当前位置:网站首页>The function of extern, static, register, volatile keywords in C language; Nanny level teaching!
The function of extern, static, register, volatile keywords in C language; Nanny level teaching!
2022-07-24 07:03:00 【C language ex boyfriend】
Catalog
Preface :
stay C In language , These are the key words , They all have their own personalities .static and extern It's used a lot , especially static At school C Language tests often get .register and volatile These two keywords are seldom used , If you already know the role of these two keywords , Then Xiaobian will give you a thumb , The young man is amazing . Xiaobian himself has also been in the exam static This keyword is suffocating , To think oneself C In the case of good linguistics , see register and volatile I'm also confused , Today, I want to talk about these keywords .
One .extern
extern Declare external symbols , Used to declare that it is not in the same source file ( .c file ) The variable of , This is very similar to the reference header file , But the reference header file is limited to , Variable in .h In file , We can use #include"xxx.h", But if it's true .c Header files cannot be used in files .
See code example , Here is the case of referencing header files .

Let's demonstrate again , External variables are .c In file ;
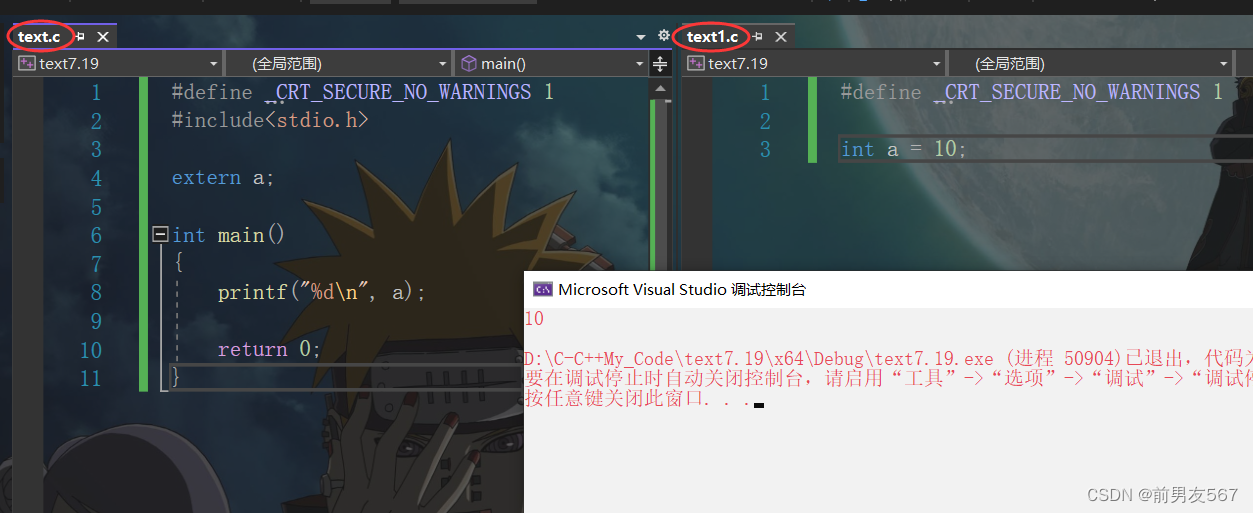
Be careful : there a adopt extern To declare , Here, the external files are pressed a, Must be a global variable , Because the scope of a local variable is only in its local scope , The life cycle of local variables is also the beginning of entering the scope and the end of leaving the scope , And global variables The scope of action is the whole project , Life cycle is the life cycle of the whole program , If a It's a local variable , Declared externally a, and a The life cycle of is over , The compiler will not compile .

extern It's the same for functions , The usage is the same as that of ordinary global variables .

But functions are generally OK without adding , But there may be an undeclared warning .
Two .static
1.static The role of is , By static Modify local variables , Will change the storage type of local variables , For ordinary local variables, they are stored in the stack , By static Decorated variables are stored in static areas . The variables stored in the static area will not be destroyed when they are out of scope , There is still a . So the life cycle of static variables is the life cycle of the whole program , Only when the program ends, the variables in the static area will be recycled . Is the variable description of the static area here very similar to the global variable , ha-ha , Yes, global variables are also stored in static areas . In fact, in addition to the static area and stack area , There's also a heap area .

Write a piece of code to see static How to prolong the life cycle of variables :
#include<stdio.h>
void text()
{
int a = 0;
a++;
printf("%d ", a);
}
int main()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
text();
}
return 0;
}Friends can calculate the running result of this code .

Are you guys right , Because of the a It's a local variable ; So every time you enter the function text(),a Variables will be recreated , So every time a The values of variables are all a=0+1; Out of function a The variable will be destroyed .
Now let's take a look at this code :
#include<stdio.h>
void text()
{
static int a = 0;
a++;
printf("%d ", a);
}
int main()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
text();
}
return 0;
}Let's calculate the result, buddy

Why is this so ?

thus it can be seen , The life cycle of local variables is extended , But the scope remains the same .
2. If static Modify global variable , What will it be like ? Let's have a look .
First, global variables have external link attributes ,static After modification , The external connection attribute becomes , Internal connection properties . This global variable can only be in its own .c See the document , Other source files cannot be accessed .

Modifying a function will also make the external connection attribute of the function become the internal connection attribute . Functions can only be in their own .c See the document , Other source files cannot be accessed .

3、 ... and .register
register be called register , The variable modified by it is called , Register variables . What is a register? Let's briefly introduce , The storage location of the computer is , Hard disk , Memory , Cache , register .

When a variable , Later, when it needs a lot of use , Every time CPU To register , Cache , Memory level by level to find , In this way, the access speed will be very slow , In this case , If we just store such variables in registers , that CPU Get it directly from the register every time , The access speed will be greatly improved . therefore register Keywords appear here , however register Modifying variables , It is only recommended to store variables in registers , It will depend on the situation , Not by register If you decorate it, you must put it in the register , Pay special attention to this . The compiler will intelligently add , The variables that need to be processed are put into registers . And being register Decorated variables cannot take addresses , Because & Only the address in memory can be retrieved , Regardless of being register Decorated variable , Is it really stored in the register , Can't take the address .
Four .volatile
volaile There are unstable , Easy to change meaning . When we have a variable that needs a lot of use , This variable will , It may be stored in registers , Now let's see , It seems nothing, but there is a certain risk , Because the code we write now is single threaded , If the code has more than one thread , In another thread, variables will be modified , and CPU Still get variables from registers , What you get is not the modified variable , Will cause problems . and volatile Is to make the modified variable not to optimize , Always in memory , Improve access to special address locations , Make subsequent access more secure . here volatile and register A little opposite , Can compare memory .
It is worth noting that ,volatile Decorated variables also remind the compiler , This variable may change later , Take care to protect . Not by volatile Modification and certain changes . This and register Very much like .
Last
Rome wasn't built in a day . Since we choose the distance , When you live up to your youth , Self-motivated forward , Every crack is an effort to reveal light , Only the ultimate struggle , To deserve the ultimate scenery . Gentlemen , See you at the top of the mountain !
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

GE口:SGMII模式和serdes模式

(static, dynamic, file) three versions of address book

MGR_ mysqlsh_ Keepalive high availability architecture deployment document

Sealos 打包部署 KubeSphere 容器平台

渗透学习-SQL注入篇-靶场篇-安全狗的安装与绕过实验(后续还会更新)
Tensorflow Einstein function

Redis 主从机制

SparkSQL核心使用,220724,
(笔记整理未完成)【图论:求单源最短路径】

STM32 ADC based on Hal library uses DMA multi-channel sampling and solves the problems encountered
随机推荐
华为专家自述:如何成为优秀的工程师
[lvgl (important)] style attribute API function and its parameters
Lambda expressions sort list objects in multiple fields
Sealos packages and deploys kubesphere container platform
处理树形结构数据
Redis basic type - ordered set Zset
Redis特殊数据类型-GEO
Jsonobject is sorted in A-Z order of key
别太在意别人的眼光,那会抹杀你的光彩
Redis distributed cache learning notes
Don't compare with anyone, just be yourself
(笔记整理未完成)【图论:求单源最短路径】
You can't satisfy everyone!
Redis基本类型-有序集合Zset
It can be written in 10 minutes -- 25~30k foreign enterprise recruitment interview questions, isn't it easy~
Don't care too much about others' eyes, it will erase your glory
Redis 哨兵机制
An AI plays 41 games, and the comprehensive performance score of Google's latest multi game decision transformer is twice that of dqn
XXL execute node error log swiping
使用root用户为创建新用户并设置密码