当前位置:网站首页>GOF mode-03-behavioral mode (bottom)
GOF mode-03-behavioral mode (bottom)
2022-06-21 19:04:00 【Development, operation and maintenance Xuande company】
List of articles
7. Observer mode (Observer)
Refers to when the state of the target object changes , An object that responds to or handles state change events .
interpretation :
The observer pattern is sometimes called “ Publisher — Subscriber pattern ”(Publisher-Subscriber Pattern), In the event processing scenario , Also called a listener (Listener) Pattern .
The observer pattern defines the many to one relationship between dependent and dependent objects , When a dependent object ( Or target object ) When the state of , Dependent objects can receive notifications and respond in a timely manner .
7.1 Use scenarios
(1) When the state of the target object changes , State change events need to be notified to other dependent objects , But do not know the specific number or type of dependent objects .
(2) Objects with dependencies in the abstraction layer need to be encapsulated independently , To reuse or extend .
7.2 Class structure
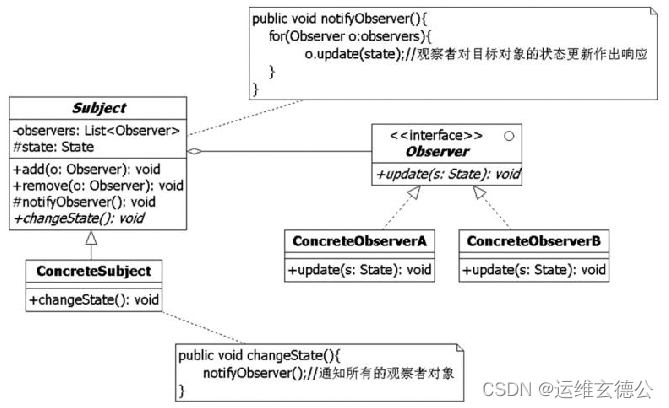
because Subject The aggregate is Observer Objects defined by abstract types , therefore Observer Changes to implementation classes do not affect Subject, Again ,Subject You can also freely extend subclasses .
When Subject When the state changes , Use notifyObserver() Method to change the new state ( It can be a message or an event ) Inform all Observer object ,Observer After the object receives the notification , Choose whether to respond or not according to the business rules .
7.3 Use the observer
stay COS In the system , Customers can subscribe to the platform discount information , The subscription method is email or SMS , New subscription methods will be added in the future . When COS When there are new offers , Customers who need to be notified of subscriptions in a timely manner .
8. The state pattern (State)
Used to encapsulate the specific state behavior of context objects , This enables the context object to change its own behavior when its internal state changes .
8.1 Use scenarios
(1) The behavior of a context object depends on its internal state , And the state will change during operation .
(2) It is necessary to eliminate the logical branch statements for state judgment in the context object .
8.2 Class structure

- Context Is the context object type , hold State Object reference of abstract type ;
- State Is encapsulating state behavior handle() Abstract type of , The concrete state behavior is implemented by subclasses ;
- StateA、StateB and StateC Is a concrete state behavior implementation class . When you need to add a new type of state behavior , Just need to achieve State The extension can be completed by the new state subclass of .
because Context Type object behavior behavior() The concrete representation of is determined by the internal state object ; therefore , Can eliminate behavior() Branch statement for internal state judgment .
- Sequence diagram :
Client call context Context The behavior corresponding to the internal state of a type object behavior() when , The context object delegates the customer request to State Type of state object processing .
8.3 Use state mode
COS The dish order in has an order being placed (Placing)、 Accepted (Accepted)、 Already prepared (Prepared)、 Completed (Finished) Equal state , Order of dishes in each state “ Cancel ” The behavior is different
- When the order status is Placing、Accepted when , If the customer cancels the order ,COS The order status will be set to “ Cancelled (Canceled)”, Customers get orders 100% refund
- When the order status is Prepared when , Customer cancels order ,COS The order status will be set to Canceled, Customers get orders 30% refund ;
- When the order status is Delivering、Delivered、Finished when , Order's “ Cancel ” Behavior not available .
To ensure the stability of the code , Developers do not want to use branching statements to construct the state behavior of the dish order object .
9. The strategy pattern (Strategy)
An object that encapsulates a single algorithm in a set of algorithms , These strategies can be substituted for each other , So that the change of a single algorithm does not affect the client using it .
9.1 Use scenarios
(1) Algorithms need to implement different 、 Replaceable variants .
(2) To the client class that uses the algorithm ( Or context class ) Mask the data structure inside the algorithm .
(3) Customer class ( Or context class ) Defines a set of interchangeable behaviors , You need to eliminate the branch statements that invoke this set of behaviors .
(4) A set of classes differ only in behavior , But developers do not want to achieve behavior polymorphism through subclass extension .
9.2 Class structure

- Context Is the context class of algorithm policy , It is also a customer class that uses policy objects ;
- Strategy The interface defines the behavior of the algorithm behavior(), Implementation class ConcreteStrategyA、ConcreteStrategyB And so on .
- It is worth noting that , The data needed to execute the policy algorithm is obtained from the context . therefore ,Context Context object when using policy object , You need to transfer all the data required by the policy behavior into the policy object , Or an access interface that passes itself in and provides the data required by the algorithm behavior ( The diagram structure uses the context object as a method parameter to be passed into the policy behavior ).
Sequence diagram :
When the client uses the service of the context object , Pass in a specific policy object reference to it ; After the context object receives the client request , Delegate the policy object to complete the business request processing .
6.3 Example
The customer is browsing COS Menu time , You can choose to sort by price or name ( In ascending or descending order ) Browse . stay COS In the upgraded version of , A new sort method is added ( By heat 、 Seasonal order, etc ).
10. Template method (Template Method)
A framework for defining algorithms , The variable steps in the algorithm are defined as abstract methods , Specify subclasses that implement or override .
interpretation :
The template method defines the invariant part of the algorithm ( Including the algorithm process 、 Execution order 、 Input / Output, etc ), The variable part ( Generally, some sub steps in the algorithm process ) Delay implementation into subclasses . advantage :
- Avoid code redundancy .
The immutable part of the algorithm is defined by the template method , Reused by all subclasses , You can avoid subclasses defining the same code repeatedly .- Improve code stability .
The variable part of the algorithm is unstable , Define unstable sub steps as abstract methods , Template methods depend on abstract methods , It can ensure the stability of the algorithm framework .
10.1 Use scenarios
(1) When the algorithm contains variable steps and immutable steps , Let subclasses determine the concrete implementation of variable steps .
(2) When multiple classes contain common business behaviors , Developers want to avoid redefining redundant code .
(3) Want to control the extension behavior of subclasses , Only subclasses are allowed to implement specific extension points .
10.2 Class structure

abstract class AbstractClass The template method is defined templateMethod(), Template methods are algorithmic behaviors ( Or business process ) Framework , Algorithm framework contains immutable steps invariantStep() And variable steps variantStep().
- templateMethod() Used final Modifiers , Subclasses are not allowed to redefine it .
- invariantStep() The visibility is private— Subclass not visible , Nor can we redefine ;
- variantStep() Visibility is protected, Allow subclasses to inherit and redefine .
- therefore , Parent class AbstractClass Subclasses are specified ConcreteClass Only extension points can be overridden variantStep().
When AbstractClass Objects of type provide... To the client templateMethod() The service , The client selects or specifies a specific ConcreteClass example .
Sequence diagram :
10.3 Example
COS The step for the customer to pay the order is to check and confirm the order 、 Payment order 、 Generate receipt . The way to pay the order can be card payment or payroll deduction , The customer is free to choose the payment method , and COS Make sure the payment process is consistent .
11. Visitor mode (Visitor)
Used to encapsulate the operation of aggregating elements applied to the polymer ( Or algorithm ), So that the operation ( Or algorithm ) Separate from the aggregate object , Realize free extension without affecting the aggregated objects .
When performing element operations on an aggregate object composed of several types of elements , Different operations need to be applied according to the element type . If you encapsulate the operation of an aggregate element in an aggregate object , The code has two major defects :
- High code complexity
Because different operations are applied to different types of aggregation elements , Aggregate objects not only implement the management of aggregate elements , You also need to define the operations of different elements , As a result, the code complexity of aggregated objects increases- Poor stability
Aggregate objects encapsulate operations that are imposed on different aggregate elements , When the element operation needs to be extended , The business logic of the aggregate object must be modified , To complete the code extension .
11.1 Use scenarios
(1) The target aggregate object contains different aggregate element types , Developers need to implement different business operations or algorithm behaviors for different aggregation element types .
(2) The target aggregate object structure is stable , But operations on aggregated elements require different extensions .
(3) There are multiple single and unrelated operations imposed on the aggregate element , But I don't want to “ Pollution ” The code of the aggregate element class .
11.2 Class structure

- ObjectStructure It is a polymer type , from Element Aggregate elements of type ;
- Element Is an abstract class of aggregate elements , There are different implementation types ElementA、ElementB etc. ;
- Interface Visitor Defines the imposed on Element The operating visit(), For different Element Implementation types define different visit() Overloading methods .
because Visitor Encapsulated for Element Implement the operation behavior of the type , therefore , When a new operation needs to be extended , Definition Visitor A new implementation class is all you need .
Sequence diagram
Client Create and use specific Visitor object , adopt ObjectStructure Defined interfaces service() Apply actions to aggregate elements .
- When ObjectStructure When an object of type receives a client request , Will carry Visitor The instance request passed accept() Method is distributed to the corresponding aggregate element .
- Aggregate element object received ObjectStructure After distributing the request , adopt visit() Method again distributes the request to Visitor example , And pass itself as a method parameter ;
- Visitor Object received the... Submitted by the aggregation element visit() After the request , Apply the corresponding overload operation behavior according to the aggregation element instance carried by the request , And access the interface provided by the aggregation element when necessary operation().

边栏推荐
- Initialization of typescript class objects
- Canvas dynamic background text luminous JS effect
- Must the database primary key be self incremented? What scenarios do not suggest self augmentation?
- 删除指定的screen
- Dao and encapsulation of entity classes
- C1—Qt实现简易计算器的思路2021.10.15
- Day15Qt中字符串的常用操作2021-10-20
- C语言__attribute__(packed)属性(学习一下)
- R language bug? report errors? As for the outcome of sub variables 0 and 1, the original content of the outcome variable is changed through the process of factor and numeric?
- canvas交互式颜色渐变js特效代码
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Day11QPainter2021-09-26
Foreign capital staged a "successful flight" and domestic capital took over the offer. Is New Oriental online "square"?
The best network packet capturing tool mitmproxy
Generic type checking for typescript
Microbial personal notes taxonkit
Three.js 3d粒子动画js特效代码
Ropsten测试网的水龙头上得到一些ETH
Niuke: merging two ordered arrays
Internet communication process
写着玩的处理框架
宏基因组 (个人笔记)
URL module of node
Basic data type and structure data type of TS
C1—Qt实现简易计算器的思路2021.10.15
Three. JS 3D particle animation JS special effect code
挖财学堂属于证券公司吗?开户安全吗?
El expression
国产API管理平台横向比较,到底哪家强?
Leetcode (210) - Schedule II
I/0多路转接之select








