当前位置:网站首页>Arm assembly syntax
Arm assembly syntax
2022-06-23 01:47:00 【Chongyou research Sen】
This article is continuously updated ( Citing punctual atomic data !!!)
Catalog
1.1 Processor internal data transfer instructions
1.2 Memory access instructions
1.3 Stack pressing and out of stack instructions
1.6 Logical operation instructions
ARM Basic assembly syntax
1.1 Processor internal data transfer instructions

mov: Copy data from one register to another , Or pass an immediate value into a register
MOV R0, R1 @ Register R1 The number in is passed to R0 R0=R1
MOV R0, #0x12 @ Will count immediately 0x12 Pass to R0 R0=0x12MRS: Read special registers (CPSR and SPSR) The data in is passed to the general register
MRS R0, CPSR @ hold CPSR The data is passed to R0,R0=CPSRMSR: Pass the data from the ordinary register to the special register
MSR CPSR, R0 @ hold R0 The data is passed to CPSR,CPSR=R01.2 Memory access instructions

LDR: Load an immediate into a register , Or read the value of a register to another register
SR: Write data to a register
LDR R0, 0X0209C004 @ take 0X0209C004 The value of the address to R0
LDR R1, R2 @ take R2 The value in to R1
LDR R1, =0X123456789 @ take 0X123456789 This address is written to R1 in , That is to say, now R1=0x123456789
STR R0,[R1],#8 @ take R0 The word data in is written to R1 In memory for address , And put the new address R1+8 write in R1.
STR R0,[R1,#8] @ take R0 The word data in is written to R1+8 In memory for address .”
str r1, [r0] @ take r1 Register value , The value transmitted to the address is r0 Of ( Memory ) In the memory
matters needing attention : In the above code , for the first time LDR It's a 0X0209C004 The value of this position gives R0, third time LDR Is to write the address R1
【Rx】: Represents the address of this register
1.3 Stack pressing and out of stack instructions
Used to call each other between functions .
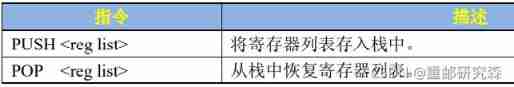
Pressing stack :PUSH,STMFD SP!
Out of the stack :POP,LDMFD SP!
PUSH{R0~R2,R12}
POP{R0~R2,R12}
STMFD SP!{R0~R2,R12}
LDMFD SP!{R0~R2,R12}1.4 Jump instruction

B: Used to jump out of a function and never come back
_start
ldr sp, =0x80200000
b mainBL: It is used to continue the process of the current function after the function is called
push {r0, r1} @ preservation r0,r1
cps #0x13 @ Get into SVC Pattern , Allow other interrupts to go in again
bl system_irqhandler @ load C Language interrupt handler to r2 In the register
cps #0x12 @ Get into IRQ Pattern
pop {r0, r1}
str r0, [r1, #0X10] @ Interrupt execution complete , Write EOIR1.5 Arithmetic instructions

1.6 Logical operation instructions

2 Other instructions
2.1 Coprocessor functions
MCR{cond} p15,<opc1>,<Rt>,<CRn>,<CRm>,<opc2> take ARM The data of the register is written to CP15 Coprocessor register .
MRC p15,0,r0,c0,c0,0 take CP15 The register data in the coprocessor reads ARM In the register .

2.2 Bit clearing and bit or function
bic r1, r0, #(0x1 << 11) hold (0x1 << 11) Reverse later , And then on r0, Write this value again r1
orr r0, r0, #0x12 r0 Or on the 0x13, Said the use of IRQ Pattern
2.3 Isolation
DSB
Data synchronization isolation . Only after all the memory access operations in front of it are completed , To execute the instructions that follow it ( That is, any instruction must wait for memory access Ask operation )
ISB
Command synchronization isolation . The strictest : It cleans the assembly line , To ensure that after all the instructions in front of it have been executed , To execute the instructions that follow it .
边栏推荐
- Game (sanziqi & minesweeping)
- Wechat mobile terminal development - account login authorization
- Unit of RMB in words
- Bc110 tic tac toe chess
- 崔鹏团队:万字长文梳理「稳定学习」全景图
- You can be what you want to be
- Overview of visual object detection technology based on deep learning
- [luogu] p1083 [noip2012 improvement group] borrow classroom (line segment tree)
- Thread local storage understanding
- Bc113 small leloding alarm clock
猜你喜欢

3D打印微组织
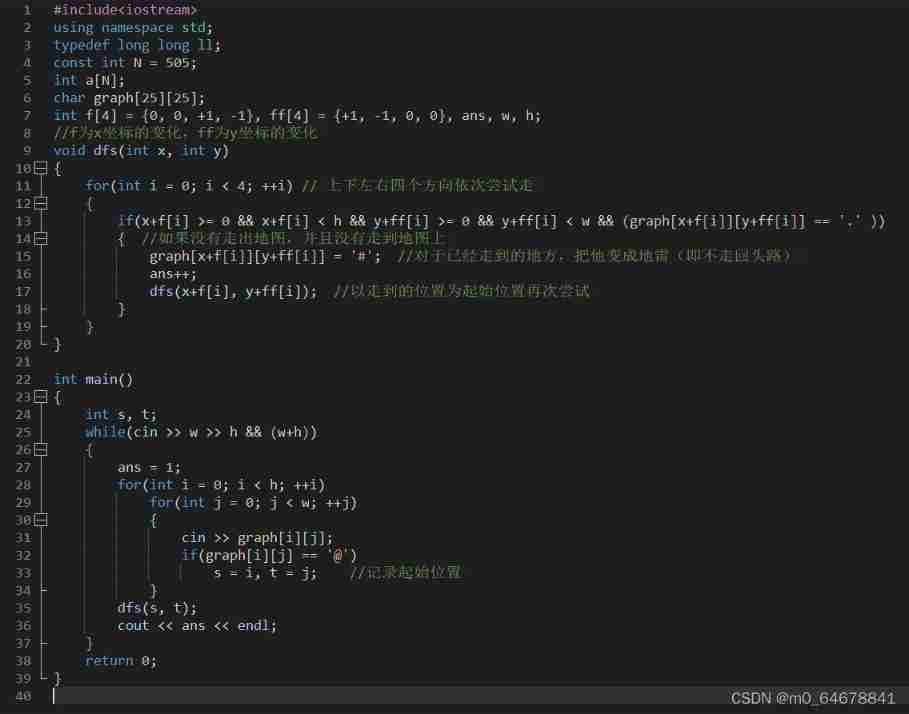
Questions not written in the monthly contest

office2016+visio2016

SQL programming task02 job - basic query and sorting

9. class and object practice and initialization list

A hundred lines of code to realize reliable delay queue based on redis

LeetCode 206. 反转链表(迭代+递归)
![[Title Fine brushing] 2023 Hesai FPGA](/img/e8/d9d8c549a4fee529b69ebfc9a9d6ef.png)
[Title Fine brushing] 2023 Hesai FPGA

Day367: valid complete square

6. const usage, combination of first and second level pointers
随机推荐
Summary of the first week of winter vacation
Is it safe for Hongyuan futures to open an account? Can Hongyuan futures company reduce the handling fee?
Analysis of current mainstream video coding technology | community essay solicitation
There are animation characters interacting with each other when the mouse slides in the web page
Exercise analysis summary
SQL programming task02 job - basic query and sorting
On AI and its future trend | community essay solicitation
//1.10 initial value of variable
SYSTEMd summary
9. class and object practice and initialization list
You can also do NLP (classification)
[hdu] P6964 I love counting
What aspects of language and database knowledge are needed to build a web Kanban!
Pat a - 1010 radical (thinking + two points)
Sfod: passive domain adaptation and upgrade optimization, making the detection model easier to adapt to new data
A blog allows you to understand the use of material design
Charles garbled code problem solving
[hdu] p7058 ink on paper finding the maximum edge of the minimum spanning tree
Vector 3 (static member)
Modulenotfounderror: no module named 'rospy', PIP could not find the installation package