当前位置:网站首页>PWN entry (3) heap
PWN entry (3) heap
2022-07-23 16:58:00 【Day-3】
1 The heap manager
1.1 Heap overview
What is a heap ?
Is a continuous linear region of the virtual address space
Provide dynamically allocated memory , Allow programs to request memory of unknown size
Between the user and the operating system , As the middleman of dynamic memory management
Respond to the user's request for memory , Request memory from the operating system , And then return it to the user program
Manage the memory released by users , optimum Return to the operating system

Various heap managers
The heap manager is not implemented by the operating system , But by the libc.so.6 Link library implementation . Encapsulates some system calls , While providing users with a convenient dynamic memory allocation interface , Strive to efficiently manage the memory requested by the system call .dlmalloc – General purpose allocator
ptmalloc2 – glibc ( On the blackboard )
jemalloc – FreeBSD and Firefox
tcmalloc – Google libumem – Solaris

1.2 arena

1.3 chunk
The unit of memory requested by the user , It is also the basic unit of memory managed by the heap manager malloc() The returned pointer points to a chunk The data area of .
chunk The concrete realization of
struct malloc_chunk {
INTERNAL_SIZE_T prev_size; /* Size of previous chunk (if free). */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T size; /* Size in bytes, including overhead. */
struct malloc_chunk* fd; /* double links -- used only if free. */
struct malloc_chunk* bk;
/* Only used for large blocks: pointer to next larger size. */
struct malloc_chunk* fd_nextsize; /* double links -- used only if free. */
struct malloc_chunk* bk_nextsize;
};
chunk The classification of
By status
- malloced
- free
By size - fast
- small
- targe
- tcache
By specific function - top chunk
- last remainder chunk
malloced chunk
Have been assigned and filled in the corresponding data chunk
free chunk
Released malloced chunk Become free chunk
top chunk
arena Memory area that has never been used in 
last remainder chunk
malloc Segmented original chunk And the rest of it 
Chunk Microstructure of 
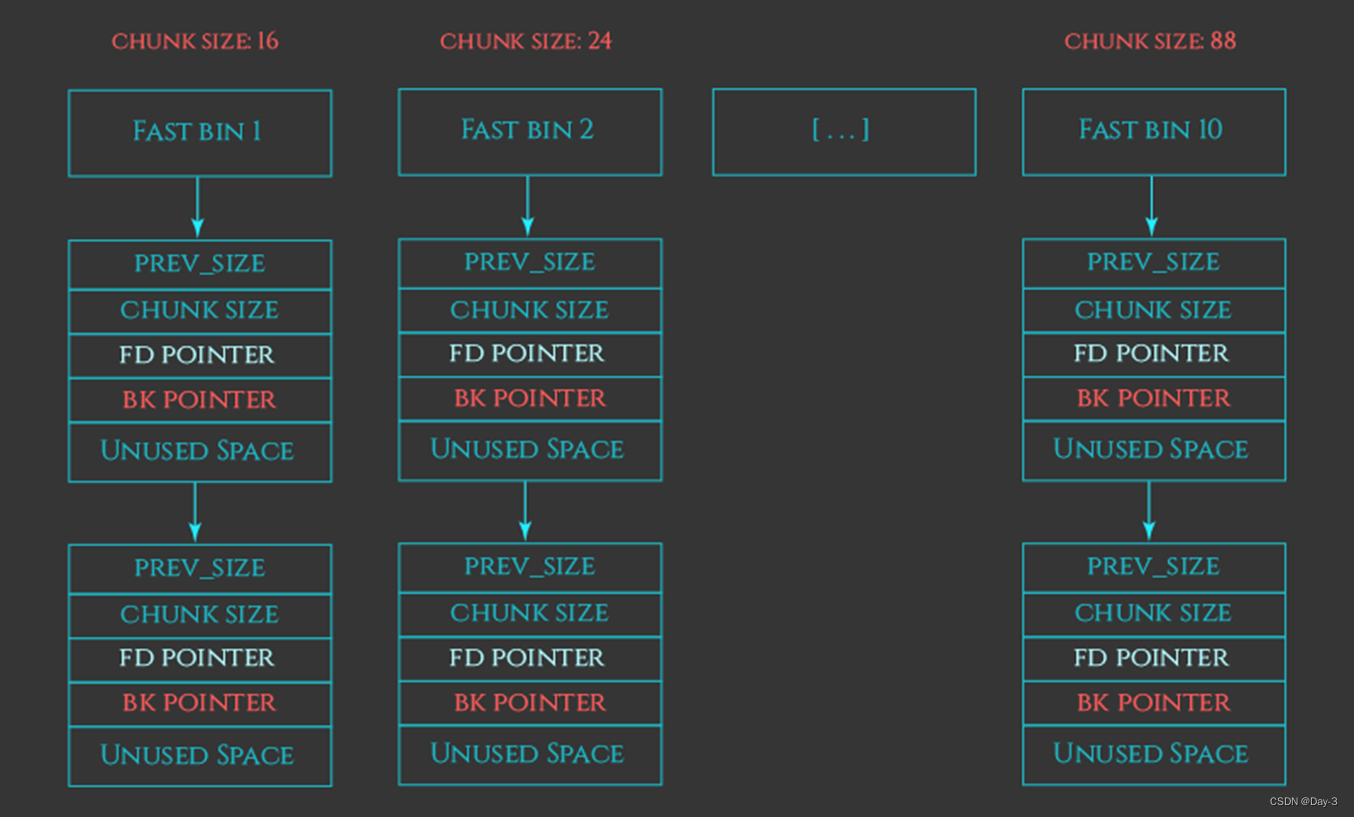
1.4 bin
management arena Free time chunk Structure , Exist as an array , The array elements are of corresponding size chunk The head of a linked list , Exist in arena Of malloc_state in
- unsorted bin
- fast bins
- small bins
- large bins
- (tcache)
prev_size
If the previous one is physically adjacent chunk yes free chunk, Indicates its size . Otherwise, it is used to store the previous chunk The data of 
size
Occupy a word long low 3bits Later address , Used to indicate the present chunk Size ( Whole chunk Size , Include chunk head )

A flag
NON_MAIN_ARENA, Record the current chunk Whether it does not belong to the main thread ,1 Does not belong to ,0 Indicates belonging to .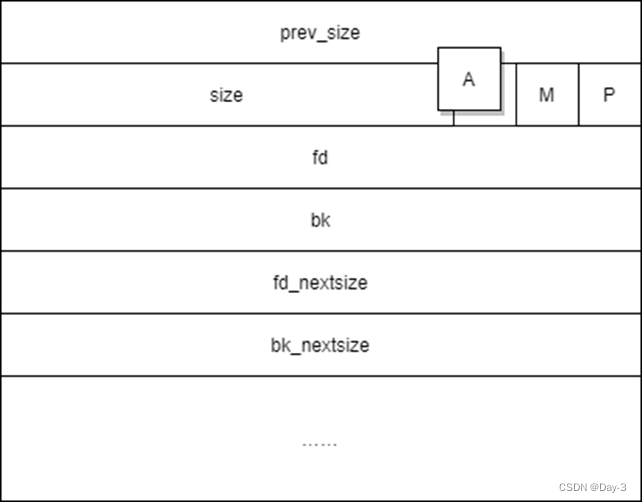
M flag
IS_MAPPED, Record the current chunk Is it by mmap The distribution of .
P flag
PREV_INUSE, Record the previous chunk Whether the block is allocated . Generally speaking , Of the first allocated memory block in the heap size Field P Bits will be set to 1, In order to prevent access to the previous illegal memory . When one chunk Of size Of P Position as 0 when , We can get through prev_size Field to get the previous chunk Size and address . It's also convenient for idle chunk A merger between .
fd pointer
stay bin Point to the next ( Non physical adjacency ) Idle chunk.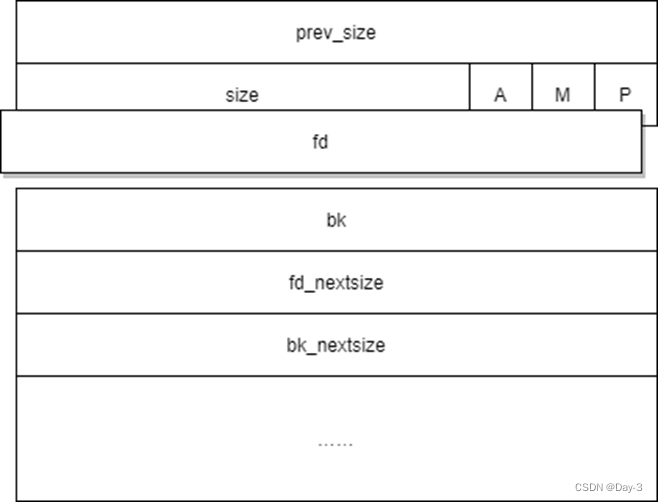
bk pointer
stay bin Middle points to the previous ( Non physical adjacency ) Idle chunk

fd_nextsize
stay large bin The middle finger moves forward with the current chunk The first free block with different sizes , It doesn't contain bin The head pointer of

bk_nextsize
stay large bin The middle finger is backward and current chunk The first free block with different sizes , It doesn't contain bin The head pointer of

Generally free large chunk stay fd In the traversal order of , Arrange in order from big to small . This can avoid looking for the right chunk Go through it one by one
main arena Of malloc_state Not at all heap segment Part of , It's a global variable , Stored in libc.so Data section of
struct malloc_state {
/* Serialize access. */
__libc_lock_define(, mutex); /* Flags (formerly in max_fast). */
int flags; /* Fastbins */
mfastbinptr fastbinsY[ NFASTBINS ]; /* Base of the topmost chunk -- not otherwise kept in a bin */
mchunkptr top; /* The remainder from the most recent split of a small request */
mchunkptr last_remainder; /* Normal bins packed as described above */
mchunkptr bins[ NBINS * 2 - 2 ]; /* Bitmap of bins, help to speed up the process of determinating if a given bin is definitely empty.*/
unsigned int binmap[ BINMAPSIZE ]; /* Linked list, points to the next arena */
struct malloc_state *next; /* Linked list for free arenas. Access to this field is serialized by free_list_lock in arena.c. */
struct malloc_state *next_free; /* Number of threads attached to this arena. 0 if the arena is on the free list. Access to this field is serialized by free_list_lock in arena.c. */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T attached_threads; /* Memory allocated from the system in this arena. */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T system_mem;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T max_system_mem;
};







2 Heap allocation policy
malloc
- It depends on the size of the memory block requested by the user and the corresponding size chunk The usual frequency of use (fastbin chunk, small chunk, large chunk), Different allocation methods are implemented in turn .
- It checks different from small to large bin Is there a corresponding free block in the memory that can meet the user's request .
- When all free chunk Can't be satisfied , It will consider top chunk.
- When top chunk Can't be satisfied , The heap allocator will apply for memory blocks .
free
- It will not be used by users for the time being chunk Recycle to the heap manager , It will be returned to the operating system when appropriate .
- It is based on chunk Size comes first try to put free chunk Chain in tcache Or is it fast bin. If you are not satisfied, you will be linked usorted bin in .
- When conditions are met free Ergodic function usorted bin And physically adjacent free chunk Merge , Put the corresponding size chunk Sort into small bin or large bin in .
- except tcache chunk And fast bin chunk, Other chunk stay free Time will be physically adjacent to it free chunk Merge
边栏推荐
- 移动、电信、联通:5G To B的花式解法
- UiPath Studio Enterprise 22.4 Crack
- 【Web漏洞探索】SQL注入漏洞
- Scale Match for Tiny Person Detection
- go run,go build,go install有什么不同
- What are the principal guaranteed financial products with an annual interest rate of about 6%?
- Tan Zhangxi, director of risc-v Foundation: risc-v has gradually expanded from the edge to the center
- General paging function
- 国内生产总值(GDP)数据可视化
- C语言基础篇 —— 2-5 指针与函数知识点
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Eureka笔记
启牛商学院上面开户安全不
General paging function
微机原理与技术接口随堂练习
面试官:生成订单30分钟未支付,则自动取消,该怎么实现?
Object.defineProperty方法、数据代理
C语言基础篇 —— 2-6 指针、数组与sizeof运算符
学习笔记7--交通环境行为预测
tensorflow一层神经网络训练手写体数字识别
学习MySQL这一篇就够了
Bag of Tricks for Image Classification with Convolutional Neural Networks(卷积神经网络在图像分类中的技巧)
Pinia (pineapple)
Solve data functions should return an object (property "visible" must be accessed with "$data.visible")
Leetcode-67. binary sum
uni-app进阶之认证【day12】
Leetcode-168.excel table column name
anchor free yolov1
UPC 2022暑期个人训练赛第12场(B 组合数)
Less than 10 days before the PMP Exam on July 30, what should be done?
微机原理与技术接口笔记