components and detail components
‘db4’
Wavelet signals used
1/2/3/4
The first 1/2/3/4 Layer signals
Output :
name
significance
d1
The detail component decomposed from the first layer cD1
d2
The detail component decomposed from the second layer cD2
d3
The detail component decomposed from the third layer cD3
d4
The detail component decomposed from the fourth layer cD4
a4
The approximate components decomposed by the fourth layer cA4
wrcoef The actual internal action of a function can be roughly divided into three steps :
L sampling —— Convolution —— Intercept the data to make it the same length as the original signal
- L sampling
When simply using the decomposed data for reconstruction , Cannot restore to original length , Therefore, it is necessary to carry out ascending sampling first . The upsampling here is essentially interpolation and zeroing .
( Take a chestnut )
Raw data :1,2,3,4,5,6
After L sampling :0,1,0,2,0,3,0,4,0,5,0,6 - Convolution
The data to be reconstructed is the same as the two reconstruction quantities mentioned above Lo_R( Low pass reconfiguration ) and Hi_R( High pass reconfiguration ) Convolution .
! Here is a very critical point !
It can be seen from the above schematic diagram of wavelet decomposition , Except for the first floor cA And cD It is directly decomposed from the original data , After each floor cA and cD It's all from the upper layer cA It's broken down , Therefore, attention should be paid to the signal reconstruction : What is another quantity convoluted with the decomposed signal . There are only two options for this quantity :Lo_R perhaps Hi_R. When the decomposed signal belongs to the detail component , To work with Hi_R Convolution ; When the decomposed signal belongs to the approximate component , To work with Lo_R Convolution .
The description is not very clear , The following is an example to show :
% Example 1: restructure d3 Signal to raw data length
d3 From the second floor cA2 It's broken down , and d3 It belongs to the detail component , be d3 With the first Hi_R Convolution , And then reconstruct to get cA2;
cA2 From the first floor cA1 It's broken down , and cA2 It is an approximate component , be cA2 And Lo_R Convolution , And then reconstruct to get cA1;
cA1 From the original data , and cA1 It is an approximate component , be cA1 And Lo_R Convolution , And then reconstruct to get the final result ;
% Example 2: restructure a4 Signal to raw data length
a4 From the third floor cA3 It's broken down , and a4 It is an approximate component , be a4 With the first Lo_R Convolution , And then reconstruct to get cA3;
cA3 From the second floor cA2 It's broken down , and cA3 It is an approximate component , be cA3 And Lo_R Convolution , And then reconstruct to get cA2;
cA2 From the first floor cA1 It's broken down , and cA2 It is an approximate component , be cA2 And Lo_R Convolution , And then reconstruct to get cA1;
cA1 From the original data , and cA1 It is an approximate component , be cA1 And Lo_R Convolution , And then reconstruct to get the final result ;
The reconstruction of other signals is similar to the above two examples .
- Intercept the data to make it the same length as the original signal
The length of the convolution result will be greater than the length of the original signal , Therefore, it is necessary to intercept the reconstructed results . in the light of ’db4’ wavelet , From the convolution result of the 8 Data is intercepted , Until the approximate component of the previous layer is intercepted cA Data of the same length , Then it recurs up layer by layer , The final result is the same length as the original data .( If you change to something else ‘dbn’ wavelet , From 2n Data begins to be intercepted )
Two 、C Language to realize wavelet decomposition and reconstruction
1. Signal decomposition
The signal decomposition is described above , Is the approximate component of the original signal or each layer (cA) Discrete wavelet transform (dwt), To obtain the approximate component and detail component of the next layer . therefore C The language implements signal decomposition as follows :
( It should be noted that , The raw data here rawdata Better not to exceed 512 individual , Otherwise, it is easy to make mistakes . When the raw data is more than 512 Time , Need to change WaveletDB4 Functions cA and cD Array size of .)
double cA[300], cD[300], cA1[150], cD1[150];
double cA2[100], cD2[100], cA3[50], cD3[50];
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
double rawdata[16] = { 24,34,49,48,25,17,34,50,64,71,64,54,53,55,56,60 };
double db4_Lo_D[8] = { -0.0105974017850690, 0.0328830116668852, 0.0308413818355607, -0.1870348117190931, -0.0279837694168599, 0.6308807679398587, 0.7148465705529154, 0.2303778133088964 };
double db4_Hi_D[8] = { -0.2303778133088964, 0.7148465705529154, -0.6308807679398587, -0.0279837694168599, 0.1870348117190931, 0.0308413818355607, -0.0328830116668852, -0.0105974017850690 };
void WaveletDwt(double sourceData[], int dataLen, double *cA, double *cD) // rawData, the length of rawData , cA, cD
{
int filterLen = 8; // The length of the filter
int n, k, p;
int decLen = (dataLen + filterLen - 1) / 2;
double tmp = 0;
for (n = 0; n < decLen; n++)
{
cA[n] = 0;
cD[n] = 0;
for (k = 0; k < filterLen; k++)
{
p = 2 * n - k + 1;
if ((p < 0) && (p >= -filterLen + 1))
tmp = sourceData[-p - 1];
else if ((p > dataLen - 1) && (p <= dataLen + filterLen - 2))
tmp = sourceData[2 * dataLen - p - 1];
else if ((p >= 0) && (p < dataLen - 1 + 1))
tmp = sourceData[p];
else
tmp = 0;
cA[n] += db4_Lo_D[k] * tmp; // cA
cD[n] += db4_Hi_D[k] * tmp; // cD
}
}
return;
}
void WaveletDB4(double sourceData[], int dataLen, double *C, int *L)
{
double cA[300], cD[300], cA1[150], cD1[150];
double cA2[100], cD2[100], cA3[50], cD3[50];
L[0] = dataLen;
int i;
WaveletDwt(sourceData, dataLen, cA, cD); //One-layer decomposition
L[1] = (dataLen + 7) / 2;
for (i = 0; i < L[1]; i++)
{
C[i] = cD[i];
}
WaveletDwt(cA, L[1], cA1, cD1); //Two-layer decomposition
L[2] = (L[1] + 7) / 2;
for (i = L[1]; i < L[1] + L[2]; i++)
{
C[i] = cD1[i - L[1]];
}
WaveletDwt(cA1, L[2], cA2, cD2); //Three-layer decomposition
L[3] = (L[2] + 7) / 2;
for (i = L[1] + L[2]; i < L[1] + L[2] + L[3]; i++)
{
C[i] = cD2[i - L[1] - L[2]];
}
WaveletDwt(cA2, L[3], cA3, cD3); //Four-layer decomposition
L[4] = (L[3] + 7) / 2;
for (i = L[1] + L[2] + L[3]; i < L[1] + L[2] + L[3] + L[4]; i++)
{
C[i] = cD3[i - L[1] - L[2] - L[3]];
}
L[5] = (L[3] + 7) / 2;
for (i = L[1] + L[2] + L[3] + L[4]; i < L[1] + L[2] + L[3] + L[4] + L[5]; i++)
{
C[i] = cA3[i - L[1] - L[2] - L[3] - L[4]];
}
return;
}
//=========================================end of WaveletDB4===============================================//
int main() {
int L[6];
double C[600];
int DataLen = sizeof(rawdata) / sizeof(double);
WaveletDB4(rawdata, DataLen, C, L); //C: CD1 CD2 CD3 CD4 CA4 L: (length of) raw data, CD1, CD2, CD3, CD4, CA4
for(int i = 0; i < (L[1]+L[2]+L[3]+L[4]+L[5]); i++)
{
printf("C[");printf("%d",i);printf("]:");
printf("%f
", C[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
printf("L["); printf("%d", i); printf("]:");
printf("%d
", L[i]);
}
}
2. Signal reconstruction
The essence of signal reconstruction is to Signals that need to be reconstructed Perform single branch reconfiguration ( L sampling — Convolution — Intercept ). The principle of single branch reconstruction here is the same as that of ordinary inverse wavelet transform , Just omit “ Add the high and low frequency parts together ” This step , See wrcoef The actual action of the function This article . By continuously reconstructing the signal of the previous layer , Until reconstituted to the same length as the original signal , Form the final result . therefore C The language implements signal reconstruction as follows :
double db4_Lo_R[8] = { 0.2303778133088964, 0.7148465705529154, 0.6308807679398587, -0.0279837694168599, -0.1870348117190931, 0.0308413818355607, 0.0328830116668852, -0.0105974017850690 };
double db4_Hi_R[8] = { -0.0105974017850690, -0.0328830116668852, 0.0308413818355607, 0.1870348117190931, -0.0279837694168599, -0.6308807679398587, 0.7148465705529154, -0.2303778133088964 };
void WaveletIdwt_CD(double cD[], int cALength, double *recData, int recLength)
{
int filterLen = 8;
int recLen = recLength;
int num = cALength * 2;
double *temp = (double *)malloc(num * sizeof(double));
int k = 0;
// Upsampling
for (int n = 0; n < num; n++)
{
if (n % 2 == 0)
{
temp[n] = 0;
}
else
{
temp[n] = cD[k];
k++;
}
}
int num_conv = cALength * 2 + 8 - 1;
double *xx = (double *)malloc(num_conv * sizeof(double));
// Initialization
for (int i = 0; i < num_conv; i++) {
xx[i] = 0;
}
// Convolution
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cALength * 2; j++) {
xx[i + j] += temp[j] * db4_Hi_R[i];
}
}
// Results
for (int i = 7; i < recLen + 7; i++) {
recData[i - 7] = xx[i];
}
free(temp);
free(xx);
return;
}
void WaveletIdwt_CA(double *cA, int cALength, double *recData, int recLength)
{
int filterLen = 8;
int recLen = recLength;
int num = cALength * 2;
double *temp = (double *)malloc(num * sizeof(double));
int k = 0;
// Upsampling
for (int n = 0; n < num; n++)
{
if (n % 2 == 0)
{
temp[n] = 0;
}
else
{
temp[n] = cA[k];
k++;
}
}
int num_conv = cALength * 2 + 8 - 1;
double *xx = (double *)malloc(num_conv * sizeof(double));
// Initialization
for (int i = 0; i < num_conv; i++) {
xx[i] = 0;
}
// Convolution
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cALength * 2; j++) {
xx[i + j] += temp[j] * db4_Lo_R[i];
}
}
// Results
for (int i = 7; i < recLen + 7; i++) {
recData[i - 7] = xx[i];
}
free(temp);
free(xx);
return;
}
//============================================end of Single branch reconstruction===================================//
void getcD1(double *C, int *L, double *cD1) {
int recLen = L[0];
int num = L[1];
double *cD = (double *)malloc(num * sizeof(double));
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
cD[i] = C[i];
}
WaveletIdwt_CD(cD, num, cD1, recLen);
free(cD);
return;
}
void getcD2(double *C, int *L, double *cD2)
{
int recLen = L[0];
int num_cd1 = L[1];
int num_cd2 = L[2];
double *cD = (double *)malloc(num_cd2 * sizeof(double));
double *rec1 = (double *)malloc(num_cd1 * sizeof(double));
for (int i = num_cd1; i < num_cd1 + num_cd2; i++) {
cD[i - num_cd1] = C[i];
}
WaveletIdwt_CD(cD, num_cd2, rec1, num_cd1);
WaveletIdwt_CA(rec1, num_cd1, cD2, recLen);
free(cD);
free(rec1);
return;
}
void getcD3(double *C, int *L, double *cD3)
{
int recLen = L[0];
int num_cd1 = L[1];
int num_cd2 = L[2];
int num_cd3 = L[3];
double *cD = (double *)malloc(num_cd3 * sizeof(double));
double *rec1 = (double *)malloc(num_cd2 * sizeof(double));
double *rec2 = (double *)malloc(num_cd1 * sizeof(double));
for (int i = num_cd1 + num_cd2; i < num_cd1 + num_cd2 + num_cd3; i++) {
cD[i - num_cd1 - num_cd2] = C[i];
}
WaveletIdwt_CD(cD, num_cd3, rec1, num_cd2);
WaveletIdwt_CA(rec1, num_cd2, rec2, num_cd1);
WaveletIdwt_CA(rec2, num_cd1, cD3, recLen);
free(cD);
free(rec1);
free(rec2);
return;
}
void getcD4(double *C, int *L, double *cD4)
{
int recLen = L[0];
int num_cd1 = L[1];
int num_cd2 = L[2];
int num_cd3 = L[3];
int num_cd4 = L[4];
double *cD = (double *)malloc(num_cd4 * sizeof(double));
double *rec1 = (double *)malloc(num_cd3 * sizeof(double));
double *rec2 = (double *)malloc(num_cd2 * sizeof(double));
double *rec3 = (double *)malloc(num_cd1 * sizeof(double));
for (int i = num_cd1 + num_cd2 + num_cd3; i < num_cd1 + num_cd2 + num_cd3 + num_cd4; i++) {
cD[i - num_cd1 - num_cd2 - num_cd3] = C[i];
}
WaveletIdwt_CD(cD, num_cd4, rec1, num_cd3);
WaveletIdwt_CA(rec1, num_cd3, rec2, num_cd2);
WaveletIdwt_CA(rec2, num_cd2, rec3, num_cd1);
WaveletIdwt_CA(rec3, num_cd1, cD4, recLen);
free(cD);
free(rec1);
free(rec2);
free(rec3);
return;
}
void getcA4(double *C, int *L, double *cA4)
{
int recLen = L[0];
int num_cd1 = L[1];
int num_cd2 = L[2];
int num_cd3 = L[3];
int num_cd4 = L[4];
int num_ca4 = L[5];
double *cA = (double *)malloc(num_ca4 * sizeof(double));
double *rec1 = (double *)malloc(num_cd3 * sizeof(double));
double *rec2 = (double *)malloc(num_cd2 * sizeof(double));
double *rec3 = (double *)malloc(num_cd1 * sizeof(double));
for (int i = num_cd1 + num_cd2 + num_cd3 + num_cd4; i < num_cd1 + num_cd2 + num_cd3 + num_cd4 + num_ca4; i++) {
cA[i - num_cd1 - num_cd2 - num_cd3 - num_cd4] = C[i];
}
WaveletIdwt_CA(cA, num_ca4, rec1, num_cd3);
WaveletIdwt_CA(rec1, num_cd3, rec2, num_cd2);
WaveletIdwt_CA(rec2, num_cd2, rec3, num_cd1);
WaveletIdwt_CA(rec3, num_cd1, cA4, recLen);
free(cA);
free(rec1);
free(rec2);
free(rec3);
return;
}
int main() {
int L[6];
double C[600];
int DataLen = sizeof(rawdata) / sizeof(double);
double cD1[512];
double cD2[512];
double cD3[512];
double cD4[512];
double cA4[512];
WaveletDB4(rawdata, DataLen, C, L); //C: CD1 CD2 CD3 CD4 CA4 L: (length of) raw data, CD1, CD2, CD3, CD4, CA4
getcD1(C, L, cD1);
getcD2(C, L, cD2);
getcD3(C, L, cD3);
getcD4(C, L, cD4);
getcA4(C, L, cA4);
for (int i = 0; i < DataLen; i++) {
printf("cA4["); printf("%d", i); printf("]:");
printf("%f
", cA4[i]);
}
}
3、 ... and 、 Results comparison
1. Signal decomposition and wavedec function
matlab Run in wavedec function , The results are as follows .
C:
L:
use C The signal decomposition results of the language implementation are as follows :
It can be seen that , here C The size of each quantity in L Is corresponding to (L[0] Is the size of the raw data , And C The corresponding size ranges from L[1] Start ), And with the matlab The results are consistent .
2. Signal reconstruction and wrcoef function
stay matlab Run in wrcoef function , Running at the same time C Language implementation of signal reconstruction , The results are as follows .
cD1
matlab result :
C Language implementation results :
cD2
matlab result :
C Language implementation results :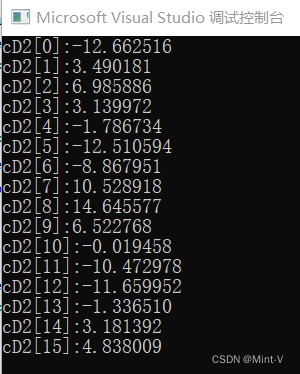
cD3
matlab result :
C Language implementation results :
cD4
matlab result :
C Language implementation results :
cA4
matlab result :
C Language implementation results :
In conclusion, we can see that C The language implements matlab Signal reconstruction with the same result .
summary
This article passes C The language implements ’db4’ Four layer wavelet decomposition and reconstruction of wavelet , The result is matlab The results are consistent , Proved its feasibility . After understanding the decomposition and reconstruction principle of wavelet transform , The program can be extended to other wavelets with different decomposition levels .
The article is incomprehensible or unclear , Forgive me (′`)
Reference article
One of wavelet learning ( Single layer one-dimensional discrete wavelet transform DWT Of Mallat Algorithm C++ and MATLAB Realization ) — Reprint
analysis matlab function wrcoef Internal implementation
wrcoef The actual action of the function
边栏推荐
- std::enable_ shared_ from_ This error: error: expected template name before '<' token
- 故障分析 | 从 data_free 异常说起
- mini-Web框架:模板替换与路由列表功能开发 | 黑马程序员
- 通过base64下载文件(将base64转为blob)
- AUTOCAD——五种标注快捷键
- Screw database document generator
- IPLOOK 5GC与亚信国际CHF(计费功能)对接成功
- Screw数据库文档生成器
- 插槽里如何判断text为数组
- Iplook, as a member of o-ran alliance, will jointly promote the development of 5g industry
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
PostgreSQL 字符串分隔函数(regexp_split_to_table)介绍以及示例应用
IPLOOK 5GC与亚信国际CHF(计费功能)对接成功
Iplook and SBC establish long-term cooperation
NLP-D57-nlp比赛D26&刷题D13&读论文&&找了一个多小时bug
结构型模式之适配器模式
200亿VS 50亿,“脱水”小红书,到底值多钱?
贪心之区间问题(1)
实验4 NoSQL和关系数据库的操作比较
Aiops intelligent operation and maintenance experience sharing
Thread pool: reading the source code of threadpoolexcutor
Makefile does not compile some files
canvas给图片画框框
故障分析 | 从 data_free 异常说起
贪心之区间问题(3)
Digital commerce cloud: analyze the design idea of B2B2C multi-user mall system architecture, and open a new era of intelligent mall
Shell script explanation (II) -- conditional test, if statement and case branch statement
shell脚本详解(二)——条件测试、if语句和case分支语句
IPLOOK 成为 RedHat(红帽)业务合作伙伴
数字赋能机械制造业,供应链协同管理系统解决方案助力企业供应链再升级
codeup最长回文子串








