当前位置:网站首页>Judge whether the binary tree is a binary search tree
Judge whether the binary tree is a binary search tree
2022-07-01 16:47:00 【Bright morning light】
1、 subject
Given the root node of a binary tree , Determine whether it is a binary search tree .
2、 analysis
Binary search tree : The root node of each subtree , The value of the left subtree is smaller than that of the root node , The value of the right subtree is larger than that of the root node .
The classic binary search tree has no duplicate values . If you want to put duplicate values , Then it must be stored in a node with some kind of data structure , Instead of generating multiple nodes with duplicate values .
The method to judge whether a tree is a search binary tree :
Method 1 : Traverse the whole tree in middle order , If the sequence traversed by the middle order is ascending , Is to search the binary tree , Otherwise, it's not .
Method 2 : Solve with recursive routine :
① The goal is : Suppose X Whether the binary tree whose node is the root is a search binary tree ;
② possibility : Get some information from the left tree , List the possibilities when you get some information from the right tree ;
③ X Is the principle of searching binary tree :
(1)X The left tree is a search binary tree ;
(2)X The right tree is a search Binary Tree ;
(3)X The maximum value of the left tree < X The value of the node ;
(4)X The value of the node < X The minimum value of the right tree ;So for the root node of each subtree , Just the top 4 Information can support judging whether the subtree is a search binary tree .
You can get , You need to get information from the left tree :1. Whether to search Binary Tree ;2. Maximum .
Get information from the right tree :1. Whether to search Binary Tree ;2. minimum value .
At this time, it is found that the left tree and the right tree need different information , What shall I do? ? Find the complete set !!
That is , Both left and right trees need to get information, including (1) Whether to search Binary Tree ;(2) Maximum ;(3) minimum value .
Recursion treats all nodes equally , Do not customize the information of any node .
3、 Realization
C++ edition
/************************************************************************* > File Name: 035. Judge whether the binary tree is a binary search tree .cpp > Author: Maureen > Mail: [email protected] > Created Time: 5、 ... and 7/ 1 15:56:01 2022 ************************************************************************/
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class TreeNode {
public:
int value;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int data) : value(data) {
}
};
// Method 1 : In the sequence traversal
void inOrder(TreeNode *node, vector<int> &arr) {
if (node == nullptr) return ;
inOrder(node->left, arr);
arr.push_back(node->value);
inOrder(node->right, arr);
}
bool process1(TreeNode *root) {
vector<int> ans;
inOrder(root, ans);
for (int i = 1; i < ans.size(); i++) {
if (ans[i - 1] > ans[i])
return false;
}
return true;
}
bool isBST1(TreeNode *root) {
if (root == nullptr) return true;
return process1(root);
}
// Method 2 : Recursive routine of binary tree
class Info {
public:
bool isBST;
int maxVal;
int minVal;
Info(bool i, int ma, int mi) : isBST(i), maxVal(ma), minVal(mi) {
}
};
Info *process2(TreeNode *root) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return nullptr;
}
// Get left tree information
Info *leftInfo = process2(root->left);
// Get right tree information
Info *rightInfo = process2(root->right);
// Set the maximum value
int maxVal = root->value;
int minVal = root->value;
// The left tree is not empty , Update the latest value
if (leftInfo != nullptr) {
maxVal = max(maxVal, leftInfo->maxVal);
minVal = min(minVal, leftInfo->minVal);
}
// The right tree is not empty , Update the latest value
if (rightInfo != nullptr) {
maxVal = max(maxVal, rightInfo->maxVal);
minVal = min(minVal, rightInfo->minVal);
}
bool isBST = true;
// The left tree is not empty , And the maximum of the left tree >= Value of root node
if (leftInfo != nullptr && (!leftInfo->isBST || leftInfo->maxVal >= root->value) ) {
isBST = false;
}
// The right tree is not empty , And the minimum value of the right tree <= Value of root node
if (rightInfo != nullptr && (!rightInfo->isBST || rightInfo->minVal <= root->value) ) {
isBST = false;
}
return new Info(isBST, maxVal, minVal);
}
bool isBST2(TreeNode *root) {
if (root == nullptr) return true;
return process2(root)->isBST;
}
//for test
TreeNode *generate(int level, int maxlevel, int maxval) {
if (level > maxlevel || (rand() % 100 / 101) < 0.5)
return nullptr;
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(rand() % maxval);
root->left = generate(level + 1, maxlevel, maxval);
root->right = generate(level + 1, maxlevel, maxval);
return root;
}
TreeNode *generateRandomBST(int maxlevel, int maxval) {
return generate(1, maxlevel, maxval);
}
int main() {
srand(time(0));
int level = 4;
int value = 100;
int testTime = 1000001;
for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) {
TreeNode *root = generateRandomBST(level, value);
if (isBST1(root) != isBST2(root)) {
cout << "Failed!" << endl;
return 0;
}
}
cout << "Success!" << endl;
return 0;
}
Java edition
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class isBST {
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
// Method 1 :
public static boolean isBST1(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
ArrayList<Node> arr = new ArrayList<>();
in(head, arr);
for (int i = 1; i < arr.size(); i++) {
if (arr.get(i).value <= arr.get(i - 1).value) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static void in(Node head, ArrayList<Node> arr) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
in(head.left, arr);
arr.add(head);
in(head.right, arr);
}
// Method 2 : Use recursive routines
public static boolean isBST2(Node head) {
if (head == null) return true;
return process2(head).isBST;
}
public static class Info {
boolean isBST; // Whether to search Binary Tree
public int min; // minimum value
public int max; // Maximum
public Info(boolean is, int mi, int ma) {
isBST = is;
min = mi;
max = ma;
}
}
// I realized this information , To get the same information from the left and right subtrees in recursion
public static Info process2(Node x) {
// Empty trees are hard to set min and max, So it directly returns null , Let the upstream caller handle
if (x == null) {
return null;
}
// Get information from the left tree
Info leftInfo = process2(x.left);
// Get information from the right tree
Info rightInfo = process2(x.right);
// Fill the obtained information into Info in , To know the present x Whether the node is a search binary tree
int min = x.value;
int max = x.value;
if (leftInfo != null) {
max = Math.max(max, leftInfo.max);
min = Math.min(min, leftInfo.min);
}
if (rightInfo != null) {
max = Math.max(max, rightInfo.max);
min = Math.min(min, rightInfo.min);
}
boolean isBST = true;
// The left tree is not empty , But the left tree is not a search binary tree
if (leftInfo != null && !leftInfo.isBST) {
isBST = false;
}
// The right tree is not empty , But the left tree is not a search binary tree
if (rightInfo != null && !rightInfo.isBST) {
isBST = false;
}
// The left tree is not empty , But the maximum value of the left tree >=x The value of the node
if (leftInfo != null && leftInfo.max >= x.value) {
isBST = false;
}
// The right tree is not empty , But the minimum value of the right tree <=x The value of the node
if (rightInfo != null && rightInfo.min <= x.value) {
isBST = false;
}
return new Info(isBST, min, max);
}
// Logarithmic apparatus
// for test
public static Node generateRandomBST(int maxLevel, int maxValue) {
return generate(1, maxLevel, maxValue);
}
// for test
public static Node generate(int level, int maxLevel, int maxValue) {
if (level > maxLevel || Math.random() < 0.5) {
return null;
}
Node head = new Node((int) (Math.random() * maxValue));
head.left = generate(level + 1, maxLevel, maxValue);
head.right = generate(level + 1, maxLevel, maxValue);
return head;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int maxLevel = 4;
int maxValue = 100;
int testTimes = 1000000;
for (int i = 0; i < testTimes; i++) {
Node head = generateRandomBST(maxLevel, maxValue);
if (isBST1(head) != isBST2(head)) {
System.out.println("Oops!");
}
}
System.out.println("finish!");
}
}
边栏推荐
- 广东用电量大跌,说明高新技术产业替代高能耗产业已取得初步成果
- How does go use symmetric encryption?
- 模板引擎Velocity 基礎
- sql刷题584. 寻找用户推荐人
- Principes et applications du système de base de données (006) - - compilation et installation de MySQL 5.7 (environnement Linux)
- Sqlserver query: when a.id is the same as b.id, and the A.P corresponding to a.id cannot be found in the B.P corresponding to b.id, the a.id and A.P will be displayed
- [SQL statement] Why do you select two Shanghai and query different counts here? I want it to become a Shanghai, and count only displays a sum
- 【PyG】文档总结以及项目经验(持续更新
- P2592 [zjoi2008] birthday party (DP)
- Activity的生命周期和启动模式详解
猜你喜欢
![[observation] where is the consulting going in the digital age? Thoughts and actions of softcom consulting](/img/82/3bb382893682a30e8af130365ec4ef.jpg)
[observation] where is the consulting going in the digital age? Thoughts and actions of softcom consulting

The supply of chips has turned to excess, and the daily output of Chinese chips has increased to 1billion, which will make it more difficult for foreign chips
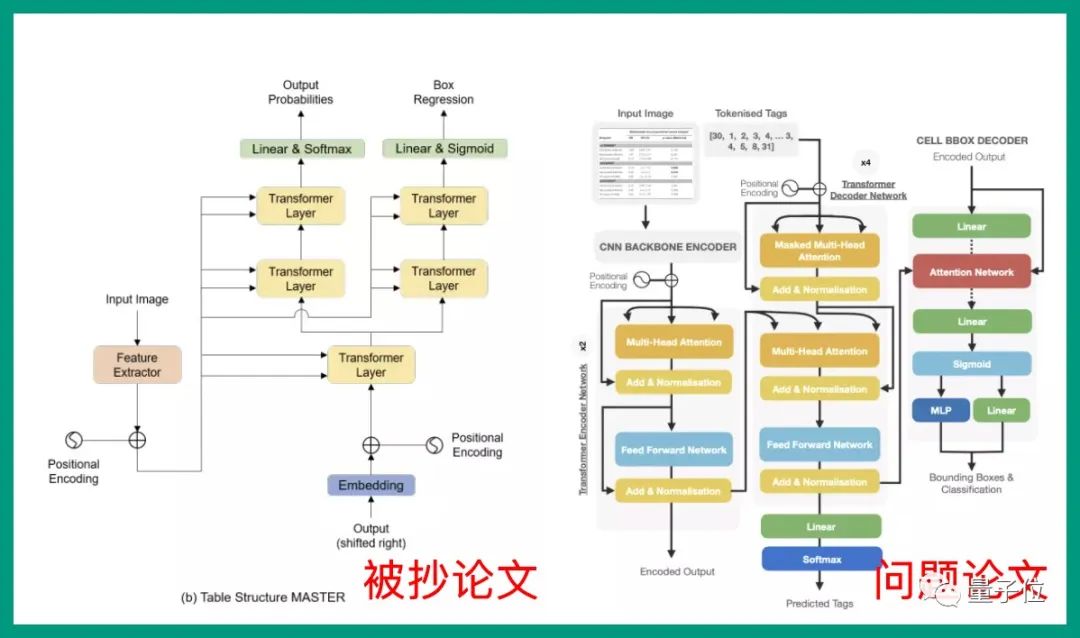
Korean AI team plagiarizes shock academia! One tutor with 51 students, or plagiarism recidivist

Endeavouros mobile hard disk installation

游戏行业安全选择游戏盾,效果怎么样?

Is the programmer's career really short?
巴比特 | 元宇宙每日必读:奈雪币、元宇宙乐园、虚拟股票游戏...奈雪的茶这波“操作拉满”的营销活动你看懂了吗?...
Tutorial on the principle and application of database system (003) -- MySQL installation and configuration: manually configure MySQL (Windows Environment)

接口测试框架中的鉴权处理

【直播预约】数据库OBCP认证全面升级公开课
随机推荐
Principes et applications du système de base de données (006) - - compilation et installation de MySQL 5.7 (environnement Linux)
The sharp drop in electricity consumption in Guangdong shows that the substitution of high-tech industries for high-energy consumption industries has achieved preliminary results
Today, at 14:00, 15 ICLR speakers from Hong Kong University, Beihang, Yale, Tsinghua University, Canada, etc. continue!
Flux d'entrées / sorties et opérations de fichiers en langage C
Installation and use of sqoop
[nodemon] app crashed - waiting for file changes before starting... resolvent
游戏行业安全选择游戏盾,效果怎么样?
PostgreSQL 存储结构浅析
Rhcsa Road
數據庫系統原理與應用教程(006)—— 編譯安裝 MySQL5.7(Linux 環境)
sql刷题1050. 合作过至少三次的演员和导演
Germany if was crowned with many awards. How strong is this pair of headphones? In depth evaluation of yinpo GTW 270 hybrid
【PyG】文档总结以及项目经验(持续更新
数据库系统原理与应用教程(001)—— MySQL 安装与配置:MySQL 软件的安装(windows 环境)
Tutorial on the principle and application of database system (005) -- Yum offline installation of MySQL 5.7 (Linux Environment)
[observation] where is the consulting going in the digital age? Thoughts and actions of softcom consulting
数据库系统原理与应用教程(004)—— MySQL 安装与配置:重置 MySQL 登录密码(windows 环境)
挖财学堂班主任给的证券账户安全吗?能开户吗?
VMware 虚拟机启动时出现故障:VMware Workstation 与 Hyper-v 不兼容...
FPN network details