当前位置:网站首页>Blocking queue - delayedworkqueue source code analysis
Blocking queue - delayedworkqueue source code analysis
2022-06-11 00:38:00 【Be valuable】

Preface
Thread pool runtime , It keeps getting tasks from the task queue , And then execute the task . If we want to delay or schedule tasks , The important thing is that the task queue is sorted according to the delay time of the task , The shorter the delay, the higher the queue , Gets executed first .
Queues are first in first out data structures , That's the data that goes into the queue first , Be obtained . But there is a special kind of queue called Priority queue , It prioritizes the inserted data , Ensure that the higher priority data is retrieved first , Regardless of the order in which the data is inserted .
One common way to make priority queues efficient is to use the heap . The implementation of the heap can be seen 《 Implementation and characteristics of heap and binary heap 》
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor Thread pool
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor Inherited from ThreadPoolExecutor, So its internal data structure and ThreadPoolExecutor Is essentially the same , On the basis of it, the function of scheduling tasks according to time is added , It is divided into delayed execution task and periodic execution task .
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor Constructor of can only be passed 3 Parameters corePoolSize、ThreadFactory、RejectedExecutionHandler, Default maximumPoolSize by Integer.MAX_VALUE.
Work queues are highly customized delay blocking queues DelayedWorkQueue, In fact, the principle and DelayQueue Is essentially the same , The core data structure is the priority queue of binary minimum heap , When the queue is full, it will be automatically expanded , therefore offer Operations never block ,maximumPoolSize It would be useless , So there will always be at most... In the thread pool corePoolSize Worker threads are running .
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue(), threadFactory, handler);
}
DelayedWorkQueue Delay blocking queue
DelayedWorkQueue It is also a delay queue designed for timed tasks , Its realization and DelayQueue equally , It's just a combination of priority queues and DelayQueue The implementation process of is migrated to its own method body , Thus, it is possible to flexibly add method calls specific to the scheduled task in this process .
working principle
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor The reason why I want to implement the blocked work queue myself , Because ScheduleThreadPoolExecutor The required work queue is somewhat special .
DelayedWorkQueue Is a heap based data structure , Be similar to DelayQueue and PriorityQueue. When performing scheduled tasks , The execution time of each task is different , therefore DelayedWorkQueue Your job is to arrange in ascending order of execution time , The task whose execution time is closer to the current time is in front of the queue ( Be careful : The order here is not absolute , Sorting in the heap only ensures that the next execution time of the child node is greater than that of the parent node , Leaf nodes are not necessarily sequential ).
The heap structure is shown in the figure below : so ,DelayedWorkQueue Is a queue based on the minimum heap structure . Heap structures can be represented by arrays , It can be converted into the following array :
so ,DelayedWorkQueue Is a queue based on the minimum heap structure . Heap structures can be represented by arrays , It can be converted into the following array : In this structure , The following features can be found : hypothesis “ First element ” The index in the array is 0 Words , Then the positional relationship between the parent node and the child node is as follows :
In this structure , The following features can be found : hypothesis “ First element ” The index in the array is 0 Words , Then the positional relationship between the parent node and the child node is as follows :
- The index for The left child's index is ;
- The index for The right child's index is ;
- The index for The index of the parent node of is ;
Why use DelayedWorkQueue Well ?
- When executing a scheduled task, you need to retrieve the task to be executed recently , Therefore, every time a task leaves the queue, it must be the one with the highest execution time in the current queue , So it's natural to use priority queues .
- DelayedWorkQueue It's a priority queue , It can ensure that every task out of the queue has the highest execution time in the current queue , Because it is a queue based on heap structure , The worst time complexity of the heap structure when performing insert and delete operations is O(logN).
Source code analysis
Definition
DelayedWorkQueue The class inheritance relationship of is as follows : The methods included are defined as follows :
The methods included are defined as follows :
Member attribute
// At the beginning , Array size .
private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
// Use arrays to store the elements in the queue , Create... Based on initial capacity RunnableScheduledFuture An array of types
private RunnableScheduledFuture<?>[] queue = new RunnableScheduledFuture<?>[INITIAL_CAPACITY];
// Use lock To ensure the safety of multi-threaded concurrency issues .
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// The size of the elements stored in the queue
private int size = 0;
// It refers to the queue header task leader Threads
private Thread leader = null;
// When the task delay time of the queue head is up , Or the new thread may need to be leader, To wake up the waiting thread
private final Condition available = lock.newCondition();
DelayedWorkQueue An array is used to store the elements in a queue , The core data structure is the priority queue of binary minimum heap , When the queue is full, it will be automatically expanded .
Notice the leader, It is Leader-Follower A variant of the pattern , It is used to reduce unnecessary scheduled waiting . What does that mean ?
For a multithreaded network model : All threads have one of three identities :leader and follower, And a working state :proccesser. Its basic principle is , There will always be at most one leader. And all follower Are waiting to become leader. A thread pool is automatically generated when the thread pool is started Leader Responsible for waiting for the network IO event , When an event occurs ,Leader The thread first notifies a Follower Threads promote it to a new Leader, Then he went to work , To deal with this network event , After processing, add Follower Thread wait queue , Waiting for the next time to be Leader. This method can enhance CPU Cache similarity , And eliminate dynamic memory allocation and data exchange between threads .
Constructors
DelayedWorkQueue yes ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor Static class part of , By default, there is only one parameterless constructor .
static class DelayedWorkQueue extends AbstractQueue<Runnable>
implements BlockingQueue<Runnable> {
// ...
}
The method of entrance
DelayedWorkQueue Provides put/add/offer( Take time ) Three insert element methods . We found that compared to normal blocking queues , All three add methods are called offer Method . That's because it doesn't have a full queue condition , In other words, you can keep going DelayedWorkQueue Additive elements , When the number of elements exceeds the length of the array , It's going to expand the array .
public void put(Runnable e) {
offer(e);
}
public boolean add(Runnable e) {
return offer(e);
}
public boolean offer(Runnable e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
return offer(e);
}
offer Additive elements
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor When submitting a task, you call DelayedWorkQueue.add, and add、put And other externally provided methods for adding elements have called offer.
public boolean offer(Runnable x) {
if (x == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> e = (RunnableScheduledFuture<?>)x;
// Use lock Ensure the safety of concurrent operations
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
int i = size;
// If you want to exceed the array length , I'm going to expand the array
if (i >= queue.length)
// Array capacity
grow();
// Increment the number of elements in the queue by one
size = i + 1;
// If it's the first element , So you don't have to sort , Just assign it directly
if (i == 0) {
queue[0] = e;
setIndex(e, 0);
} else {
// call siftUp Method , Order the inserted elements .
siftUp(i, e);
}
// Indicates that the newly inserted element is the queue header , The queue head has been replaced ,
// Then wake up the thread that is waiting to get the task .
if (queue[0] == e) {
leader = null;
// Wakes up the thread that is waiting to get the task
available.signal();
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
return true;
}
The basic process is as follows :
- It serves as an entry point for producers , First get the lock .
- Determine whether the queue is going to be full (
size >= queue.length), Expand the capacity when it is fullgrow(). - The queue is under ,size+1.
- Determine whether the added element is the first , Yes, there is no need to heap .
- The added element is not the first , You need to heap
siftUp. - If the top element of the heap happens to be the element added at this time , Then wake up take Thread consumption .
- Finally release the lock .
offer The basic flow chart is as follows :

Capacity expansion grow()
You can see , When the queue is full , It doesn't block waiting , Instead, it continues to expand . New capacity newCapacity In old capacity oldCapacity On the basis of expansion 50%(oldCapacity >> 1 amount to oldCapacity /2). Last Arrays.copyOf, First, according to newCapacity Create a new empty array , Then copy the data from the old array to the new array .
private void grow() {
int oldCapacity = queue.length;
// Each expansion increases the number of the original array by half .
// grow 50%
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity < 0) // overflow
newCapacity = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// Use Arrays.copyOf To copy a new array
queue = Arrays.copyOf(queue, newCapacity);
}
Pile it up siftUp
The newly added elements will be added to the bottom of the heap first , Then compare with the parent node above step by step , If it is smaller than the parent node, it will exchange positions with the parent node , Loop comparison does not end the loop until it is greater than the parent node . Through the loop , To find the elements key It should be inserted in the node of the heap binary tree , And interact with the location of the parent node .
Pile it up siftUp You can view the detailed process of 《 Implementation and characteristics of heap and binary heap 》
private void siftUp(int k, RunnableScheduledFuture<?> key) {
// When k==0 when , We're at the root of the heap binary tree , Out of the loop
while (k > 0) {
// Parent position coordinates , amount to (k - 1) / 2
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;
// Gets the parent node location element
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> e = queue[parent];
// If key The element is greater than the parent location element , Meet the conditions , So get out of the loop
// Because it goes from small to large .
if (key.compareTo(e) >= 0)
break;
// Otherwise, the parent element is placed in k Location
queue[k] = e;
// This is only if the element is ScheduledFutureTask Object instances are useful , Used to quickly cancel tasks .
setIndex(e, k);
// Reassign k, Looking for elements key The node that should be inserted into the heap binary tree
k = parent;
}
// The loop ends ,k Is the element key The node location that should be inserted
queue[k] = key;
setIndex(key, k);
}
The code is easy to understand , Is the basis of the cycle key Node and its parent node , If key The execution time of the node is less than that of the parent node , Then the two nodes are exchanged , Arrange the nodes with the highest execution time in front of the queue .
Suppose the delay time of the newly queued node ( call getDelay() Methods to get ) yes 5 , The execution process is as follows :
- First add the new node to the end of the array , The index of the new node k by 7

- Calculate the index of the new parent node :parent = (k - 1) >>> 1,parent = 3, that queue[3] The interval value of is 8, because 5 < 8 , Will perform queue[7] = queue[3]

- This will be k Set to 3, Continue to cycle , Calculate again parent by 1,queue[1] The time interval of is 3, because 5 > 3 , Then exit the loop , Final k by 3

so , Each time a node is added , Only based on the parent node , Without affecting sibling nodes .
A team approach
DelayedWorkQueue The following methods are provided
- take(), Wait to get the queue header element
- poll() , Get the queue header element immediately
- poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) , Timeout waits to get the queue header element
take Consumption elements
Worker After the worker thread starts, it will cycle through the elements in the work queue , because ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor Of keepAliveTime=0, So the consumption task only calls DelayedWorkQueue.take.take The basic process is as follows :
- First, get the interruptible lock , Determine whether the heap top element is empty , Empty blocks waiting
available.await(). - The heap top element is not empty , Get the delay execution time
delay,delay <= 0It indicates that the execution time is up , Outgoing queuefinishPoll. delay > 0It's not time to execute , JudgeleaderWhether the thread is empty , If it is not blank, it indicates that there are other take Threads are also waiting , At present take Will block waiting indefinitely .leaderThread is empty , At present take Thread set toleader, And block waitingdelayDuration .- At present leader Thread waiting delay The length of time automatically wakes up to protect the quilt take Thread wake up , The final will
leaderSet tonull. - Recycle once to judge
delay <= 0Outgoing queue . - Jump out of the loop and judge leader Is empty and the heap top element is not empty , Awaken others take Threads , Whether to lock at last .
public RunnableScheduledFuture<?> take() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
for (;;) {
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> first = queue[0];
// If there is no task , Let the thread available Conditional waiting .
if (first == null)
available.await();
else {
// Gets the remaining latency of the task
long delay = first.getDelay(NANOSECONDS);
// If the delay time is up , Return to this task , Used to perform .
if (delay <= 0)
return finishPoll(first);
// take first Set to null, While the thread is waiting , Don't hold first References to
first = null; // don't retain ref while waiting
// If the same thread is waiting for the queue header task ,
// Indicates that the delay time for the queue header task is not up , Continue to wait for .
if (leader != null)
available.await();
else {
// Record the current thread waiting for the queue header task
Thread thisThread = Thread.currentThread();
leader = thisThread;
try {
// When the delay time for the task is up , Can automatically wake up over time .
available.awaitNanos(delay);
} finally {
if (leader == thisThread)
leader = null;
}
}
}
}
} finally {
if (leader == null && queue[0] != null) // Wakes up a thread waiting for a task
available.signal();
ock.unlock();
}
}
take The basic flow chart is as follows :

take Thread blocking waiting
It can be seen that this producer take Threads can block waiting in two cases :
- The heap top element is empty .
- Top of pile elements delay > 0 .
take When was the method called ?
stay ThreadPoolExecutor in ,getTask Method , The worker thread will loop from workQueue To take the task . But timed tasks are different , Because if once getTask The method takes out the task and starts to execute , At this time, it may not be time to execute , So in take In the method , Make sure that the task can only be taken away when it reaches the specified execution time .
leader Threads
Let's talk about it again leader The role of , there leader To reduce unnecessary waiting time .leader Thread design , yes Leader-Follower A variation of the pattern , To wait for unnecessary time . When one take The thread becomes leader Thread time , Just wait for the next delay , instead of leader Other threads take Threads need to wait leader When the thread is out of the queue, it wakes up others take Threads .
for instance , without leader, Then in execution take when , To perform all available.awaitNanos(delay), Suppose the current thread executes the code , There is no such thing as signal, The second thread also executes the code , The second thread will also be blocked . It is useless to execute this code at this time , Because there can only be one thread from take Back in queue[0]( Because there is lock), Other threads will return at this time for When the loop is executed, the queue[0], Not before queue[0] 了 , And then continue to block .
therefore , In order not to make multiple threads frequently do useless timed waiting , There is an increase in leader, If leader Not empty , It means that the first node in the queue is already waiting to leave the queue , At this time, other threads will be blocked all the time , Reduces unwanted blocking ( Be careful , stay finally Called in signal() To wake up a thread , instead of signalAll()).
finishPoll Outgoing queue
Heap top element delay<=0, It's time for execution , Out of the queue is a downward heap process siftDown.
// Removes the queue header element
private RunnableScheduledFuture<?> finishPoll(RunnableScheduledFuture<?> f) {
// Subtract one from the number of elements in the queue
int s = --size;
// Gets the end element of the queue x
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> x = queue[s];
// The original queue end element is set to null
queue[s] = null;
if (s != 0)
// Because the queue header element is removed , So let's reorder it .
siftDown(0, x);
setIndex(f, -1);
return f;
}
The heap deletion method is mainly divided into three steps :
- So let's subtract one from the number of elements in the queue ;
- Set the end element of the original queue as the queue header element , Then set the end of the queue element to null;
- call setDown(O,x) Method , Ensure that the elements are sorted by priority .
Pile it down siftDown
Since the top of the heap element is out of the queue , It destroys the structure of the heap , Need to organize , Move the tail of the heap element to the top of the heap , Then heap it down :
- Start at the top of the pile , The parent node is compared with the smaller child node in the left and right child nodes ( The left child is not necessarily smaller than the right child ).
- The parent node is less than or equal to the child node , End cycle , There's no need to swap places .
- If the parent node is larger than the younger node , Then switch places .
- Continue to cycle down to determine the relationship between the parent node and the child node , The loop does not end until the parent node is less than or equal to the child node .
Pile it down siftDown You can view the detailed process of 《 Implementation and characteristics of heap and binary heap 》
private void siftDown(int k, RunnableScheduledFuture<?> key) {
// unsigned right shift , amount to size/2
int half = size >>> 1;
// Through the loop , Ensure that the value of the parent node is not greater than that of the child node .
while (k < half) {
// The left child node , amount to (k * 2) + 1
int child = (k << 1) + 1;
// Left child node location element
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> c = queue[child];
// The right child node , amount to (k * 2) + 2
int right = child + 1;
// If the left child element value is greater than the right child element value , Then the right child node is the smaller child node .
// will c And child Value reassignment
if (right < size && c.compareTo(queue[right]) > 0)
c = queue[child = right];
// If the parent element value is less than the smaller child element value , So get out of the loop
if (key.compareTo(c) <= 0)
break;
// otherwise , The parent element is swapped with the child node
queue[k] = c;
setIndex(c, k);
k = child;
}
queue[k] = key;
setIndex(key, k);
}
siftDown Method execution contains two cases , One is that there are no child nodes , One is to have child nodes ( according to half Judge ).
for example : No child nodes :
Assume that the initial heap is as follows :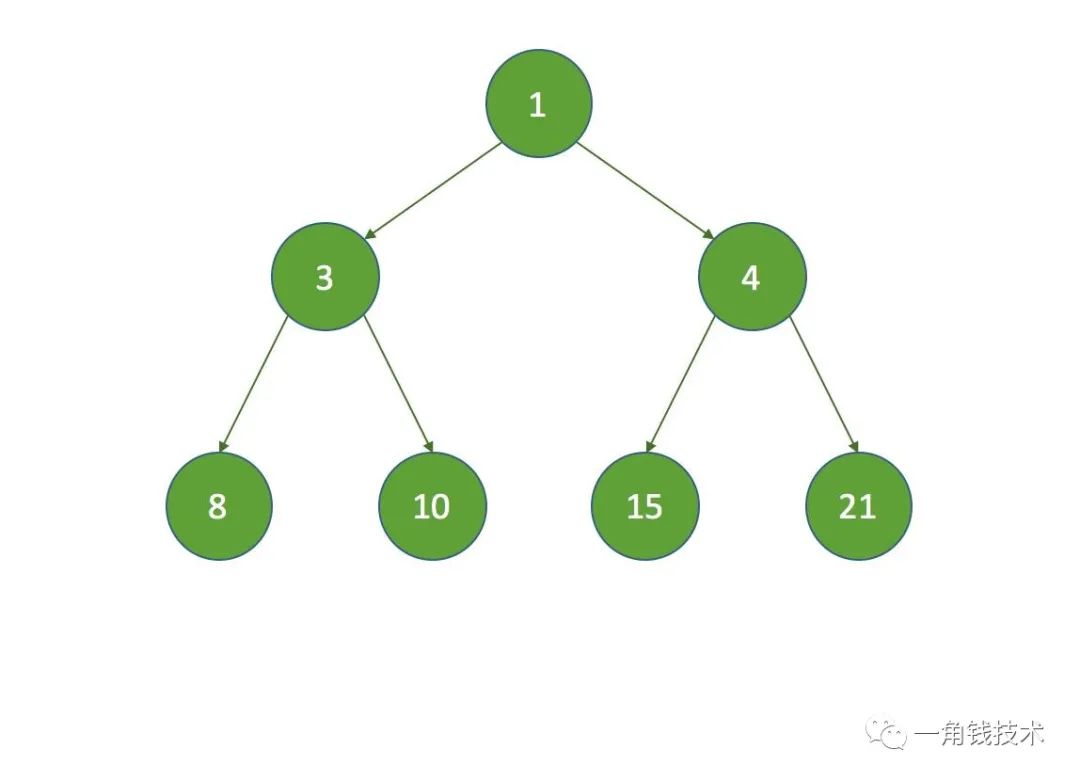
- hypothesis k = 3 , that k = half , No child node , In execution siftDown Method is directly indexed as 3 The node of the array is set to the last node of the array :

There are child nodes :
hypothesis k = 0 , Then perform the following steps :
- Gets the left child node ,child = 1 , Get the right child node , right = 2 :

- because right < size , At this time, compare the time interval between the left child node and the right child node , here 3 < 7 , therefore c = queue[child] ;
- Compare key Whether the time interval of is less than c Time interval of , It's not enough here , Carry on , Index to k The node of is set to c, And then k Set to child;

- because half = 3 ,k = 1 , Continue the loop , The index changes to :

- At this time, after the above judgment , take k The value of is 3, The final result is as follows :

- Last , If in finishPoll Call in method , Will index as 0 The index of the node of is set to -1, Indicates that the node has been deleted , also size Also reduced 1, The final result is as follows :
 so ,siftdown Methods are not ordered after execution , But it can be found that , The next execution time of the child node must be greater than that of the parent node , Each time, the node with the lowest next execution time among the left and right child nodes will be selected , So we can still guarantee that take and poll It is orderly to go out in time .
so ,siftdown Methods are not ordered after execution , But it can be found that , The next execution time of the child node must be greater than that of the parent node , Each time, the node with the lowest next execution time among the left and right child nodes will be selected , So we can still guarantee that take and poll It is orderly to go out in time .
poll()
Get the queue header element immediately , When the queue header task is null, Or the task delay time is not up , Indicates that the task cannot be returned , So go straight back null. Otherwise, call finishPoll Method , Removes the queue header element and returns .
public RunnableScheduledFuture<?> poll() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> first = queue[0];
// The queue header task is null, Or the task delay time is not up , All back to null
if (first == null || first.getDelay(NANOSECONDS) > 0)
return null;
else
// Removes the queue header element
return finishPoll(first);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
Timeout waits to get the queue header element , And take Method comparison , Consider the timeout time you set , If the timeout is up , No useful tasks have been obtained , So return null. The other with take Same logic in the method .
public RunnableScheduledFuture<?> poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
for (;;) {
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> first = queue[0];
// If there is no task .
if (first == null) {
// The timeout has expired , So just go back null
if (nanos <= 0)
return null;
else
// Otherwise let the threads in available Conditional waiting nanos Time
nanos = available.awaitNanos(nanos);
} else {
// Gets the remaining latency of the task
long delay = first.getDelay(NANOSECONDS);
// If the delay time is up , Return to this task , Used to perform .
if (delay <= 0)
return finishPoll(first);
// If the timeout is up , So just go back null
if (nanos <= 0)
return null;
// take first Set to null, While the thread is waiting , Don't hold first References to
first = null; // don't retain ref while waiting
// If the timeout time is less than the task's remaining delay time , Then you might not get the task .
// This is where the thread waits for a timeout nanos
if (nanos < delay || leader != null)
nanos = available.awaitNanos(nanos);
else {
Thread thisThread = Thread.currentThread();
leader = thisThread;
try {
// When the delay time for the task is up , Can automatically wake up over time .
long timeLeft = available.awaitNanos(delay);
// Calculate the remaining timeout time
nanos -= delay - timeLeft;
} finally {
if (leader == thisThread)
leader = null;
}
}
}
}
} finally {
if (leader == null && queue[0] != null)
// Wakes up a thread waiting for a task
available.signal();
lock.unlock();
}
}
remove Deletes the specified element
Deleting a specified element is usually used to cancel a task , The task is still in the blocking queue , You need to delete it . When the deleted element is not a heap tail element , Heap processing is required .
public boolean remove(Object x) {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
int i = indexOf(x);
if (i < 0)
return false;
// maintain heapIndex
setIndex(queue[i], -1);
int s = --size;
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> replacement = queue[s];
queue[s] = null;
if (s != i) {
// It is not the tail of the heap element that is deleted , It needs to be piled up
// First heap it down
siftDown(i, replacement);
if (queue[i] == replacement)
// If it is piled down ,i The element of position is still replacement, Note 4. There is no need to stack down ,
// You need to heap up
siftUp(i, replacement);
}
return true;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
Suppose the initial heap structure is as follows :[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-SqhXOn3E-1653913362599)(data:image/gif;base64,iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAAAEAAAABCAYAAAAfFcSJAAAADUlEQVQImWNgYGBgAAAABQABh6FO1AAAAABJRU5ErkJggg==)] In this case, delete 8 The node of , Then at this time k = 1,key For the last node : At this time, through the above to siftDown Method analysis ,siftDown The result of method execution is as follows :
At this time, through the above to siftDown Method analysis ,siftDown The result of method execution is as follows : At this time, you will find , The value of the last node is smaller than that of the parent node , So here we need to execute once siftUp Method to ensure that the next execution time of the child node is greater than that of the parent node , So the final result is as follows :
At this time, you will find , The value of the last node is smaller than that of the parent node , So here we need to execute once siftUp Method to ensure that the next execution time of the child node is greater than that of the parent node , So the final result is as follows :
summary
Use priority queues DelayedWorkQueue, Ensure that tasks are added to the queue , Sort by task delay time , Tasks with less latency are captured first .
- DelayedWorkQueue The data structure of is implemented based on heap ;
- DelayedWorkQueue Use array to realize heap , Root node out of team , Replace with the last leaf node , Then push it down until the heap establishment condition is met ; Finally, the leaf nodes join the team , Then push it upward until the heap establishment conditions are met ;
- DelayedWorkQueue When the added elements are full, the original capacity will be automatically expanded 1/2, That is, it will never block , The maximum capacity expansion can reach Integer.MAX_VALUE, So there are at most... In the thread pool corePoolSize Worker threads are running ;
- DelayedWorkQueue Consumption elements take, At the top of the heap, the elements are empty and delay >0 when , Block waiting ;
- DelayedWorkQueue It is a production that will never be blocked , Consumption can block the producer consumer model ;
- DelayedWorkQueue There is one leader Thread variables , yes Leader-Follower A variation of the pattern . When one take The thread becomes leader Thread time , Just wait for the next delay , instead of leader Other threads take Threads need to wait leader When the thread is out of the queue, it wakes up others take Threads .
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
![[untitled] test](/img/6c/df2ebb3e39d1e47b8dd74cfdddbb06.gif)
[untitled] test
![[JVM] memory model](/img/01/4a9ab79e340f19c5f6cf682577bf2a.jpg)
[JVM] memory model
![[network counting] 1.4 network delay, packet loss and throughput](/img/a8/74a1b44ce4d8b0b1a85043a091a91d.jpg)
[network counting] 1.4 network delay, packet loss and throughput

452. detonate the balloon with the minimum number of arrows
![[MVC&Core]ASP. Introduction to net core MVC view value transfer](/img/c2/3e69cda2fed396505b5aa5888b9e5f.png)
[MVC&Core]ASP. Introduction to net core MVC view value transfer

安全培训管理办法

How to install mathtype6.9 and related problem solutions in office2016 (word2016)

Things about Bluetooth development (1) -- starting with packet capturing data

非重叠矩形中的随机点
Bluetooth development (4) -- about flow control
随机推荐
Bluetooth development (2) -- initialization
微信小程序实现OCR扫描识别
What are absolute and relative paths, and what are their advantages and disadvantages?
How about the CSC account of qiniu business school? Is it safe?
【JVM】类加载机制
测试下吧先
Bluetooth development (8) -- avdtp connection process
【无标题】4555
Chapter I General introduction - Fundamentals of accounting
Database table structure
网络工程师必修课防火墙安全区域及安全策略基础操作
圖的最短路徑問題 詳細分解版
Njupt Nanyou Discrete Mathematics_ Experiment 1
Excel单元格
[database] types of NoSQL database
数的奥秘之幂数与完全平方数
[go language learning] - Concurrent Programming
【JVM】线程
The mystery of number idempotent and perfect square
Bluetooth development (4) -- about flow control