当前位置:网站首页>Alibaba interview question: multi thread related
Alibaba interview question: multi thread related
2022-06-24 00:36:00 【Abin abin】
List of articles
- One 、 Preface
- Two 、 subject
One 、 Preface
- Interview questions about thread synchronization , Those who consider the idea of solving problems from the perspective of time or priority , Basically not at all
- Always from join sleep Considered ,99.99% It's not right . The thread ends gracefully , Generally do not use 【interrupt: interrupt 】、【stop: stop it 】、 【resume: recovery 】
Two 、 subject
1、 The first question is : Point out the difference between the following two procedures , And analyze ( From the perspective of multithreading )
final class Accumulator {
// Thread 2 may be reading this value without stopping
private double result = 0.0D;
public void addAll(double[] values) {
for (double value : values) {
// Thread one is constantly accumulating
result += value;
}
}
}
final class Accumulator2 {
private double result = 0.0D;
public void addAll(double[] values) {
double sum = 0.0D;
for (double value : values) {
sum += value;
}
result += sum;
}
}
- From the question we can We can see that if we consider multiple threads , So the problem with the first method is : There must be a thread to read this result The probability reading is an intermediate value , Not the final result value , because for The cycle is not over yet
- The problem of the second method : When a thread is constantly reading this :result When I read it that way, it was : Initial or final value , Never read the middle value .
- If you consider thread safety , The second is much safer than the first
Conclusion
The second way of writing is less likely to be inconsistent than the first way of writing , Because before the method is completed , Dirty data in intermediate state cannot be read
Minimize the exposure of the intermediate state of the thread computing process
Can use a small range of variables , Don't use a wide range of variables
2、 I know : The case of philosophers' dining problem
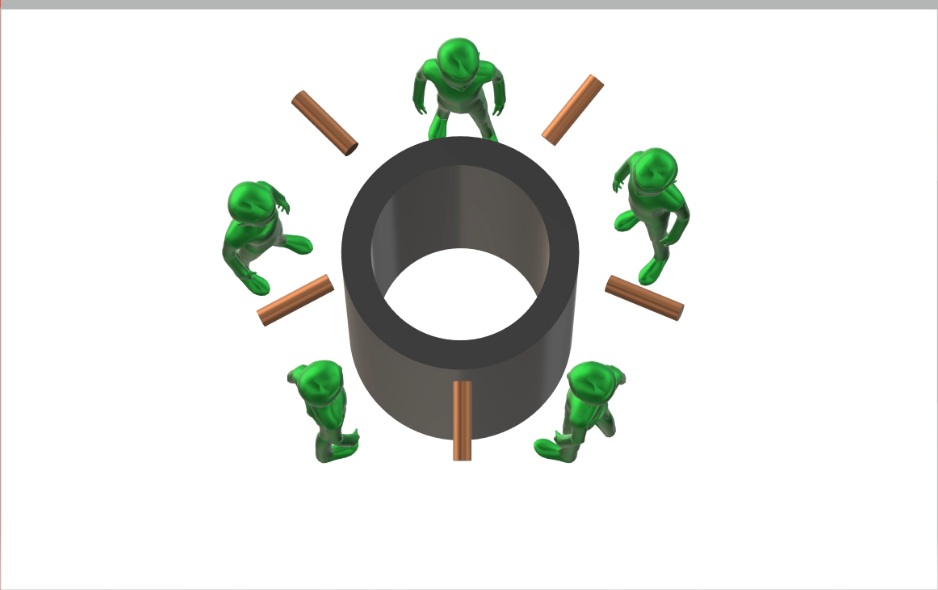
What is the dining problem of philosophers
- The dining problem of philosophers is a classic problem in computer science , Used to demonstrate multithreading synchronization in parallel computing (Synchronization) Problems arising from .
- There are five philosophers , They share a round table , Sit on five chairs . There are five bowls and five chopsticks on the round table , Usually a philosopher thinks , When I'm hungry, I try to use the left side 、 Right is closest to his chopsticks , Only when he has two chopsticks can he eat . After dinner , Put down your chopsticks and continue to think .
Their thinking
- First write a code to simulate this question type , Let's start with two classes : philosopher 、 chopsticks
- Chopsticks : With numbering attribute
- Philosophers : Left chopsticks 、 Right hand chopsticks 、 Number attributes
Code parsing
Scheme 1 :
public class T01_DeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ChopStick cs0 = new ChopStick();
ChopStick cs1 = new ChopStick();
ChopStick cs2 = new ChopStick();
ChopStick cs3 = new ChopStick();
ChopStick cs4 = new ChopStick();
Philosohper p0 = new Philosohper("p0", 0, cs0, cs1);
Philosohper p1 = new Philosohper("p1", 1, cs1, cs2);
Philosohper p2 = new Philosohper("p2", 2, cs2, cs3);
Philosohper p3 = new Philosohper("p3", 3, cs3, cs4);
Philosohper p4 = new Philosohper("p4", 4, cs4, cs0);
p0.start();
p1.start();
p2.start();
p3.start();
p4.start();
}
public static class Philosohper extends Thread {
private ChopStick left, right;
private int index;
public Philosohper(String name, int index, ChopStick left, ChopStick right) {
this.setName(name);
this.index = index;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
/** * 1、 Lock the right side first , Lock the left side again, and then it indicates that someone has finished , Because you can only eat with two chopsticks * 2、 Be careful : This method is problematic , When a deadlock occurs , Then no one can get chopsticks , Everyone has to starve to death **/
@Override
public void run () {
// Lock the right chopsticks
synchronized (left) {
Thread.sleep(1 + index);
// Lock the left chopsticks
synchronized (right) {
SleepHelper.sleepSeconds(1);
// Print this to show that one is full
System.out.println(index + " Number The philosopher has finished ");
}
}
}
}
Problem of scheme 1 :
- There will be deadlock problems
- Concept : Deadlocks generally have 2 Put the above lock , Wait for another lock while locking one
Option two : Optimized version
- Ideas : Two locks merge into one (5 hold , 5 Turn the lock into a lock , Chopsticks collection , Lock the entire object )
- Mix in a left-handed
- More efficient writing , Odd number Even numbers separate , Mix in half of the left-handed
public void run() {
// try {
// Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(5));
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// System.out.println(e);
// }
if (index == 0) {
// Left handed algorithm It's fine too index % 2 == 0
synchronized (left) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
synchronized (right) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println(index + " I'm full !");
}
}
} else {
synchronized (right) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
synchronized (left) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println(index + " I'm full !");
}
}
}
}
3、 Alternating output problem
Concept
- Be sure to ensure alternate output , This involves the synchronization of two threads .
- One might think of , Use sleep time difference to realize , But as long as it is multithreaded , Thread synchronization play sleep() Functional ,99.99% All wrong .
- 【 Alternating output 】 The problem is classic , There are many solutions . Let's start with :【 The easiest way 】 Realize this problem .
Be careful : The key function
- Locksupport.park(): Block the current thread
- Locksupport.unpark(“”): Wake up a thread
Mode one :LockSupport( Lock support ) Simplest solution

public class T02_00_LockSupport {
static Thread t1 = null, t2 = null;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
char[] aI = "1234567".toCharArray();
char[] aC = "ABCDEFG".toCharArray();
t1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (char c : aI) {
System.out.print(c);
LockSupport.unpark(t2); // Wake up t2
LockSupport.park(); // t1 Blocking The current thread is blocked
}
}, "t1");
t2 = new Thread(() -> {
for (char c : aC) {
LockSupport.park(); // t2 Hang up
System.out.print(c);
LockSupport.unpark(t1); // Wake up t1
}
}, "t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
- The execution result is :1A2B3C4D5E6F7G
Mode two :Sync wait notify( Sync 、 wait for 、 notice ) Optimized version
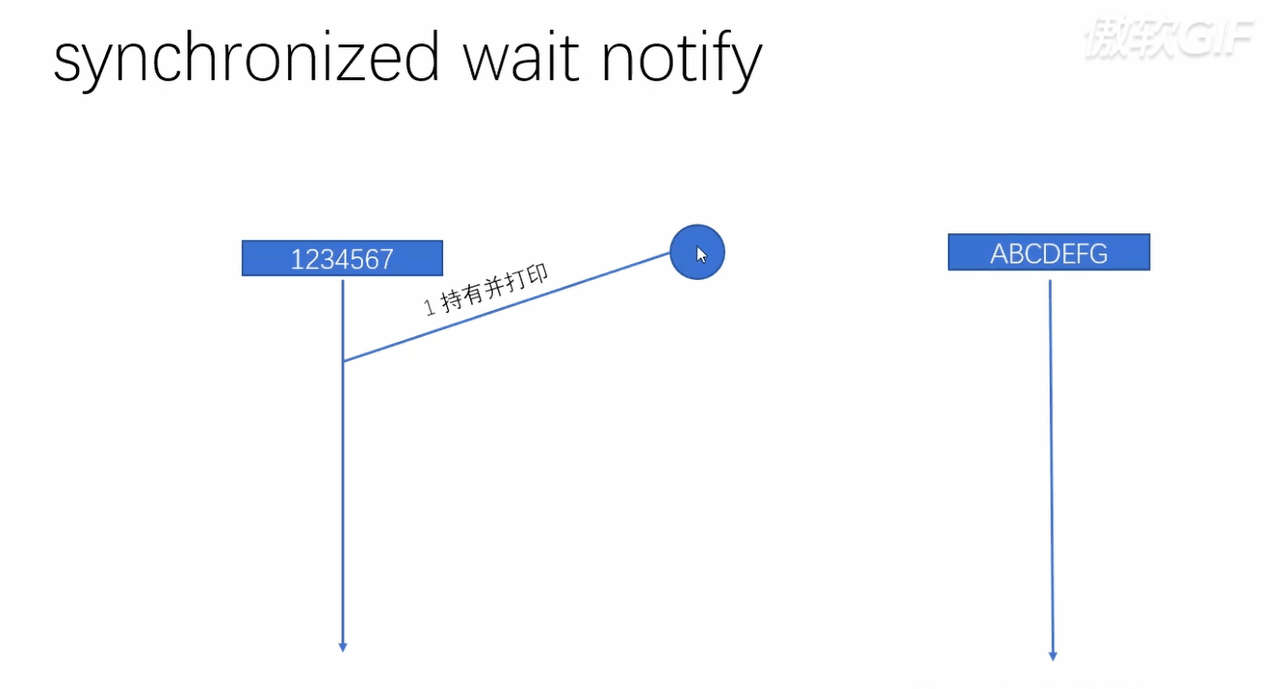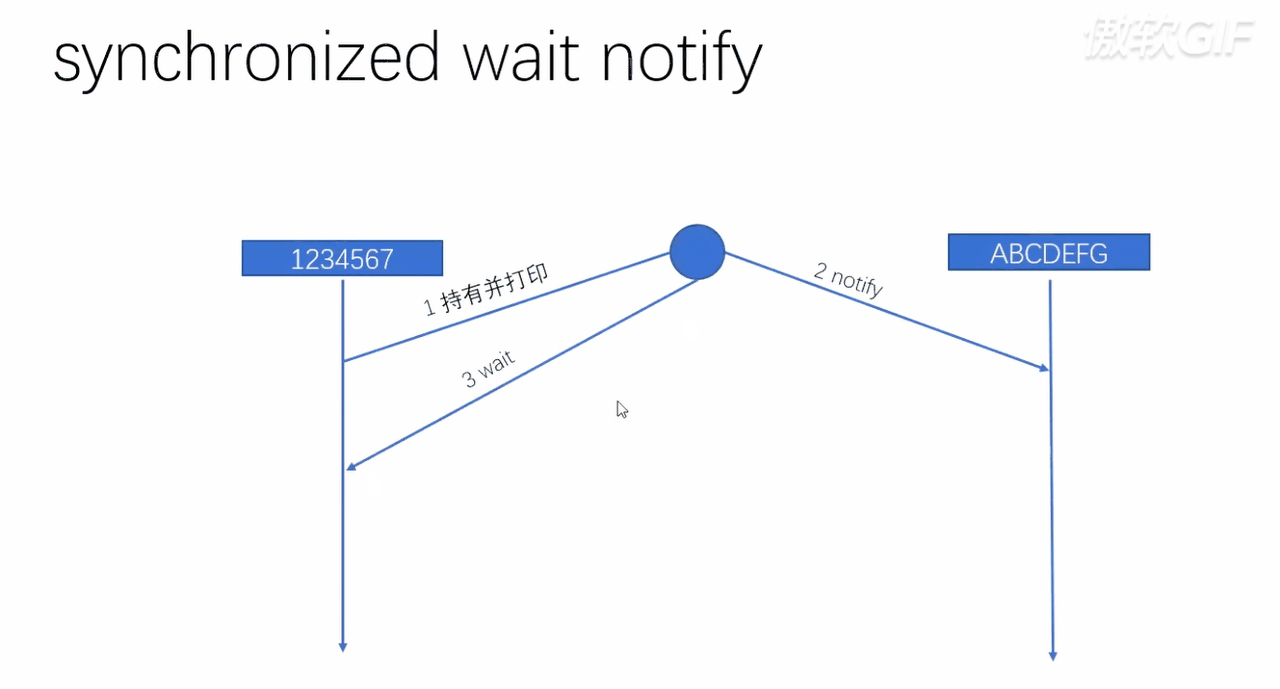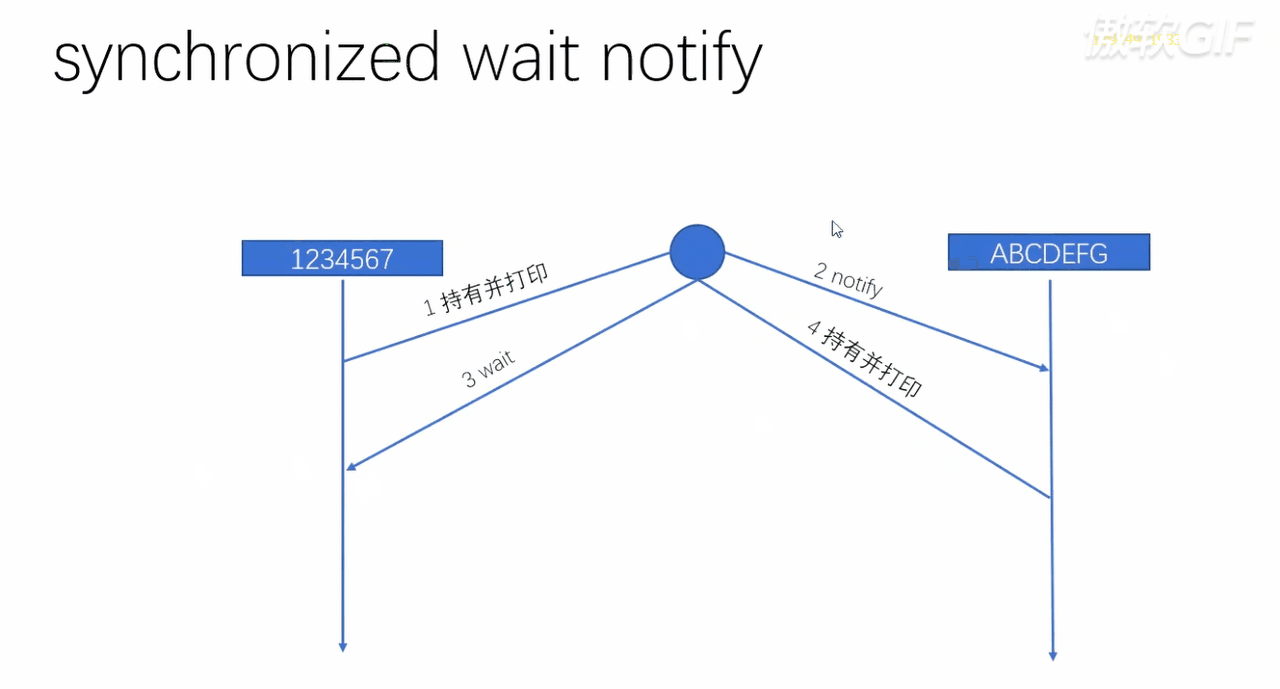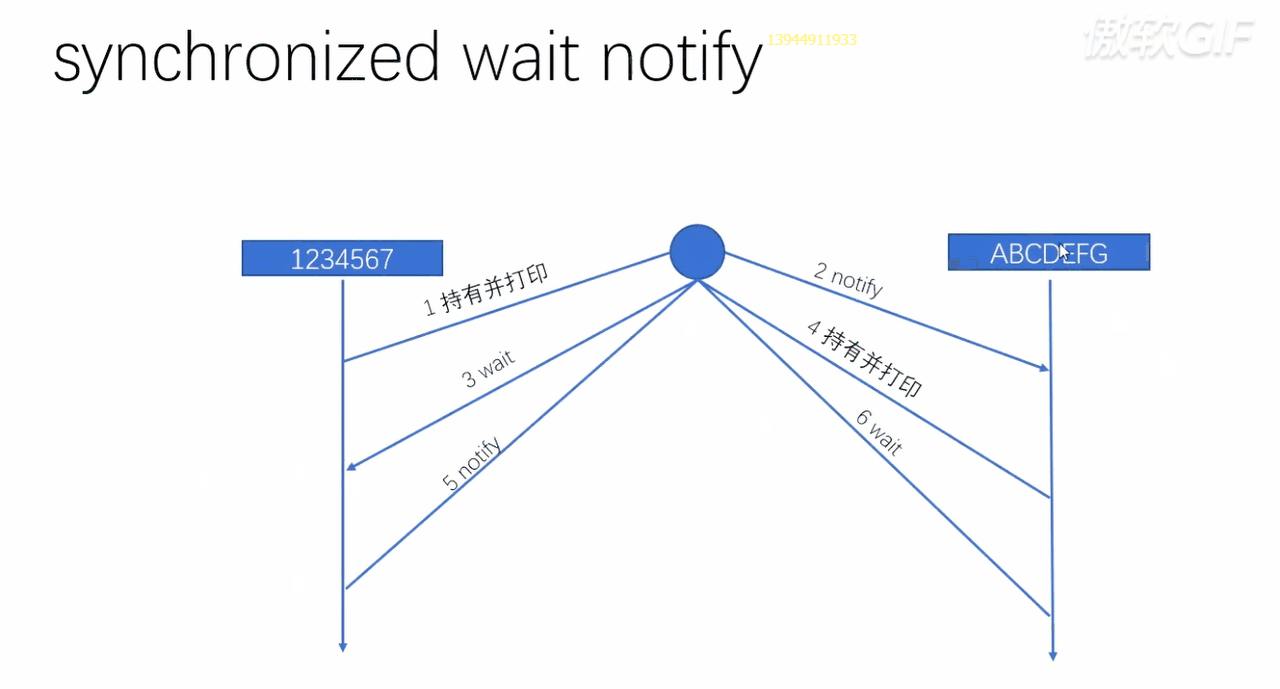
public class T06_00_sync_wait_notify {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Object o = new Object();
char[] aI = "1234567".toCharArray();
char[] aC = "ABCDEFG".toCharArray();
new Thread(() -> {
// First create a lock
synchronized (o) {
for (char c : aI) {
System.out.print(c);
try {
o.notify(); // Wake up a thread in the waiting queue , For this program, it is another thread
o.wait(); // Get out of the lock
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
o.notify(); // must , Otherwise, the program cannot be stopped
}
}, "t1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (o) {
for (char c : aC) {
System.out.print(c);
try {
o.notify();
o.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
o.notify();
}
}, "t2").start();
}
}
From the above code, we may raise a problem , So that is :notify() and wait() Whether the calling sequence has a direct impact ?
answer : Yes , So let's take a look at ,notify() and wait() The implementation process of
This question was once Huawei's written test

As you can see from the code snippet above , If we execute first wait(), Will first let oneself directly into the waiting queue . Then you and another thread are waiting in the waiting queue , Two threads have been waiting , No one can wake the other , That is, it cannot be implemented at all notify()
A pit :
- We found that , There is another one at the end of the program notify(), And there must be , Why is it necessary ? Let's comment it out , Take a look at the output :1A2B3C4D5E6F7G
- We can see from the output , There is no problem with the execution result , But the program will not stop .
- principle : We can find out from the dynamic graph , Finally, there must be a thread in wait() State of , No one woke it up , It will always be waiting , Thus the program cannot end , To avoid this , We're going to add one after that notify()
Pit two :
- Those who have played with threads should have discovered this problem long ago , If the second thread preempts first , So the output is A1B2C3 了 , How to ensure that the first output is always the number first ?
- We can use CountDownLatch This class , It is JUC New synchronization tools , This class can be thought of as a door bolt , When we have threads executing to the gate , It will wait for the bolt to open the door , Threads will execute .
- If t2 Take the lead , Then it will execute await() Method , Because of the existence of the door bolt , It can only wait outside the door , therefore t1 The thread will execute directly , Execute to countDown() Method , To create CountDownLatch(1) The parameter is set to 0, Release the door latch , So it will always be t1 The thread is finished ,t2 Threads will execute
Complete code
- Pit avoiding writing
public class T07_00_sync_wait_notify {
private static CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1); // Set the parameters of the door bolt to 1, That is, there is only one bolt
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Object o = new Object();
char[] aI = "1234567".toCharArray();
char[] aC = "ABCDEFG".toCharArray();
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (o) {
for (char c : aI) {
System.out.print(c);
latch.countDown(); // The value of the door bolt -1, That is, open the door
try {
o.notify();
o.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
o.notify();
}
}, "t1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
latch.await(); // Which thread do you want to execute after ,await() In which thread
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (o) {
for (char c : aC) {
System.out.print(c);
try {
o.notify();
o.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
o.notify();
}
}, "t2").start();
}
}
Lock ReentrantLock await signal( Wait for the signal )
- JDK Many new synchronization tools are available , stay JUC It's a bag , There is a special alternative synchronized Lock of :Lock
public class T08_00_lock_condition {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] aI = "1234567".toCharArray();
char[] aC = "ABCDEFG".toCharArray();
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
new Thread(() -> {
lock.lock();
try {
for (char c : aI) {
System.out.print(c);
condition.signal(); // notify()
condition.await(); // wait()
}
condition.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}, "t1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
lock.lock(); // synchronized
try {
for (char c : aC) {
System.out.print(c);
condition.signal(); // o.notify
condition.await(); // o.wait
}
condition.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}, "t2").start();
}
}
- From the above code , We can see that : Create a lock , Call methods with synchronized There is no difference between , But the point is Condition This class
- You should know the concept of producer and consumer , Producers produce steamed buns , The production is full and enters the waiting queue , Consumers eat steamed buns , Eat up the same into the waiting queue
- If we use traditional synchronized , When the producer is full , The consumer needs to be awakened from the waiting queue , But the call notify When the method is used
- Can we guarantee that it is the consumers who must wake up ? You can't , This is impossible , How can we ensure that the consumers must wake up ?
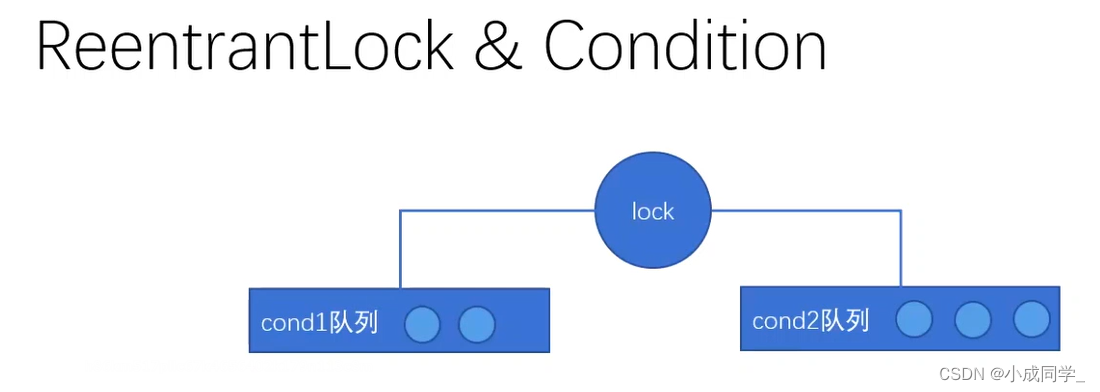
4、 Producer consumer issues ReentantLock Condition
Two solutions
Scheme 1 :
- If the basket is full , The producer waits for a thread to wake up in the queue , But if the waking thread is still a producer , After the new producer gets up, he must check whether the basket is full , You can't just come up and produce , If it's full , Then go and wake up the next thread , Repeat in this order , We will definitely wake up the consumers once
Option two :
- notifyAll() Method : All producers and consumers in the waiting queue will wake up , Consumer finds basket full , Just consume , The producer found the basket full , Just go back to the waiting queue .
Be careful
- But either of these solutions , The threads we wake up are all imprecise , There is waste ; This is it. synchronized The problem of synchronization
Code explanation

Lock It can solve this problem by itself , It depends on Condition,Condition It can wake up accurately
Condition It means conditional , But we can think of it as a queue
One condition It is a waiting queue
Code demonstration ( Optimized version )
public class T08_00_lock_condition {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] aI = "1234567".toCharArray();
char[] aC = "ABCDEFG".toCharArray();
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition conditionT1 = lock.newCondition(); // queue 1
Condition conditionT2 = lock.newCondition(); // queue 2
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
new Thread(() -> {
lock.lock(); // synchronized
try {
for (char c : aI) {
System.out.print(c);
latch.countDown();
conditionT2.signal(); // o.notify()
conditionT1.await(); // o.wait()
}
conditionT2.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}, "t1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
lock.lock(); // synchronized
try {
for (char c : aC) {
System.out.print(c);
conditionT1.signal(); // o.notify
conditionT2.await(); // o.wait
}
conditionT1.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}, "t2").start();
}
}
- From the code optimized online, we can see , First thread t1 First come up and hold the lock , Wake up the contents of the second queue after holding the lock
- Then I enter the first queue and wait , Empathy ,t2 The thread wakes up the contents of the first queue , Enter the second queue and wait , In this way, you can wake up accurately
边栏推荐
- 抓取开机logcat
- Definition of logic
- Android App bundle exploration, client development interview questions
- VS2022保存格式化插件
- Superscalar processor design yaoyongbin Chapter 3 virtual memory -- Excerpt from subsection 3.1~3.2
- Throttling and anti shake
- Interview notes for Android outsourcing workers for 3 years. I still need to go to a large factory to learn and improve. As an Android programmer
- Android App Bundle探索,客户端开发面试题目
- Delegation attack of Intranet penetration and lateral mobility
- Jimureport building block report - table linkage chart topic
猜你喜欢

What are the two types of digital factories

【红绿灯识别】基于matlab GUI红绿灯识别【含Matlab源码 1908期】
Chaos engineering, learn about it

Accompanist组件库中文指南 - Glide篇,劲爆

Use of reverse tools IDA and GDB
Mip-NeRF:抗混叠的多尺度神经辐射场ICCV2021

数字化工厂可以分为哪两类
Cloud native architecture (05) - Application Architecture Evolution
When the IOT network card device is connected to easycvr, how can I view the streaming IP and streaming time?

Andorid development art exploration notes (2), cross platform applet development framework
随机推荐
元宇宙中的社会秩序
JS language precision problem
苹果Iphone14搭载北斗导航系统,北斗VS GPS有哪些优势?
What do NLP engineers do? What is the work content?
Keywords such as extern and struct
How much business do you need to know to do data analysis
C语言:百马百担问题求驮法
逻辑的定义
Vulnerability recurrence - redis vulnerability summary
What is the difference between overload and override?
C language: structure array implementation to find the lowest student record
阿里巴巴面试题:多线程相关
Complete collection of development environment configuration -- Visual Studio 2022 installation
国内首款开源MySQL HTAP数据库即将发布,三大看点提前告知 石原子科技重磅推出
Empty encoded password warning reason
The easycvr program started abnormally as a service, but the process started normally. What is the reason?
UART protocol timing summary
Jimureport building block report - table linkage chart topic
How to get started with machine learning?
Do280openshift access control -- manage projects and accounts