当前位置:网站首页>How to use redis ordered collection
How to use redis ordered collection
2022-07-02 01:55:00 【Yisu cloud】
Redis How to use ordered sets
This article mainly introduces “Redis How to use ordered sets ”, In daily operation , I believe a lot of people are Redis There are doubts about how to use ordered sets , Xiao Bian consulted all kinds of materials , Sort out simple and easy-to-use operation methods , I hope to answer ”Redis How to use ordered sets ” Your doubts help ! Next , Please follow Xiaobian to learn !

Redis data structure : Ordered set
An orderly collection . Each element consists of a member and a score associated with the member , Members are stored as strings , Score in 64 Bit double precision floating-point number storage . Members cannot be duplicated , Sort by score , Sort in member dictionary order when the same score .
data structure
character string
hash
list
aggregate
Ordered set
HyperLogLog
Bitmap
Geographical coordinates
flow
Ordered set (sorted set)
Add or update members
1.zadd command Format :zadd key [NX|XX] [GT|LT] [CH] [INCR] score member [score member …]
Returns the number of new members successfully added , If the execution is to update the member score, return 0.zadd key score member [score member ...]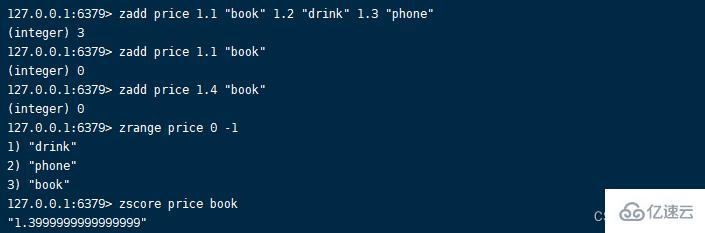
XX The function of the option is to update only without adding , Go back to 0.zadd key XX score member [score member ...]
NX The function of the option is to add only without updating , The number of added elements returned after successful execution .zadd key NX score member [score member ...]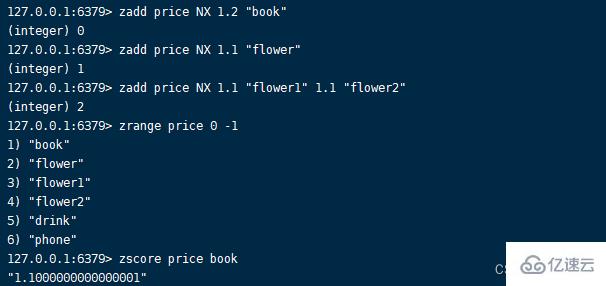
CH The function of this option is to return the number of members modified rather than the number of members successfully added , Modified including newly added .zadd key CH score member [score member ...]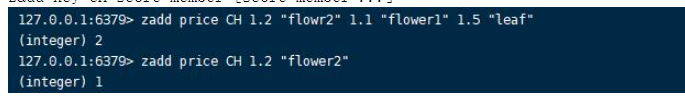
Remove the specified member
1.zrem command Format :zrem key member [member …]
Returns the number of removed members , Automatically ignore when members do not exist in the collection .zrem key member [member ...]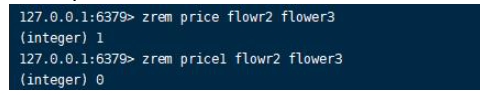
2.zremrangebyrank command Format :zremrangebyrank key start stop
Remove members within the specified ranking range , Returns the number of removed members , The ranking can be positive or negative .zremrangebyrank key start stop
3.zremrangebyscore command Format :zremrangebyscore key min max
Remove members within the specified score range , Returns the number of removed members .min or max Before to add “(” It means that the open interval does not contain boundary values .zremrangebyscore key min max
4.zremrangebylex command Format :zremrangebylex key min max
For an ordered set arranged in dictionary order ( That is, the score is the same ), Remove members within the specified lexicographic range . Returns the number of removed members ,min、max Of Value for Include : belt “[” The value of indicates that the dictionary order boundary is included , belt “(” Indicates that the dictionary order boundary is not included ,“+” Infinity ,“-” Represents infinitesimal .zremrangebylex key min max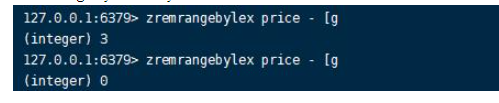
Pop up elements
1.zpopmax command Format :zpopmax key [count]
Pop up the one with the highest score count Members , When there are multiple elements with the highest score, the member with the largest dictionary order pops up , If not specified count Default 1 individual , After execution, return the member and score of the ejected element .zpopmax key [count]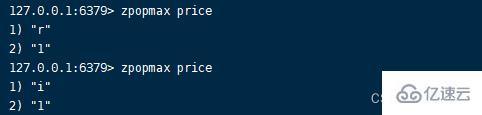
2.zpopmin command Format :zpopmin key [count]
Pop up the lowest score count Members , When there are multiple elements with the lowest score, the member with the lowest dictionary order will pop up , If not specified count Default 1 individual , After execution, return the member and score of the ejected element .zpopmin key [count]
3.bzpopmax command Format :bzpopmax key [key …] timeout
Blocking zpopmax command ,timeout Second accuracy . The command checks the given ordered set in turn , And pop up the element with the largest score from the first non empty set , Otherwise, block the current client until there are elements or it returns after the timeout nil. A list will be returned when the element is successfully popped , Contains the ordered set of ejected elements 、 Members and scores .bzpopmax key [key ...] timeout
4.bzpopmin command Format :bzpopmin key [key …] timeout
Blocking zpopmin command ,timeout Second accuracy . The command checks the given ordered set in turn , And pop up the element with the lowest score from the first non empty set , Otherwise, block the current client until there are elements or it returns after the timeout nil. A list will be returned when the element is successfully popped , Contains the ordered set of ejected elements 、 Members and scores .bzpopmin key [key ...] timeout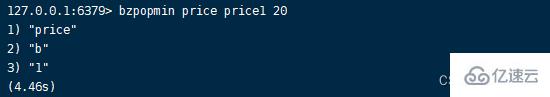
client 2:
Get member score
1.zscore command Format :zscore key member
Get the score of a given member , When the collection does not exist or the member does not exist nil.zscore key member
Calculate the member score
1.zincrby command Format :zincrby key increment member
After execution, return the current member score ,increment It is timing self increase , Otherwise, it is self subtraction ; If the key does not exist or the member does not exist, perform the create operation .zincrby key increment member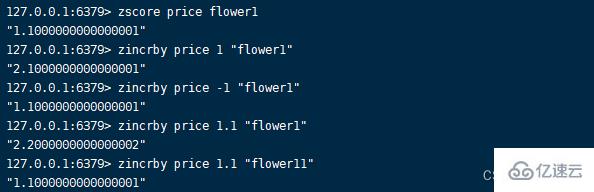
Get the number of members
1.zcard command Format :zcard key
Returns the number of members contained in the collection , Returns... When the collection does not exist 0.zcard key
2.zcount command Format :zcount key min max
Get the number of members within the specified score range ,min or max Before to add “(” It means that the open interval does not contain boundary values , value +inf Infinity ,-inf Represents infinitesimal .zcount key min max
3.zlexcount command Format :zlexcount key min max
For an ordered set arranged in dictionary order ( That is, the score is the same ), Get the number of members in the specified dictionary order range ,min、max Of Value for Include : belt “[” The value of indicates that the dictionary order boundary is included , belt “(” Indicates that the dictionary order boundary is not included ,“+” Infinity ,“-” Represents infinitesimal .zlexcount key min max
Get member rankings
1.zrank command Format :zrank key member
Return the ascending ranking of members , Returns when the collection or member does not exist nil.zrank key member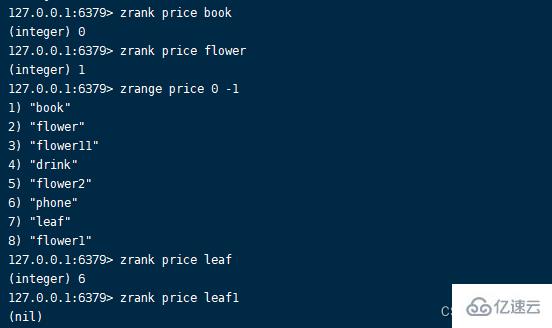
2.zrevrank command Format :zrevrank key member
Return the descending ranking of members , Returns when the collection or member does not exist nil.zrevrank key member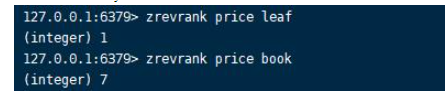
Get members
1.zrange command Format :zrange key min max [BYSCORE|BYLEX] [REV] [LIMIT offset count] [WITHSCORES]
Gets the members within the specified index range , Sort in ascending order according to the score .WITHSCORES Option can return the score after the command is executed , Returns the odd digits of the list as members , Even digits are corresponding scores . Returns... When the collection does not exist empty.zrange key min max [WITHSCORES]
2.zrevrange command Format :zrevrange key start stop [WITHSCORES]
Gets the members within the specified index range , Arrange in descending order according to the score .WITHSCORES Option can return the score after the command is executed , Returns the odd digits of the list as members , Even digits are corresponding scores . Returns... When the collection does not exist empty.zrevrange key start stop [WITHSCORES]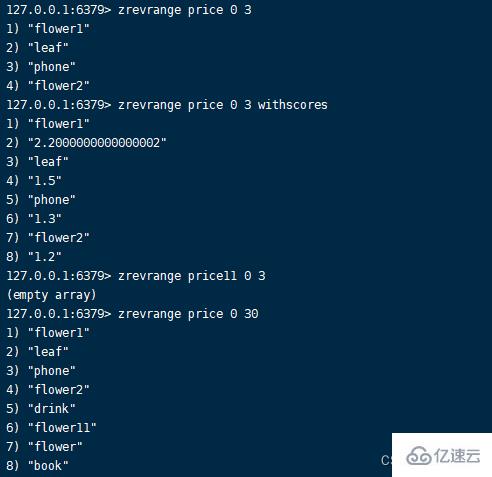
3.zrangebyscore command Format :zrangebyscore key min max [WITHSCORES] [LIMIT offset count]
Get the members within the specified score range , Sort in ascending order according to the score .WITHSCORES Option can return the score after the command is executed , Returns the odd digits of the list as members , Even digits are corresponding scores . Returns... When the collection does not exist empty.zrangebyscore key min max [WITHSCORES] [LIMIT offset count]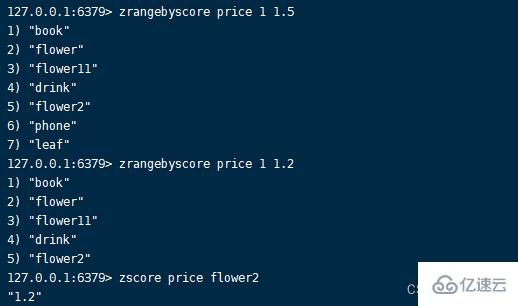
[LIMIT offset count] The function of option is to limit the number of returned members ,offset Specify the number of members to skip ,count Execute the maximum number of returned members ,count Take the absolute value when it is negative .
min or max Before to add “(” It means that the open interval does not contain boundary values , value +inf Infinity ,-inf Represents infinitesimal .
4.zrevrangebyscore command Format :zrevrangebyscore key max min [WITHSCORES] [LIMIT offset count]
Get the members within the specified score range , Arrange in descending order according to the score , Be careful max min The order .zrevrangebyscore key max min [WITHSCORES] [LIMIT offset count]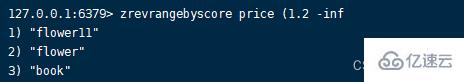
5.zrangebylex command Format :zrangebylex key min max [LIMIT offset count]
When the members have the same score , Get the members in the specified dictionary order range , Arrange in ascending dictionary order ,min、max Of Value for Include : belt “[” The value of indicates that the dictionary order boundary is included , belt “(” Indicates that the dictionary order boundary is not included ,“+” Infinity ,“-” Represents infinitesimal .zrangebylex key min max [LIMIT offset count]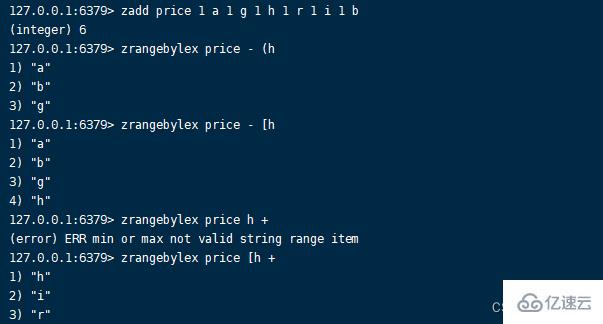
6.zrevrangebylex command Format :zrevrangebylex key max min [LIMIT offset count]
When the members have the same score , Get the members in the specified dictionary order range , Arrange in descending dictionary order ,max、min Of Value for Include : belt “[” The value of indicates that the dictionary order boundary is included , belt “(” Indicates that the dictionary order boundary is not included ,“+” Infinity ,“-” Represents infinitesimal .zrevrangebylex key max min [LIMIT offset count]Set operations
1. Combine
1)zunionstore command Format :zunionstore destination numkeys key [key …] [WEIGHTS weight] [AGGREGATE SUM|MIN|MAX]
numkeys Is the number of sets involved in the operation , Return when it doesn't correspond error, After execution, return the number of members of the new set . The result of union is the member set , If there are the same members in the set participating in the operation , By default, the member score of the new set is the sum of the member scores of the original set .zunionstore destination numkeys key [key ...]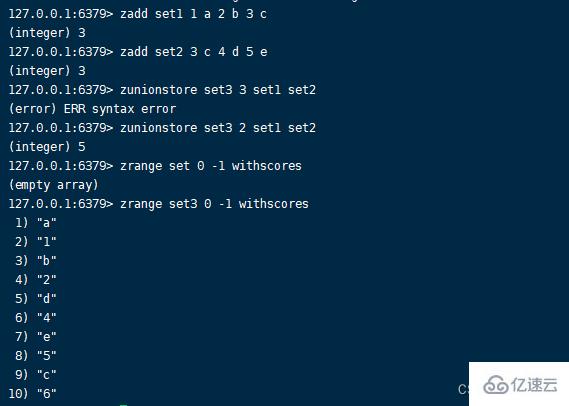
AGGREGATE The function of the option is to specify the aggregate function to be used , If not specified, default SUM.SUM Point value addition ,MIN Refers to the minimum score ,MAX Refers to the maximum score .zunionstore destination numkeys key [key ...] [AGGREGATE SUM|MIN|MAX]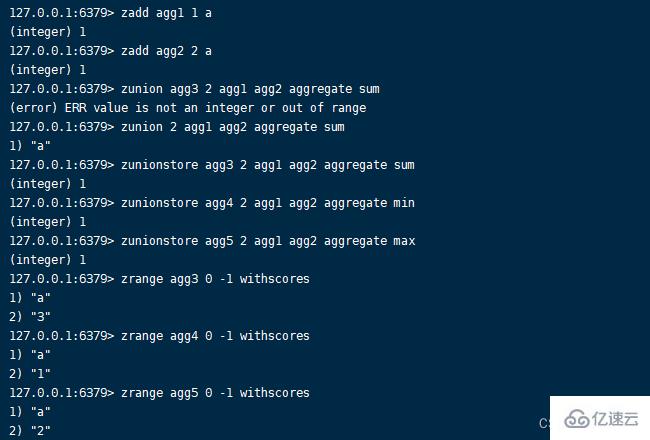
WEIGHTS The function of this option is to set a weight for each set before performing aggregation , The weights are multiplied by the scores of the members in the set to get new scores , Then perform aggregation calculation .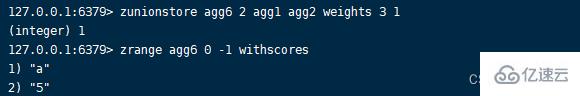
2)zunion command Format :zunion numkeys key [key …] [WEIGHTS weight] [AGGREGATE SUM|MIN|MAX] [WITHSCORES]
After execution, return to the new collection member .zunion numkeys key [key ...] [WEIGHTS weight] [AGGREGATE SUM|MIN|MAX] [WITHSCORES]
2. intersection
1)zinterstore command Format :zinterstore destination numkeys key [key …] [WEIGHTS weight] [AGGREGATE SUM|MIN|MAX]
After execution, return the number of members of the new set .zinterstore destination numkeys key [key ...] [WEIGHTS weight] [AGGREGATE SUM|MIN|MAX]
2)zinter command Format :zinter numkeys key [key …] [WEIGHTS weight] [AGGREGATE SUM|MIN|MAX] [WITHSCORES]
After execution, return to the new collection member .zinter numkeys key [key ...] [WEIGHTS weight] [AGGREGATE SUM|MIN|MAX] [WITHSCORES]
Be careful :
1. Set operation can use set as input , By default , The score of set members is regarded as 1 Participate in operation , You can use WEIGHTS Option set the weight to change the set score .Common use
1. Ranking List
2. Timeline
Here we are , About “Redis How to use ordered sets ” That's the end of my study , I hope we can solve your doubts . The combination of theory and practice can better help you learn , Let's try ! If you want to continue to learn more related knowledge , Please continue to pay attention to Yisu cloud website , Xiaobian will continue to strive to bring you more practical articles !
边栏推荐
- 跨域?同源?一次搞懂什么是跨域
- leetcode2312. 卖木头块(困难,周赛)
- Construction and maintenance of business websites [10]
- Automatically browse pinduoduo products
- np. Where and torch Where usage
- "C language programming", 4th Edition, edited by he Qinming and Yan Hui, after class exercise answers Chapter 3 branch structure Exercise 3
- Should enterprises choose server free computing?
- Implementation of Weibo system based on SSM
- Is the knowledge of University useless and outdated?
- The concepts and differences between MySQL stored procedures and stored functions, as well as how to create them, the role of delimiter, the viewing, modification, deletion of stored procedures and fu
猜你喜欢

SAP ui5 beginner tutorial 20 - explanation of expression binding usage of SAP ui5
遊戲思考15:全區全服和分區分服的思考
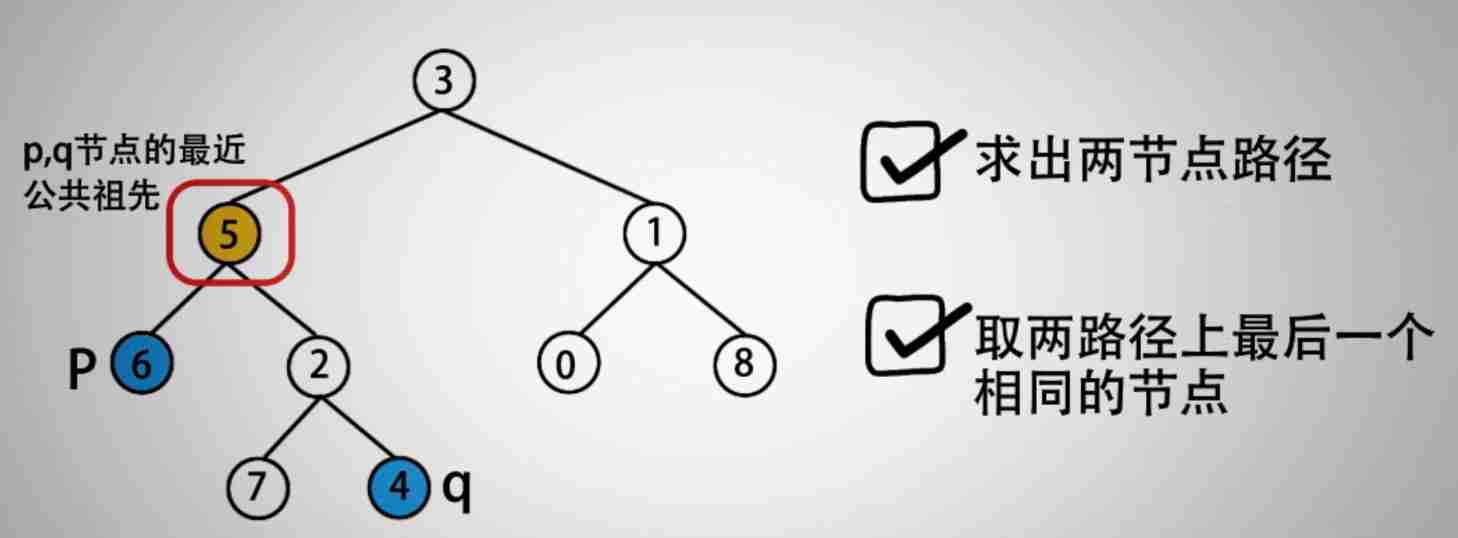
【LeetCode 43】236. The nearest common ancestor of binary tree
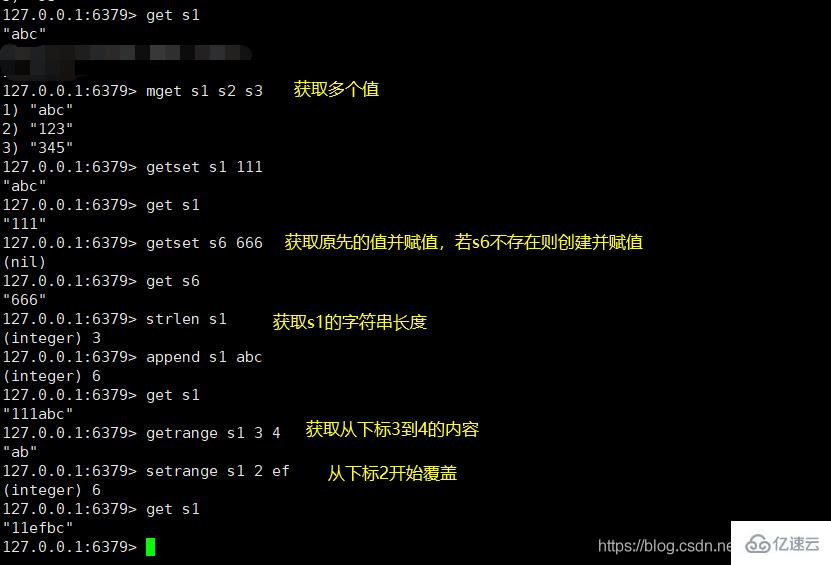
Redis环境搭建和使用的方法

What are the skills of spot gold analysis?

The role of artificial intelligence in network security

Data analysis on the disaster of Titanic
Pyldavis installation and use | attributeerror: module 'pyldavis' has no attribute' gensim '| visual results are exported as separate web pages

From January 11, 2007 to January 11, 2022, I have been in SAP Chengdu Research Institute for 15 years
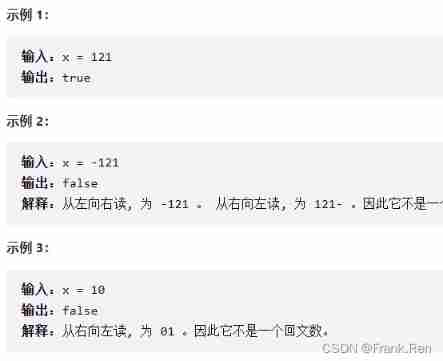
Number of palindromes in C language (leetcode)
随机推荐
Word search applet design report based on cloud development +ppt+ project source code + demonstration video
Learn basic K-line diagram knowledge in three minutes
Logging only errors to the console Set system property ‘log4j2. debug‘ to sh
MySQL如何解决delete大量数据后空间不释放的问题
剑指 Offer 29. 顺时针打印矩阵
Is the knowledge of University useless and outdated?
迁移云计算工作负载的四个基本策略
【LeetCode 43】236. The nearest common ancestor of binary tree
k线图形态这样记(口诀篇)
1069. Division of convex polygons (thinking, interval DP)
np. Where and torch Where usage
Construction and maintenance of business websites [13]
matlab 使用 resample 完成重采样
This is the report that leaders like! Learn dynamic visual charts, promotion and salary increase are indispensable
企业应该选择无服务器计算吗?
This is the report that leaders like! Learn dynamic visual charts, promotion and salary increase are indispensable
Implementation of Weibo system based on SSM
【C#】使用正则校验内容
Automatically browse pinduoduo products
剑指 Offer 62. 圆圈中最后剩下的数字