当前位置:网站首页>EF Core中的三类事务(SaveChanges、DbContextTransaction、TransactionScope)
EF Core中的三类事务(SaveChanges、DbContextTransaction、TransactionScope)
2022-06-23 22:18:00 【我把生活交给了工作】
默认事务(SaveChanges)
(1).默认情况下,如果数据库提供程序支持事务,单个 SaveChanges() 调用中的所有变更都会在一个事务中被提交。如果其中任何一个变更失败了, 那么事务就会回滚,没有任何变更会被应用到数据库。这意味着 SaveChanges() 能够确保要么成功保存,要么在发生错误时不对数据库做任何修改。
(2).关闭默认事务:context.Database.AutoTransactionsEnabled = false; 如:Test3()方法,第一条数据保存成功,第二条失败。
/// <summary>
/// 全部成功
/// </summary>
public static void Test1()
{
using (EFDB01Context db = new EFDB01Context())
{
db.T_RoleInfor.Add(new T_RoleInfor() {
roleName = "管理员1", addTime = DateTime.Now });
db.T_RoleInfor.Add(new T_RoleInfor() {
roleName = "管理员2", addTime = DateTime.Now });
db.SaveChanges();
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 全部失败
/// </summary>
public static void Test2()
{
using (EFDB01Context db = new EFDB01Context())
{
try
{
db.T_RoleInfor.Add(new T_RoleInfor() {
roleName = "管理员1", addTime = DateTime.Now });
db.T_RoleInfor.Add(new T_RoleInfor() {
id = 123, roleName = "管理员2", addTime = DateTime.Now });
db.SaveChanges();
}
catch (Exception)
{
Console.WriteLine("出错了,两条数据都没有执行成功");
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 第一条成功,第二条失败
/// </summary>
public static void Test3()
{
using (EFDB01Context db = new EFDB01Context())
{
try
{
//关闭SaveChanges的默认事务
db.Database.AutoTransactionsEnabled = false;
db.T_RoleInfor.Add(new T_RoleInfor() {
roleName = "管理员1", addTime = DateTime.Now });
db.T_RoleInfor.Add(new T_RoleInfor() {
id = 123, roleName = "管理员2", addTime = DateTime.Now });
//db.T_UserInfor.Add(new T_UserInfor() { id = Guid.NewGuid().ToString("N"), userName = "管理员1", addTime = DateTime.Now });
//db.T_UserInfor.Add(new T_UserInfor() { id = Guid.NewGuid().ToString("N")+"123", userName = "管理员2", addTime = DateTime.Now });
db.SaveChanges();
}
catch (Exception)
{
Console.WriteLine("出错了,第一条数据插入成功了");
}
}
}
DbContextTransaction
1. 使用方式
BeginTransaction开启事务、Commit提交事务、Rollback回滚事务、Dispose销毁,如果用Using包裹的话,不再需要手动Rollback,走完Using会自动回滚。如果不用Using包裹事务,就需要在Catch中手动RollBack回滚,并且最好最后手动的Dispose一下。(如SameDbContext文件夹中的Test1和Test2方法)
2. 使用场景
A. 同一个上下文多个SaveChanges的方法(如:自增主键后续要用到,如Test2方法)、SaveChanges和EF调用SQL语句混用(如Test2方法)
/// <summary>
/// 三条添加语句共享同一个事务,最后使用 transaction.Commit() 统一提交,三条全部执行成功,则影响到数据库,
/// 如果任何一个命令失败,则在事务被回收(Dispose)时会自动回滚,对数据库无影响。
/// </summary>
public static void Test1()
{
using (EFDB01Context db = new EFDB01Context())
{
using (var transaction = db.Database.BeginTransaction())
{
try
{
db.T_RoleInfor.Add(new T_RoleInfor() {
roleName = "管理员1", addTime = DateTime.Now });
db.SaveChanges();
db.T_RoleInfor.Add(new T_RoleInfor() {
id = 111, roleName = "管理员2", addTime = DateTime.Now }); //报错
db.SaveChanges();
string sql1 = @"insert into T_RoleInfor (roleName,roleDescription,addTime) values (@roleName,@roleDescription,@addTime)";
SqlParameter[] pars1 ={
new SqlParameter("@roleName","管理员3"),
new SqlParameter("@roleDescription","txt11"),
new SqlParameter("@addTime",DateTime.Now)
};
db.Database.ExecuteSqlCommand(sql1, pars1);
transaction.Commit();
Console.WriteLine("成功了");
}
catch (Exception)
{
Console.WriteLine("失败了");
}
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 如果不用Using包裹事务,就需要在Catch中手动RollBack回滚
/// </summary>
public static void Test2()
{
using (EFDB01Context db = new EFDB01Context())
{
var transaction = db.Database.BeginTransaction();
try
{
var d1 = new T_RoleInfor() {
roleName = "管理员1", addTime = DateTime.Now };
db.T_RoleInfor.Add(d1);
db.SaveChanges();
db.T_RoleInfor.Add(new T_RoleInfor() {
roleName = "管理员2"+d1.id, addTime = DateTime.Now });
db.SaveChanges();
string sql1 = @"insert into T_RoleInfor (roleName,roleDescription,addTime) values (@roleName,@roleDescription,@addTime)";
SqlParameter[] pars1 ={
new SqlParameter("@roleName","管理员3"),
new SqlParameter("@roleDescription","txt11"),
new SqlParameter("@addTime",DateTime.Now)
};
db.Database.ExecuteSqlCommand(sql1, pars1);
transaction.Commit();
Console.WriteLine("成功了");
}
catch (Exception)
{
transaction.Rollback();
Console.WriteLine("失败了");
}
finally
{
transaction.Dispose();
}
}
}
B. 同一个数据库多个上下文但“同一个连接”的事务。其中一个上下文开启事务,另外上下文通过UseTransaction方法来实现共享事务。
情况①:
EFDB01Context直接在OnConfiguring中写死连接字符串,多次new上下文,如Test1方法,则是多个连接,不能共享事务。
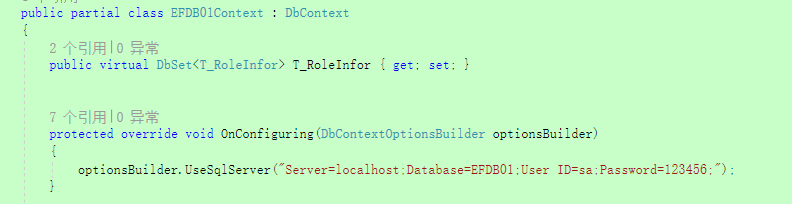
/// <summary>
/// 情况一:在OnConfiguring中书写连接字符串,创建两个上下文,相当于两个连接,两个连接之间不能通过使用UseTransaction,建立事务连接。
/// 会报下面的错。
/// The specified transaction is not associated with the current connection. Only transactions associated with the current connection may be used.
/// </summary>
public static void Test1()
{
using (EFDB01Context context1 = new EFDB01Context())
{
using (var transaction = context1.Database.BeginTransaction())
{
try
{
context1.T_RoleInfor.Add(new T_RoleInfor() {
roleName = "管理员1", addTime = DateTime.Now });
context1.SaveChanges();
using (EFDB01Context context2 = new EFDB01Context())
{
context2.Database.UseTransaction(transaction.GetDbTransaction());
context1.T_RoleInfor.Add(new T_RoleInfor() {
roleName = "管理员1", addTime = DateTime.Now });
context1.SaveChanges();
}
//统一提交
transaction.Commit();
Console.WriteLine("成功了");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
}
}
情况②:
EFDB01Context2通过 public EFDB01Context2(DbContextOptions options) : base(options)这种形式的构造函数,然后new的时候 统一传入: new DbContextOptionsBuilder().UseSqlServer(new SqlConnection(connectionString)).Options;,从而共享连接,如Test2方法。

/// <summary>
/// 情况二:通过父类构造函数
/// </summary>
public static void Test2()
{
var connectionString = "Server=localhost;Database=EFDB01;User ID=sa;Password=123456;";
//将连接拿出来,传到多个上下文中,这样是共享同一个连接
var option = new DbContextOptionsBuilder<EFDB01Context2>().UseSqlServer(new SqlConnection(connectionString)).Options;
using (var context1 = new EFDB01Context2(option))
{
using (var transaction = context1.Database.BeginTransaction())
{
try
{
context1.T_RoleInfor.Add(new T_RoleInfor() {
roleName = "管理员1", addTime = DateTime.Now });
context1.SaveChanges();
using (var context2 = new EFDB01Context2(option))
{
context2.Database.UseTransaction(transaction.GetDbTransaction());
context1.T_RoleInfor.Add(new T_RoleInfor() {
roleName = "管理员1", addTime = DateTime.Now });
context1.SaveChanges();
}
//统一提交
transaction.Commit();
Console.WriteLine("成功了");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
}
}
情况③:
EFDB01Context3通过 传入SqlConnection来实现共享连接,如Test3方法。

public static void Test3()
{
var connectionString = "Server=localhost;Database=EFDB01;User ID=sa;Password=123456;";
//将连接拿出来,传到多个上下文中,这样是共享同一个连接
var connection = new SqlConnection(connectionString);
using (var context1 = new EFDB01Context3(connection))
{
using (var transaction = context1.Database.BeginTransaction())
{
try
{
context1.T_RoleInfor.Add(new T_RoleInfor() {
roleName = "管理员1", addTime = DateTime.Now });
context1.SaveChanges();
using (var context2 = new EFDB01Context3(connection))
{
context2.Database.UseTransaction(transaction.GetDbTransaction());
context1.T_RoleInfor.Add(new T_RoleInfor() {
roleName = "管理员1", addTime = DateTime.Now });
context1.SaveChanges();
}
//统一提交
transaction.Commit();
Console.WriteLine("成功了");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
}
}
C. 多种数据库技术同一个数据库的事务
如ADO.Net和EF共同使用,利用方法 “UseTransaction”共享同一个事务,共同提交。 如:Test1方法
/// <summary>
/// ADO.Net 和 EF混用,多种数据库技术访问同一个数据库
/// </summary>
public static void Test1()
{
var conStr = @"Server=localhost;Database=EFDB01;User ID=sa;Password=123456;";
using (var connection=new SqlConnection(conStr))
{
connection.Open();
using (var transaction=connection.BeginTransaction())
{
try
{
//ADO.Net
var command = connection.CreateCommand();
command.Transaction = transaction;
command.CommandText = "DELETE FROM T_RoleInfor";
command.ExecuteNonQuery();
//EF
var options = new DbContextOptionsBuilder<EFDB01Context>().UseSqlServer(connection).Options;
using (var context = new EFDB01Context(options))
{
context.Database.UseTransaction(transaction);
context.T_RoleInfor.Add(new T_RoleInfor() {
roleName = "管理员1", addTime = DateTime.Now });
context.SaveChanges();
}
//综合提交
transaction.Commit();
Console.WriteLine("成功了");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
}
}
环境事务(TransactionScope)
1.使用方式
new TransactionScope创建事务、Complete提交事务、 Transaction.Current.Rollback();回滚事务、Dispose销毁对象。如果用Using包裹的话,不再需要手动Rollback,走完Using会自动回滚。如果不用Using包裹事务,就需要在Catch中手动RollBack回滚,并且最好最后手动的Dispose一下。
2.用途
A. 同一个上下文的事务。(多个SaveChanges(自增主键后续用到的情况)、SaveChanges和EF调用SQL语句混用)(如Test1方法)
/// <summary>
/// A. 同一个上下文的事务。(多个SaveChanges(自增主键后续用到的情况)、SaveChanges和EF调用SQL语句混用)
/// </summary>
public static void Test1()
{
using (EFDB01Context1 db = new EFDB01Context1())
{
using (var scope = new TransactionScope(/*TransactionScopeOption.Required, new TransactionOptions { IsolationLevel = IsolationLevel.ReadCommitted }*/))
{
try
{
var data1 = new T_RoleInfor() {
roleName = "管理员1", addTime = DateTime.Now };
db.T_RoleInfor.Add(data1);
db.SaveChanges();
db.T_RoleInfor.Add(new T_RoleInfor() {
roleName = "管理员2" + data1.id, addTime = DateTime.Now }); //报错
db.SaveChanges();
string sql1 = @"insert into T_RoleInfor (roleName,roleDescription,addTime) values (@roleName,@roleDescription,@addTime)";
SqlParameter[] pars1 ={
new SqlParameter("@roleName","管理员3"),
new SqlParameter("@roleDescription","txt11"),
new SqlParameter("@addTime",DateTime.Now)
};
db.Database.ExecuteSqlCommand(sql1, pars1);
scope.Complete();
Console.WriteLine("成功了");
}
catch (Exception)
{
Console.WriteLine("失败了");
}
}
}
}
B. 多种数据库技术访问同一个数据库的事务 (如Test2方法)
/// <summary>
/// B. 多种数据库技术访问同一个数据库的事务
/// </summary>
public static void Test2()
{
var conStr = @"Server=localhost;Database=EFDB01;User ID=sa;Password=123456;";
using (var connection = new SqlConnection(conStr))
{
connection.Open();
using (var scope = new TransactionScope())
{
try
{
//ADO.Net
var command = connection.CreateCommand();
command.CommandText = "DELETE FROM T_RoleInfor";
command.ExecuteNonQuery();
//EF
using (var context = new EFDB01Context1())
{
context.T_RoleInfor.Add(new T_RoleInfor() {
roleName = "管理员1", addTime = DateTime.Now });
context.SaveChanges();
}
//综合提交
scope.Complete();
Console.WriteLine("成功了");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
}
}
C. 同一个数据库多个不同的上下文是支持的(如Test3方法)
1 public partial class EFDB01Context1 : DbContext
2 {
3 public virtual DbSet<T_RoleInfor> T_RoleInfor {
get; set; }
4 public virtual DbSet<T_UserInfor> T_UserInfor {
get; set; }
5
6 protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
7 {
8 optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer("Server=localhost;Database=EFDB01;User ID=sa;Password=123456;");
9 }
10
11 protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
12 {
13 modelBuilder.HasAnnotation("ProductVersion", "2.2.0-rtm-35687");
14
15 modelBuilder.Entity<T_RoleInfor>(entity =>
16 {
17 entity.Property(e => e.roleDescription).IsUnicode(false);
18
19 entity.Property(e => e.roleName).IsUnicode(false);
20 });
21
22 modelBuilder.Entity<T_UserInfor>(entity =>
23 {
24 entity.Property(e => e.id)
25 .IsUnicode(false)
26 .ValueGeneratedNever();
27
28 entity.Property(e => e.userName).IsUnicode(false);
29
30 entity.Property(e => e.userSex).IsUnicode(false);
31 });
32 }
33 }
EFDB01Context1
1 public partial class EFDB01Context2 : DbContext
2 {
3 public virtual DbSet<T_RoleInfor> T_RoleInfor {
get; set; }
4 public virtual DbSet<T_UserInfor> T_UserInfor {
get; set; }
5
6 protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
7 {
8 optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer("Server=localhost;Database=EFDB01;User ID=sa;Password=123456;");
9 }
10
11 protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
12 {
13 modelBuilder.HasAnnotation("ProductVersion", "2.2.0-rtm-35687");
14
15 modelBuilder.Entity<T_RoleInfor>(entity =>
16 {
17 entity.Property(e => e.roleDescription).IsUnicode(false);
18
19 entity.Property(e => e.roleName).IsUnicode(false);
20 });
21
22 modelBuilder.Entity<T_UserInfor>(entity =>
23 {
24 entity.Property(e => e.id)
25 .IsUnicode(false)
26 .ValueGeneratedNever();
27
28 entity.Property(e => e.userName).IsUnicode(false);
29
30 entity.Property(e => e.userSex).IsUnicode(false);
31 });
32 }
33 }
EFDB01Context2
运行代码:
/// <summary>
///C. 同一个数据库两个不同上下文是支持的
/// </summary>
public static void Test3()
{
using (var scope = new TransactionScope())
{
try
{
using (var context = new EFDB01Context1())
{
context.T_RoleInfor.Add(new T_RoleInfor() {
roleName = "管理员1", addTime = DateTime.Now });
context.SaveChanges();
}
using (var context = new EFDB01Context2())
{
context.T_RoleInfor.Add(new T_RoleInfor() {
roleName = "管理员1", addTime = DateTime.Now });
context.SaveChanges();
}
//综合提交
scope.Complete();
Console.WriteLine("成功了");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
}
D. 不同数据库的上下文是不支持的,(如Test4方法,开启msdtc服务的步骤: cmd命令→ net start msdtc ,然后发现报错:This platform does not support distributed transactions.说明目前Core平台下不支持分布式事务)
上下文代码:
1 public partial class dbCore1Context : DbContext
2 {
3 public dbCore1Context()
4 {
5 }
6
7 public dbCore1Context(DbContextOptions<dbCore1Context> options)
8 : base(options)
9 {
10 }
11
12 public virtual DbSet<UserInfors> UserInfors {
get; set; }
13
14 protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
15 {
16 optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer("Server=localhost;Database=dbCore1;User ID=sa;Password=123456;");
17
18 }
19
20 protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
21 {
22 modelBuilder.HasAnnotation("ProductVersion", "2.2.0-rtm-35687");
23
24 modelBuilder.Entity<UserInfors>(entity =>
25 {
26 entity.Property(e => e.id).ValueGeneratedNever();
27 });
28 }
29 }
dbCore1Context
1 public partial class EFDB01Context1 : DbContext
2 {
3 public virtual DbSet<T_RoleInfor> T_RoleInfor {
get; set; }
4 public virtual DbSet<T_UserInfor> T_UserInfor {
get; set; }
5
6 protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
7 {
8 optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer("Server=localhost;Database=EFDB01;User ID=sa;Password=123456;");
9 }
10
11 protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
12 {
13 modelBuilder.HasAnnotation("ProductVersion", "2.2.0-rtm-35687");
14
15 modelBuilder.Entity<T_RoleInfor>(entity =>
16 {
17 entity.Property(e => e.roleDescription).IsUnicode(false);
18
19 entity.Property(e => e.roleName).IsUnicode(false);
20 });
21
22 modelBuilder.Entity<T_UserInfor>(entity =>
23 {
24 entity.Property(e => e.id)
25 .IsUnicode(false)
26 .ValueGeneratedNever();
27
28 entity.Property(e => e.userName).IsUnicode(false);
29
30 entity.Property(e => e.userSex).IsUnicode(false);
31 });
32 }
33 }
EFDB01Context1
运行代码:
/// <summary>
///D. 不同数据库之间的事务
/// </summary>
public static void Test4()
{
using (var scope = new TransactionScope())
{
try
{
using (var context = new EFDB01Context1())
{
context.T_RoleInfor.Add(new T_RoleInfor() {
roleName = "管理员1", addTime = DateTime.Now });
context.SaveChanges();
}
using (var context = new dbCore1Context())
{
context.UserInfors.Add(new UserInfors() {
id = Guid.NewGuid().ToString("N"), userName = "管理员1", userSex = "男" });
context.SaveChanges();
}
//综合提交
scope.Complete();
Console.WriteLine("成功了");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
}
注:EF Core中的 System.Transactions 实现将不包括对分布式事务的支持,因此不能使用
TransactionScope 或 CommittableTransaction 来跨多个资源管理器协调事务。主要分布式事务需要依赖于
Windows 系统的 MSDTC 服务,但.NET Core要实现跨平台,基于跨平台的分布式事务没有统一的标准,后续版希望改进。
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
PyQt5_QTableWidget分页单选右键菜单控件
STM32 ------ external interrupt
Acrel-3000WEB电能管理系统在都巴高速的应用
2018/GAN:Self-Attention Generative Adversarial Networks自我注意生成对抗网络
2022山东健博会,济南国际大健康产业博览会,中国营养健康展
多门店药品进销存系统源码 大型连锁药店管理系统源码
Niuke.com: the double pointer problem of receiving rainwater
Graph theory (nearest common ancestor LCA)
再来一个高仿开眼的短视频APP
文言文能编程???
[Xilinx ax7103 microbalze Learning Notes 6] MicroBlaze custom IP core packaging experiment
【HackTheBox】Fawn
思考(八十六):主从实现思路
MySQL导致索引失效的情况详解
电子元器件行业B2B交易管理系统:提升数据化驱动能力,促进企业销售业绩增长
Stm32-------adc (voltage detection)
Golang 类型断言
企业网站的制作流程是什么?设计和制作一个网站需要多长时间?
这个高仿小米商城项目太惊艳了
One person even broke up a Netease cloud music Cloud Village