当前位置:网站首页>my_ Ls summary
my_ Ls summary
2022-07-27 16:32:00 【Xavier】
Realization my_ls
I'm learning linuxC In programming practice, we will first encounter how to realize ls function , The following will briefly introduce the implementation method .
ls Function is introduced
-l : Displays a list of contents in a long format . The output information includes the file name from left to right , file type 、 Access mode 、 Number of hard connections 、 owner 、 Group 、 The size of the file and the last modification time of the file .
-a : Show all files and directories .
-R : Return the output files of all folders .
-i : Show file index node number (inode).
-r : Output files and directories in reverse order .
-t : Sort files by time .
-s : Show the size of files and directories ( In blocks ).
ls Operation flow chart of
Through the operation flow chart ls Have a deeper understanding of the operation process of 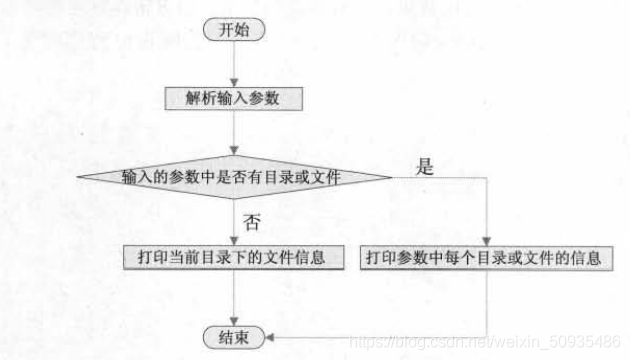
Introduction of main functions
1.opendir
1. The header file :#include<sys/types.h>#include<dirent.h>
2. The function prototype :struct dirent * opendir(DIR * dir);
3. The functionality :opendir() Returns the parameter dir A list of files and directories in a subdirectory . Structure DIR The definition is as follows :
struct __dirstream
{
void *__fd;
char *__data;
int __entry_data;
char *__ptr;
int __entry_ptr;
size_t __allocation;
size_t __size;
__libc_lock_define (, __lock)
};
typedef struct __dirstream DIR;
4. Return value : Returns the parameter dir A list of files and directories in a subdirectory , if dir If it is blank, return NULL.
2.readdir
1. The header file :#include <sys/types.h>#include <dirent.h>
2. The function prototype :struct dirent * readdir(DIR * dir);
3. The functionality :readdir() Returns the parameter dir The next entry point of the directory stream . Structure dirent The definition is as follows :
struct dirent
{
ino_t d_ino; //d_ino The entry point of this directory is inode
ff_t d_off; //d_off The beginning of the directory file is the displacement of the entry point of this directory
signed short int d_reclen; //d_reclen _name The length of , It doesn't contain NULL character
unsigned char d_type; //d_type d_name The type of file you are referring to
har d_name[256]; //d_name file name
};
4. Return value : If successful, the next directory entry point will be returned . If an error occurs or the end of the directory file is read, it returns NULL.
3.lstat
1. The header file :#include <sys/types.h>#nclude <sys/stat.h>#include <unistd.h>
2. The function prototype :int lstat(const char *path, struct stat *buf);( Here are three similar functions ,stat、fstat、lstat, Here we only know lstat).
3. The functionality : Function returns information about a file or symbolic connection . Structure lstat The definition is as follows :
Specific introduction :https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33883085/article/details/88695946
struct stat {
dev_t st_dev; /* The equipment number of the document */
ino_t st_ino; /* Index node number */
mode_t st_mode; /* File types and permissions */
nlink_t st_nlink; /* Hard link number */
uid_t st_uid; /* user ID*/
gid_t st_gid; /* Group ID*/
dev_t st_rdev; /* Device type ( If this file is a device file , Is the equipment number */
off_t st_size; /* file size */
blksize_t st_blksize; /* File system I/O Buffer size */
blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* Number of blocks */
time_t st_atime; /* Access time */
time_t st_mtime; /* Modification time */
time_t st_ctime; /* Change the time */
};
4. Return value : Successfully returns 0, Failure to return -1, And assign detailed error information to errno Global variables .
ls The implementation of the :
1. Header file and macro definition
Before the concrete implementation, we need to know what macro is defined in the header file he needs .
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<linux/limits.h>
#include<dirent.h>
#include<grp.h>
#include<pwd.h>
#include<errno.h>
#include<signal.h>
// The following is the macro definition , In the process of execution, bit operation is used to obtain instructions , It greatly improves the operation efficiency
#define PARAM_A 1//-a: Display all files in this directory , Including hidden files
#define PARAM_L 2//-l: One line only shows the details of one file , Include access to files , File size, etc
#define PARAM_R 4//-R: Read files recursively
#define PARAM_T 8//-t: Sort by time
#define PARAM_r 16//-r: Sort the documents in reverse order
#define PARAM_I 32//-i: Show node information
#define PARAM_S 64//-s: Output the size of the file after each file name
#define MAXROWLEN 80// The maximum number of characters displayed on a line
ls No parameters after
When ls When there is no parameter condition after , We print directly ( Before that, you can sort the file names , To ensure beauty ), Here are the main code snippets .
char colorname[NAME_MAX + 30];
int i,len,j=0;
l++;
// If this line is not enough to print a file name, a new line
// if(g_leave_len < g_maxlen){
// printf("\n");
// g_leave_len = MAXROWLEN;
// }
len = strlen(name);
for(i=0;i<len;i++){
if(name[i]<0){
j++;
}
}
len = g_maxlen - len + j/3;
sprintf(colorname,"\033[%dm%s\033[0m",filecolor,name);// Output the file in different colors
printf("%s",colorname);
for(i=0;i<len+5;i++){
printf(" "); // Print five spaces after each file name
}
if(l == Line){
l=0;
printf("\n");
}
// Below 2 Indicate two empty spaces
g_leave_len -=(g_maxlen + 2);
ls -a
This function is to display all the directories under the directory , Include hidden directories , So just delete the judgment conditions
if(name[0]!='.') // Delete the conditions of your own judgment to hide the file
ls -l
This function is to display the detailed information in the file , So we need to understand the relevant contents of file permissions
| Character constant value | Octal corresponding to character constant value | meaning |
|---|---|---|
| S_IRUSR(S_IREAD) | 00400 | The file owner has readable permissions ; |
| S_IWUSR(S_IWRITE) | 00200 | The file owner has writable permissions ; |
| S_IXUSR(S_IEXEC) | 00100 | The file owner has executable rights ; |
| S_IRGRP | 00040 | User groups have read permissions ; |
| S_IWGRP | 00020 | User groups have writable permissions ; |
| S_IXGRP | 00010 | The user group has executable rights ; |
| S_IROTH | 00004 | Other users have readable permissions ; |
| S_IWOTH | 00002 | Other users have writable permissions ; |
| S_IXOTH | 00001 | Other users have executable rights ; |
| S_ISUID | 04000 | Of documents (set user -id on execution) position ; |
| S_ISGID | 02000 | Of documents (set group-id on execution) position ; |
| S_ISVTX | 01000 | Of documents sticky position ; |
The following is part of the code for printing file attributes
char buf_time[32];
struct passwd *psd; // Get the user name of the file owner from this structure
struct group *grp; // Get the group name of the file owner from this structure
// Get and print file types
if(S_ISLNK(buf.st_mode)){
printf("l");
}else if(S_ISREG(buf.st_mode)){
printf("-");
}else if(S_ISDIR(buf.st_mode)){
printf("d");
}else if(S_ISCHR(buf.st_mode)){
printf("c");
}else if(S_ISBLK(buf.st_mode)){
printf("b");
}else if(S_ISFIFO(buf.st_mode)){
printf("f");
}else if(S_ISSOCK(buf.st_mode)){
printf("s");
}
// Get and print the permission of the file owner
if(buf.st_mode & S_IRUSR){
printf("r"); // Can be read
}else {
printf("-");
}
if(buf.st_mode & S_IWUSR){
printf("w"); // Can write
}else {
printf("-");
}
if(buf.st_mode & S_IXUSR){
printf("x"); // Executable
}else {
printf("-");
}
// Obtain and print the operation permissions of users in the same group as the file owner
if(buf.st_mode & S_IRGRP){
printf("r");
}else {
printf("-");
}
if(buf.st_mode & S_IWGRP){
printf("w");
}else {
printf("-");
}
if(buf.st_mode & S_IXGRP){
printf("x");
}else {
printf("-");
}
// Obtain and print the operation permissions of other users on the file
if(buf.st_mode & S_IROTH){
printf("r");
}else {
printf("-");
}
if(buf.st_mode & S_IWOTH){
printf("w");
}else {
printf("-");
}
if(buf.st_mode & S_IXOTH){
printf("x");
}else {
printf("-");
}
printf(" ");
// according to uid And gid Get the user name and group name of the file owner
psd = getpwuid(buf.st_uid);
grp = getgrgid(buf.st_gid);
printf("%4d ",buf.st_nlink); // Number of links to print file
printf("%-8s",psd->pw_name); // Print the user name of the file owner
printf("%-8s",grp->gr_name); // Print the group name of the file owner
printf("%6d",buf.st_size); // Print file size
strcpy(buf_time,ctime(&buf.st_mtime));
buf_time[strlen(buf_time)-1] = '\0'; // Remove the newline
printf(" %s",buf_time); // Print the time information of the file
ls -i
Print the node data of the file
int i,j=0,len;
l++;
printf("%d ",buf.st_ino); // Print the node data of the file
len = strlen(name);
for(i=0;i<len+5;i++){
if(name[i]<0)
j++;
}
len = g_maxlen - len + j/3;
sprintf(colorname,"\033[%dm%s\033[0m",filecolor,name);
printf("%-s", colorname);
// Output less than required , Fill in enough blanks
for(i=0;i<len;i++)
printf(" ");
if( l == Line)
{
printf("\n");
l = 0;
}
ls -s
Part of the code is as follows :
char colorname[NAME_MAX + 30];
int i,len,j=0;
int a=0,b=0;
l++;
len=strlen(name);
for(i=0;i<len;i++)
if(name[i] < 0)
j++;
len = g_maxlen -len + j/3;
sprintf(colorname,"\033[%dm%s\033[0m",filecolor,name);
printf("%2d ",buf.st_blocks/2); // Because the capacity of the system is different from its own implementation , So change according to the system , Here is the difference 2 times
printf("%-s",colorname);
// Output less than required , Fill in the blanks
for(i=0;i<len;i++)
printf(" ");
if( l == Line)
{
printf("\n");
l=0;
}
ls -R
void display_R(int flag_param,char *path)
{
DIR *dir;
struct dirent *ptr;
int count=0;
int filecolor;
int y=0;
int flag_param_temp;
char filenames[256][PATH_MAX + 1],temp[PATH_MAX + 1];
char muluname[256][PATH_MAX + 1];
long filetime[256][1];
long t;
struct stat buf;
struct stat name;
flag_param_temp = flag_param;
// Get the total number of files in this directory and the longest file name
dir = opendir(path);
if(dir == NULL){
my_err("opendir",__LINE__);
}
while ((ptr = readdir(dir))!=NULL){
if(g_maxlen < strlen (ptr->d_name))
g_maxlen = strlen(ptr->d_name);
count++;
}
closedir(dir);
if(count>256)
my_err("too many files under this dir",__LINE__);
int i,j,len = strlen(path);
// Get all the file names in this directory
dir = opendir(path);
for(i=0;i < count;i++){
ptr = readdir(dir);
if(ptr == NULL){
my_err("readdir",__LINE__);
}
strncpy(filenames[i],path,len);
filenames[i][len] = '\0';
strcat(filenames[i],ptr->d_name);
filenames[i][len+strlen(ptr->d_name)] = '\0';
}
// Use bubble method to sort file names , After sorting, the file names are stored in filenames
if(flag_param & PARAM_T){
flag_param -= PARAM_T;
for(i=0;i<count;i++){
stat(filenames[i],&buf);
filetime[i][0] = buf.st_mtime;
}
for(i=0;i < count;i++)
for(j=i;j < count;j++){
if(filetime[i][0] < filetime[j][0]){
t = filetime[j][0];
filetime[j][0] = filetime[i][0];
filetime[i][0] = t;
strcpy(temp,filenames[j]);
strcpy(filenames[j],filenames[i]);
strcpy(filenames[i],temp);
}
}
}
else if(flag_param & PARAM_r){
flag_param -= PARAM_r;
for(i=0;i < count-1;i++)
for(j=0;j < count-1-i;j++){
if(strcmp(filenames[j],filenames[j+1])<0){
strcpy(temp,filenames[j+1]);
temp[strlen(filenames[j+1])] = '\0';
strcpy(filenames[j+1],filenames[j]);
filenames[j+1][strlen(filenames[j])] = '\0';
strcpy(filenames[j],temp);
filenames[j][strlen(temp)] = '\0';
}
}
}
else{
for(i=0;i < count-1;i++)
for(j=0;j < count-1-i;j++){
if(strcmp(filenames[j],filenames[j+1])>0){
strcpy(temp,filenames[j+1]);
temp[strlen(filenames[j+1])] = '\0';
strcpy(filenames[j+1],filenames[j]);
filenames[j+1][strlen(filenames[j])] = '\0';
strcpy(filenames[j],temp);
filenames[j][strlen(temp)] = '\0';
}
}
}
// Calculate the total consumption total
if(flag_param & PARAM_A)
{
for(i = 0;i<count;i++)
{
stat(filenames[i],&name);
total = total + name.st_blocks/2;
}
}
else
{
for(i = 0;i<count;i++)
{
stat(filenames[i],&name);
if(filenames[i][2] != '.')
{
total = total + name.st_blocks/2;
}
}
}
printf("\n");
printf("\n Total usage :%d",total);
printf("\n%s:\n",path);
for(i = 0;i < count;i++)
{
stat(filenames[i],&buf);
if(S_ISDIR(buf.st_mode))
{
len = strlen(filenames[i]);
//-R It's just ./ The root directory opens , other ../ ./. Wait, the directory doesn't open
if((filenames[i][len-1] =='.' && filenames[i][len-2] == '/')||(filenames[i][len-1] == '.' && filenames[i][len-2] == '.' && filenames[i][len-3] == '/'))
continue;
strncpy(muluname[y],filenames[i],len);
len = strlen(muluname[y]);
muluname[y][len] = '/';
muluname[y][len+1] = '\0';
y++;
}
display(flag_param,filenames[i]);
}
for(i = 2;i < y; i++)
{
list_dir(muluname[i],flag_param);
}
}
void list_dir(char *pathname,int param){
char nextpath[PATH_MAX+1];
int len=0;
DIR *ret_opendir = opendir(pathname);// Open Directory
if(ret_opendir == NULL)
error_printf("opendir");
printf("\n%s:\n",pathname);// Show pathname The path of
display_DIR(ret_opendir,34);// Show pathname Names of all non hidden files in the directory
//display(param,pathname);
struct dirent*ret_readdir = NULL;// Definition readdir The struct variable returned by the function
while((ret_readdir = readdir(ret_opendir))!=NULL)// Determine whether to read the end of the directory
{
char *filename = ret_readdir->d_name;// Get the file name
int end=0;// Optimize the display path ( Handle ./text/ And ./text)
while(pathname[end])
end++;
strcpy(nextpath,pathname);
if(pathname[end-1]!='/')
strcat(nextpath,"/");
strcat(nextpath,filename);
struct stat file_message = {
};// Definition stat Function returns the struct variable
int ret_stat = lstat(nextpath,&file_message);// Get file information
len = strlen(filename);
if(ret_stat == -1)//stat If the file is read incorrectly, a prompt message will be displayed
printf("%s error!",filename);
else if(S_ISDIR(file_message.st_mode) && filename[0] != '.')// Screening ‘.''..' With hidden files
{
list_dir(nextpath,param);
}
}
closedir(ret_opendir);
}
The idea here is to use the method of recursive traversal of the previous root order , To prevent stack explosion during root directory traversal .
ls -r
Sort by the length of the file name .
else if(flag_param & PARAM_r){
flag_param -= PARAM_r;
for(i=0;i < count-1;i++)
for(j=0;j < count-1-i;j++){
if(strcmp(filenames[j],filenames[j+1])<0){
strcpy(temp,filenames[j+1]);
temp[strlen(filenames[j+1])] = '\0';
strcpy(filenames[j+1],filenames[j]);
filenames[j+1][strlen(filenames[j])] = '\0';
strcpy(filenames[j],temp);
filenames[j][strlen(temp)] = '\0';
}
}
}
ls -t
Sort by parsing the file time information .
if(flag_param & PARAM_T){
flag_param -= PARAM_T;
for(i=0;i<count;i++){
stat(filenames[i],&buf);
filetime[i][0] = buf.st_mtime;
}
for(i=0;i < count;i++)
for(j=i;j < count;j++){
if(filetime[i][0] < filetime[j][0]){
t = filetime[j][0];
filetime[j][0] = filetime[i][0];
filetime[i][0] = t;
strcpy(temp,filenames[j]);
strcpy(filenames[j],filenames[i]);
strcpy(filenames[i],temp);
}
}
}
When sorting, you should also sort the corresponding files .
File names are output in different colors
First understand linux The meaning of color in
| Color categories | meaning |
|---|---|
| white | Ordinary documents |
| blue | Catalog |
| green | Executable file |
| red | Compressed files |
| The light blue | Link to the file |
| Flashing red | There is a problem with the linked file |
| yellow | Device file |
| gray | Other documents |
Use sprintf Function to change the color
sprintf(colorname,"\033[%dm%s\033[0m",filecolor,ret_readdir->d_name);
| F( The foreground ) | B( Background color ) | Color |
|---|---|---|
| 30 | 40 | black |
| 31 | 41 | red |
| 32 | 42 | green |
| 33 | 43 | yellow |
| 34 | 44 | blue |
| 35 | 45 | Purplish red |
| 36 | 46 | Bluish green |
| 37 | 47 | white |
shielding ctrl + c Kill the program
Here we use signal Function to implement .
1.signal( Parameters 1, Parameters 2);
Parameters 1:: The signal we're going to process ( System defined macros ). The signal of the system can be typed into the terminal kill -l see ( common 64 individual ).
Parameters 2: The way we have to deal with ( Is it the system default, ignore or capture ).
2. The header file :#include<signal.h>
3. The functionality :
4. Concrete realization :
signal(SIGINT,Signhandler);
int main(int argc,char*argv[]){
signal(SIGINT,Signhandler);
printf(" Get the signal %d, Jump out of ...\n",signum);
exit(1);
}
for instance
#include<stdio.h>
#include<signal.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
void signalhander(int signum){
printf("get signal %d",signum);
}
int main(int argc,char* argv[]){
//signal(SIGINT,signalhander);
int i=0;
int a[10];
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
return 0;
}
When we run this program, we use ctrl + c You can directly kill the program 
But when used signal Function, we can't jump out of the program 
The above is for me to my_ls Summary , I hope you can give me some advice , thank you .
边栏推荐
- The first week of C language learning - the history of C language
- Supplement - example of integer programming
- Thesis reduction
- Log management
- 2021-06-02
- Brief description of tenant and multi tenant concepts in cloud management platform
- word中插入度的方法
- 2021-06-02
- Replication of complex linked list
- 【论文阅读】Single- and Cross-Modality Near Duplicate Image PairsDetection via Spatial Transformer Compar
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
HowNet and Wanfang database download papers for free ----- several times faster than connecting to the school intranet (some schools Wanfang database does not support downloading)
KMEANS 实现
Analysis of PHP keyword replacement classes (avoid repeated replacement, keep and restore the original links)
指针总结
爬取常见英文名
Replication of complex linked list
Chuanyin holdings disclosed that it was prosecuted by Huawei: a case has been filed, involving an amount of 20million yuan
DRF use: get request to get data (small example)
Pointer summary
EXE程序加密锁
const小结
Common Oracle statements
最大子段和 Go 四种的四种求解
OpenCV(四)——图像特征与目标检测
Leetcode 226 flip binary tree (recursive)
TP5 paging some small points
Gpt-2 text generation
Firefox old version
Product axure9 English version, using repeater repeater to realize drop-down multi selection box
201403-1