当前位置:网站首页>山东大学增强现实实验四
山东大学增强现实实验四
2022-06-11 08:59:00 【小白不吃肉】
注意:本人尚处在opencv的入门学习阶段,本博客仅为个人学习笔记见解,如有不当,欢迎指出
题目
(实验/理论)平面标志物的视觉跟踪,要求:
- 选择一个标志物,可以是人工标志物,也可以是自然标志物;实现和实验二相同的效果。
- 用手机或摄像头拍摄标志物的影像,建议读取视频流中的影像;
- 写一个视觉算法获得标志物与相机的相对位姿;
- 测量算法的帧率;
- 添加虚拟物体;
- 算法自己完成,不得使用ARCore/easyAR等现成SDK。可以使用opencv中自带的函数。
注:使用OpenCV/OpenGL来实现一些滤波、矩阵运算、优化、画图等低层的算法。
实验思路
步骤:识别标志物→空间注册→跟踪→绘图
识别标志物
可以使用的方法有:模板匹配、前景分离、边缘提取、特征点匹配、训练级联分类器
模板匹配
模板匹配是一种用于在较大图像中搜索和查找模板图像位置的方法。它只是将模板图像滑动到输入图像上(就像在2D卷积中一样),然后在模板图像下比较模板和输入图像的拼图。
模板匹配具有自身的局限性,主要表现在它只能进行平行移动,若原图像中的匹配目标发生旋转或大小变化,该算法无效。
前景分离
可以用于车辆识别,就是在视频中有动的物体和静止的物体,通过前景分离,可以把静的物体过滤掉,实现对动的车辆的识别
边缘提取
提取图片的边缘,如果视频背景是纯色的,可以用这个方法提取标志物,但是如果视频中还有其他物体,则还需要再进行处理
特征点匹配(本实验使用)
这是我这次实验使用的方法。因为匹配了特征点后,物体的旋转、平移都是可以检测到的,方便在这个基础上绘制虚拟物体
训练级联分类器
这个方法尝试过,但最后因为匹配结果比较差,就放弃了。这个方法就是对标志物进行样本采集,然后训练一个分类器,在视频中调用该分类器对每帧进行识别,很多人脸识别、车辆识别是用的这个方法
空间注册
将视频第一帧的图像与标志物图像进行特征匹配,找到标志物特征点对应在相机图像上的坐标,跟踪这些坐标的移动
跟踪
本实验采用的是Meanshift跟踪方法,因为它比较简单,而且可以实现想要的效果
原理:
由于相邻两帧之间目标的偏移量非常小,而当前帧F1的目标框B1已知,所以一种启发式的做法是在下一帧F2中依旧框选已知的B1区域,根据F2中B1区域和F1中B1区域的相似性推断出目标框所需的偏移量,进而得到F2的目标框B2,这就是MeanShift算法所需要解决的事
绘图
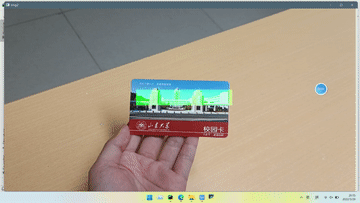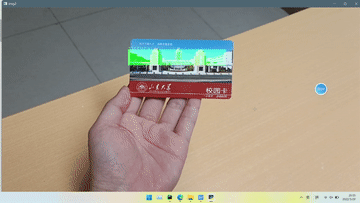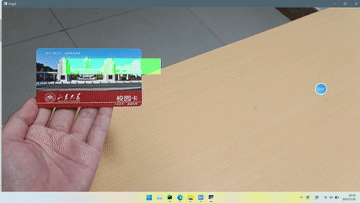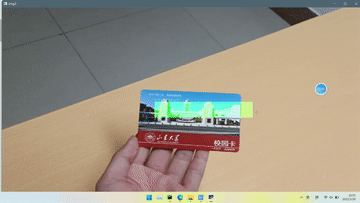
本实验只是绘制了一个半透明矩形在标志物上方,因为找不到使用opencv绘制3D物体的方法,好像用openGL可以
另外,如果使用相机校准棋盘格的方法,也可以绘制出一个立体图形,参考:Docs » 相机校准和3D重建 » 7_2_姿态估计
代码
import numpy as np
import cv2 as cv
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 视频的位置
cap = cv.VideoCapture(r"C:\Users\ccy\Desktop\video3.mp4")
# 拍摄第一帧
ret, first_frame = cap.read()
# 对第一帧进行特征匹配
if ret:
img1 = cv.cvtColor(first_frame, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 训练图像
img_train = cv.imread(r'C:\Users\ccy\Desktop\1.png')
img2 = cv.cvtColor(img_train, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 初始化ORB检测器
orb = cv.ORB_create()
# 基于ORB找到关键点和检测器
kp1, des1 = orb.detectAndCompute(img1, None)
kp2, des2 = orb.detectAndCompute(img2, None)
# 创建BF匹配器的对象
# 第一个参数normType表示距离度量方法
# 第二个参数crossCheck是布尔型变量,如果为true,表示进行双向匹配,这样就可以增强匹配鲁棒性
bf = cv.BFMatcher(cv.NORM_HAMMING, crossCheck=True)
# 匹配描述符,返回最佳匹配
matches = bf.match(des1, des2)
leftQueryIdx = matches[0].queryIdx
bottomQueryIdx = matches[0].queryIdx
for mat in matches:
# Get the matching keypoints for each of the images
img1_idx = mat.queryIdx
img2_idx = mat.trainIdx
# x - columns
# y - rows
# Get the coordinates
(x1, y1) = kp1[img1_idx].pt
# 找到矩形最左上角的点和最右下角的点,这个可能得根据不同的标志物稍作调整
if y1 < kp1[leftQueryIdx].pt[1]:
leftQueryIdx = img1_idx
if x1 > kp1[bottomQueryIdx].pt[0]:
bottomQueryIdx = img1_idx
# (x2, y2) = kp2[img2_idx].pt
# print("kp1[img1_idx].pt[0]:", kp1[img1_idx].pt[0])
# print("kp1[img1_idx].pt[1]:", kp1[img1_idx].pt[1])
# print("(x2,y2):", (x2, y2))
# -1是thickness参数,即CV_FILL,其结果是使用与边一样的颜色填充圆内部
# 下面这行代码会标记出匹配到的特征点
# first_frame = cv.circle(first_frame, (int(x1), int(y1)), 5, (255, 0, 0), -1)
# print("kp1[leftQueryIdx].pt", kp1[leftQueryIdx].pt)
# print("kp1[bottomQueryIdx].pt", kp1[bottomQueryIdx].pt)
leftIntCd = tuple(map(lambda x: int(x), kp1[leftQueryIdx].pt))
bottomIntCd = tuple(map(lambda x: int(x), kp1[bottomQueryIdx].pt))
# 对后面每帧进行meanshift跟踪
(x, y) = leftIntCd
w = bottomIntCd[0] - leftIntCd[0]
h = bottomIntCd[1] - leftIntCd[1]
track_window = (x, y, w, h)
# 设置初始ROI来追踪
roi = first_frame[y:y + h, x:x + w]
hsv_roi = cv.cvtColor(roi, cv.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
mask = cv.inRange(hsv_roi, np.array((0., 60., 32.)), np.array((180., 255., 255.)))
roi_hist = cv.calcHist([hsv_roi], [0], mask, [180], [0, 180])
cv.normalize(roi_hist, roi_hist, 0, 255, cv.NORM_MINMAX)
# 设置终止条件,可以是10次迭代,也可以至少移动1 pt
term_crit = (cv.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS | cv.TERM_CRITERIA_COUNT, 10, 1)
while (1):
retOtherFrame, frame = cap.read()
if retOtherFrame:
# 测量帧率
loop_start = cv.getTickCount()
# 灰度处理
hsv = cv.cvtColor(frame, cv.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
dst = cv.calcBackProject([hsv], [0], roi_hist, [0, 180], 1)
# 应用meanshift来获取新位置
ret, track_window = cv.meanShift(dst, track_window, term_crit)
# 在图像上绘制
x, y, w, h = track_window
# 绘制半透明矩形
blk = np.zeros(frame.shape, np.uint8)
cv.rectangle(blk, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 255, 0), -1) # 注意在 blk的基础上进行绘制;
cv.putText(blk, 'virtural', (x, y), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX_SMALL, 1.3, (0, 255, 0), 1)
img2 = cv.addWeighted(frame, 1.0, blk, 0.8, 1)
# 中间测帧率的代码段
loop_time = cv.getTickCount() - loop_start
total_time = loop_time / (cv.getTickFrequency()) # 使用getTickFrequency()更加准确
running_FPS = int(1 / total_time) # 帧率取整
print("running_FPS:", running_FPS)
# 显示图片
cv.namedWindow('img2', cv.WINDOW_FREERATIO)
cv.imshow('img2', img2)
k = cv.waitKey(1) & 0xff
if k == 27:
break
else:
break
效果
参考资料
边栏推荐
- Analysis of EN 45545 R24 oxygen index test method
- Sword finger offer II 036 Postfix Expression
- 【新手上路常见问答】关于数据可视化
- BS 7176软垫家具阻燃防火测试
- 1721. exchange nodes in the linked list
- 20. valid brackets
- 智能控制理论小题库
- 硅树脂油漆申请美国标准UL 790 Class A 合适吗?
- (2) Analysis of AAC source code from the perspective of architecture design - my livedata
- 203. remove linked list elements
猜你喜欢

领导让我重写测试代码,我也要照办嘛?

Typescript high level feature 1 - merge type (&)

Getting started with Zipkin
How to apply for BS 476-7 sample for display? Is it the same as the display

leetcode - 739. Daily temperature

What is the process of en 1101 flammability test for curtains?

MATLAB R2022a 安装教程

Screaming Frog Log File Analyser 中文版安装教程

哪些Apple设备支持这次系统更新?来看你的旧Apple设备支持最新系统吗

【C语言-数据存储】数据在内存中是怎样存储的?
随机推荐
File system check of the root filesystem failed
【237. 删除链表中的节点】
SQL basic query
How to apply for ASTM E108 flame retardant test for photovoltaic panels?
显示屏DIN 4102-1 Class B1防火测试要求
19. delete the penultimate node of the linked list
Usage and difference between map and set in JS
Android 面试笔录(精心整理篇)
Sword finger offer 62 The last remaining number in the circle
c的printf相关
领导让我重写测试代码,我也要照办嘛?
Are the two flame retardant standards of European furniture en 597-1 and en 597-2 the same?
[C language - function stack frame] analyze the whole process of function call from the perspective of disassembly
1721. 交换链表中的节点
K8S应用(四)—— 搭建redis5 集群(可供外部直接访问)
En45545-2 R26 vertical combustion test introduction
Codetop - sort odd ascending even descending linked list
445. adding two numbers II
Mazhiqiang: research progress and application of speech recognition technology -- RTC dev Meetup
206. reverse linked list