当前位置:网站首页>Credit card number recognition (openCV, code analysis)
Credit card number recognition (openCV, code analysis)
2022-07-26 15:25:00 【csp_】
Catalog
Project source code
Can be found in github download :
https://github.com/chenshunpeng/Credit-card-digital-identification
Environment configuration and pretreatment
Import toolkit
# imutils Is in OPenCV Based on a package , To achieve a simpler call OPenCV Purpose of the interface
from imutils import contours
# It is mainly used to calculate multidimensional arrays , It greatly simplifies the operation of vectors and matrices
import numpy as np
# argparse yes python Standard module for parsing command line arguments and options
import argparse
# OpenCV2(OpenCV It's based on BSD The license ( Open source ) Distributed cross-platform computer vision library )
import cv2
# Import myutils.py The method in the document
import myutils
Set parameters
About argparse The use of can be seen :
Python, argparse, and command line arguments( recommend )
python And parser.add_argument() usage —— Command line options 、 Parameter and subcommand parsers
First of all Parameter form Set the position of the input image and template , Here the parameter specifies the default value , Therefore, it is necessary to required=True Change to required=False, Otherwise, an error will be reported ( reference : Resolve errors : Default parameters are set , Still report a mistake :error: the following arguments are required:)
# argparse The module is Python A built-in module for command options and parameter parsing ,
# argparse Module makes it easy to write user-friendly command-line interface .
# By defining the parameters we need in the program , then argparse Will be from sys.argv Resolve these parameters .
# argparse The module also automatically generates help and user manuals , And report an error message when the user passes in invalid parameters to the program .
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add_argument("-i", "--image",default='./images/credit_card_03.png', required=False,
help="path to input image")
ap.add_argument("-t", "--template",default='./images/ocr_a_reference.png', required=False,
help="path to template OCR-A image")
args = vars(ap.parse_args())
Template processing method
Turn binary image
cv2.threshold() The method can be seen :CV2 Simple threshold function :cv2.threshold()
# Graphic display
def cv_show(name,img):
cv2.imshow(name, img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# Read a template image ( because BGR, So every pixel is [255 255 255])
img = cv2.imread(args["template"])
cv_show('img',img)
# Convert to grayscale (BGR To GRAY)
ref = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv_show('ref',ref)
# Binary image ( The options are cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
ref = cv2.threshold(ref, 10, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)[1]
cv_show('ref',ref)
- grayscale : stay RGB In the model , If R=G=B when , Then color represents a grayscale color , among R=G=B The value of is called gray value , therefore , Gray image each pixel only needs one byte to store the gray value ( Also called strength value 、 Brightness value ), The gray range is 0-255. Generally, the weighted average method is commonly used to obtain the gray value of each pixel .
- Binary figure : Binary image , Is to set the gray value of pixels on the image to 0 or 255, That is to say, the whole image has only black and white visual effects .
- Color image : A special case of multispectral images , The three primary colors corresponding to human vision are red 、 green 、 Blue three bands , It is an approximation of the spectral quantization properties of the human eye .
It can be seen that the gray image and binary image occupy less space , It's a color image (BGR) One third
Step by step debugging ( The method can be seen : Portal ):


Original picture :

The binary image is as follows :

Calculate the contour
Then calculate this 10 The outline of the number , Because of this 10 The order of the outlines does not necessarily follow this 0-9 The outline of corresponds to , We need to calculate the coordinates of the upper left corner of each contour , Sort from small to large , So that's a guarantee When matching, the order is corresponding ( such as “354” The corresponding is indeed template pass the civil examinations 4,6,5 A digital )
# Calculate the contour
#cv2.findContours() The parameters accepted by the function are binary graphs , Black and white ( It's not grayscale ),cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL Only the outer contour is detected ,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE Keep only the end coordinates
# Back to list Each element in is an outline in the image
# ref_, refCnts, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(ref.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
refCnts, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(ref.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# -1 Means to draw all the contours , Behind is the brush color , Brush size
# refCnts Return to the image with the outline drawn
cv2.drawContours(img,refCnts,-1,(0,0,255),3)
cv_show('img',img)
print (np.array(refCnts).shape)
refCnts = myutils.sort_contours(refCnts, method="left-to-right")[0] # Sort , From left to right , From top to bottom
digits = {
}
Before ordering refCnts:
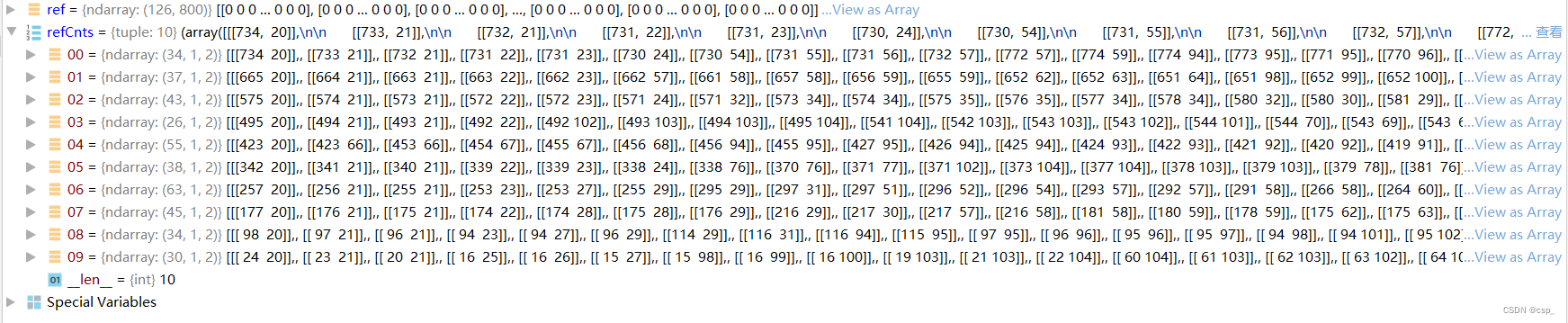
After ordering refCnts:

Sorting function sort_contours:
boundingBoxes Yes 4 Return values (x,y,h,w), By virtue of x You can judge the position relationship between the front and back of the number
def sort_contours(cnts, method="left-to-right"):
reverse = False
i = 0
if method == "right-to-left" or method == "bottom-to-top":
reverse = True
if method == "top-to-bottom" or method == "bottom-to-top":
i = 1
boundingBoxes = [cv2.boundingRect(c) for c in cnts] # Use the smallest rectangle , Wrap the shapes you find x,y,h,w
(cnts, boundingBoxes) = zip(*sorted(zip(cnts, boundingBoxes), key=lambda b: b[1][i], reverse=reverse))
return cnts, boundingBoxes
result :

Then corresponding to each number ,resize To the right size , Put in digits Make a template in the array 
# Traverse every contour
for (i, c) in enumerate(refCnts):
# Calculate the circumscribed rectangle and resize To the right size
(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(c)
roi = ref[y:y + h, x:x + w]
roi = cv2.resize(roi, (57, 88))
# Each number corresponds to each template
digits[i] = roi
digits The final result of the array :

Input data processing method
Initialize convolution kernel , Image preprocessing
First, initialize the convolution kernel , Read input image , Preprocessing
# Initialize convolution kernel
rectKernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (9, 3))
sqKernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (5, 5))
# Read input image , Preprocessing
image = cv2.imread(args["image"])
cv_show('image',image)
image = myutils.resize(image, width=300)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv_show('gray',gray)
rectKernel:

sqKernel:

Images :

Resize , After converting to grayscale :

Top hat operation
Some morphological operations can be seen
Top hat operation of image morphological operation (TopHat) Operate with black hat (BlackHat)
# Top hat operation , Highlight brighter areas
# Carry out the top hat operation according to the core size specified by yourself
tophat = cv2.morphologyEx(gray, cv2.MORPH_TOPHAT, rectKernel)
cv_show('tophat',tophat)
result :

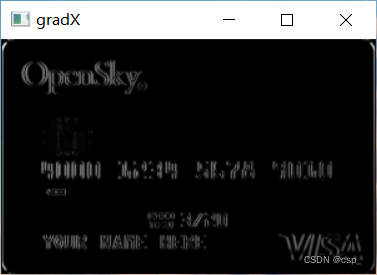
Sobel Operator for high pass filtering
Some morphological operations can be seen :Sobel operator
# ksize: yes Sobel The size of the operator , That is, the size of the convolution kernel , Must be odd , The default value is 3(ksize=-1 Equivalent to using 3*3 Of )
gradX = cv2.Sobel(tophat, ddepth=cv2.CV_32F, dx=1, dy=0, ksize=-1)
# The absolute value
gradX = np.absolute(gradX)
# normalization
(minVal, maxVal) = (np.min(gradX), np.max(gradX))
gradX = (255 * ((gradX - minVal) / (maxVal - minVal)))
gradX = gradX.astype("uint8")
print (np.array(gradX).shape)
cv_show('gradX',gradX)
result :
Close your operations , Two valued
after 2 Secondary closing operation ( Inflate first , Corrode again ) Put the numbers together , You can use THRESH_OTSU Binarization , Its advantage is that it can automatically find the appropriate threshold
# By closing ( Inflate first , Corrode again ) Put the numbers together
gradX = cv2.morphologyEx(gradX, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, rectKernel)
cv_show('gradX',gradX)
#THRESH_OTSU Will automatically find the right threshold , Suitable for bimodal , The threshold parameter needs to be set to 0
thresh = cv2.threshold(gradX, 0, 255,
cv2.THRESH_BINARY | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
cv_show('thresh',thresh)
# Repeat the closing operation once
thresh = cv2.morphologyEx(thresh, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, sqKernel)
cv_show('thresh',thresh)
The first 1 Secondary closing operation :

binarization :

The first 2 Secondary closing operation :

Calculate the contour
# Calculate the contour
# thresh_, threshCnts, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
threshCnts, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
Draw the outline on the color map
cnts = threshCnts
cur_img = image.copy()
cv2.drawContours(cur_img,cnts,-1,(0,0,255),3)
cv_show('img',cur_img)
result :

Filter profile
Then filter the contour , That is, by calculating the size of all outline circumscribed rectangles , Find valuable digital areas , Put this 4 Put areas locs Sort the list
locs = []
# Traverse the outline
for (i, c) in enumerate(cnts):
# Calculate rectangle
(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(c)
ar = w / float(h)
# Choose the right area , According to the actual task , It's basically a set of four numbers
if ar > 2.5 and ar < 4.0:
if (w > 40 and w < 55) and (h > 10 and h < 20):
# The right ones stay
locs.append((x, y, w, h))
# Sort the matching contours from left to right
locs = sorted(locs, key=lambda x:x[0])
locs List content :

Template matching results in recognition
Template matching
First enlarge the outline slightly , Then traverse the numbers in each contour , Similar to the above method , Find each number , Calculate each score in the template , Get the most appropriate number and draw it :
output = []
# Go through the numbers in each profile
for (i, (gX, gY, gW, gH)) in enumerate(locs):
# initialize the list of group digits
groupOutput = []
# Extract each group from the coordinates
group = gray[gY - 5:gY + gH + 5, gX - 5:gX + gW + 5]
cv_show('group',group)
# Preprocessing
group = cv2.threshold(group, 0, 255,
cv2.THRESH_BINARY | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
cv_show('group',group)
# Calculate the outline of each group
# group_,digitCnts,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(group.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
digitCnts,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(group.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
digitCnts = contours.sort_contours(digitCnts,
method="left-to-right")[0]
# Calculate each value in each group
for c in digitCnts:
# Find the outline of the current value ,resize To the right size
(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(c)
roi = group[y:y + h, x:x + w]
roi = cv2.resize(roi, (57, 88))
cv_show('roi',roi)
# Calculate the match score
scores = []
# Calculate each score in the template
for (digit, digitROI) in digits.items():
# Template matching
result = cv2.matchTemplate(roi, digitROI,
cv2.TM_CCOEFF)
(_, score, _, _) = cv2.minMaxLoc(result)
scores.append(score)
# Get the most appropriate number
groupOutput.append(str(np.argmax(scores)))
# Draw out
cv2.rectangle(image, (gX - 5, gY - 5),
(gX + gW + 5, gY + gH + 5), (0, 0, 255), 1)
cv2.putText(image, "".join(groupOutput), (gX, gY - 15),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.65, (0, 0, 255), 2)
# Get the results
output.extend(groupOutput)
Part of the result :



output list :

Print the results
# Print the results
print("Credit Card Type: {}".format(FIRST_NUMBER[output[0]]))
print("Credit Card #: {}".format("".join(output)))
cv2.imshow("Image", image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
result :

边栏推荐
- Zhaoqi science and technology innovation high-end talent project was introduced and implemented, mass entrepreneurship and innovation competition was organized, and online live roadshow was broadcast
- R language ggplot2 visualization: use the ggdotplot function of ggpubr package to visualize dot plot, set the add parameter to add the mean and standard deviation vertical lines, and set the error.plo
- Huawei applications have called the checkappupdate interface. Why is there no prompt for version update in the application
- [leetcode daily question] - 121. The best time to buy and sell stocks
- VP video structured framework
- pytorch---进阶篇(函数使用技巧/注意事项)
- 怎样在nature上查文献?
- 北京的大学排名
- Jintuo shares listed on the Shanghai Stock Exchange: the market value of 2.6 billion Zhang Dong family business has a strong color
- R语言检验相关性系数的显著性:使用cor.test函数计算相关性系数的值和置信区间及其统计显著性(如果变量来自正态分布总体使用皮尔森方法pearson)
猜你喜欢

Chuhuan technology is listed on Shenzhen Stock Exchange: Minsheng securities, with a market value of 2.7 billion, is a shareholder
In the changing era of equipment manufacturing industry, how can SCM supply chain management system enable equipment manufacturing enterprises to transform and upgrade
NAT/NAPT地址转换(内外网通信)技术详解【华为eNSP】

谷歌尝试为ChromeOS引入密码强度指示器以提升线上安全性

anaconda No module named ‘cv2‘

The civil construction of the whole line of Guangzhou Metro Line 13 phase II has been completed by 53%, and it is expected to open next year
![[basic] the difference between dynamic link library and static link library](/img/d5/fe7880e3fa91faff10a1c31870cce0.png)
[basic] the difference between dynamic link library and static link library

如何查找国内各大学本科学位论文?

二叉树的创建以及遍历

数据中台、BI业务访谈(四)—— 十个问题看本质
随机推荐
Where is the foreign literature needed to write the graduation thesis?
How to find undergraduate dissertations of domestic universities?
数商云:引领化工业态数字升级,看摩贝如何快速打通全场景互融互通
Devsecops, speed and security
No module named ‘win32gui‘
Database expansion can also be so smooth, MySQL 100 billion level data production environment expansion practice
anaconda No module named ‘cv2‘
本科毕业论文外文文献翻译怎么找?
jetson nano上远程桌面
What is the transport layer protocol tcp/udp???
Bluetooth ble4.0-hm-10 device pairing Guide
Deep Packet Inspection Using Cuckoo Filter论文总结
Zhaoqi science and technology innovation high-end talent project was introduced and implemented, mass entrepreneurship and innovation competition was organized, and online live roadshow was broadcast
QCF for deep packet inspection paper summary
外文文献查找技巧方法有哪些
[leetcode daily question] - 268. Missing numbers
Deep packet inspection using cuckoo filter paper summary
NAT/NAPT地址转换(内外网通信)技术详解【华为eNSP】
Chuhuan technology is listed on Shenzhen Stock Exchange: Minsheng securities, with a market value of 2.7 billion, is a shareholder
如何查询外文文献?