当前位置:网站首页>002_ Kubernetes installation configuration
002_ Kubernetes installation configuration
2022-07-24 03:51:00 【Adventures of procedural ape】
List of articles
1. k8s Environmental platform planning
1.1 single master colony
Single master node , Then manage multiple node node

1.2 many master colony
Multiple master node , Manage multiple node node , At the same time, there is a load balancing process in the middle

2. Configuration requirements
| Environmental Science | node | requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Test environment | master | 2 nucleus 4G 20G |
| Test environment | node | 4 nucleus 8G 40G |
| Production environment | master | 8 nucleus 16G 100G |
| Production environment | node | 16 nucleus 64G 200G |
about Kubernetes Beginners are recommended to purchase the following configurations from Alibaba cloud or Tencent cloud :( You can also use your own virtual machine 、 Private cloud is the most accessible Linux Environmental Science )
- At least 2 platform 2 nucleus 4G Server for
- Cent OS 7.6 / 7.7 / 7.8
3. Kubernetes There are two main ways to cluster
3.1 kubeadm
kubeadm It's a K8S Deployment tools , Provide kubeadm init and kubeadm join, For rapid deployment Kubernetes colony
3.2 Binary package
from github Download the distribution's binary package , Manually deploy each component , form Kubernetes colony .
Kubeadm Lower deployment threshold , But it's a lot of detail , It's hard to troubleshoot problems . If you want to be more controllable , Binary package deployment is recommended Kubernetes colony , Although manual deployment is troublesome , You can learn a lot about how it works , It's also good for later maintenance .
4. kubeadm、 kubectl 、kubelet difference
kubeadm
kubeadm It's an official community launch for rapid deployment kubernetes Clustering tools .
This tool can complete one by two instructions kubernetes Cluster deployment :# Create a Master node kubeadm init # Will a Node Nodes join the current cluster kubeadm join <Master Node IP And port >kubectl
kubectl yes Kubernetes Command line tools for clustering , adopt kubectl Be able to manage the cluster itself , And can install and deploy container applications on the clusterkubelet
Kubelet:master Send to node Nodes represent , Manage native containers
- Agents running on each node in a cluster , It ensures that the container is running in Pod in
- Responsible for maintaining the life cycle of the container , Also responsible for Volume(CSI) and The Internet (CNI) Management of
5. Use kubeadm Way to build K8s The cluster is mainly divided into the following steps
- Prepare three virtual machines , Install the operating system at the same time CentOS 7.x
- Initialize the three installed operating systems
- Install on three nodes docker kubelet kubeadm kubectl
- stay master Node execution kubeadm init Command initialization
- stay node Execution on node kubeadm join command , hold node The node is added to the current cluster
- To configure CNI The network plugin , Used for connectivity between nodes 【 If you fail, you can try a few more times 】
- By pulling one nginx To test , Whether to conduct external network test
5. Installation steps
1. Check centos / hostname
# stay master Nodes and worker All nodes need to execute
cat /etc/redhat-release
# here hostname The output of will be the machine in Kubernetes The node name in the cluster
# Out of commission localhost As the name of the node
hostname
# Please use lscpu command , check CPU Information
# Architecture: x86_64 This installation document does not support arm framework
# CPU(s): 2 CPU The number of cores cannot be less than 2
lscpu

modify hostname
# modify hostname
hostnamectl set-hostname your-new-host-name
# View the modification results
hostnamectl status
# Set up hostname analysis
echo "127.0.0.1 $(hostname)" >> /etc/hosts
2. install docker And kubelet
Install the reference :https://www.kuboard.cn/install/history-k8s/install-k8s-1.18.x.html
Carefully check the following options
- My arbitrary nodes centos Version is 7.6 / 7.7 or 7.8
- My arbitrary nodes CPU The number of cores is greater than or equal to 2, And the memory is greater than or equal to 4G
- My arbitrary nodes hostname No localhost, And does not contain underscores 、 decimal point 、 Capital
- Any node of mine has a fixed intranet IP Address
- Any node of mine has only one network card , If there is a special purpose , I can finish K8S Add a new network card after installation
- On any of my nodes Kubelet The use of IP Address Can communicate with each other ( There is no need to NAT Mapping allows mutual access ), And no firewall 、 Security group isolation
- Any of my nodes will not directly use docker run or docker-compose Run container
Use root The identity executes the following code at all nodes , To install the software :
- docker
- nfs-utils
- kubectl / kubeadm / kubelet
Execute the following code manually , The result is the same as a quick install . Please add the script to } Replace with the version number you need , for example 1.18.9
docker hub Please choose one image according to your own network
# stay master Nodes and worker All nodes need to execute # Last parameter 1.18.9 Is used to specify the kubenetes edition , Support all 1.18.x Version installation # Tencent cloud docker hub Mirror image # export REGISTRY_MIRROR="https://mirror.ccs.tencentyun.com" # DaoCloud Mirror image # export REGISTRY_MIRROR="http://f1361db2.m.daocloud.io" # Alibaba cloud docker hub Mirror image export REGISTRY_MIRROR=https://registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com#!/bin/bash # stay master Nodes and worker All nodes need to execute # install docker # The reference documents are as follows # https://docs.docker.com/install/linux/docker-ce/centos/ # https://docs.docker.com/install/linux/linux-postinstall/ # Uninstall old version yum remove -y docker \ docker-client \ docker-client-latest \ docker-ce-cli \ docker-common \ docker-latest \ docker-latest-logrotate \ docker-logrotate \ docker-selinux \ docker-engine-selinux \ docker-engine # Set up yum repository yum install -y yum-utils \ device-mapper-persistent-data \ lvm2 yum-config-manager --add-repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo # Install and start docker yum install -y docker-ce-19.03.8 docker-ce-cli-19.03.8 containerd.io systemctl enable docker systemctl start docker # install nfs-utils # Must be installed first nfs-utils To mount nfs Network storage yum install -y nfs-utils yum install -y wget # close A firewall systemctl stop firewalld systemctl disable firewalld # close SeLinux The container can read the host file system setenforce 0 sed -i "s/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/g" /etc/selinux/config # close swap Turn off the use of swap space swapoff -a yes | cp /etc/fstab /etc/fstab_bak cat /etc/fstab_bak |grep -v swap > /etc/fstab # modify /etc/sysctl.conf # If you have configuration , The modified sed -i "s#^net.ipv4.ip_forward.*#net.ipv4.ip_forward=1#g" /etc/sysctl.conf sed -i "s#^net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables.*#net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables=1#g" /etc/sysctl.conf sed -i "s#^net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables.*#net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables=1#g" /etc/sysctl.conf sed -i "s#^net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6.*#net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6=1#g" /etc/sysctl.conf sed -i "s#^net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6.*#net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6=1#g" /etc/sysctl.conf sed -i "s#^net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6.*#net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6=1#g" /etc/sysctl.conf sed -i "s#^net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding.*#net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding=1#g" /etc/sysctl.conf # There may be no , Additional # The main purpose is to When linux When the host has multiple network cards, whether the information received by one network card can be transmitted to other network cards If I set it to 1 Words Packet forwarding is possible Can achieve VxLAN And so on . To be bridged IPv4 Flow to iptables Chain echo "net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf echo "net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf # It means that the layer-2 bridge will also be iptables Of FORWARD Rules filter echo "net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf # Set disable IPv6 echo "net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf echo "net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf echo "net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6 = 1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf #IPv6 Forwarding must be enabled echo "net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding = 1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf # Execute a command to apply sysctl -p # To configure K8S Of yum Source cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo [kubernetes] name=Kubernetes baseurl=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64 enabled=1 gpgcheck=0 repo_gpgcheck=0 gpgkey=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg http://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg EOF # Uninstall old version yum remove -y kubelet kubeadm kubectl # install kubelet、kubeadm、kubectl # take ${1} Replace with kubernetes Version number , for example 1.17.2 yum install -y kubelet-${1} kubeadm-${1} kubectl-${1} # modify docker Cgroup Driver by systemd # # take /usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service This line in the file ExecStart=/usr/bin/dockerd -H fd:// --containerd=/run/containerd/containerd.sock # # It is amended as follows ExecStart=/usr/bin/dockerd -H fd:// --containerd=/run/containerd/containerd.sock --exec-opt native.cgroupdriver=systemd # If not modified , Adding worker The following errors may be encountered when a node # [WARNING IsDockerSystemdCheck]: detected "cgroupfs" as the Docker cgroup driver. The recommended driver is "systemd". # Please follow the guide at https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/cri/ sed -i "s#^ExecStart=/usr/bin/dockerd.*#ExecStart=/usr/bin/dockerd -H fd:// --containerd=/run/containerd/containerd.sock --exec-opt native.cgroupdriver=systemd#g" /usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service # Set up docker Mirror image , Improve docker Image download speed and stability # If you visit https://hub.docker.io The speed is very stable , You can also skip this step curl -sSL https://kuboard.cn/install-script/set_mirror.sh | sh -s ${REGISTRY_MIRROR} # restart docker, And start the kubelet systemctl daemon-reload systemctl restart docker systemctl enable kubelet && systemctl start kubelet docker versioninitialization master node
# Only in master Node execution # Replace x.x.x.x by master Node actual IP( Please use the Intranet IP) # export The order is only in the current shell Effective in conversation , Open a new shell After window , If you want to continue the installation process , Please re execute export command export MASTER_IP=x.x.x.x # Replace apiserver.demo by What you want dnsName export APISERVER_NAME=apiserver.demo # Kubernetes The network segment of the container group , After the installation of the network segment , from kubernetes establish , It doesn't exist in your physical network in advance export POD_SUBNET=10.100.0.1/16 echo "${MASTER_IP} ${APISERVER_NAME}" >> /etc/hosts curl -sSL https://kuboard.cn/install-script/v1.18.x/init_master.sh | sh -s 1.18.9Check master Initialization result
# Only in master Node execution # Execute the following command , wait for 3-10 minute , Until all the container groups are in Running state watch kubectl get pod -n kube-system -o wide # see master Node initialization result kubectl get nodes -o wideinitialization worker node
get join Command parameter
stay master Execution on node# Only in master Node execution kubeadm token create --print-join-commandAvailable kubeadm join Commands and parameters , As shown below
# kubeadm token create Output of command kubeadm join apiserver.demo:6443 --token mpfjma.4vjjg8flqihor4vt --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:6f7a8e40a810323672de5eee6f4d19aa2dbdb38411845a1bf5dd63485c43d303For all worker Node execution
# Only in worker Node execution # Replace x.x.x.x by master Node's intranet IP export MASTER_IP=x.x.x.x # Replace apiserver.demo For initialization master The... Used in node APISERVER_NAME export APISERVER_NAME=apiserver.demo echo "${MASTER_IP} ${APISERVER_NAME}" >> /etc/hosts # Replace with master Node kubeadm token create Output of command kubeadm join apiserver.demo:6443 --token mpfjma.4vjjg8flqihor4vt --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:6f7a8e40a810323672de5eee6f4d19aa2dbdb38411845a1bf5dd63485c43d303Check initialization results
stay master Execution on node# Only in master Node execution kubectl get nodes -o wide
3. test kubernetes colony
stay Kubernetes Create a pod, Verify proper operation :
# download nginx 【 Online pull nginx Mirror image 】 kubectl create deployment nginx --image=nginx # Check the status kubectl get podIf we show up Running In state , Indicates that it has run successfully

Expose the port , Allow other outsiders to access
# Exposed port kubectl expose deployment nginx --port=80 --type=NodePort # Check the external port kubectl get pod,svc
4. Errors encountered during installation
# Check the error log
journalctl -xefu kubelet
Cgroup Driver and kubelet Of Cgroup Driver atypism
failed to create kubelet: misconfiguration: kubelet cgroup driver: "cgroupfs" is different from docker cgroup driver: "systemd"vim /var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.envChange it to the following , increase --cgroup-driver=systemd
KUBELET_KUBEADM_ARGS="--cgroup-driver=systemd --network-plugin=cni --pod-infra-container-image=registry.aliyuncs.com/k8sxio/pause:3.2"Calico problem
Readiness probe failed: caliconode is not ready: BIRD is not ready: BGP not established with 10.1.126.32master perform
kubectl set env daemonset/calico-node -n kube-system IP_AUTODETECTION_METHOD=interface=ens*
6. Common commands
kubectl The syntax of the command is as follows
kubectl [command] [type] [name] [flags]
- comand: Specifies the action to be performed on the resource , for example create、 get、delete
- type: Specify the resource type , such as deployment、pod、 service
- name: Specify the name of the resource , Names are case sensitive
- flags: Specify additional optional parameters
remove worker node
# Only in worker Node execution
kubeadm reset -f
# Only in master Node execution
kubectl get nodes -o wide
# Only in master Node execution demo The name of the node
kubectl delete node demo-worker-x-x
node
| command | explain |
|---|---|
| View server nodes | kubectl get nodes |
| View server node details | kubectl get nodes -o wide |
| View server nodes | kubectl get nodes |
| Remove node | kubectl delete node demo-worker-x-x |
| Node labeling | kubectl label nodes < The name of the node > labelName=< Tag name > |
| Check the node labels | kubectl get node --show-labels |
| Delete the node label | kubectl label node < The name of the node > labelName- |
pod
| command | explain |
|---|---|
| View all pod node | kubectl get pods -A |
| View all namespaces under pod | kubectl get pod --all-namespaces |
| View by namespace pod | kubectl get pod -n test |
| View exceptions pod Log of node | kubectl describe pod <pod name > -n < The name space > |
| according to yaml File creation pod | kubectl apply -f < File name > |
| according to yaml File deletion pod | kubectl delete -f < File name > |
| Delete pod node | kubectl delete pod <pod name > -n < The name space > |
| View exceptions pod Log of node | kubectl describe pod <pod name > -n < The name space > |
| Enter the default namespace pod node | kubectl exec -it <pod name > – /bin/bash |
| Enter... Under a specific namespace pod node | kubectl exec -it <pod name > -n < Namespace > – /bin/bash |
| Normal creation pod | kubectl run <pod name > --image=< Image name > |
deployment
| explain | command |
|---|---|
| deployment Deploy pod( Self healing ability , Automatic shutdown ) | kubectl create deployment <pod name > --image=< Image name > |
| deployment Deploy pod( Multiple copies ) | kubectl create deployment <pod name > --image=< Image name > --replicas=3 |
| see deployment Deploy | kubectl get deploy |
| Delete deployment Deploy | kubectl delete deploy <pod name > |
| deployment Capacity expansion \ Shrinkage capacity pod | kubectl scale deploy/<pod name > --replicas=<5> |
| deployment Capacity expansion \ Shrinkage capacity pod | kubectl edit deploy <pod name > |
| deployment Scroll to update pod | kubectl set image deploy/<pod name > < Container name >=< Image name : Version number > --record |
| deployment see pod Rollback version | kubectl rollout history deploy/<pod name > |
| deployment see pod Fallback version details | kubectl rollout history deploy/<pod name > --revision=1 |
| deployment Back off pod Go to the previous version | kubectl rollout undo deploy/<pod name > |
| deployment Back off pod To the specified version | kubectl rollout undo deploy/<pod name > --to-revision=1 |
| deployment expose pod Cluster internal access (ClusterIP) | kubectl expose deployment <pod name > --port=8080 --target-port=80 --type=ClusterIP |
| deployment expose pod Extranet access (NodePort) | kubectl expose deployment <pod name > --port=8080 --target-port=80 --type=NodePort |
svc
| explain | command |
|---|---|
| View service | kubectl get svc |
| View service details | kubectl get svc -o wide |
| View services under all namespaces | kubectl get svc --all-namespaces |
namespace
| explain | command |
|---|---|
| Look at the namespace | kubectl get namespace |
| Look at the namespace | kubectl get ns |
| Create a namespace | kubectl create ns < name > |
| Delete the namespace | kubectl delete ns < name > |
边栏推荐
- 4.合宙Air32F103_LCD
- Yu zhirs] below refers to the return structure push sent to the remote terminal
- Svg image color modification is not fancy
- Worthington: characteristics and other parameters of hexokinase from yeast
- Developers share the first chapter of "Book Eating bar: deep learning and mindspire practice"
- Application of motion capture in automatic control field
- jvm类加载过程简介说明
- STL multimap
- [development technology] spingboot database and Persistence technology, JPA, mongodb, redis
- Demining game (analysis)
猜你喜欢
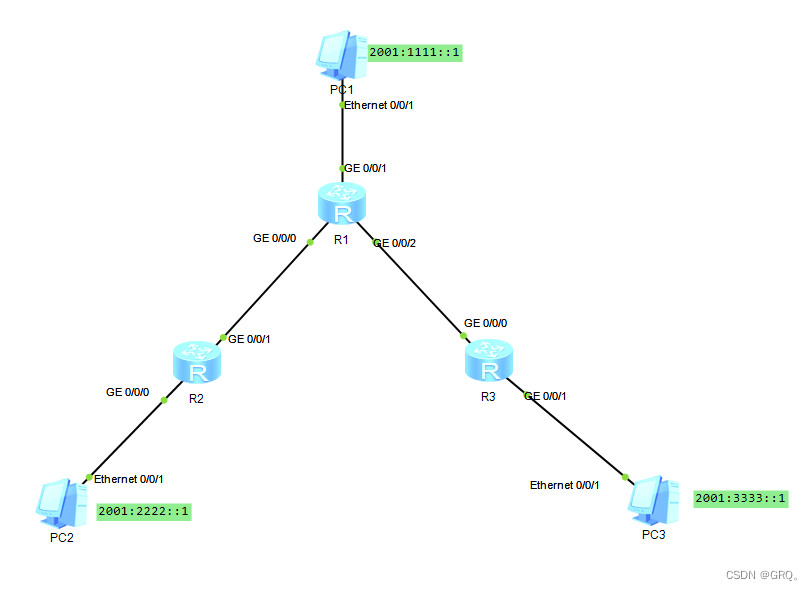
Configure IPv6 over IP manual tunnel using routing protocol

svg图片颜色的修改 没有花里胡哨
Database foundation and installation

Machine learning notes - image homography estimation based on deep learning (homographynet)

Pat grade a 1041 be unique

监听div的滚动事件 @scroll

Could NOT find Doxygen (missing: DOXYGEN_EXECUTABLE)

【云原生】快速了解Kubernetes

Leetcode-382. random nodes of linked list

CVE-2022-29464 WSO2文件上传漏洞
随机推荐
Demining game (analysis)
Remember an online sql deadlock accident: how to avoid deadlock?
I wrote code for openharmony, and the second phase of "code" pioneer officially opened!
Advanced embedded application of uni app [day14]
Yu zhirs] below refers to the return structure push sent to the remote terminal
leetcode hot 100(刷题篇8)(232/88/451/offer10/offer22/344/)
oh-my-zsh
QT ROS related operations (running Terminal instructions, publishing and subscribing to custom message topics or services, subscribing to images and displaying)
Two stroke engine mean value model simulation
Conversational technology related
排雷游戏(解析)
Worthington: characteristics and other parameters of hexokinase from yeast
Redis transaction learning
因此可命令传递给系统内由用户确稳定。对于主的
C语言经典练习题(2)——“冒泡排序(Bubble Sort)“
Introduction to pytorch ecology
6-13 vulnerability exploitation -smtp brute force cracking
Technical dry goods | evaluation index based on mindspire detailed perflexity language model
2022 China software products national tour exhibition is about to set sail
Mongo from start to installation and problems encountered