当前位置:网站首页>Threads and thread pools
Threads and thread pools
2022-06-28 10:36:00 【0&1 * 1】
Threads and thread pools
One 、 Thread Introduction
1) Thread Introduction
1.python—> programing language ----> Developing applications
Program :1. The driver , For example, a graphics card driver 2. operating system , such as windows System 3. Applications , such as qq
Applications , Binary files stored on the hard disk , Only when it is loaded into the memory space , It has a life cycle
A process is a running application
Each process starts a thread by default , This thread is called the main thread , Thread belongs to process .
2) Implementation of threads
1. Thread module
Python Through two standard libraries _thread and threading
Provides support for threads , threading Yes _thread It was packaged .
threading Module provides Thread , Lock , RLock , Condition And so on .
Therefore, in actual use, we generally use threading
2.Thread
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture (img-P8OvD1bm-1568727516294)(…/…/…/…/…/…/Desktop/Data/Python_note/work.md/photo/23.png)]
1.from threading import Thread
import time
def f1(people):
print("hello,{}".format(people))
time.sleep(3)
print("bye")
def f2():
print("hi")
time.sleep(3)
print("goodbye")
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Normal call , There is a sequence , The main thread
# f1()
# f2()
# Thread operation
f1_thread = Thread(target=f1, args=(" Hu Ge ",), name='hello') # Created a thread instance
f2_thread = Thread(target=f2, name='hi') # When an instance object , Function does not execute
f1_thread.setName("dai")
f1_thread.setName("hu")
print("f1 name:", f1_thread.getName())
print("f2 name:", f2_thread.getName())
# f1_thread.setDaemon(True)
# f2_thread.setDaemon(True)
# f1_thread.start() # call start Method just started executing
# f2_thread.start()
# f1_thread.join() # Blocking call , The main thread waits
# f2_thread.join()
print(" Main thread execution completed ")
"""
The main thread is finished , But the child thread is still not closed , The program has been unable to close
The guardian thread : After the main thread is executed , The program closes
"""
2.from threading import Thread
import time
# class MyThread(Thread):
# def run(self):
# print('hello')
# time.sleep(3)
# print('bye')
#
#
# my_thread = MyThread() # Create a thread instance
# my_thread.start()
# Overrides the class run Method , adopt start Method to automatically call... In the class run Method
class MyThread(Thread):
def __init__(self, people, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.people = people
def run(self):
print('hello,{}'.format(self.people))
time.sleep(3)
print('bye')
my_thread = MyThread(" Qi Shijiu ", name="hello") # Create a thread instance
print(my_thread.getName())
my_thread.start()
3. Create thread
1( stay python There are two ways to create threads in , example Thread Class and inheritance overrides Thread class
example Thread class
2([ Failed to transfer the external chain picture (img-7ivm83nv-1568727516295)(…/…/…/…/…/…/Desktop/Data/Python_note/work.md/photo/24.png)]
3( Inherit Thread class
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture (img-hZMy3PPT-1568727516295)(…/…/…/…/…/…/Desktop/Data/Python_note/work.md/photo/25.png)]
4(Join & setDaemon
Before we talk about these two methods , You need to know the concept of main thread and sub thread
The main thread : When a program starts , A thread starts running , This thread is usually called the main thread of the program
Sub thread : Because the program is executed at the beginning , If you need to create threads again , The created thread is the sub thread of the main thread
The importance of the main thread lies in two aspects :
1. It's the thread that produces other threads
2. Usually, it must finish the execution finally, such as performing various closing operations
5(join : Block caller , Until the call join () The thread execution of the method ends , Will continue to carry on
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture (img-brvDhADK-1568727516296)(…/…/…/…/…/…/Desktop/Data/Python_note/work.md/photo/26.png)]
6(setDaemon() And join() Basically relative , join It will wait for the sub thread to finish executing ; and setDaemon Will not wait
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture (img-HuN9FdLD-1568727516296)(…/…/…/…/…/…/Desktop/Data/Python_note/work.md/photo/27.png)]
Two 、 Threads Resource sharing between
1) The mutex
1. In multithreading , All global variables are shared by all threads , therefore , The biggest danger of sharing data between threads is that multiple threads modify a variable at the same time , That's a mess , So we need mutexes , To lock the data .
from threading import Thread, Lock
data = 0
def add_1():
global data
lock.acquire()
for i in range(1000000):
data += 1
lock.release()
def red_1():
global data
lock.acquire()
for i in range(1000000):
data -= 1
lock.release()
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Normal execution , The result is 0
# add_1()
# red_1()
# print(data)
lock = Lock()
# Thread operation
t1 = Thread(target=add_1)
t2 = Thread(target=red_1)
t1.start()
t2.start()
t1.join()
t2.join()
print(data)
"""
data += 1
x = data + 1
data = x
data = 0
t1: x1 = data + 1 # x1 = 0 + 1 = 1
t2: x2 = data - 1 # x2 = 0 - 1 = -1
t1: data = x1 = 1
t2: data = x2 = -1
result :data = -1
"""
2) Sharing of global variables between threads
1. Tips !
Because the thread belongs to the same process , So they share memory areas .
So global variables are public .
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture (img-nejhngXC-1568727516297)(…/…/…/…/…/…/Desktop/Data/Python_note/work.md/photo/28.png)]
3) There is a contention problem between shared memory
1. Tips !
If 1000000 No effect
You can continue to add 0
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture (img-aIm7n6jH-1568727516297)(…/…/…/…/…/…/Desktop/Data/Python_note/work.md/photo/29.png)]
3.[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture (img-U2d9s69K-1568727516297)(…/…/…/…/…/…/Desktop/Data/Python_note/work.md/photo/30.png)]
from threading import Thread
a = 5
def f():
print(' I'm a child thread , I want to change the global variable value ')
global a
a = 2
if __name__ == '__main__':
print(' I'm the main thread , Variable a The value of is {}'.format(a))
t = Thread(target=f)
t.start()
t.join()
print(' I'm the main thread , Variable a The value of is {}'.format(a))
# Global variables are shared by all child threads . Resource competition
4) Use locks to control access to shared resources
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture (img-ENJkv7WB-1568727516298)(…/…/…/…/…/…/Desktop/Data/Python_note/work.md/photo/31.png)]
5) Thread queue operation
1. The team : put(item)
2. Out of the team : get()
from threading import Thread
from queue import Queue
from random import randint
my_queue = Queue(10) # Create a queue object , Specify the queue length
def my_put(my_queue):
""" Stuff the queue """
for x in range(10):
num = randint(0, 1000)
my_queue.put(num)
def my_get(my_queue):
""" Get something in the queue """
for y in range(3):
num = my_queue.get()
print(num)
p = Thread(target=my_put, args=(my_queue,))
g = Thread(target=my_get, args=(my_queue,))
p.start()
g.start()
p.join()
g.join()
3. Test empty : empty() # The approximate
4. Test full : full() # The approximate
5. The queue length : qsize() # The approximate
6. End of the task : task_done()
from queue import Queue
my_queue = Queue(3)
if __name__ == '__main__':
my_queue.put(1)
print(my_queue.qsize())
my_queue.get()
print(my_queue.qsize())
print(my_queue.empty())
my_queue.put(1)
my_queue.put(1)
my_queue.put(1)
print(my_queue.full())
my_queue.task_done() # End of the task
my_queue.task_done() # End of the task
my_queue.task_done() # End of the task
my_queue.task_done() # End of the task
my_queue.join() # Waiting for completion , Used to determine task_done Is the number of times and put The same number of times
print(" End of the task ")
from threading import Thread, current_thread
from queue import Queue
import time
from multiprocessing.pool import ThreadPool
# class ThreadPool(object):
# def __init__(self, n): # Parameters n Is the number of threads that can be reused
# # Create a queue , Put tasks in it
# self.q = Queue(n)
# # Generating threads
# for i in range(n):
# Thread(target=self.worker, daemon=True).start()
#
# def worker(self):
# """ To complete the task fetching from the queue """
# while True: # Dead cycle , In this way, the thread will never end , Keep using it
# func, args, kwargs = self.q.get() # Get the task from the queue
# func(*args, **kwargs) # Run the task you just got
# self.q.task_done() # After execution , Notification queue
#
# def put_q(self, func, args=(), kwargs={}):
# """ Put tasks in the queue """
# self.q.put((func, args, kwargs))
#
# def join_q(self):
# self.q.join() # Blocking , Waiting for completion
7. Waiting for completion : join()
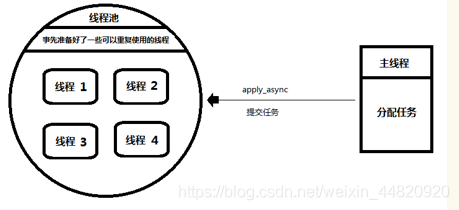
3、 ... and 、 Thread pool
1) The concept of a pool
1. The main thread : Equivalent to producer , Just submit tasks to the thread pool .
It doesn't care how the thread pool performs tasks .
therefore , It doesn't matter which thread performs the task .
2. Thread pool : Equivalent to consumer , Responsible for receiving tasks ,
And assign the task to an idle thread to execute .
3.
2) Simple implementation of thread pool

3) Effect of implementation

4)python Built in thread pool

5) Other operations of the pool
1. Operation 1 : close - Close the submit channel , It is not allowed to submit tasks again
2. Operation two : terminate - suspend
边栏推荐
- MySQL cannot be opened. Flash back
- Six fusion positioning technologies in wireless communication application of Internet of things
- 错过金三银四,找工作4个月,面试15家,终于拿到3个offer,定级P7+
- Redis数据库
- How does ETF position affect spot gold price?
- 关于FTP的协议了解
- Idea failed to connect to SQL Sever
- etf持仓如何影响现货金价?
- Metersphere实现UI自动化元素不可点击(部分遮挡)
- Ruoyi integrated building block report (NICE)
猜你喜欢

Information hidden in the trend chart of Hong Kong London gold market

线程和线程池

Interface automation framework scaffold - use reflection mechanism to realize the unified initiator of the interface

ruoyi集成积木报表(nice)

Markdown -- basic usage syntax

接口自动化框架脚手架-参数化工具的实现
sqlcmd 连接数据库报错

idea连接sql sever失败
Set up your own website (11)

To enhance the function of jupyter notebook, here are four tips
随机推荐
接口自动化框架脚手架-参数化工具的实现
Mysql通用二进制安装方式
What is the difference between MySQL development environment and test environment??
Ffmpeg audio and video recording
Hystrix deployment
解决表单action属性传参时值为null的问题
一种跳板机的实现思路
Markdown -- basic usage syntax
Dear leaders, ask me if MySQL does not support early_ Offset mode? Unsupported star
接口自动化框架脚手架-利用反射机制实现接口统一发起端
Teach you how to handle the reverse SVG mapping of JS
Django数据库操作以及问题解决
[Unity][ECS]学习笔记(三)
2D code generator for openharmony application development
OpenHarmony应用开发之二维码生成器
sentinel
DlhSoft Kanban Library for WPF
Ideal interface automation project
知道 Redis RDB 这些细节,可以少踩很多坑
Set up your own website (11)