当前位置:网站首页>Summary of APP test interview questions, which must be taken in the interview
Summary of APP test interview questions, which must be taken in the interview
2022-06-12 09:13:00 【Software testing Lao Mo】
Catalog
1、 Please introduce ,APP Testing process ?
2、APP What test resources need to be prepared in advance for testing ?
3、APP Testing and Web Test differences ?
4.、 be relative to Wed project ,APP There are special tests
4、Android Mobile phones and IOS mobile phone , What's the difference between systems ?
5、IOS and Android Of APP What's the difference between tests ?
6、 Introduce a APP Caught tools ?
8、 frequently-used adb What are the orders ?
9、adb The three components refer to ?
1、 Introduce to you Android Four components ?
3、 Please introduce ,Android SDK Several tools included in ?
4、 What you know APP Testing tools ?
5、 Introduce cold start 、 Warm start 、 Hot start 、 The first screen starts ?
6、 Talk about the understanding of cold start ?
One 、 The basic chapter
1、 Please introduce ,APP Testing process ?
APP Test process and web The test process is similar , It is divided into the following seven stages :
1. Write the test plan according to the requirements specification ;
2. Develop test plan , Mainly testing tasks 、 Allocation of testers and test time ;
3. Test preparation , Including setting up a test environment , Prepare test data , Determine the test method ;
4. Design and writing of test cases , Review and supplement use cases ;
5. Perform the smoke test first when performing the test , Then test the main function flow , Including a single functional module of the client , And business logic function interaction , regression testing ;
6. Submit test results , Including test cases , test plan ;
7. Routine maintenance test ;
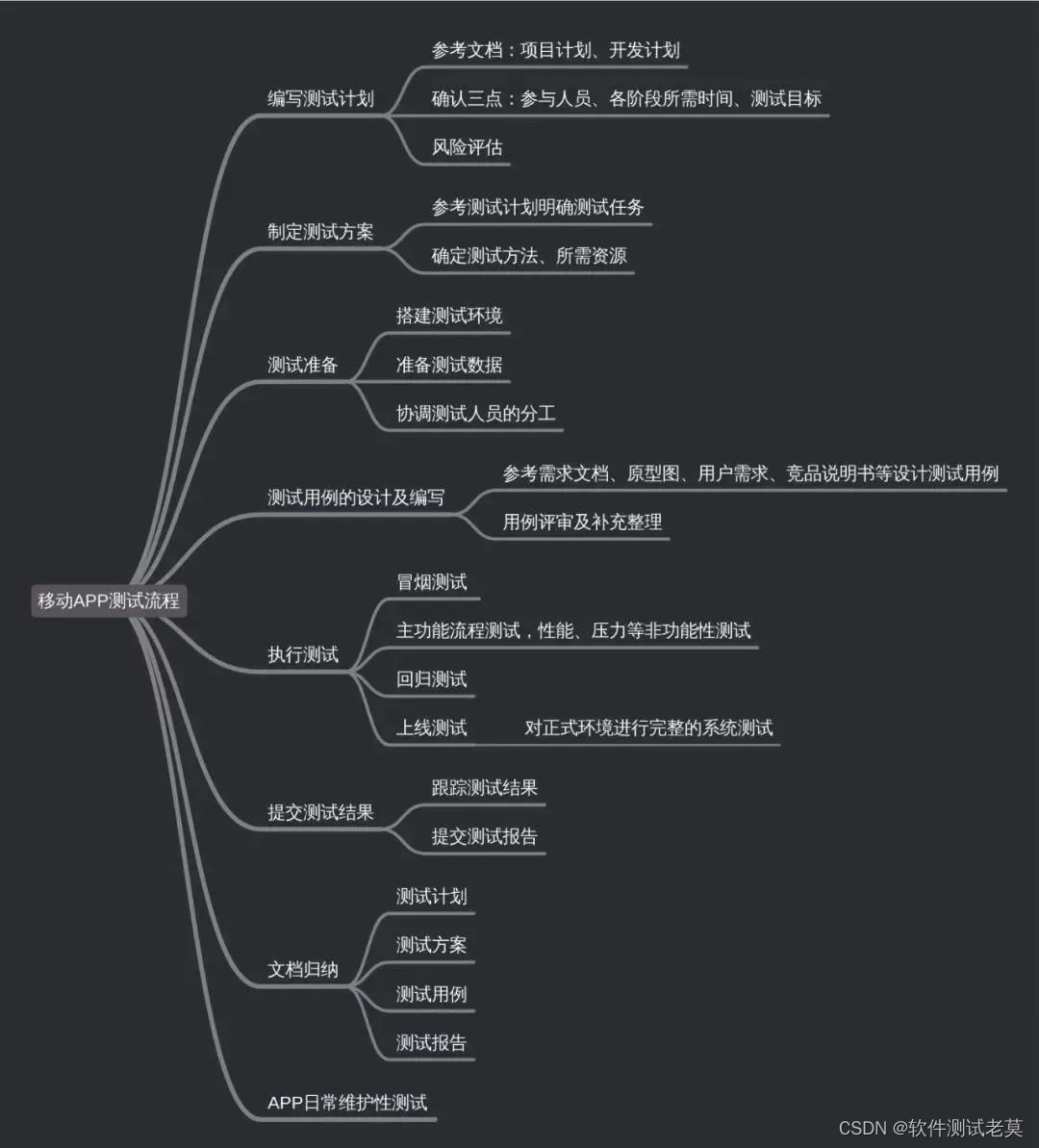
APP The test cycle can determine the test time according to the development cycle of the project , The general test time is two or three weeks , According to the project situation and version quality, the test time can be shortened or extended .
2、APP What test resources need to be prepared in advance for testing ?
Specific test resources to be prepared , According to the actual project , We can start from the following aspects :
1.IOS equipment 、Android equipment ( Select the mainstream mobile phone products on the market );
2. Alipay / Items paid by UnionPay , You need to apply for Alipay in advance / UnionPay account and so on ;
3. There is a topic of second kill , We need to plan a second kill schedule ;
4. Items with coupons , Coupon data needs to be added ;
3、APP Testing and Web Test differences ?
Just from the level of functional testing ,APP test 、web There is no difference between process and functional testing .
The same thing :
1. The same test case design method ;
2. The same test method : Will be checked according to the prototype drawing or effect drawing UI;
3. Test the speed of page loading and page flipping 、 Login duration 、 Memory overflow, etc ;
4. Test the stability of the application system ;
Difference :
1. In terms of system structure
- web project ,b/s framework , browser-based ;web Test as long as the server side is updated , The client will update synchronously .
- app project ,c/s Structural , There must be a client ;app Modified the server , Then all core versions of client users need to be regression tested once .
2. Performance aspect
- web project Need to monitor response time 、CPU、Memory;
- app project Except for monitoring response time 、CPU、Memory Outside , It needs to be monitored Traffic 、 Electric quantity, etc ;
3. Compatibility
- web project : browser ( firefox 、 Google 、IE etc. ); operating system (Windows7、Windows10、Linux etc. ).
- app project : Equipment system :iOS(ipad、iphone)、Android( samsung 、 Huawei 、 Lenovo, etc ) 、Windows(Win7、Win8)、OSX(Mac); Mobile devices can be based on Mobile phone model 、 The resolution of the 、 Different screen sizes .
4.、 be relative to Wed project ,APP There are special tests
1) Interference test : interrupt , Incoming call , SMS , To turn it off , Restart, etc. .
2) Weak network test ( simulation 2g、3g、4g、5g,wifi Network status and packet loss ); Network switching test ( Disconnect the network and reconnect 、3g Switch to 4g、5g/wifi etc. ).
3) install 、 to update 、 uninstall , interrupt 、 Front and rear station switching .
- install : Consider interruptions during installation 、 Weak net 、 Delete installation files after installation , New installation 、 upgrade installation 、 Installation of third-party tools, etc ;
- uninstall : Unloading of third-party tools should be considered 、 Direct unloading , Delete after loading app Related documents ;
- to update : Sub forced update 、 Non mandatory update 、 Incremental package update 、 Breakpoint continuation 、 Update in weak network state ;
- interrupt : Incoming call interrupted 、 SMS interrupt 、 The alarm clock is broken 、 The phone is locked 、 The cell phone is powered off 、 Cell phone crash ;
4) interface : About mobile terminal test , Pay attention to gestures , Horizontal and vertical screen switching , multi-touch , Front and rear station switching .
5) Security testing : Whether the installation package can decompile the code 、 Is the installation package signed 、 permissions , For example, visit the address book .
6) Boundary test : Less memory available 、 No, SD card / double SD card 、 Flight Mode 、 The system time is wrong 、 Third party reliance (QQ、 Wechat login ) etc. .
7) Authority test : Set up a App Can I get this permission , For example, can I access the address book 、 Photo album 、 Camera, etc .
5. Testing tools
- Automation tools :APP In general use Appium; Web In general use Selenium;
- Performance testing tools :APP In general use Monkey、 JMeter; Web In general use LR、JMeter;
4、Android Mobile phones and IOS mobile phone , What's the difference between systems ?
1. The operation mechanism of the two is different :IOS The sandbox mechanism is adopted , Android uses a virtual machine operating mechanism .
IOS Sandbox operation mechanism :
- Each program has its own virtual address space . therefore , No access between programs .
- By default, only the last running data of the application will be , Recorded in the RAM Inside .
Android Virtual machine operation mechanism :
- All applications are running in virtual machines , The user interface is actually passed by the virtual machine , And through the virtual machine ,Android Any program can easily access other program files .
- be-all Android All applications run on RAM Inside , So you will find that sometimes Android It started to get a little stuck .
2. They have different backstage systems :IOS No third-party program can run in the background ; Any program in Android can run in the background , Don't shut down until there's no memory .
3.IOS For UI The command has the highest authority , Data processing instructions have the highest authority in Android .
5、IOS and Android Of APP What's the difference between tests ?
1. Physical buttons :Android Long press home Key call out application list and switch application , Then slide right to terminate the application ;iOS All return to the previous level , It can only be realized by page function .
2. Multi resolution testing :Android End 20 Varied ;IOS Less .
3. Mobile operating system :Android More ,IOS Less and cannot be degraded , You can only upgrade one way ; new IOS The repository in the system is not fully compatible with the lower version of IOS Applications in the system , Low version IOS The application in the system calls the new resource library , It's a direct cause of flashback .
4. Operation habit :Android,Back Whether the key is overridden , Test click Back Is the feedback after the key correct ; Application data is moved from memory to SD After the card can be normal operation, etc .
5.push test :Android Click on home key , When the program runs in the background , At this time, we receive push, Click to wake up the app , Whether it can jump correctly at this time ;IOS Click on home Key to close the program and screen lock screen situation ( Red dot display ).
6. Install uninstall test :Android It can be downloaded through the mobile phone's own application market or a third-party mobile assistant , There are many platforms, tools and channels to download and install ;IOS There are mainly app store,iTunes and testflight download .
7. Upgrade test : The necessary conditions that can be upgraded : The old and new versions have the same signature ; The old and new versions have the same package name ; There is an identifier to distinguish the old from the new ( Such as version number ).
8. Method of payment : For some with internal purchase function APP,Android Directly call the third-party payment channel to complete the payment ;IOS You need to be in APP store Binding payment method in , And then through APP store To complete the payment operation .
9. Message push mechanism :Android Use a third party or self built platform to push messages ;IOS The news push channel is officially provided by Apple .
6、 Introduce a APP Caught tools ?
It's usually used Fiddler, It's mainly used to do app Use of bag grabbing , First in Fiddler Configure the client , Port set to 8888; Then set up a proxy on the phone , You can grab the bag , It mainly depends on the value returned by the server 、 You can also modify the incoming parameters 、 Outgoing parameters 、 Analog network delay , Construct different scenes .
7、APP How to capture logs ?
- have access to adb command :adb logcat | find "com.sankuai.meituan" >d:\test.txt
- It can also be used. ddms Grab , Mobile phone connected to computer , open ddms Tools ;
- Or in Android Studio Development tools , open DDMS;
8、 frequently-used adb What are the orders ?
1. Check the help manual to list all options, descriptions and subcommands :
adb help
2. Get device list and device status :
adb devices
3. Install application :adb install route \xx.apk, Install application ;adb install -r reinstall .
adb install
adb install -r
4. Get the status of the device , The state of the device is device , offline , unknown3 Kind of , among device: The device is connected properly ,offline: Connection exception , Device not responding ,unknown: No device connected .
adb get-state
5. Uninstall app :adb uninstall < Package name >, The following parameter is the package name of the application , The difference in apk file name .
adb uninstall
6. take Android Copy files or folders on your device to your computer :adb pull < Remote path > < The local path >, Like copying Sdcard Under the pull.txt File to D disc :adb pull sdcard/pull.txt d:\, rename :adb pull sdcard/pull.txt d:\rename.txt.
adb pull
7. Push local files to Android equipment :adb push < The local path > < Remote path >, Such as push D On the plate ITester.txt to Sdcard:adb push d:\ITester.txt sdcard/ ( Be careful sdcard The slash at the back can't be less ).
adb push
8. End and start adb service :adb kill-server /adb start-server , end adb service / start-up adb service , Usually two commands are used together , Use when the equipment is abnormal kill-server, function start-server Restart the service .
adb kill-server
adb start-server
9. Print and clear system logs :adb logcat , Print Android The system log of ;adb logcat -c, Clear log .
adb logcat
adb logcat -c
10. Find the package name / Activity name
adb logcat | findstr START
9、adb The three components refer to ?
ADB As a client / Command line tools for server architecture , Mainly by 3 Component composition .
- adb clent( client ): You can use it to Android Application for installation 、 Unloading and debugging .
- adb service( The server ): Manage clients to Android On the device abd Background process connection , Responsible for managing the client and damon communicate .
- adb daemon( Daemon ): Running on the Android On the device adb Background processes .
Two 、 Advanced
1、 Introduce to you Android Four components ?
Android Four basic components :Activity、BroadcastReceiver Radio receiver 、ContentProvider content provider 、Service service .
- Activity: In the application , One Activity It's like a cell phone screen , It's a component that can contain a user interface , It is mainly used to interact with users . An application can contain many activities , For example, the click of an event , It usually triggers a new Activity.
- BroadcastReceiver Radio receiver : Applications can use it to filter external events, only those of interest ( When the phone calls in , Or when the data network is available ) To receive and respond to . The broadcast receiver has no user interface . However , They can start a activity or serice To respond to the messages they receive , Or use NotificationManager To inform users of . Notifications can be used in many ways to attract users' attention ── Flash the backlight 、 shock 、 Play sound, etc . Generally speaking, it is to put a persistent icon on the status bar , Users can open it and get messages .
- ContentProvider content provider : Content providers are mainly used to share data between different applications , It provides a complete set of mechanisms , Allow one program to access data in another program , At the same time, it can ensure the security of the accessed data . Content providers are needed only when data needs to be shared across multiple applications . for example : Address book data is used by multiple applications , And must be stored in a content provider . Its benefits : Unified data access .
- Service service : yes Android In the background of the implementation of the program running solutions , It's perfect for tasks that don't need to interact with users and run for a long time ( On the phone , In the background QQ). The operation of the service does not depend on any user interface , Even if the program is switched to the background , Or the user opens another application , The service is still up and running , But services don't run in a separate process , It depends on the application process in which the service was created . When an application process is killed , All services that depend on the process will also stop running ( Listening to music , Then exit the music program ).
2、Activity Life cycle ?
Life cycle refers to the various states experienced by an activity from the beginning to the end , The transition from one state to another , From nothing to nothing ,Activity There are essentially four states :
- function (Active/Running):Activity Active , here Activity At the top of the stack , It's the visible state , Can interact with users .
- Pause (Paused): When Activity When you lose focus , Or by a new non full screen Activity, Or by a transparent Activity At the top of the stack ,Activity It's converted into Paused state . It's not going to be destroyed at the moment , Just lost the ability to interact with users , All of its state information and its member variables are still in use , Only when the system memory is tight , Could be recycled by the system .
- stop it (Stopped): When Activity When completely covered by the system , Covered Activity Will enter Stopped state , It's no longer visible , But the resources have not been withdrawn .
- System recovery (Killed): When Activity Recycled by the system ,Activity It's in Killed state .
If an activity is in a stopped or suspended state , When the system is short of memory, it will end (finish) Or kill (kill). In this abnormal situation , The system will call... Before killing or ending onSaveInstance() Method to save information , meanwhile , When Activity When moved to the front desk , Restart the Activity And call onRestoreInstance() Method to load the reserved information , To maintain the original state .
Between the four usual states above , There are other life cycles to transition between different states , Used to transition between different states .
3、 Please introduce ,Android SDK Several tools included in ?
There are several tools :
- ddms:Dalvik Debug Monitor Service, yes Android In the development environment Dalvik[ virtual machine ] Debug monitoring service .
- monkey:Android A command line tool in , It can run in a simulator or in a real device . It sends a pseudo-random stream of user events to the system ( Such as key input 、 Touch screen input 、 Gesture input, etc ), Implement stress testing on the developing application .
- uiautomator:UIAutomator yes Eclipse Bring your own for UI Automated test tool , Can simulate APP Click on 、 slide 、 Input text and so on .
- monitor: Same as uiautomator
- adb:ADB The full name is Android Debug Bridge, Is to play the role of debugging bridge . adopt ADB We can do it in Eclipse The Chinese side has passed DDMS To debug Android Program , Namely debug Tools .
4、 What you know APP Testing tools ?
frequently-used APP The test tools are as follows ,, View the corresponding tool address .APP Automated test tool :
- Appium
- Airtest
- uiautomator2(python)
APP Stability testing tools :
- Monkey
- MonkeyRunner
- Maxim
- UICrawler
APP Performance testing tools :
- GT
- Perfdog
- SoloPi
APP Weak network test & Caught tools :
- QNET
- Fiddler
- Charles
APP Compatibility testing tools :
- TestIn
- Tencent excellent test
- Baidu MTC
- Ali MQC
APP Safety test tools :
- OWASP ZAP
- Drozer
- MobSF
- QARK
5、 Introduce cold start 、 Warm start 、 Hot start 、 The first screen starts ?
APP Multiple events occur during startup , The tester needs to know if there is a problem in the whole process , We need to know which link has the problem :
- Cold start : When the process does not exist , The process from process creation to interface display ;
- Warm start : Some resources already exist , The process exists , It consumes more resources than hot start . When the user exits the application , The process will still exist , Compared with cold start, warm start only has less process creation ;
- Hot start : Most of the resources are in , Just switching between applications ;
- The first screen starts : The first screen is loaded completely ;
standard :
- Cold start : need 5 Seconds or more ;
- Warm start : need 2 Seconds or more ;
- Hot start : need 1.5 Seconds or more ;
The whole startup process can be used adb Tools for analysis , utilize adb logcat Get the boot data , Or video recording , Use ffmpeg Framing analysis .
- adb logcat
Define a variable first , This variable is used to fill in the package name .
- package=com.xueqiu.android
Clear cached data :
- adb shell pm clear $package
Stop the process :
- adb shell am force-stop $package
Through the above command, the cold start environment is ready , Start below app And get the data . start-up App
- adb shell am start -S -W $package/.view.WelcomeActivityAlias
- -S It means to stop the application process before starting
- -W Is to wait for the corresponding activity Start up
get data :
- bash adb logcat |grep -i displayed
The time obtained is as follows :

6、 Talk about the understanding of cold start ?
Application startup can be divided into cold startup , Hot start and warm start , And start the slowest 、 The longest time-consuming is cold start .
At the beginning of cold start , The system will execute three tasks in turn to start APP:
- Loading and starting applications ;
- APP After starting , Immediately create a blank startup Window;
- establish APP The process of ;
After the implementation of these three tasks , The system creates the application process , Then the application process will perform the next step :
- establish APP object ;
- Start a main thread ;
- To create a startup page Activity;
- load View;
- Layout view To screen ;
- Perform the initial drawing to display the view ;
After the application process completes the initial drawing , The system process uses the Activity To replace the currently displayed blank Window, At this moment, users can use App 了 .

Thank everyone who reads my article carefully !!!
If you can use the following information, you can take it away directly :
1、 Self study development or test the necessary complete project source code and environment
2、 Test all templates in the work ( test plan 、 The test case 、 Test report, etc )
3、 Classic interview questions for software testing
4、Python/Java Automation test practice .pdf
5、Jmeter/postman Interface test full set of video acquisition
I personally sorted out some technical materials I have sorted out in my software testing career in recent years , contain : e-book , Resume module , Various work templates , Interview treasure , Self study projects, etc .
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

Distributed task scheduling
APP测试面试题汇总,面试必考一定要看

2022 low voltage electrician retraining question bank and online simulation examination

数据库不知道哪里出问题

90%以上软件公司都会问的软件测试面试题赶紧来背吧

MFS详解(四)——MFS管理服务器安装与配置
Use NVM to dynamically adjust the nodejs version to solve the problem that the project cannot be run and packaged because the node version is too high or too low

Description of string

Minimum transfer times

Chapter IV - first procedure
随机推荐
Cookies and sessions
2024. maximum difficulty of the exam - sliding window
Permutation (greedy strategy)
Building a cluster: and replacing with error
2022 simulated examination platform operation of high voltage electrician work license question bank
Codecraft-22 and codeforces round 795 (Div. 2)
sql中的Exists用法
自动化测试学习路线,快来学吧
测试计划应该怎么写?一个思路教会你
Bash tutorial
2022 melting welding and thermal cutting test questions and answers
Minimum transfer times
Description of string
Jenkins pipeline syntax
解压缩zip文件的工具类
Xshell startup encountered "unable to continue code execution because mfc110.dll cannot be found"
Node sample background setup
Occupied occupied occupied occupied occupied
Leetcode 336 palindrome pair (palindrome string + hash)
Permission modifiers and code blocks



 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzU1ODc2NzAxMw==&mid=2247483738&idx=1&sn=32e1bfb005ad0fdf609e86186fb5eaf8&chksm=fc20cf90cb5746865ecc97a3a3c4ef4a4eec8e26c16358f743194e548469c90af1a2dc6c0078#rd
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzU1ODc2NzAxMw==&mid=2247483738&idx=1&sn=32e1bfb005ad0fdf609e86186fb5eaf8&chksm=fc20cf90cb5746865ecc97a3a3c4ef4a4eec8e26c16358f743194e548469c90af1a2dc6c0078#rd