当前位置:网站首页>Dcgan:deep volume general adaptive networks -- paper analysis
Dcgan:deep volume general adaptive networks -- paper analysis
2022-07-28 04:56:00 【gongyuandaye】
One 、 Summary
DCGAN take CNN and GAN combination , Stable during training , And can effectively achieve high-quality image generation , So now many GAN All of them are improved on its basis .
Two 、 Methods and Architecture
1、 Use convolution layer instead of pool layer ( Such as maxpooling), This allows the network to learn its own upsampling and discriminator D.
2、 Remove the full connection layer , Connect the highest convolution feature directly to the input of the generator and the output of the discriminator , The effect is very good .
3、 Use batch normalization ( Zero mean unit variance ), Solve the problem of low gradient in deep network , Prevent generator G Compress all samples to one point . But not the generator G Output layer and discriminator D The input layer uses , Otherwise, the model will be unstable .
4、 Generate network usage ReLU, The output layer adopts Tanh; Identify network usage LeakyReLU.
3、 ... and 、 Training details
1、DCGAN The generation network of is as follows , Use transpose convolution (fractionally-strided convolutions):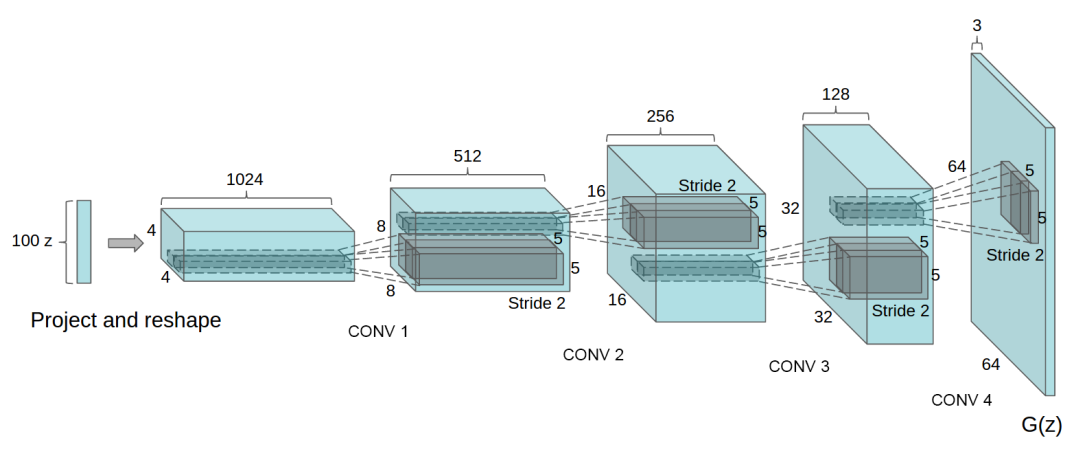
2、 Use Adam The algorithm updates the parameters ,betas=(0.5, 0.999);batch size Selected as 128; Weights are normally distributed , The mean for 0, The standard deviation is 0.02; Learning rate 0.0002.
3、 The author is also right later DCGAN Explore the interior of .
Four 、 Code
import argparse
import os
import numpy as np
import math
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
from torchvision.utils import save_image
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision import datasets
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch
os.makedirs("images", exist_ok=True)
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--n_epochs", type=int, default=200, help="number of epochs of training")
parser.add_argument("--batch_size", type=int, default=64, help="size of the batches")
parser.add_argument("--lr", type=float, default=0.0002, help="adam: learning rate")
parser.add_argument("--b1", type=float, default=0.5, help="adam: decay of first order momentum of gradient")
parser.add_argument("--b2", type=float, default=0.999, help="adam: decay of first order momentum of gradient")
parser.add_argument("--n_cpu", type=int, default=8, help="number of cpu threads to use during batch generation")
parser.add_argument("--latent_dim", type=int, default=100, help="dimensionality of the latent space")
parser.add_argument("--img_size", type=int, default=32, help="size of each image dimension")
parser.add_argument("--channels", type=int, default=1, help="number of image channels")
parser.add_argument("--sample_interval", type=int, default=400, help="interval between image sampling")
opt = parser.parse_args()
print(opt)
cuda = True if torch.cuda.is_available() else False
def weights_init_normal(m):
classname = m.__class__.__name__
if classname.find("Conv") != -1:
torch.nn.init.normal_(m.weight.data, 0.0, 0.02)
elif classname.find("BatchNorm2d") != -1:
torch.nn.init.normal_(m.weight.data, 1.0, 0.02)
torch.nn.init.constant_(m.bias.data, 0.0)
class Generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Generator, self).__init__()
self.init_size = opt.img_size // 4
self.l1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(opt.latent_dim, 128 * self.init_size ** 2))
self.conv_blocks = nn.Sequential(
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2),
nn.Conv2d(128, 128, 3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128, 0.8),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2),
nn.Conv2d(128, 64, 3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64, 0.8),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(64, opt.channels, 3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.Tanh(),
)
def forward(self, z):
out = self.l1(z)
out = out.view(out.shape[0], 128, self.init_size, self.init_size)
img = self.conv_blocks(out)
return img
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Discriminator, self).__init__()
def discriminator_block(in_filters, out_filters, bn=True):
block = [nn.Conv2d(in_filters, out_filters, 3, 2, 1), nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True), nn.Dropout2d(0.25)]
if bn:
block.append(nn.BatchNorm2d(out_filters, 0.8))
return block
self.model = nn.Sequential(
*discriminator_block(opt.channels, 16, bn=False),
*discriminator_block(16, 32),
*discriminator_block(32, 64),
*discriminator_block(64, 128),
)
# The height and width of downsampled image
ds_size = opt.img_size // 2 ** 4
self.adv_layer = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(128 * ds_size ** 2, 1), nn.Sigmoid())
def forward(self, img):
out = self.model(img)
out = out.view(out.shape[0], -1)
validity = self.adv_layer(out)
return validity
# Loss function
adversarial_loss = torch.nn.BCELoss()
# Initialize generator and discriminator
generator = Generator()
discriminator = Discriminator()
if cuda:
generator.cuda()
discriminator.cuda()
adversarial_loss.cuda()
# Initialize weights
generator.apply(weights_init_normal)
discriminator.apply(weights_init_normal)
# Configure data loader
os.makedirs("../../data/mnist", exist_ok=True)
dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
datasets.MNIST(
"../../data/mnist",
train=True,
download=True,
transform=transforms.Compose(
[transforms.Resize(opt.img_size), transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize([0.5], [0.5])]
),
),
batch_size=opt.batch_size,
shuffle=True,
)
# Optimizers
optimizer_G = torch.optim.Adam(generator.parameters(), lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.b1, opt.b2))
optimizer_D = torch.optim.Adam(discriminator.parameters(), lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.b1, opt.b2))
Tensor = torch.cuda.FloatTensor if cuda else torch.FloatTensor
# ----------
# Training
# ----------
for epoch in range(opt.n_epochs):
for i, (imgs, _) in enumerate(dataloader):
# Adversarial ground truths
valid = Variable(Tensor(imgs.shape[0], 1).fill_(1.0), requires_grad=False)
fake = Variable(Tensor(imgs.shape[0], 1).fill_(0.0), requires_grad=False)
# Configure input
real_imgs = Variable(imgs.type(Tensor))
# -----------------
# Train Generator
# -----------------
optimizer_G.zero_grad()
# Sample noise as generator input
z = Variable(Tensor(np.random.normal(0, 1, (imgs.shape[0], opt.latent_dim))))
# Generate a batch of images
gen_imgs = generator(z)
# Loss measures generator's ability to fool the discriminator
g_loss = adversarial_loss(discriminator(gen_imgs), valid)
g_loss.backward()
optimizer_G.step()
# ---------------------
# Train Discriminator
# ---------------------
optimizer_D.zero_grad()
# Measure discriminator's ability to classify real from generated samples
real_loss = adversarial_loss(discriminator(real_imgs), valid)
fake_loss = adversarial_loss(discriminator(gen_imgs.detach()), fake)
d_loss = (real_loss + fake_loss) / 2
d_loss.backward()
optimizer_D.step()
print(
"[Epoch %d/%d] [Batch %d/%d] [D loss: %f] [G loss: %f]"
% (epoch, opt.n_epochs, i, len(dataloader), d_loss.item(), g_loss.item())
)
batches_done = epoch * len(dataloader) + i
if batches_done % opt.sample_interval == 0:
save_image(gen_imgs.data[:25], "images/%d.png" % batches_done, nrow=5, normalize=True)
边栏推荐
- (克隆虚拟机步骤)
- [函数文档] torch.histc 与 paddle.histogram 与 numpy.histogram
- Do you know several assertion methods commonly used by JMeter?
- Odoo action analysis (action.client, action.act_window, action.server)
- [Sylar] framework -chapter12 bytearray module
- Redis type
- C语言ATM自动取款机系统项目的设计与开发
- Method of converting UI file to py file
- Redis类型
- [function document] torch Histc and paddle Histogram and numpy.histogram
猜你喜欢

What is the core value of testing?
![[high CPU consumption] software_ reporter_ tool.exe](/img/3f/2c1ecff0a81ead0448e1215567ede7.png)
[high CPU consumption] software_ reporter_ tool.exe

RT_ Use of thread message queue

Improve the core quality of steam education among students
![[daily one] visual studio2015 installation in ancient times](/img/b1/066ed0b9e93b8f378c89ee974163e5.png)
[daily one] visual studio2015 installation in ancient times

你必需要了解的saas架构设计?

MySQL(5)

The go zero singleton service uses generics to simplify the registration of handler routes

05.01 string

Analysis of the reason why easycvr service can't be started and tips for dealing with easy disk space filling
随机推荐
Introduction to testcafe
Do you know several assertion methods commonly used by JMeter?
欧拉路/欧拉回路
Use and expansion of fault tolerance and fusing
HDU 1530 maximum clique
外卖系统 文件上传
(2.4) [service Trojan -slimftp] introduction and use
Use animatedbuilder to separate components and animation, and realize dynamic reuse
[high CPU consumption] software_ reporter_ tool.exe
Artificial intelligence and RPA technology application (I) -rpa Hongji product introduction, designer interface function explanation
Research on the design of robot education in stem course
基于MPLS构建虚拟专网的配置实验
Special topic of APP performance design and Optimization - poor implementation affecting performance
MySQL(5)
Performance comparison between set and list
Automated test tool playwright (quick start)
Printf() print char* str
【CPU占用高】software_reporter_tool.exe
Evolution of ape counseling technology: helping teaching and learning conceive future schools
Real intelligence has been certified by two of the world's top market research institutions and has entered the global camp of excellence