当前位置:网站首页>MySQL log management, backup and recovery
MySQL log management, backup and recovery
2022-06-24 14:18:00 【Kiro Jun】
MySQL Log management 、 Backup and recovery
- preparation
- One 、MySQL Log management
- Two 、MySQL Common log types
- 3、 ... and 、 Check log status
- MySQL Backup and recovery
- One 、 Introduction to data backup
- Two 、 Classification of database backup
- 3、 ... and 、MySQL Full backup and recovery
- Four 、MySQL Incremental backup and recovery
- MySQL Incremental backup
- 1. Turn on binary log function
- 2. The database or table can be fully backed up every week
- 3. Incremental backup operations can be performed every day , Generate a new binary log file ( for example mysql-bin.000002)
- 4、 Insert new data , To simulate the addition or change of data
- 5、 Generate a new binary log file again ( for example mysql-bin.000003)
- 6、 View the contents of the binary log file
- MySQL Incremental backup recovery
preparation
- install MySQL database
- Shell Script one click deployment – Source code compilation and installation MySQL
One 、MySQL Log management
- MySQL The default log for is saved in /usr/local/mysql/data
- There are two ways to open logs : Through the configuration file or through the command
- The log opened by command modification is temporary , When the service is shut down or restarted, it will shut down
- Can be found in /etc/my.cnf In the configuration file [mysqld] To modify the log 、 Turn on 、 Shut down etc
vim /etc/my.cnf
[mysqld]
......
Two 、MySQL Common log types
2.1 Error log
- Used to record when MySQL start-up 、 Error message when stopping or running , The default is on
- It can be updated by the next paragraph
vim /etc/my.cnf
log-error=/usr/local/mysql/data/mysql_error.log
# Specify the save location and file name of the log
2.2 General query log
- Used to record MySQL All connections and statements , The default is off
vim /etc/my.cnf
general_log=NO
genaral_log_file=/usr/local/mysql/data/mysql_genaral.log
2.3 Binary log (binlog)
- A statement used to record all updated data or potentially updated data , Changes to the data are recorded , Can be used for data recovery , The default is on
vim /etc/my.cnf
Opening mode :
vim /etc/my.cnf
log-bin=mysql-bin
perhaps
log_bin=mysql-bin
2.4 relay logs
- In general , It's in mysql Master slave synchronization ( Copy )、 The slave node of the read-write separation cluster is enabled
- The primary node generally does not need this log
2.5 Slow query log
- Used to record all execution times exceeding long_query_time Second statement , You can find which query statements take a long time to execute , In order to optimize , The default is off
vim /etc/my.cnf
slow_query_log=ON
slow_query_log_file=/usr/local/mysql/data/mysql_slow_query.log
long_query_time=5
2.6 Log configuration summary
1. # modify my.cnf The configuration file
# Error log
log-error=/usr/local/mysql/data/mysql_error.log
# General query log
general_log=ON
general_log_file=/usr/local/mysql/data/mysql_general.log
# Binary log
log-bin=mysql-bin
# Slow query log
slow_query_log=ON
slow_query_log_file=/usr/local/mysql/data/mysql_slow_query.log
long_query_time=5
2. # again mysql service
systemctl restart mysqld.service


3、 ... and 、 Check log status
3.1 Check whether the general query log is enabled
mysql -u root -p
show variables like 'general%';

3.2 Check whether the binary log is enabled
show variables like 'log_bin%';

3.3 Check whether the slow query log function is enabled
show variables like '%slow%';

3.4 View slow query time settings
show variables like 'long_query_time';

3.5 Set the method of starting slow query in the database
set global slow_query_log=ON;
# This method restarts the service and fails
MySQL Backup and recovery
One 、 Introduction to data backup
1.1 summary
- The main purpose of backup is disaster recovery
- It can also be used to test applications 、 Roll back data modification 、 Query historical data 、 Audit, etc
- In the production environment , Data security is crucial
- Any loss of data can have serious consequences
1.2 Severity of backup
- In the enterprise , The value of data is crucial , Data guarantee the normal operation of enterprise business
- therefore , Data security and reliability are the top priority of operation and maintenance , Any data loss may cause serious consequences to the enterprise
- Usually , There are several reasons why the data are all :
- Program error
- Think the operation is wrong
- Arithmetic error
- Disk failure
- disaster ( fire 、 The earthquake 、 Theft, etc )
Two 、 Classification of database backup
2.1 Classify from a physical and logical point of view
2.1.1 The physical backup
- Physical backup is the physical backup of the database operating system ( Such as data files 、 Log files, etc ) Backup of
- Physical backup is suitable for large and important databases that need to be restored quickly in case of problems
- Physical backup can be divided into cold backup ( Offline backup )、 Hot backup ( Online backup ) Hewen backup
Physical backup method :
- Cold backup ( Offline backup ): When closing the database
- Hot backup ( Online backup ): The database is running , Database dependent log files
- Warm backup : Database lock table ( Not writable but readable ) Backup operation in the state of
2.1.2 Logical backup
- For database logic components ( Such as : Database objects such as tables ) Backup of
2.2 Classify from the perspective of database backup strategy
1) Full backup : Every time you make a full backup of the database
For the entire database 、 Backup of database structure and file structure
What you save is the database at the time of backup completion
The difference between backup and incremental backup is
advantage : Backup and recovery is simple and convenient shortcoming : There's a lot of duplication of data 、 It takes up a lot of backup space and takes a long time for backup and recovery
2) Differential backup : Back up files that have been modified since the last full backup
- When recovering data , Just restore the last full backup and the last differential backup
3) Incremental backup : Only files modified after the last full backup or incremental backup will be backed up
- When recovering data , From the last full backup to the last incremental backup All increments are restored in sequence , For example, the backup data in the middle is damaged , Will result in the loss of data

3、 ... and 、MySQL Full backup and recovery
InnoDB The database of the storage engine is stored in three files on disk :
- db.opt( Table properties file )
- Table name .frm( Table structure file )
- Table name .ibd( Table data file ).
Experimental environment
| host | operating system | IP Address | The tools needed / Software / Installation package |
|---|---|---|---|
| MySQL | CentOS7 | 192.168.61.11 | mysql-boost-5.7.20.tar.gz |

3.1 Physical cold backup and recovery
- The database is closed at the time of backup , Directly package database files
- Fast backup , Recovery is also the simplest
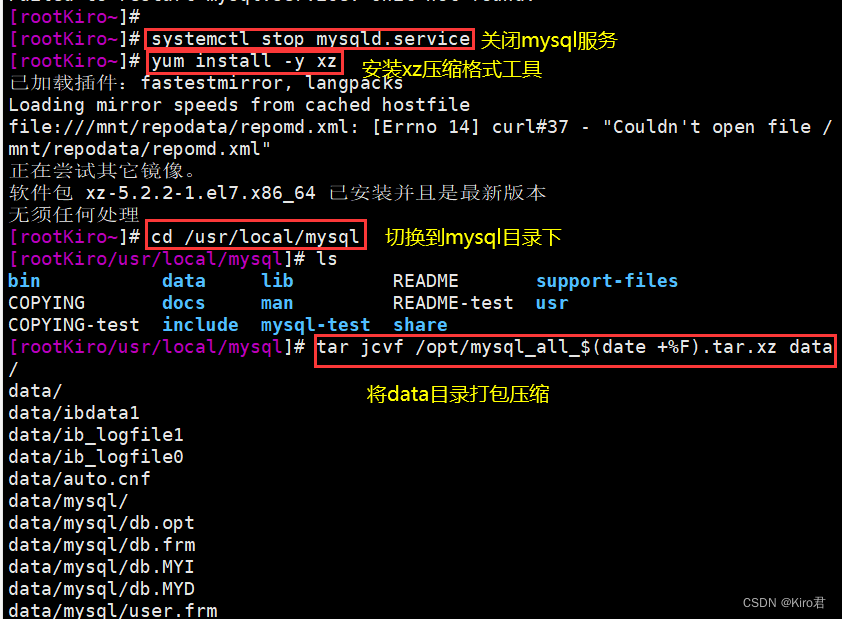
# close mysql, Backup data Catalog
systemctl stop mysqld
yum -y install xz
cd /usr/local/mysql
# Compressed backup data Catalog
tar Jcvf /opt/mysql_all_$(date +%F).tar.xz data/
- # Sign in mysql, Delete kgc library
systemctl start mysqld.service
mysql -u root -p123123
- # Unzip the previously backed up database data Catalog , No need to delete the original directory , Will automatically replace
cd /opt
ls
cd /usr/local/mysql
tar Jxvf /opt/mysql_all_2021-11-28.tar.xz -C ./
# Restart the service to view the deleted library
1) close mysql, Backup data Catalog
2) Sign in mysql, Delete school library 
3) Unzip the previously backed up database data Catalog , No need to delete the original directory , Will automatically replace 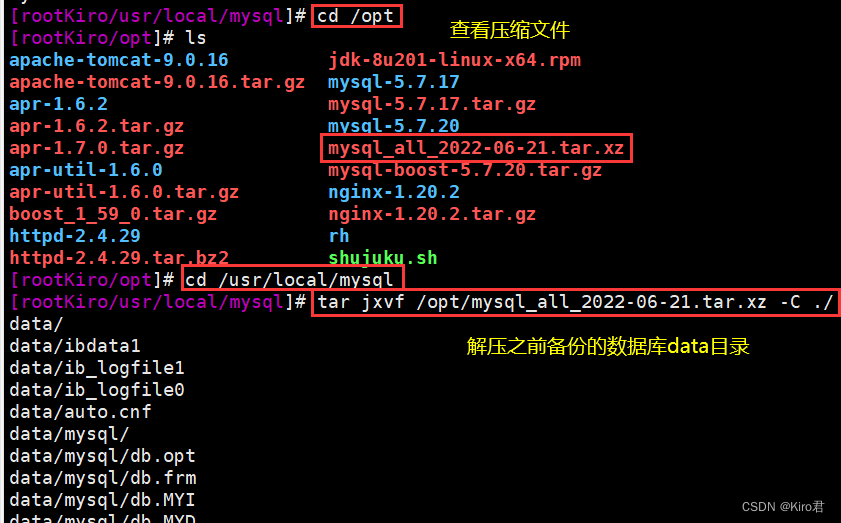
4) Restart the service to view the deleted library

3.2 Special backup tool mydump and mysqlhotocopy
- mysqldump Common logical backup tools
- mysqlhotcopy Only have backup MyISAM and ARCHIVE surface
Law 1 : Full backup of one or more complete libraries ( Contains all the tables in it )
# What is exported is the database script file
mysqldump -u root -p[ password ] --databases Library name 1 [ Library name 2] … > / Backup path / Backup filename .sql
Example : Back up single and multiple libraries
mysqldump -uroot -p --databases kgc > /opt/school.sql
mysqldump -uroot -p --databases mysql kgc > /opt/mysql-kgc.sql

Law two : Full backup MySQL All libraries in the server
mysqldump -u root -p[ password ] --all-databases > / Backup path / Backup filename .sql
Example : Back up all libraries
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases > /opt/all.sql

Law three : Full backup of some tables in the specified library
mysqldump -u root -p[ password ] Library name [ Table name 1] [ Table name 2] … > / Backup path / Backup filename .sql
Example : Backup school Two tables in the library
mysqldump -uroot -p kgc [-d] info1 info2 > /opt/mysql_bak/kgc_info1_info2.sql
## -d Represents replication data table structure nothing -d Backup together with data

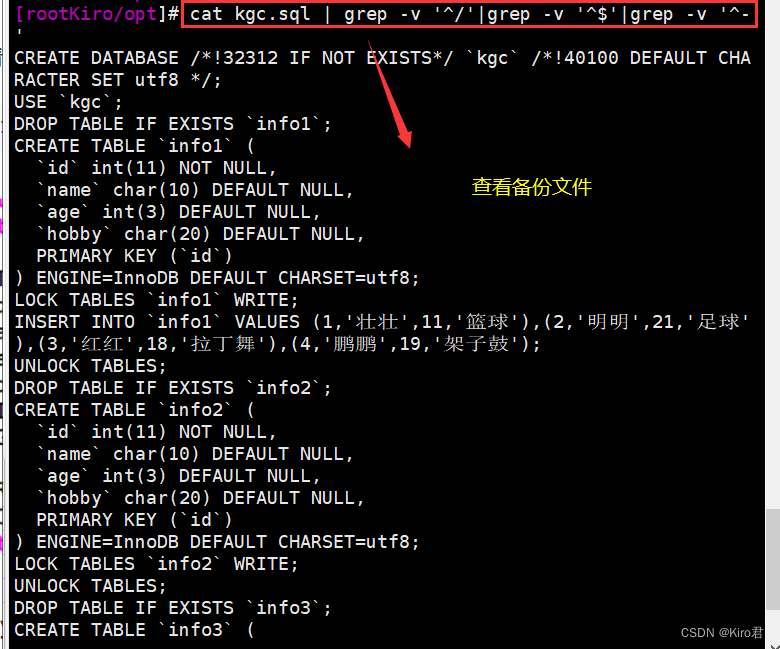
Law four : View backup files
cat kgc.sql | grep -v '^/'|grep -v '^$'|grep -v '^-'
3.3 MySQL Full backup ( Use interaction free )
systemctl start mysqld
Recover database
mysql -u root -p -e 'drop database kgc;'
#“-e” Options , Used to specify the connection MySQL Command executed after , Automatically exit after the command is executed
mysql -u root -p -e 'show databases;'
# recovery kgc database
mysql -u root -p < /opt/kgc.sql
mysql -u root -p -e 'show databases;'

Restore data table
When the backup file contains only the backup of tables , Without the statement of the created library , The library name must be specified when performing the import operation , And the target library must exist .
mysqldump -uroot -p school info1 info2 > /opt/mysql_bak/school_info1_info2.sql
1. # Delete school Medium info1 surface
mysql -u root -p -e 'drop table school.info1;'
mysql -u root -p -e 'show tables from school;'
2. # recovery school The table in the library
mysql -u root -p school < /opt/mysql_bak/school_info1_info2.sql
mysql -u root -p -e 'show tables from school;'
Delete kgc Medium info1 surface

recovery kgc In the table 
Four 、MySQL Incremental backup and recovery
MySQL Incremental backup
1. Turn on binary log function
vim /etc/my.cnf
[mysqld]
log-bin=mysql-bin
# Specify binary log (binlog) The record format of is MIXED
binlog_format = MIXED
server-id = 1

Binary log (binlog) Yes 3 Two different record formats :
- STATEMENT( be based on SQL sentence )
- ROW( Based on line )
- MIXED( Mixed mode ), The default format is STATEMENT
# As long as you restart, the binary file will be automatically generated
systemctl start mysqld
ls -l /usr/local/mysql/data/mysql-bin.*

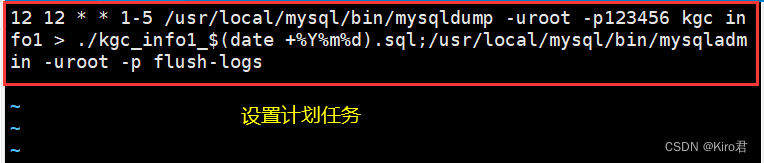
2. The database or table can be fully backed up every week
# Backup the specified table
mysqldump -u root -p school info1 > /opt/school_info1_$(date +%F).sql
mysqldump -u root -p --all-databases school > /opt/school_$(date +%F).sql
3. Incremental backup operations can be performed every day , Generate a new binary log file ( for example mysql-bin.000002)
Complete the full backup first ( On the basis of creating tables and Libraries )
Generating new binaries ( Incremental backup operations can be performed every day )
mysqladmin -uroot -p123456 flush-logs
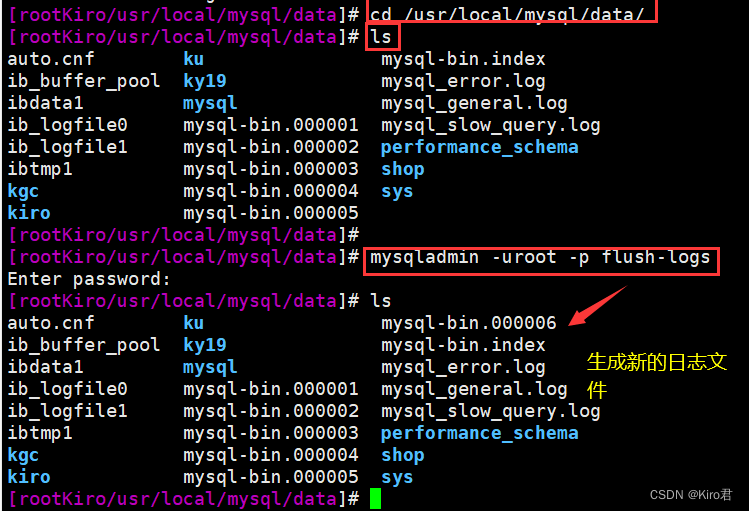
4、 Insert new data , To simulate the addition or change of data
mysql -uroot -p123123
use kgc;
insert into info1 values(3,'user3','male','game');
insert into info1 values(4,'user4','female','reading');

5、 Generate a new binary log file again ( for example mysql-bin.000003)
mysqladmin -uroot -p123456 flush-logs

# Previous steps 4 The database operation will be saved to mysql-bin.000006 In file , After that, if the database data changes again, it is saved in mysql-bin.000007 In file
6、 View the contents of the binary log file
cp /usr/local/mysql/data/mysql-bin.000007 /opt/
mysqlbinlog --no-defaults --base64-output=decode-rows -v /opt/mysql-bin.000007
#–base64-output=decode-rows: Use 64 Bit encoding mechanism to decode and read by line
#-v: Show details

MySQL Incremental backup recovery
1、 General recovery
Restore all backup binary log contents
(1) Simulate recovery steps for lost changed data
mysql -uroot -p123456
use kgc;
delete from info1 where id=2;
delete from info1 where id=3;
select * from kgc;
quit
mysqlbinlog --no-defaults /usr/local/mysql/data/mysql-bin.000004 | mysql -u root -p
mysql -uroot -p123456 -e "select * from kgc.info1;"

2、 Simulate recovery steps for all lost data ( Is essentially the same , Note the log date )
mysql -uroot -p123456
use kgc;
drop table info1;
quit
mysqlbinlog --no-defaults /usr/local/mysql/data/mysql-bin.000014 | mysql -uroot -p123456;
mysql -uroot -p123456 -e "select * from kgc.info1;"

Breakpoint recovery
mysqlbinlog --no-defaults --base64-output=decode-rows -v /opt/mysql-bin.000002
Use the same as just 64 Bit encoding mechanism to decode and read binary files by line 000007 Details of
(1) Based on location recovery
- The database may have wrong operations and correct operations at a certain point in time
- You can skip the wrong operation based on the precise position
- A node before the error node occurs , Stop at the position of the last correct operation
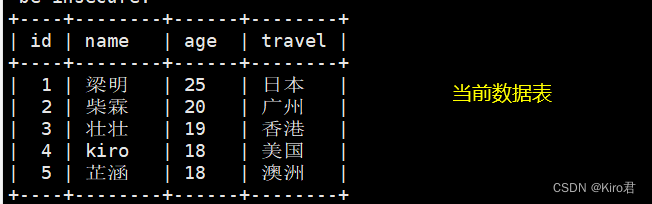
# Refresh to generate a new binary log file
mysqladmin -uroot -p1234566 flush-logs;
## Enter into data Catalog
cd /usr/local/mysql/data
## View binary log files
mysqlbinlog --no-defaults --base64-output=decode-rows -v mysql-bin.000015
example :
mysql -uroot -p123123 -e “select * from SCHOOL.CLASS1;”
mysqlbinlog --no-defaults --start-position=‘609’ /opt/mysql-bin.000002 | mysql -uroot -p123123
mysql -uroot -p123123 -e “select * from SCHOOL.CLASS1;”
(2) Based on point in time recovery
# Only restore to 0:39:13 Previous data , I.e. no recovery “user4” The data of
example : Clear the watch first info1, Convenient experimental
mysql -uroot -p123456 -e "truncate table kgc.info1;"
mysql -uroot -p123456 -e "select * from kgc.info1;"
mysqlbinlog --no-defaults --stop-datetime='2022-06-22 0:39:13' /opt/mysql-bin.000007 |mysql -uroot -p123456
mysql -uroot -p123456 -e "select * from SCHOOL.CLASS1;"
# Restore only “user4” The data of , skip “user3” Data recovery ( Almost the same )
mysqlbinlog --no-defaults --start-datetime='2022-06-22 0:39:13' /opt/mysql-bin.000007|mysql -uroot -p
边栏推荐
- Return to new list
- 4个不可不知的“安全左移”的理由
- 10_那些格調很高的個性簽名
- GO语言-init()函数-包初始化
- 3环杀掉360安全卫士进程
- Rasa 3. X learning series - it is a great honor to be a source code contributor of Rasa contributors, and to build and share the rasa community with rasa source code contributors all over the world!
- Overview of SAP marketing cloud functions (III)
- How to avoid placing duplicate orders
- v-for 中 key的作用和原理
- Kotlin shared mutable state and concurrency
猜你喜欢

Daily knowledge popularization

如何解决 Iterative 半监督训练 在 ASR 训练中难以落地的问题丨RTC Dev Meetup
![Generate binary tree according to preorder & inorder traversal [partition / generation / splicing of left subtree | root | right subtree]](/img/f7/8d026c0e4435fc8fd7a63616b4554d.png)
Generate binary tree according to preorder & inorder traversal [partition / generation / splicing of left subtree | root | right subtree]

How to avoid placing duplicate orders

【LeetCode】10、正则表达式匹配

unity 等高线创建方法

Second, the examinee must see | consolidate the preferred question bank to help the examinee make the final dash

Antd checkbox, limit the selected quantity

数字臧品系统开发 NFT数字臧品系统异常处理源码分享

How to solve the problem that iterative semi supervised training is difficult to implement in ASR training? RTC dev Meetup
随机推荐
Unity 热力图建立方法
【深度学习】NCHW、NHWC和CHWN格式数据的存储形式
**Puzzling little problem in unity - light and sky box
Convolution kernel and characteristic graph visualization
Jerry's serial port receiving IO needs to set the digital function [chapter]
JS remove string spaces
Kunpeng arm server compilation and installation paddlepaddle
Overview of SAP marketing cloud functions (III)
Three efficient programming skills of go language
c语言---18 函数(自定义函数)
如何避免下重复订单
tongweb使用之端口冲突处理办法
Online text entity extraction capability helps applications analyze massive text data
文本对比学习综述
Jericho turns on shouting in all modes to increase mic automatic mute [chapter]
greendao使用问题
leetcode:1504. 统计全 1 子矩形的个数
puzzle(016.2)指画星河
鲲鹏arm服务器编译安装PaddlePaddle
Simulated 100 questions and answers of fluorination process examination in 2022