当前位置:网站首页>Seven parameters of thread pool and custom thread pool
Seven parameters of thread pool and custom thread pool
2022-06-22 06:18:00 【Kuxiaoya】
The first part describes three methods of thread pool , First review the following :
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); Single thread
Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5); Fixed number of threads
Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); Buffer pool , Scalable
Let's see “ Three ways ” Source code analysis , In this way, we can better understand “ Seven parameters ”:
//Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); Single thread
// Source code analysis :
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
//Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5); Fixed number of threads
// Source code analysis :
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
//Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); Buffer pool , Scalable
// Source code analysis :
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,//21 Billion OOM:Out Of Memory, out of memory
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}
Source code analysis :( There are three methods ThreadPoolExecutor)
Continue clicking ThreadPoolExecutor , View source code :
// The essence : ThreadPoolExecutor
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,// Core thread pool size
int maximumPoolSize,// Maximum core thread pool size
long keepAliveTime,// If no one calls after the timeout, it will be released
TimeUnit unit, // Timeout unit
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,// Blocking queues
ThreadFactory threadFactory,// Thread factory : Create thread of , Generally don't move
RejectedExecutionHandler handler// Refusal strategy ) {
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.acc = System.getSecurityManager() == null ?
null :
AccessController.getContext();
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
this.workQueue = workQueue;
this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.handler = handler;
}
Get seven parameters :
int corePoolSize,// Core thread pool size
int maximumPoolSize,// Maximum core thread pool size
long keepAliveTime,// If no one calls after the timeout, it will be released
TimeUnit unit, // Timeout unit
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,// Blocking queues
ThreadFactory threadFactory,// Thread factory : Create thread of , Generally don't move
RejectedExecutionHandler handler// Refusal strategy
Custom thread pool :
package pool;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Custom thread pool ! Work ThreadPoolExecutor( Seven parameters )
ExecutorService threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
2,
5,
3,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(3),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
// There are four rejection strategies , Use what suits you !
new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy() // The queue is full , Try to compete with the earliest , It doesn't throw an exception !
);
try {
// Maximum bearing capacity : Deque + max
// exceed RejectedExecutionException Throw a reject execution exception
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
// After using the thread pool , Use thread pool to create threads
threadPool.execute(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" OK!");
});
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// Out of thread pool , Program end , Close thread pool
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
}
Four rejection strategies :

1、new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()
The bank is full , There are people coming in , Just don't deal with this person ,
Throw a reject execution exception RejectedExecutionException
Running results :
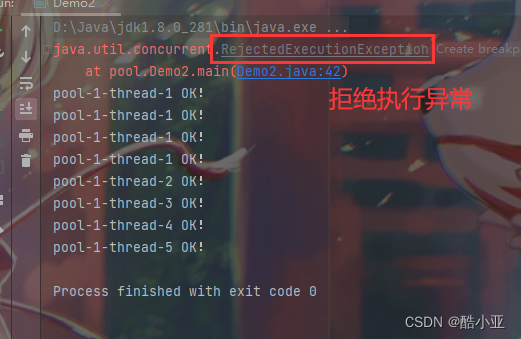
2、new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy()
Where you come from, where you go !
Running results :

3、new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy()
The queue is full , Lose the job , Does not throw an exception
Running results :

4、new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy()
The queue is full , Try to compete with the earliest , It doesn't throw an exception !
Running results :

边栏推荐
- 性能对比分析
- Use of stopwatch
- 单细胞论文记录(part9)--Spatial charting of single-cell transcriptomes in tissues
- Geoswath plus technology and data acquisition and processing
- R language observation log (part24) -- writexl package
- 单细胞论文记录(part13)--SpaGCN: Integrating gene expression, spatial location and histology to ...
- idea本地运行scope
- h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16) 详细解读以及为什么要将hashCode值右移16位并且与原来的hashCode值进行异或操作
- SQL 注入漏洞(十四)xff 注入攻击
- Vulnérabilité à l'injection SQL (XIII) injection base64
猜你喜欢

Subqueries in sqlserver

ReadWriteLock

Little bear school bearpi HM micro officially integrated into openharmony trunk

Shengxin visualization (Part2) -- box diagram

Logback custom pattern parameter resolution

Geoswath plus technology and data acquisition and processing

动态创建对象执行方法

SQL 注入漏洞(十三)base64注入

Pyg tutorial (7): dissecting neighborhood aggregation

线程和进程的区别
随机推荐
Geoswath plus technology and data acquisition and processing
ForkJoinPool
文献记录(part106)--GRAPH AUTO-ENCODER VIA NEIGHBORHOOD WASSERSTEIN RECONSTRUCTION
生信可视化(part4)--相关性图
单细胞论文记录(part12)--Unsupervised Spatial Embedded Deep Representation of Spatial Transcriptomics
Upload file prompt 413 request entity too large error
tab[i = (n - 1) & hash] 的详细解读
matlab 的离散pid控制
Vulnérabilité à l'injection SQL (XIII) injection base64
pip升级难题(已解决)You are using pip version 19.0.3, however version 22.1.2 is available.
R language observation log (part24) -- writexl package
生信文献学习(part1)--PRECISE: a ... approach to transfer predictors of drug response from pre-clinical ...
SQL injection vulnerability (XI) wide byte injection
postgresql数据库中根据某个字段判断存在则更新(update)操作,不存在则插入(insert)
simulink中搭建专家pid控制
动态创建对象执行方法
Huiding technology gr551x series development board supports openharmony
SQL injection vulnerability (XIII) Base64 injection
Flink核心功能和原理
swagger常用注解汇总