当前位置:网站首页>ThreadLocal基础及高级使用
ThreadLocal基础及高级使用
2022-06-09 12:40:00 【little-peter】
解决线程安全问题:ThreadLocal
- ThreadLocal简介:
ThreadLocal从字面上来理解是线程本地变量的意思,也就是说它是线程中的私有变量,每个线程只能使用自己的变量。
以之前线程池格式化时间为例,当线程池中有 10 个线程时,SimpleDateFormat 会存入 ThreadLocal 中,它也只会创建 10 个对象,即使要执行 1000 次时间格式化任务,依然只会新建 10 个 SimpleDateFormat 对象,每个线程调用自己的 ThreadLocal 变量。
2.ThreadLocal的基础使用
ThreadLocal 常用的核心方法有三个:
- set 方法:用于设置线程独立变量副本。没有 set 操作的 ThreadLocal 容易引起脏数据。
- get 方法:用于获取线程独立变量副本。没有 get 操作的 ThreadLocal 对象没有意义
- remove 方法:用于移除线程独立变量副本。没有 remove 操作容易引起内存泄漏。
ThreadLocal基础使用如下:
public class ThreadLocalExample {
// 创建一个 ThreadLocal 对象
private static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 线程执行任务
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(threadName + " 存入值:" + threadName);
// 在 ThreadLocal 中设置值
threadLocal.set(threadName);
// 执行方法,打印线程中设置的值
print(threadName);
}
};
// 创建并启动线程 1
new Thread(runnable, "MyThread-1").start();
// 创建并启动线程 2
new Thread(runnable, "MyThread-2").start();
}
/**
* 打印线程中的 ThreadLocal 值
* @param threadName 线程名称
*/
private static void print(String threadName) {
try {
// 得到 ThreadLocal 中的值
String result = threadLocal.get();
// 打印结果
System.out.println(threadName + " 取出值:" + result);
} finally {
// 移除 ThreadLocal 中的值(防止内存溢出)
threadLocal.remove();
}
}
}以上程序的执行结果为:

从上述结果可以看出,每个线程只会读取到属于自己的 ThreadLocal 值
3.ThreadLocal 高级用法
① 初始化:initialValue
public class ThreadLocalByInitExample {
// 定义 ThreadLocal
private static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal(){
@Override
protected String initialValue() {
System.out.println("执行 initialValue() 方法");
return "默认值";
}
};
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 线程执行任务
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 执行方法,打印线程中数据(未设置值打印)
print(threadName);
}
};
// 创建并启动线程 1
new Thread(runnable, "MyThread-1").start();
// 创建并启动线程 2
new Thread(runnable, "MyThread-2").start();
}
/**
* 打印线程中的 ThreadLocal 值
* @param threadName 线程名称
*/
private static void print(String threadName) {
// 得到 ThreadLocal 中的值
String result = threadLocal.get();
// 打印结果
System.out.println(threadName + " 得到值:" + result);
}
}以上程序的执行结果为:

当使用了 #threadLocal.set 方法之后,initialValue 方法就不会被执行了,如下代码所示:
public class ThreadLocalByInitExample {
// 定义 ThreadLocal
private static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal() {
@Override
protected String initialValue() {
System.out.println("执行 initialValue() 方法");
return "默认值";
}
};
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 线程执行任务
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(threadName + " 存入值:" + threadName);
// 在 ThreadLocal 中设置值
threadLocal.set(threadName);
// 执行方法,打印线程中设置的值
print(threadName);
}
};
// 创建并启动线程 1
new Thread(runnable, "MyThread-1").start();
// 创建并启动线程 2
new Thread(runnable, "MyThread-2").start();
}
/**
* 打印线程中的 ThreadLocal 值
* @param threadName 线程名称
*/
private static void print(String threadName) {
try {
// 得到 ThreadLocal 中的值
String result = threadLocal.get();
// 打印结果
System.out.println(threadName + "取出值:" + result);
} finally {
// 移除 ThreadLocal 中的值(防止内存溢出)
threadLocal.remove();
}
}
}以上程序的执行结果为:

为什么 set 方法之后,初始化代码就不执行了?
要理解这个问题,需要从 ThreadLocal.get() 方法的源码中得到答案,因为初始化方法 initialValue 在 ThreadLocal 创建时并不会立即执行,而是在调用了 get 方法只会才会执行,测试代码如下:
import java.util.Date;
public class ThreadLocalByInitExample {
// 定义 ThreadLocal
private static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal() {
@Override
protected String initialValue() {
System.out.println("执行 initialValue() 方法 " + new Date());
return "默认值";
}
};
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 线程执行任务
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 得到当前线程名称
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
// 执行方法,打印线程中设置的值
print(threadName);
}
};
// 创建并启动线程 1
new Thread(runnable, "MyThread-1").start();
// 创建并启动线程 2
new Thread(runnable, "MyThread-2").start();
}
/**
* 打印线程中的 ThreadLocal 值
* @param threadName 线程名称
*/
private static void print(String threadName) {
System.out.println("进入 print() 方法 " + new Date());
try {
// 休眠 1s
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 得到 ThreadLocal 中的值
String result = threadLocal.get();
// 打印结果
System.out.println(String.format("%s 取得值:%s %s",
threadName, result, new Date()));
}
}以上程序的执行结果为:

从上述打印的时间可以看出:initialValue 方法并不是在 ThreadLocal 创建时执行的,而是在调用 Thread.get 方法时才执行的。
接下来来看 Threadlocal.get 源码的实现:
public T get() {
// 得到当前的线程
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
// 判断 ThreadLocal 中是否有数据
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
// 有 set 值,直接返回数据
return result;
}
}
// 执行初始化方法【重点关注】
return setInitialValue();
}
private T setInitialValue() {
// 执行初始化方法【重点关注】
T value = initialValue();
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
return value;
}从上述源码可以看出,当 ThreadLocal 中有值时会直接返回值 e.value,只有 Threadlocal 中没有任何值时才会执行初始化方法 initialValue。
注意事项—类型必须保持一致
注意在使用 initialValue 时,返回值的类型要和 ThreadLoca 定义的数据类型保持一致,如下图所示:
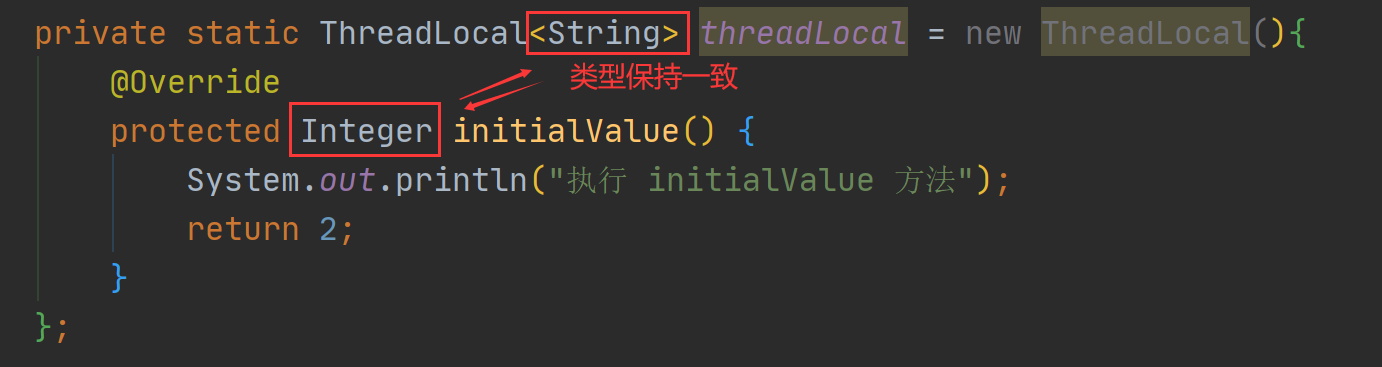
如果数据不一致就会造成 ClassCaseException 类型转换异常,如下图所示:

② 初始化2:withInitial
import java.util.function.Supplier;
public class ThreadLocalByInitExample {
// 定义 ThreadLocal
private static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal =
ThreadLocal.withInitial(new Supplier<String>() {
@Override
public String get() {
System.out.println("执行 withInitial() 方法");
return "默认值";
}
});
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 线程执行任务
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
// 执行方法,打印线程中设置的值
print(threadName);
}
};
// 创建并启动线程 1
new Thread(runnable, "MyThread-1").start();
// 创建并启动线程 2
new Thread(runnable, "MyThread-2").start();
}
/**
* 打印线程中的 ThreadLocal 值
* @param threadName 线程名称
*/
private static void print(String threadName) {
// 得到 ThreadLocal 中的值
String result = threadLocal.get();
// 打印结果
System.out.println(threadName + " 得到值:" + result);
}
}以上程序的执行结果为:

通过上述的代码发现,withInitial 方法的使用好像和 initialValue 没啥区别,那为啥还要造出两个类似的方法呢?客官莫着急,继续往下看。
③ 更简洁的 withInitial 使用
withInitial 方法的优势在于可以更简单的实现变量初始化,如下代码所示:
public class ThreadLocalByInitExample {
// 定义 ThreadLocal
private static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> "默认值");
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 线程执行任务
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
// 执行方法,打印线程中设置的值
print(threadName);
}
};
// 创建并启动线程 1
new Thread(runnable, "MyThread-1").start();
// 创建并启动线程 2
new Thread(runnable, "MyThread-2").start();
}
/**
* 打印线程中的 ThreadLocal 值
* @param threadName 线程名称
*/
private static void print(String threadName) {
// 得到 ThreadLocal 中的值
String result = threadLocal.get();
// 打印结果
System.out.println(threadName + " 得到值:" + result);
}
}
以上程序的执行结果为:

4.ThreadLocal 版时间格式化
了解了 ThreadLocal 的使用之后,我们回到本文的主题,接下来我们将使用 ThreadLocal 来实现 1000 个时间的格式化,具体实现代码如下:
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class MyThreadLocalByDateFormat {
// 创建 ThreadLocal 并设置默认值
private static ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat> dateFormatThreadLocal =
ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> new SimpleDateFormat("mm:ss"));
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建线程池执行任务
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(10, 10, 60,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1000));
// 执行任务
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
int finalI = i;
// 执行任务
threadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 得到时间对象
Date date = new Date(finalI * 1000);
// 执行时间格式化
formatAndPrint(date);
}
});
}
// 线程池执行完任务之后关闭
threadPool.shutdown();
// 线程池执行完任务之后关闭
threadPool.shutdown();
}
/**
* 格式化并打印时间
* @param date 时间对象
*/
private static void formatAndPrint(Date date) {
// 执行格式化
String result = dateFormatThreadLocal.get().format(date);
// 打印最终结果
System.out.println("时间:" + result);
}
}以上程序的执行结果为:

从上述结果可以看出,使用 ThreadLocal 也可以解决线程并发问题,并且避免了代码加锁排队执行的问题。
使用场景2:跨类传递数据
除了上面的使用场景之外,我们还可以使用 ThreadLocal 来实现线程中跨类、跨方法的数据传递。比如登录用户的 User 对象信息,我们需要在不同的子系统中多次使用,如果使用传统的方式,我们需要使用方法传参和返回值的方式来传递 User 对象,然而这样就无形中造成了类和类之间,甚至是系统和系统之间的相互耦合了,所以此时我们可以使用 ThreadLocal 来实现 User 对象的传递。
确定了方案之后,接下来我们来实现具体的业务代码。我们可以先在主线程中构造并初始化一个 User 对象,并将此 User 对象存储在 ThreadLocal 中,存储完成之后,我们就可以在同一个线程的其他类中,如仓储类或订单类中直接获取并使用 User 对象了,具体实现代码如下。
public class ThreadLocalByUser {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 初始化用户信息
User user = new User("Java");
// 将 User 对象存储在 ThreadLocal 中
UserStorage.setUser(user);
// 调用订单系统
OrderSystem orderSystem = new OrderSystem();
// 添加订单(方法内获取用户信息)
orderSystem.add();
// 调用仓储系统
RepertorySystem repertory = new RepertorySystem();
// 减库存(方法内获取用户信息)
repertory.decrement();
}
}User 实体类:
/**
* 用户实体类
*/
class User {
public User(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}ThreadLocal 操作类:
/**
* 用户信息存储类
*/
class UserStorage {
// 用户信息
public static ThreadLocal<User> USER = new ThreadLocal();
/**
* 存储用户信息
* @param user 用户数据
*/
public static void setUser(User user) {
USER.set(user);
}
}订单类:
/**
* 订单类
*/
class OrderSystem {
/**
* 订单添加方法
*/
public void add() {
// 得到用户信息
User user = UserStorage.USER.get();
// 业务处理代码(忽略)...
System.out.println(String.format("订单系统收到用户:%s 的请求。",
user.getName()));
}
}仓储类:
/**
* 仓储类
*/
class RepertorySystem {
/**
* 减库存方法
*/
public void decrement() {
// 得到用户信息
User user = UserStorage.USER.get();
// 业务处理代码(忽略)...
System.out.println(String.format("仓储系统收到用户:%s 的请求。",
user.getName()));
}
}
以上程序的最终执行结果:

从上述结果可以看出,当我们在主线程中先初始化了 User 对象之后,订单类和仓储类无需进行任何的参数传递也可以正常获得 User 对象了,从而实现了一个线程中,跨类和跨方法的数据传递。
总结
使用 ThreadLocal 可以创建线程私有变量,所以不会导致线程安全问题,同时使用 ThreadLocal 还可以避免因为引入锁而造成线程排队执行所带来的性能消耗;再者使用 ThreadLocal 还可以实现一个线程内跨类、跨方法的数据传递。
主线程中的业务代码:
ThreadLocal的缺点:
不可继承性,(子线程不能读取父线程的变量)脏读(ThreadPool复用,线程的复用会复用线程相关的静态变量)内存泄露:https://blog.csdn.net/qunqunstyle99/article/details/94717256
边栏推荐
- Yunna | how to manage fixed assets better? How to manage the company's fixed assets?
- What's the use of finding amino acids in extraterrestrial life?
- Mysql database (25): foreing key
- 云呐|行政单位固定资产管理制度,单位固定资产管理办法
- 射频同轴连接器和电缆指南--【转自微信公众号射频课堂】
- 云呐|如何做好固定资产盘点?怎么盘点固定资产
- Yunna administrative unit fixed assets management system, unit fixed assets management measures
- How can PostgreSQL in k8s export query results and import them to the database on the local windows machine
- 面试题 05.04. 下一个数
- Yunna intelligent operation and maintenance management system platform, visual operation and maintenance system management
猜你喜欢

Hit the snake seven inches

6000 字+,帮你搞懂互联网架构演变历程!
![[C language practice - merging two ordered sequences]](/img/9c/30b9440642381e74f21408883780bd.png)
[C language practice - merging two ordered sequences]
原型链?新的歪理解

How can PostgreSQL in k8s export query results and import them to the database on the local windows machine
On the difference between redistemplate and stringredistemplate

云呐|数据库监控一般监控什么

Explanation of the top command

记录下bilibili(b站)小火箭页面上划动画效果的实现

Yunna | how to manage fixed assets better? How to manage the company's fixed assets?
随机推荐
Lossy transmission instance
HCIA datacom experiment IPv4 addressing and IPv4 routing basic experiment
How can PostgreSQL in k8s export query results and import them to the database on the local windows machine
在腾讯连拿六个五星(下)
mysql中的delete,drop和truncate有什么区别
云呐|如何做好固定资产盘点?怎么盘点固定资产
谁说Redis不能存大key
云呐|服务器监控可视化工具
驻美国大使馆提醒在美中国公民注意暑期出行安全
Explain asynchronous tasks in detail: the task of function calculation triggers de duplication
What are the characteristics of Bi reporting system
How is the Internet topology constructed? What does it represent?
IDEA将现在新增加的修改合并cherry pick到之前的版本
What are the types and aspects of Yunna asset management system
Dr. Stanford put forward the idea of ultra fast and saving memory attention. The gpt-2 training speed was increased by 3.5 times, and the Bert speed reached a record
云呐|公司实物资产如何管理
Seven misconceptions of digital transformation
射频同轴连接器和电缆指南--【转自微信公众号射频课堂】
3. download stock code and other basic information
MySQL数据库(25):外键 foreing key

