当前位置:网站首页>Redis elimination strategy
Redis elimination strategy
2022-06-30 17:03:00 【We've been on our way】
One 、 Maximum memory setting
redis The default maximum memory setting is 0, Equivalent to the maximum value based on physical machine 
Two 、 Elimination strategy
1. 8 Strategies
- volatile-lru, For the set expiration time of key, Use lru The algorithm is eliminated .
- allkeys-lru, For all key Use lru The algorithm is eliminated .
- volatile-lfu, For the set expiration time of key, Use lfu The algorithm is eliminated .
- allkeys-lfu, For all key Use lfu The algorithm is eliminated .
- volatile-random, From all with expiration time set key The random elimination method is used for elimination .
- allkeys-random, For all key The random elimination mechanism is used for elimination .
- volatile-ttl, Delete the key with the most recent lifetime .
- noeviction( Default ), Do not delete keys , Value returns an error .
Mainly 4 Species algorithm , For different key, Formed strategy .
Algorithm :
- lru It has been well used recently key( According to time , The least commonly used elimination )
- lfu It has been well used recently key ( According to the counter , With the least number of times key Eliminate )
- random Most difficult to eliminate
- ttl Those that are about to expire will be eliminated first
key :
- volatile Those with expired time key
- allkeys be-all key
2. The specific working principle of the memory elimination algorithm is :
- The client executes a new command , Cause the database needs to add data ( such as set key value)
- Redis Check memory usage , If memory usage exceeds maxmemory, Some of them will be deleted according to the replacement strategy key
- The new order was executed successfully
3、 ... and 、lru and lfu Algorithm
1.lru
LRU yes Least Recently Used Abbreviation , It means that... Has been rarely used recently , It can also be understood that it has not been used for the longest time . That is, when there is not enough memory , Add one piece of data at a time , We need to discard an old piece of data that has not been used for the longest time . The standard LRU In order to reduce the time complexity of finding and deleting elements , It is generally used Hash Table and two-way linked list combined data structure ,hash Table can give the linked list to quickly find a key Whether it exists in the linked list , At the same time, it can be deleted quickly 、 Add a node , As shown in the figure .
The lookup time complexity of a two-way linked list is O(n), Deletion and insertion are O(1), With the help of HashMap structure , It can make the time complexity of search become O(1),Hash Table is used to query the data position in the linked list , Linked list is responsible for data insertion .
When new data is inserted into the head of a linked list, there are two cases
- When this is not in the linked list key, And the list is full , Discard the data at the end of the linked list , The newly added cache is directly added to the chain header .
- When a cache in the linked list is hit , Move the data directly to the head of the linked list , The cache originally at the head node moves to the end of the linked list
such , After many times Cache After the operation , Recently hit cache , There will be the direction of the head of the linked list , What didn't hit , Will be at the end of the linked list , When replacement is needed , Because the tail of the linked list is the least hit , We just need to eliminate the data at the end of the linked list .
2.redis Medium lru Algorithm
actually ,Redis The use of LRU The algorithm is actually an unreliable LRU Algorithm , The keys it actually eliminated are not necessarily the really least used data , Its working mechanism is :
- Random collection of eliminated key, Choose at random each time 5 individual key
- Then eliminate this 5 individual key The least used in key
this 5 individual key Is the default number , The specific values can be in redis.conf Middle configuration

When approximate LRU The larger the value of the algorithm, the closer it will be to the real LRU Algorithm , Because the larger the value, the more complete the data obtained , In the process of elimination 、 Data is closer to the least used data . This actually involves a trade-off problem ,
If you need to search for the most qualified data among all the data , Then it will certainly increase the overhead of the system ,Redis It's single threaded , So the time-consuming operation will be more cautious . In order to achieve relative... Within a certain cost LRU, In the early Redis The version is based on sampling LRU, That is, instead of searching the solution from all data, we search the optimal solution in sampling space .Redis3.0 After the version ,Redis The author is interested in sampling based LRU Some optimization :
- Redis Maintain a size of 16 Candidate pool , When the first random selection uses data , Will put the data into the candidate pool , And the data in the candidate pool will have more time to sort .
- When selecting data after the second time , Only those less than the minimum time in the candidate pool will be put into the candidate pool .
- When the candidate pool is full , Then the time is the biggest key Will be squeezed out of the candidate pool . When performing elimination , Select the candidate pool with the least recent access time directly key To eliminate .
Pictured 4-22 Shown , First, collect... From the target dictionary maxmemory-samples Key , Cache in a samples Array , And then from samples Take out one by one from the array , And the idle time of the later keys in the recycling pool , To update the recycle pool .
- The recycling tank is full , And the currently inserted key Minimum free time ( That is, all in the recycling pool key Than the currently inserted key Have a lot of free time ), Do nothing .
- Recycle pool is not full , And the insertion position x There is no key , Then insert it directly
- Recycle pool is not full , And the insertion position x There are already keys to be eliminated , Then put the x All subsequent elements move back one position , Then do the insert .
- The recycling tank is full , Change the current page to x Move a previous element forward ( It's actually eliminated ), Then perform the insert operation .
The purpose of this is to be able to select the most authentic and least visited key, Able to correctly use infrequently key. Because in Redis3.0 Previously, samples were randomly selected , This way is probably not the least visited in the real sense key.
shortcoming :
LRU The algorithm has one drawback , Add a key Value access frequency is low , But last time I was interviewed , that LRU Think it's hot data , Will not be eliminated . Again ,
Frequently accessed data , I haven't been visited recently , This will lead to the elimination of these data , Lead to misjudgment and eliminate hot data , So in Redis 4.0 in , A new LFU Algorithm .
2.lfu
LFU(Least Frequently Used), The least used recently , It and key Related to the number of times , The idea is : according to key The frequency of recent visits is eliminated , Less visited key Give priority to elimination , On the contrary, keep it .
LRU The principle of is to use a counter to key Sort , Every time key When interviewed , The counter will increase , When the counter is bigger , Means the current key The more frequently you visit , That means it's hot data . It's a good solution LRU Defects of algorithm : One that hasn't been visited for a long time key, Occasionally visited , Leading to problems mistaken for hot data .
LFU The implementation principle of is shown in the figure 4-23 Shown 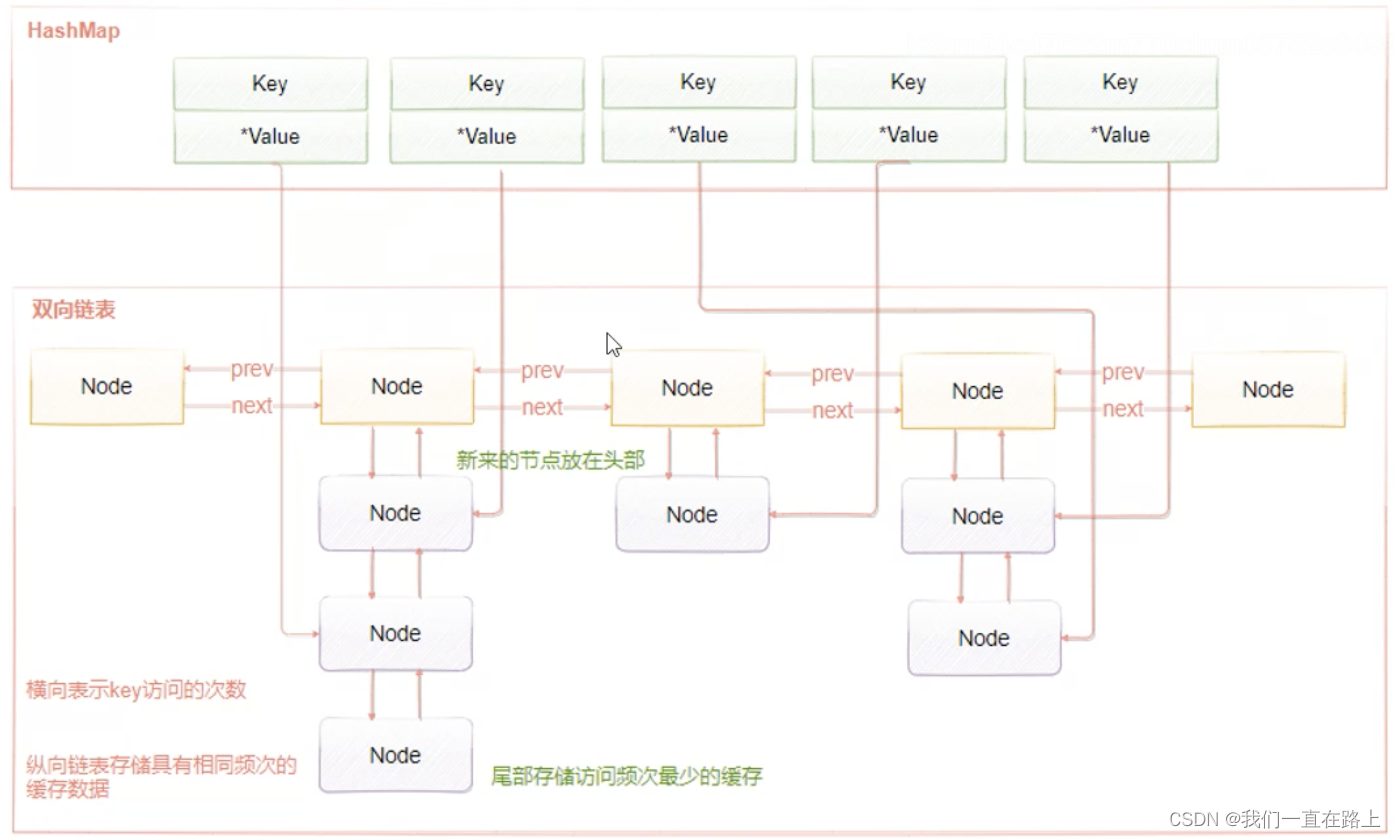
LFU Two linked lists are maintained , The horizontal linked list is used to store the access frequency , Another cache data with the same access frequency is stored under each node with the same access frequency . The specific working principle is :
- When adding elements , Find nodes with the same access frequency , Then add to the header of the data linked list of the node . If the data link list is full , Remove the node at the end of the linked list when the element is obtained or modified , Will increase the corresponding key Frequency of visits , And move the current node to the next frequency node .
- When adding elements , The default access frequency is 1, As the number of visits increases , The frequency is increasing . The currently accessed elements will also move as the frequency increases .
边栏推荐
- 安全帽佩戴检测算法研究
- Rong Lianyun launched rphone based on Tongxin UOS to create a new ecology of localization contact center
- nichenet实战silicosis
- The meaning of linetypes enumeration values (line_4, line_8, line_aa) in opencv
- 删除有序数组中的重复项 II[双指针--多情况统一]
- 利用PIL进行不失真的resize
- [machine learning] K-means clustering analysis
- 异常类_日志框架
- CGR 21 (D,E,F)
- Internet R & D efficiency practice qunar core field Devops landing practice
猜你喜欢

7 月 2 日邀你来TD Hero 线上发布会

The 25th anniversary of Hong Kong's return to China the Hong Kong Palace Museum officially opened as a new cultural landmark
![删除有序数组中的重复项 II[双指针--多情况统一]](/img/e2/cadfdbe476a86cb2d72c1ae0160a4a.png)
删除有序数组中的重复项 II[双指针--多情况统一]

山西化工园区智能化管控平台建设时间表

【牛客网刷题系列 之 Verilog快速入门】~ 位拆分与运算

On July 2, I invited you to TD Hero online conference

Mathematical modeling for war preparation 36 time series model 2

Etcd教程 — 第九章 Etcd之实现分布式锁

Exception class_ Log frame

居家办公浅谈远程协助快速提效心得 | 社区征文
随机推荐
坚果云-在新电脑上同步移动硬盘的文件
Lambda表达式_Stream流_File类
register_ Chrdev and CDEV_ init cdev_ Add usage differences
BC1.2 PD协议
redis数据结构分析
TCP Socket与TCP 连接
[demo] write file circularly
idea必用插件
Drug management system plus database, overnight, plus report
互联网研发效能实践之去哪儿网(Qunar)核心领域DevOps落地实践
POJ Project Summer
[wechat applet] basic use of common components (view/scroll-view/wiper, text/rich-text, button/image)
编译丨迅为iTOP4412开发板Makefile编译
Raft介绍
Sub chain cross technology source level exploration: an overview of xcvm
异常类_日志框架
搬运两个负载均衡的笔记,日后省的找
More dragon lizard self-developed features! Production available Anolis OS 8.6 officially released
RT-Thread 堆区大小设置
山西化工园区智能化管控平台建设时间表