当前位置:网站首页>Characteristics and classification of creation mode (single case, factory)
Characteristics and classification of creation mode (single case, factory)
2022-06-11 10:58:00 【iiiiiiiiiooooo】
Concerns : Create objects , Separate the creation and use of objects , This purpose can reduce the problem of code coupling
The singleton pattern 、 Factory mode 、 Abstract factory pattern 、 Archetypal model 、 Builder pattern
The singleton pattern (Singleton Pattern)
Definition :
The singleton pattern (Singleton Pattern): Ensure that a class has only one instance , And provide a global access point to access it
Singleton class diagram :

The roles included in the singleton :
Singleton class : Contains an instance and can create the instance class itself
Features of singleton mode :
1. A singleton class has only one instance object
2. The singleton object must be created by the singleton class itself
3. The singleton class provides an external global access point that can access the singleton
Code demonstration
The implementation of singleton has 8 Kind of
Hungry Chinese style ( static const )
Hungry Chinese style ( Static code block )
Slacker type
Double check
Static inner class
enumeration
Hungry Chinese style ( static const )
/**
* Hungry Chinese style ( Static variables )
* Thread safe , Class is loaded into memory , Yes JVM Save thread safe
* Simple , Recommended implementation
*/
public class SingLeton1 {
// Constructor privatization , prevent new object
private SingLeton1(){}
// Create objects inside this class , Static variables
private final static SingLeton1 singLeton1=new SingLeton1();
// Provide a public static method , Return instance object , For external use
public static SingLeton1 getInstance(){
return singLeton1;
}
}Advantages and disadvantages :
advantage : The writing is concise , The instantiation of the class has been completed when the class is loaded , Ensure thread safety
shortcoming : Instantiation is completed when the class is loaded ( Lazy loading is not implemented ), If this instance is not used , It's a waste of memory
Hungry Chinese style ( Static code block )
/**
* Hungry Chinese style ( Static code block )
*/
public class SingLeton2 {
// Constructor privatization
private SingLeton2(){}
// Create an object instance inside the class
private static SingLeton2 singLeton2;
// In a static block of code , Create singleton objects
static{
singLeton2=new SingLeton2();
}
// Provide public access points
public static SingLeton2 getInstance(){
return singLeton2;
}
}The advantages and disadvantages are the same as above
Slacker type ( Thread unsafe )
/**
* Slacker type , Thread unsafe
*/
public class SingLeton3 {
private static SingLeton3 singLeton3;
private SingLeton3(){}
// Provide a public access , When called , To create an instance , That's lazy
public static SingLeton3 getInstance(){
if(singLeton3==null){
singLeton3=new SingLeton3();
}
return singLeton3;
}
}advantage : The effect of lazy loading is realized , But it can only be used in a single thread
shortcoming : Under multithreading , Thread unsafe exists
Slacker type ( Thread safety , Synchronization method )
public class SingLeton4 {
private static SingLeton4 singLeton4;
private SingLeton4(){}
public static synchronized SingLeton4 getInstance(){
if(singLeton4==null){
singLeton4=new SingLeton4();
}
return singLeton4;
}
}The key point of thread safety :synchronized
advantage : Through thread safe keywords , Solving thread safety problems
shortcoming : inefficiency , When each thread gets an instance , perform getInstance All need to be synchronized , The synchronization efficiency of the method is too low
Slacker type ( Thread safety , Synchronization code block )
public class SingLeton5 {
private static SingLeton5 singLeton5;
private SingLeton5(){}
public static SingLeton5 getInstance(){
if(singLeton5==null){
synchronized (SingLeton5.class){
singLeton5=new SingLeton5();
}
}
return singLeton5;
}
}The locking has been optimized to some extent , The overall advantages and disadvantages are consistent with the above
Double check
/**
* Double check
*/
public class SingLeton6 {
private static SingLeton6 singLeton6;
private SingLeton6(){}
public static synchronized SingLeton6 getInstance(){
if(singLeton6==null){
synchronized (SingLeton6.class){
if(singLeton6==null){
singLeton6=new SingLeton6();
}
}
}
return singLeton6;
}
}Advantages and disadvantages :
The double check was carried out twice if (single == null) Check , Ensure thread safety
Thread safety , Delay loading , Efficient , Recommended
Static inner class
/**
* Static inner class
* Static internal properties , Initialize when the class is loaded , Ensure thread safety
* The static inner class is used to realize delayed loading
*/
public class SingLeton7 {
private SingLeton7(){}
// Provide a static inner class , There is a static property in this class
private static class SingleHolder{
private static SingLeton7 singLeton7=new SingLeton7();
}
// Provide a public static access
public static SingLeton7 getInstance() {
return SingleHolder.singLeton7;
}
}Advantages and disadvantages :
Thread safety : The essence is to ensure thread safety through class loading
Implement lazy loading : Only in practical use , Will trigger class initialization , It is also a form of lazy loading
Efficient : No lock mechanism is used
Recommended
Enumeration method
/**
* Enumerating way to achieve a single example
*/
public enum SingLeton8 {
INSTANCE;// attribute
// Provide a static public access
public static SingLeton8 getInstance() {
return INSTANCE;
}
}
Recommended
Single case re exploration
advantage :
Singleton mode ensures that there is only one instance in memory , Reduced memory overhead
Avoid multiple occupation of resources
Set the global access point for a single instance , Can optimize and share access to resources
shortcoming :
Singleton mode generally has no interface , Extend the difficult , If you want to expand , You need to change the code , Against the principle of opening and closing
Applicable scenario :
Some classes that need to be created frequently , Using singletons can reduce the memory pressure of the system , Reduce GC
Some object instances occupy more resources , Or an object that takes a long time and is often used , In the form of single example
Java application
1、spring Single case in
stay spring in ,Bean Two modes can be defined :Singleton( Single case ) and Prototype( Multiple cases ),Spring Singleton used in mode
Factory method model (Factory Method)
According to business scenarios : There are three different implementations of the factory pattern : They are simple factories 、 Factory method pattern and abstract factory pattern
Simple factory model
Brief factory introduction
Simple factory has a specific factory class , Can produce different products , It belongs to the creative design pattern
Be careful : The simple factory model does not belong to 23 Among the design patterns
Simple factory class diagram UML

Simple factory role description :
Simple factory (SimpleFactory): It's the core of the simple factory model , Responsible for implementing the internal logic of creating all instances , The method of creating product class of factory class can be directly accessed by the outside world , Create the required product objects
Abstract product (Product): Is a simple factory that creates the parent class of all objects , Responsible for describing the public interfaces that are public to all instances
Specific products (ConcreteProduct): Is a concrete object created by a simple factory
Code implementation :
Simple factory implementation :
/**
* Abstract product , Provide a common approach to all specific products
*/
public interface Product {
public void show();
}
/**
* Specific products 1
*/
public class ConcreteProduct1 implements Product {
@Override
public void show() {
System.out.println(" Specific products 1 Exhibition ...");
}
}
/**
* Specific products 2
*/
public class ConcreteProduct2 implements Product {
@Override
public void show() {
System.out.println(" Specific products 2 Exhibition ...");
}
}
/**
* Simple factory
*/
public class SimpleFactory {
// Provide a method , Get different instance objects based on different parameters
public static Product getConcreteProduct(int productType) {
switch (productType) {
case Const.Product1:
return new ConcreteProduct1();
case Const.Product2:
return new ConcreteProduct2();
}
return null;
}
final class Const {
static final int Product1 = 1;// Said is ConcreteProduct1 product
static final int Product2 = 2;// Said is ConcreteProduct2 product
}
Call mode :
// Get product 1
Product product = SimpleFactory.getConcreteProduct(Const.Product1);
product.show();
// Get product 2
Product product1 = SimpleFactory.getConcreteProduct(Const.Product2);
product1.show();Use steps :
1. Create abstract product classes and define public interfaces for specific products
2. Create specific product classes , Define the specific products produced
3. Create a factory class , Create different instances of specific products through static methods according to different incoming parameters
4. The outside world calls the static method of the factory class , Pass in different parameters to create different product instances
Advantages and disadvantages :
advantage :
1、 The code logic is relatively simple , The factory class contains the necessary logic to create objects , You can decide to create specific products
2、 The caller does not need to know the class name of the specific product being created , Just know the parameters
shortcoming :
Simple factories violate the opening and closing principle , The factory is too responsible for the creation of products , Once a new product is added, it is necessary to judge the internal logic of the factory class
Difficulty in system expansion , Too many products will make the logic too complex
Use scenarios :
When there are few product types , Consider using a simple factory , The caller only needs to pass in the parameters of the factory class , You don't need to focus on the logic of how to create
Factory method model
Introduction to the factory method model
Definition : The factory method pattern is a further abstraction of the simple factory pattern , The advantage is that the system can introduce new products without modifying the original code , That is to meet the opening and closing principle
Defines an interface for creating objects , Let the subclass decide which class to instantiate , Delay the instantiation of a class to subclasses
Factory method pattern class diagram UML:

The main role of the factory method pattern :
Abstract factory (AbstractFactory): Provides an interface for creating products , The caller creates the product by accessing the factory method of the specific factory
Specific factory (ConcreteFactory): Implements the method of abstract factory definition , Complete the creation of specific products
Abstract product (Product): Define the specifications of the product , Describe the main features and performance of the product
Specific products (ConcreteProduct): The method of realizing the definition of abstract products , Products are created by specific factories , Specific factories correspond to specific products one by one
Code implementation :
/**
* Abstract product : Common methods for providing specific products
*/
public interface Product {
public void show();
}
public class ConcreteProduct1 implements Product {
@Override
public void show() {
System.out.println(" Specific products 1 Exhibition ...");
}
}
public class ConcreateProduct2 implements Product {
@Override
public void show() {
System.out.println(" Specific products 2 Exhibition ...");
}
}
/**
* Abstract factory
*/
public interface AbstractFactory {
public Product createProduct();
}
/**
* Specific factory 1, Produce specific products 1
*/
public class ConcreteFactory1 implements AbstractFactory {
@Override
public Product createProduct() {
ConcreteProduct1 concreteProduct1 = new ConcreteProduct1();
System.out.println(" Specific factory 1 Create specific products 1...");
return concreteProduct1;
}
/**
* Specific factory 2, Produce specific products 2
*/
public class ConcreteFactory2 implements AbstractFactory {
@Override
public Product createProduct() {
System.out.println(" Specific factory 2 Produce specific products 2...");
return new ConcreateProduct2();
}
}
call :
// Get specific products 1
Product product = new ConcreteFactory1().createProduct();
product.show();
// Get specific products 2
Product product1 = new ConcreteFactory2().createProduct();
product1.show();Use steps :
1、 Create an abstract product class , Common methods for defining products
2、 Create specific product classes ( Implement abstract product interface ), Define the specific products generated
3、 Create an abstract factory class , Define the public interface of a specific factory
4、 Create a specific factory class , Define how to create a specific product instance
5、 The caller calls the method of the specific factory class , To create instances of different specific products
Re exploration of the factory model :
solve the problem :
It solves the problem that the method logic of factory class needs to be modified for new products of simple factory class , That is to meet the opening and closing principle .
Create a concrete product to a subclass of the factory class ( Specific factory ), At this time, the factory class is no longer responsible for the creation of all products , Instead, it gives the interface that the specific factory must implement , In this way, when adding a new product, the factory method does not need to modify the logic of the factory class, but adds a new factory subclass , Comply with opening and closing principle
advantage :
Strong flexibility , For the creation of new products , Just write one more corresponding factory class
Users only need to know the name of the factory to get the product they want , There is no need to know the specific product creation process
shortcoming :
It's easy to have too many classes , Added complexity
Each factory can produce only one product , This problem can be solved by using the abstract factory pattern
Application scenarios :
The customer only focuses on the name of the factory that created the product , You don't need to know the specific product name
Abstract factory pattern (Abstract Factory)
Definition :
Provide an interface to create a series of related or interdependent objects , There is no need to specify their specific classes , Specific factories are responsible for implementing specific examples of products
So that one factory can produce multiple products
Abstract factory class diagram UML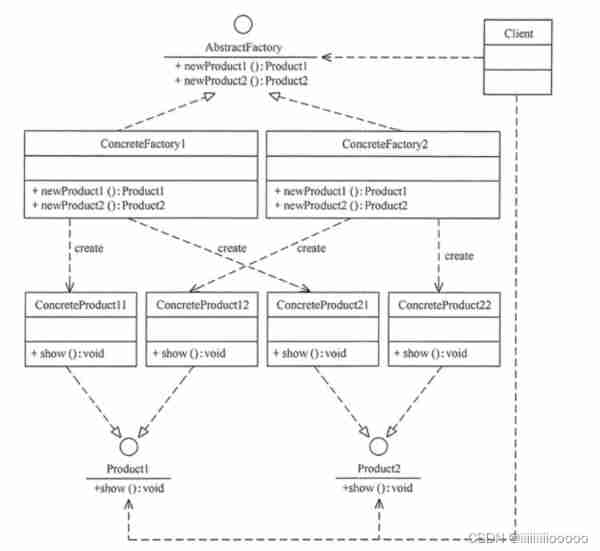
The main role of the abstract factory pattern :
Abstract factory (AbstractFactory): Provides an interface for creating products , Contains multiple interface methods for creating products , You can create many different levels of products
Specific factory (ConcreteFactory): Implements the method of abstract factory definition , Complete the creation of specific products
Abstract product (Product): Define the specifications of the product , Describe the main features and performance of the product
Specific products (ConcreteProduct): The method of realizing the definition of abstract products , There are specific factories to create products , One to many relationship between specific factories and specific products
Code implementation :
/**
* Abstract factory : Provide all methods for a specific plant
*/
public interface AbstractFactory {
public ConcreteProduct1 createProduct1();
public ConcreteProduct2 createProduct2();
}
/**
* Specific factory 1
*/
public class ConcreteFactory1 implements AbstractFactory {
@Override
public ConcreteProduct1 createProduct1() {
System.out.println(" Specific factory 1 Specific products 1");
ConcreteProduct1 product11 = new ConcreteProduct1();
return product11;
}
@Override
public ConcreteProduct2 createProduct2() {
System.out.println(" Specific factory 1 Specific products 2");
ConcreteProduct2 product12 = new ConcreteProduct2();
return product12;
}
}
/**
* Specific factory 2
*/
public class ConcreteFactory2 implements AbstractFactory {
@Override
public ConcreteProduct1 createProduct1() {
System.out.println(" Specific factory 2 Specific products 1");
ConcreteProduct1 product21 = new ConcreteProduct1();
return product21;
}
@Override
public ConcreteProduct2 createProduct2() {
System.out.println(" Specific factory 2 Specific products 2");
ConcreteProduct2 product22 = new ConcreteProduct2();
return product22;
}
}
/**
* Abstract product : All ways to provide a specific product
*/
public interface product {
public void show();
}
/**
* Specific products 1
*/
public class ConcreteProduct1 implements product {
@Override
public void show() {
System.out.println(" Specific products 1 Exhibition ");
}
}
/**
* Specific products 2
*/
public class ConcreteProduct2 implements product {
@Override
public void show() {
System.out.println(" Specific products 2 Exhibition ");
}
}call :
public static void main(String[] args) {
// From specific plant 1 Get specific products 1
ConcreteProduct1 product1 = new ConcreteFactory1().createProduct1();
product1.show();
// From specific plant 1 Get specific products 2
ConcreteProduct2 product2 = new ConcreteFactory1().createProduct2();
product2.show();
// From specific plant 2 Get specific products 1
ConcreteProduct1 product3 = new ConcreteFactory2().createProduct1();
product3.show();
// From specific plant 2 Get specific products 2
ConcreteProduct2 product4 = new ConcreteFactory2().createProduct2();
product4.show();
}Use steps :
1、 Create an abstract product class , Common methods for defining products
2、 Create specific product classes ( Implement abstract product interface ), Define the specific products generated
3、 Create an abstract factory class , Define the public interface of a specific factory , A factory class can create different levels of products
4、 Create a specific factory class , Define how to create a specific product instance
5、 The caller calls the method of the specific factory class , To create instances of different specific products
solve the problem :
A factory can create multiple products , It solves the problem that a factory can only create one product
advantage :
The multi-level products associated in the product family can be jointly managed within the factory class , Instead of introducing new classes to manage
Abstract factories increase the scalability of programs , When adding a new product family , There is no need to modify the source code , It satisfies the open close principle
shortcoming :
When a new product type is added to the product family , All factory classes need to be modified , Increases the abstractness of the system and the difficulty of understanding
JAVA application
stay Spring The use of simple factories in the framework
SPring All objects in the pass through IOC Container management , Get the object through getBean
An example is as follows :
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(path);
// stay IOC The container obtains the required object instance
Student student = (Student) applicationContext.getBean("student");Current ClassPathXmlApplicationContext yes ApplicationContext Implementation of container , and ApplicationContext yes BeanFactory The child interface of the interface ,BeanFactory Interface is the use of simple factory mode , Through the BeanFactory Method can get more objects
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

距离度量 —— 欧式距离(Euclidean Distance)

Fix the problem that uicollectionview does not reach the bottom security zone

(key points of software engineering review) Chapter IV overall design exercises

白屏时间、首屏时间

封装组件系列-(一)-插槽及动态组件

Distance measurement - Euclidean distance

地铁路线图云开发小程序源码和配置教程

使用 Hystrix 实现微服务的容错处理

【GAMES101】作业2--三角形光栅化

MySQL下载安装使用-完整详细步骤
随机推荐
封装组件系列-(一)-插槽及动态组件
Working principle analysis of rxjs fromEvent
Update failed to update bytea type PostgreSQL
[DBSCAN] DBSCAN instance
杰理之BLE 芯片供电范围及防烧芯片措施【篇】
Package component series - (I) - slots and dynamic components
新西兰是道路安全做的最好的国家之一
NFT 2.0: the next generation of NFT will be lean and trustworthy
NFT 2.0: 下一代的NFT将是精简且值得信赖的NFT
基于位置服务(LBS)的SSM的框架实现的兴趣社交软件平台设计与实现
Probability theory: calculating confidence intervals
2022 Health Expo, Beijing Great Health Industry Exhibition, moxibustion health exhibition, Beijing Health Service Exhibition
Writing the program into the microcontroller can control the forward and reverse rotation of the motor more conveniently and quickly
When installing mysql, an error occurred because msvcr120 could not be found DLL, unable to continue code resolution "
Safety related website recommendations
Team level safety training, new employee induction training education courseware, full content ppt application
Report on various activity plans of safety month 2022 (28 pages)
2022 Beijing International Nutrition and Health Industry Expo, the 9th China Great Health Industry Exhibition
[MySQL] use of stored procedures
国际多语言出海商城返佣产品自动匹配订单源码