当前位置:网站首页>Analysis of 43 cases of MATLAB neural network: Chapter 26 classification of LVQ Neural Network - breast tumor diagnosis
Analysis of 43 cases of MATLAB neural network: Chapter 26 classification of LVQ Neural Network - breast tumor diagnosis
2022-06-21 17:38:00 【mozun2020】
《MATLAB neural network 43 A case study 》: The first 26 Chapter LVQ Classification of neural networks —— Breast tumor diagnosis
1. Preface
《MATLAB neural network 43 A case study 》 yes MATLAB Technology Forum (www.matlabsky.com) planning , Led by teacher wangxiaochuan ,2013 Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Press MATLAB A book for tools MATLAB Example teaching books , Is in 《MATLAB neural network 30 A case study 》 On the basis of modification 、 Complementary , Adhering to “ Theoretical explanation — case analysis — Application extension ” This feature , Help readers to be more intuitive 、 Learn neural networks vividly .
《MATLAB neural network 43 A case study 》 share 43 Chapter , The content covers common neural networks (BP、RBF、SOM、Hopfield、Elman、LVQ、Kohonen、GRNN、NARX etc. ) And related intelligent algorithms (SVM、 Decision tree 、 Random forests 、 Extreme learning machine, etc ). meanwhile , Some chapters also cover common optimization algorithms ( Genetic algorithm (ga) 、 Ant colony algorithm, etc ) And neural network . Besides ,《MATLAB neural network 43 A case study 》 It also introduces MATLAB R2012b New functions and features of neural network toolbox in , Such as neural network parallel computing 、 Custom neural networks 、 Efficient programming of neural network, etc .
In recent years, with the rise of artificial intelligence research , The related direction of neural network has also ushered in another upsurge of research , Because of its outstanding performance in the field of signal processing , The neural network method is also being applied to various applications in the direction of speech and image , This paper combines the cases in the book , It is simulated and realized , It's a relearning , I hope I can review the old and know the new , Strengthen and improve my understanding and practice of the application of neural network in various fields . I just started this book on catching more fish , Let's start the simulation example , Mainly to introduce the source code application examples in each chapter , This paper is mainly based on MATLAB2015b(32 position ) Platform simulation implementation , This is Chapter 26 of the book LVQ Examples of neural network classification , Don't talk much , Start !
2. MATLAB Simulation example
open MATLAB, Click on “ Home page ”, Click on “ open ”, Find the sample file 
Choose chapter26_lvq.m, Click on “ open ”
chapter26_lvq.m Source code is as follows :
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% function : LVQ Classification of neural networks —— Breast tumor diagnosis
% Environmental Science :Win7,Matlab2015b
%Modi: C.S
% Time :2022-06-18
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%% LVQ Classification of neural networks —— Breast tumor diagnosis
%% Clear environment variables
clear all
clc
warning off
tic
%% Import data
load data.mat
a = randperm(569);
Train = data(a(1:500),:);
Test = data(a(501:end),:);
% Training data
P_train = Train(:,3:end)';
Tc_train = Train(:,2)';
T_train = ind2vec(Tc_train);
% Test data
P_test = Test(:,3:end)';
Tc_test = Test(:,2)';
%% Creating networks
count_B = length(find(Tc_train == 1));
count_M = length(find(Tc_train == 2));
rate_B = count_B/500;
rate_M = count_M/500;
net = newlvq(minmax(P_train),20,[rate_B rate_M],0.01,'learnlv1');
% Set network parameters
net.trainParam.epochs = 1000;
net.trainParam.show = 10;
net.trainParam.lr = 0.1;
net.trainParam.goal = 0.1;
%% Training network
net = train(net,P_train,T_train);
%% The simulation test
T_sim = sim(net,P_test);
Tc_sim = vec2ind(T_sim);
result = [Tc_sim;Tc_test]
%% Results show
total_B = length(find(data(:,2) == 1));
total_M = length(find(data(:,2) == 2));
number_B = length(find(Tc_test == 1));
number_M = length(find(Tc_test == 2));
number_B_sim = length(find(Tc_sim == 1 & Tc_test == 1));
number_M_sim = length(find(Tc_sim == 2 &Tc_test == 2));
disp([' Total number of cases :' num2str(569)...
' Benign :' num2str(total_B)...
' Malignant :' num2str(total_M)]);
disp([' Total number of training set cases :' num2str(500)...
' Benign :' num2str(count_B)...
' Malignant :' num2str(count_M)]);
disp([' Total number of cases in the test set :' num2str(69)...
' Benign :' num2str(number_B)...
' Malignant :' num2str(number_M)]);
disp([' Benign breast tumor was diagnosed :' num2str(number_B_sim)...
' Misdiagnosis :' num2str(number_B - number_B_sim)...
' Diagnostic rate p1=' num2str(number_B_sim/number_B*100) '%']);
disp([' Malignant breast tumor was diagnosed :' num2str(number_M_sim)...
' Misdiagnosis :' num2str(number_M - number_M_sim)...
' Diagnostic rate p2=' num2str(number_M_sim/number_M*100) '%']);
toc
Add completed , Click on “ function ”, Start emulating , The output simulation results are as follows :
result =
1 to 19 Column
1 1 2 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 1 2
1 1 2 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 2
20 to 38 Column
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
2 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
39 to 57 Column
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 1
1 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 2 2 2 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 1
58 to 69 Column
1 1 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 2 1
1 1 1 2 2 2 1 2 1 1 2 1
Total number of cases :569 Benign :357 Malignant :212
Total number of training set cases :500 Benign :314 Malignant :186
Total number of cases in the test set :69 Benign :43 Malignant :26
Benign breast tumor was diagnosed :41 Misdiagnosis :2 Diagnostic rate p1=95.3488%
Malignant breast tumor was diagnosed :17 Misdiagnosis :9 Diagnostic rate p2=65.3846%
Time has passed 6.838382 second .

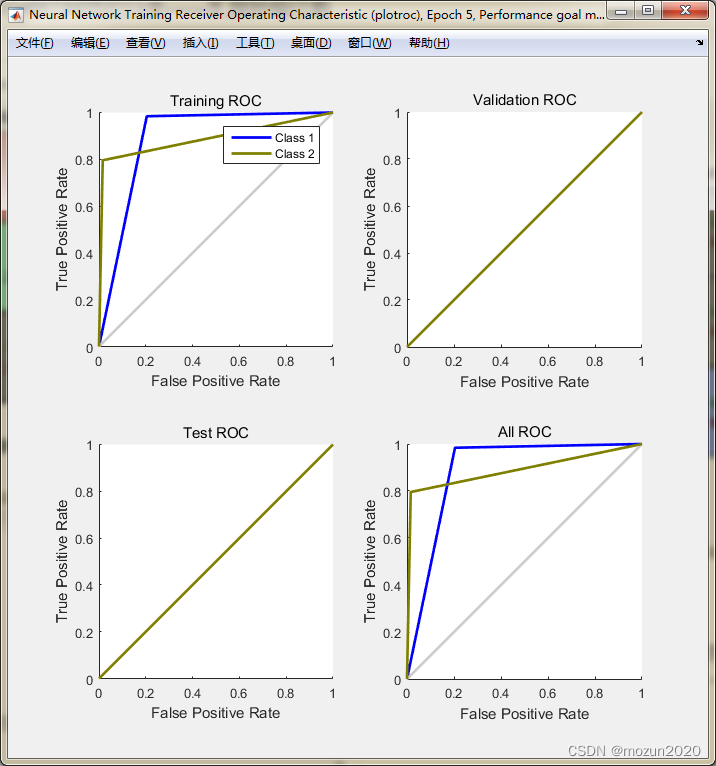
In turn, click Plots Medium Performance,Training State,Confusion,Receiver Operating Characteristic, The following figure can pop up :


go back to MATLAB in , Open file view chapter26_bp.m
chapter26_bp.m Source code is as follows :
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% function :BP Classification of neural networks —— Breast tumor diagnosis
% Environmental Science :Win7,Matlab2015b
%Modi: C.S
% Time :2022-06-19
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%% BP Classification of neural networks —— Breast tumor diagnosis
tic
%% Creating networks
net = newff(minmax(P_train),[50 1],{
'tansig','purelin'},'trainlm');
%% Set network parameters
net.trainParam.epochs = 1000;
net.trainParam.show = 10;
net.trainParam.lr = 0.1;
net.trainParam.goal = 0.1;
%% Training network
net = train(net,P_train,Tc_train);
%% The simulation test
T_sim = sim(net,P_test);
for i = 1:length(T_sim)
if T_sim(i) <= 1.5
T_sim(i) = 1;
else
T_sim(i) = 2;
end
end
result = [T_sim;Tc_test]
number_B = length(find(Tc_test == 1));
number_M = length(find(Tc_test == 2));
number_B_sim = length(find(T_sim == 1 & Tc_test == 1));
number_M_sim = length(find(T_sim == 2 &Tc_test == 2));
disp([' Total number of cases :' num2str(569)...
' Benign :' num2str(total_B)...
' Malignant :' num2str(total_M)]);
disp([' Total number of training set cases :' num2str(500)...
' Benign :' num2str(count_B)...
' Malignant :' num2str(count_M)]);
disp([' Total number of cases in the test set :' num2str(69)...
' Benign :' num2str(number_B)...
' Malignant :' num2str(number_M)]);
disp([' Benign breast tumor was diagnosed :' num2str(number_B_sim)...
' Misdiagnosis :' num2str(number_B - number_B_sim)...
' Diagnostic rate p1=' num2str(number_B_sim/number_B*100) '%']);
disp([' Malignant breast tumor was diagnosed :' num2str(number_M_sim)...
' Misdiagnosis :' num2str(number_M - number_M_sim)...
' Diagnostic rate p2=' num2str(number_M_sim/number_M*100) '%']);
toc
Click on “ function ”, Start emulating , The output simulation results are as follows :
result =
1 to 19 Column
1 1 2 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 1 2
1 1 2 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 2
20 to 38 Column
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
2 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
39 to 57 Column
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 1
1 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 2 2 2 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 1
58 to 69 Column
1 1 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 2 1
1 1 1 2 2 2 1 2 1 1 2 1
Total number of cases :569 Benign :357 Malignant :212
Total number of training set cases :500 Benign :314 Malignant :186
Total number of cases in the test set :69 Benign :43 Malignant :26
Benign breast tumor was diagnosed :41 Misdiagnosis :2 Diagnostic rate p1=95.3488%
Malignant breast tumor was diagnosed :17 Misdiagnosis :9 Diagnostic rate p2=65.3846%
Time has passed 6.838382 second .
>> chapter26_bp
result =
1 to 19 Column
1 1 2 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 2 2
1 1 2 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 2
20 to 38 Column
1 1 1 2 1 1 2 2 2 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
2 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
39 to 57 Column
1 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 1
1 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 2 2 2 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 1
58 to 69 Column
1 1 1 2 1 2 2 2 1 2 2 1
1 1 1 2 2 2 1 2 1 1 2 1
Total number of cases :569 Benign :357 Malignant :212
Total number of training set cases :500 Benign :314 Malignant :186
Total number of cases in the test set :69 Benign :43 Malignant :26
Benign breast tumor was diagnosed :34 Misdiagnosis :9 Diagnostic rate p1=79.0698%
Malignant breast tumor was diagnosed :23 Misdiagnosis :3 Diagnostic rate p2=88.4615%
Time has passed 2.954276 second .

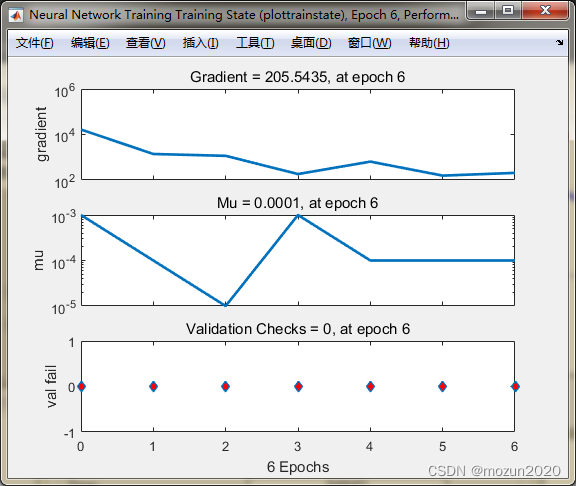
In turn, click Plots Medium Performance,Training State,Regression, The following figure can pop up :

3. Summary
LVQ(Learning Vector Quantization) Neural network is Kohonen On 1989 In, a learning vector quantization network based on competitive network was proposed , Mainly used for classification . It belongs to the type of feedforward neural network , It has a wide range of applications in the field of pattern recognition and optimization .LVQ The neural network consists of three layers , Input layer 、 The hidden layer and the output layer , The network is fully connected between the input layer and the hidden layer , The hidden layer and the output layer are partially connected , Each output layer neuron is connected to a different group of hidden layer neurons . The connection weight between hidden layer and output layer neurons is fixed as 1. The weights of the connections between the neurons in the input layer and the hidden layer establish the components of the reference vector ( Assign a reference vector to each hidden neuron ). In the process of network training , These weights are modified . Hidden layer neurons ( Also known as Kohnen Neuron ) And output neurons have binary output values . When an input mode is sent to the network , The implicit neuron whose reference vector is closest to the input mode wins the competition because of the excitation , Thus allowing it to produce a “1”, Other hidden layer neurons are forced to produce “0”. The output neuron connected to the hidden layer neuron group containing the winning neuron also emits “1”, Other output neurons all send out “0”. produce “1” The output neuron of gives the class of input pattern , thus it can be seen , Each output neuron is used to represent a different class .
This chapter will LVQ Neural networks and BP Comparative simulation of neural network in breast tumor diagnosis and prediction , It can be seen that in the prediction of benign and malignant ,LVQ Neural networks and BP Each neural network has its own advantages and disadvantages , The simulation of this example needs to run LVQ Get the corresponding data , Run again BP Conduct simulation . Interested in the content of this chapter or want to fully learn and understand , I suggest you study Chapter 26 of the book . Some of these knowledge points will be supplemented on the basis of their own understanding in the later stage , Welcome to study and exchange together .
边栏推荐
- 第八章 可编程接口芯片及应用【微机原理】
- 【mysql学习笔记15】用户管理
- Stack growth direction and memory growth direction
- Nacos注册中心-----从0开始搭建和使用
- Android kotlin class delegation by, by lazy key
- Four areas of telephone memory
- Summary of the 16th week
- go corn定时任务简单应用
- From Beijing "moisten" to Chicago, engineer Baoyu "moisten" the secret of growth
- BM19 寻找峰值
猜你喜欢

Nacos注册中心-----从0开始搭建和使用
![[MySQL learning notes 19] multi table query](/img/e6/4cfb8772e14bc82c4fdc9ad313e58a.png)
[MySQL learning notes 19] multi table query

Why did you win the first Taosi culture award of 20000 RMB if you are neither a top R & D expert nor a sales bull?

程序员进修之路

AS 3744.1标准中提及ISO8191测试,两者测试一样吗?

焱融科技 YRCloudFile 与安腾普完成兼容认证,共创存储新蓝图

Four areas of telephone memory

拉格朗日插值

PTA L3-031 千手观音 (30 分)

module.exports指向问题
随机推荐
【mysql学习笔记11】排序查询
[MySQL learning notes 15] user management
3DE 三维模型视图看不到怎么调整
【数据集】|BigDetection
In the "roll out" era of Chinese games, how can small and medium-sized manufacturers solve the problem of going to sea?
shamir
Bm22 compare version number
[MySQL learning notes 18] constraints
Leetcode 25: a group of K flipped linked lists
拉格朗日插值
关于SSM整合,看这一篇就够了~(保姆级手把手教程)
【mysql学习笔记12】分页查询
iframe跨域传值
shamir
叩富网开期货账户安全可信吗?
Android kotlin 类委托 by,by lazy关键
软件测试体系学习及构建(14)-测试基础之软件测试和开发模型概述
类、接口、函数
【mysql学习笔记13】查询语句综合练习
[Error] ‘vector‘ was not declared in this scope